Normal Language Development Exam 2-Chapter 5
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
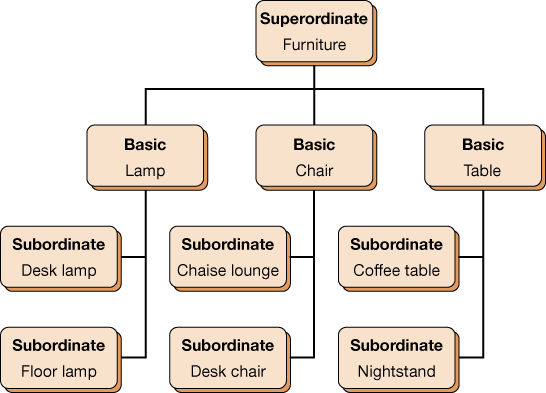
superordinate level
uppermost level in the category hierarchy-describes the most general concept in a particular category
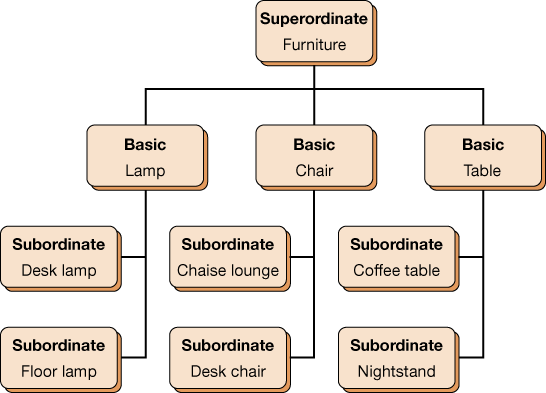
basic level
center of the category hierarchy-describes general concepts in a category
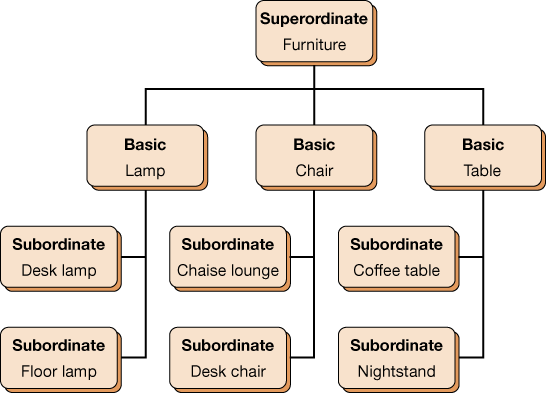
subordinate level
lowest level of the category hierarchy-describes specific concepts in a category
perceptual categories
categories based on similar-appearing features, including color, shape, texture, size, and so forth
conceptual categories
categories based on what an object does-balls roll, dogs bark, and airplanes fly
reflexive stage
sounds of discomfort and distress (crying, fussing) and vegetative sounds such as burping, coughing, and sneezing
control of phonation stage
beginning to produce cooing and gooing sounds
expansion stage
gain more control over the articulators and begin to produce isolated vowel sounds as well as vowel glides
basic canonical syllables stage
beginning to produce single consonant-vowel (C-V) syllables
advanced forms stage
beginning to produce dipthongs and more complex syllable forms including single-syllable types such as V–C (“am”) and C–C–V (“stee”), complex disyllables such as V–C–V (“abu”), and multisyllabic strings with and without varied stress intonation patterns (“odago”)
jargon
a special type of babbling containing at least two syllables and at least two different consonants and vowels, as well as varied stress or intonation patterns
paralinguistic features of IDS
Higher Overall Pitch, Exaggerated Pitch Contours, Slower Tempo
syntactic features of IDS
Shorter MