Rate of Reaction/Equillibrium
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Distinguish between strong/weak acid/base
Strong acid dissociates fully in solution and donates all of its protons.
Weak acid partially dissociates in solution and is a poor proton donor.
Strong base accepts all protons
Weak base partially accepts protons
What is the only thing that effects pressure?
Gas. NOT liquid or aqueous
When does pressure does NOT have an effect for Le Chatleier Prinicple
Changing pressire has no effect on equilibrium position if there are an equal number of moles of gas in reactants + products
Define dynamic equilibrium
The rate of forward reaction is same as reverse in a closed system. Concentration of product and reactant are CONSTANT (not equal).
The ratio of product to reactant is same so the reactions looks the same so it looks like it’s doing nothing (macroscopic property)
What is a reversible reaction
Reaction where the products can react to reform original reactants. Two half arrows drawn.
Write the equilibrium constant equation and what is excluded and included
Excluded: Solids (s) and pure liquids (no solutes in it. their concentraiton is constat)
Included: only gas and aqueous because those are the ones that affects concentration
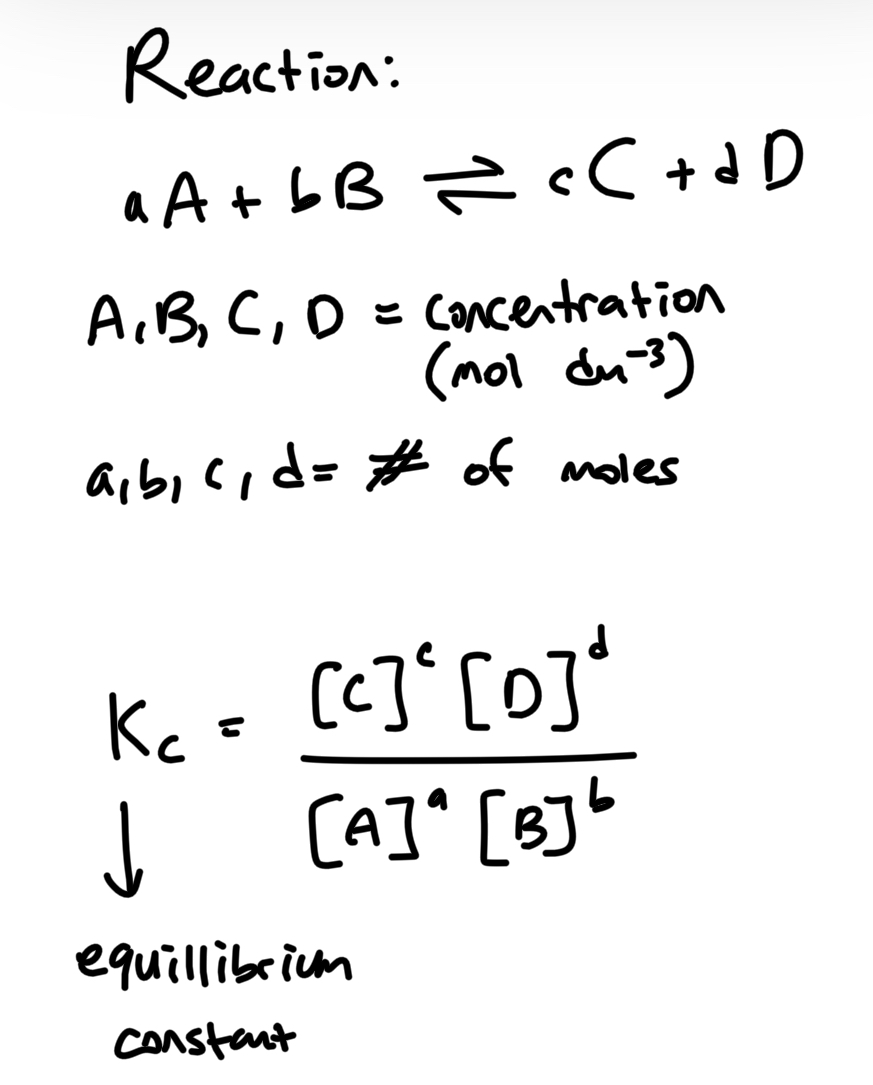
Explain what it means when the equillibrium constant K is
K> 1
K » 1
Concentration of PRODUCT is greater than concentration of reactant. Equillibrium llies on the RIGHT hand side.
When K» 1, equillibrium is on FAR right hand side and reaction almost goes into completion
Explain what it means when the equillibrium constant K is
K < 1
K « 1
Concentration of reactants is greater than concentration of products. Equillbrium is on the LEFT hand side.
When K « 1, equillibrium is on the FAR keft side and reaction HARDLY PROCEEDS.
Explain what it means when the equillibrium constant K is K=1
Concentration of reactants and prodcuts are equal. Equillibrium does not favor either reactants nor products.
Define K equillibrium constant
K is a constant at specific temperature and is therefore dependent on it.
Left = (…) reaction
Right = (…) reaction
left= reverse
right= forward
State Le Chatelier’s Principle
If there’s a change in the system of a DYNAMIC equillibrium, the POSITION OF THE EQUILLIBRIUM will shift to MINIMIZE change.
If change hapoens, it does opp cuz it wants to balance.
What would happen if the concentration of the REACTANT increased/decreased?
Increase= Position of equillibrium shifts to the RIGHT (products)
Decrease= Position of equilibrium shifts to the LEFT (reactants)
Why? To reduce the effect of the concentration of the reactant
What would happen if the concentration of the PRODUCT increased/decreased?
increase= Position of equillibrium shifts to the LEFT (reactant)
decrease= Position of equilibrium shifts to the RIGHT (product)
Why. Minimize the effect of increased/decreased product concentration
What is the only factor that changes equillibrium constant K
Temperature as K is effected by temperature
Effect of increase/decrease in temperature?
Increase/decrease temperature of endothermic reaction?
Increase/decrease temperature of exothermic reaction?
Increase= shifts to ENDOthermic direction in order to ABSORB new energy
Decrease= shifts to EXOthermic direction in order to RELEASE old energy
Endothermic:
Increase=
Decrease=
Factors of rate of reaction
(Increasing concentration) Temperature = kinetic energy
(Volume) Pressure = increase density = more collision
Increase surface area = more particles can be collided
Catalyst= decrease activation energy = greater fraction of particles collided already = less energy required for collision
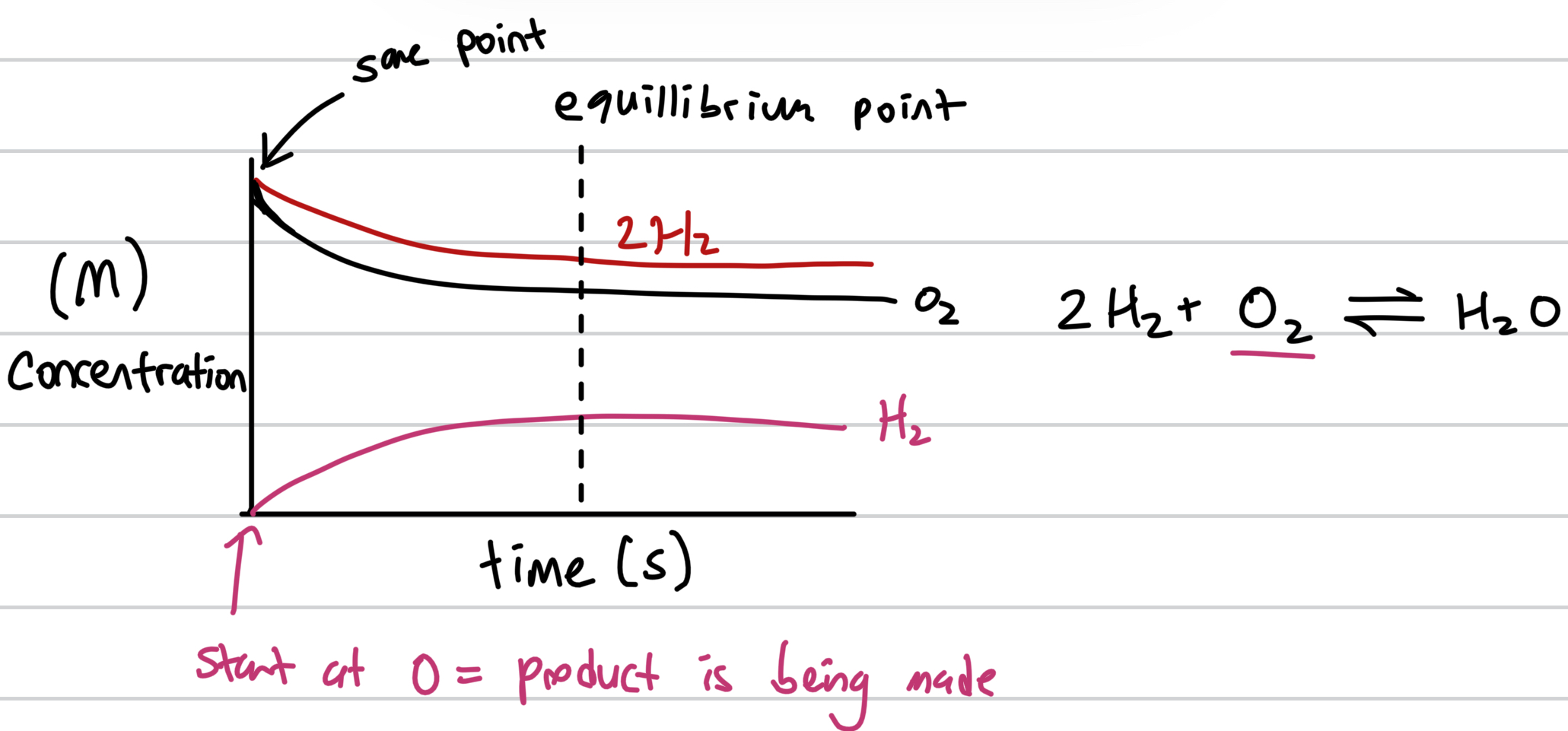
Draw equillbirum graph of H2 + O2 → H2O
What would happen if the product/reactant is a solid/pure liquid?
Product = numerator is 1
Reactant = denominator is 1
Because x/x= 1 NOT 0
What would happen to K if double coefficient, switch reaction (reverse to forward and vice versa)
Double = K²
Switch = K-1
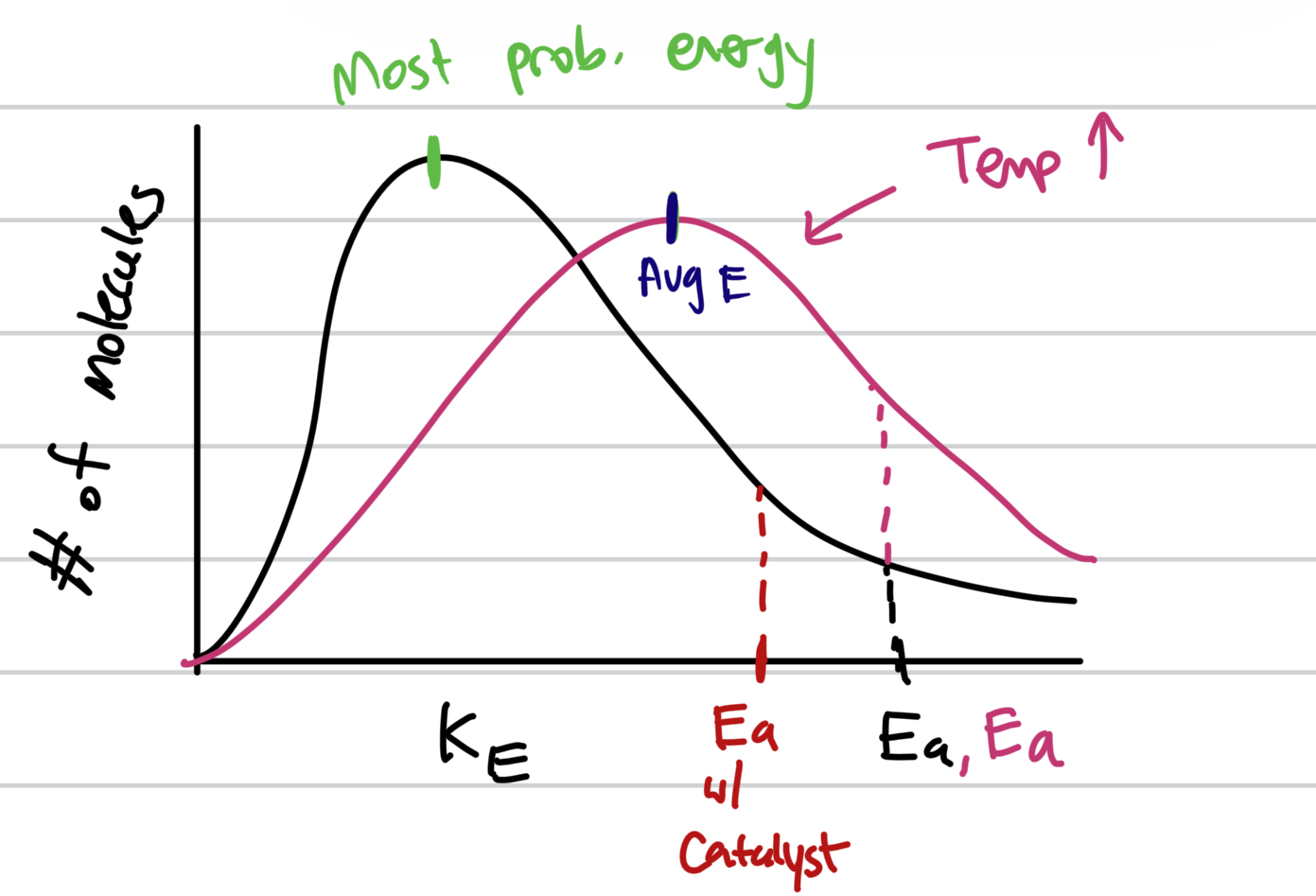
Draw a Boltzmann graph for regular, catalyst added, and high/lowered temperature
Draw the graph for forward and reverse reaction (exo and endothermic) and label the catalyst
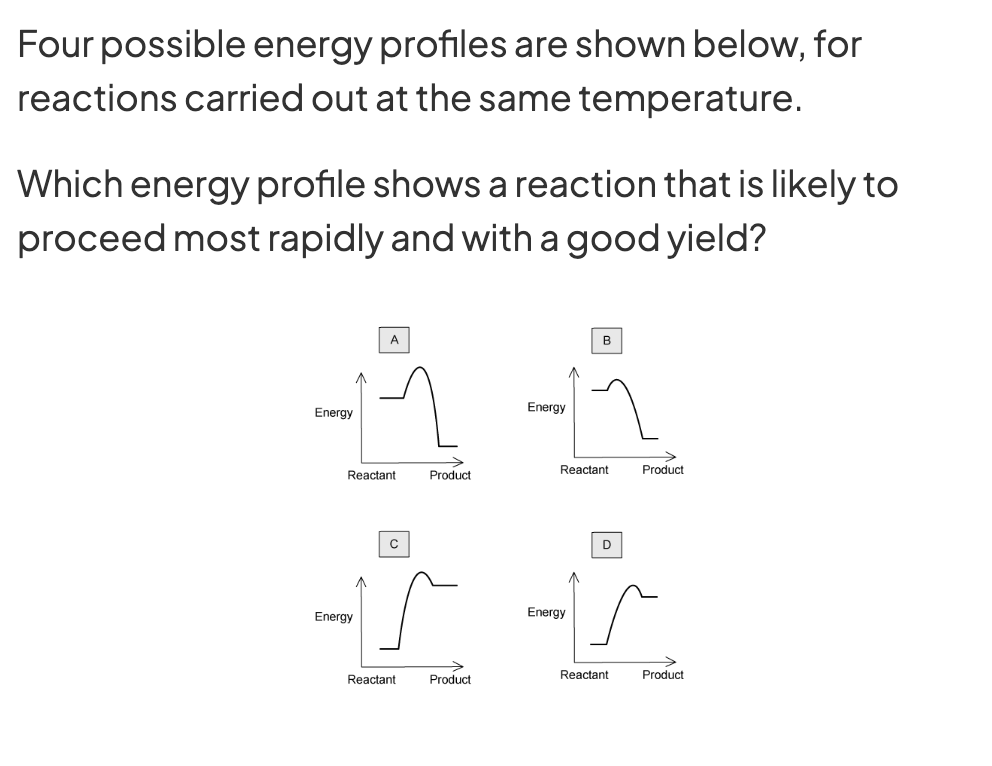
B because all are carried in same temerature (does not matter if exothermic or endothermic because looking at YIELD) so look at CATLAYST hump.
B has smallest.
What are some factors and some NOT factors for the effectiveness of collision?
NOT by concentration
YES: orientation and energy of colliding particles. Higher energy = collision. Better orientation (packed or small SA:V ratio) = more likely for collisions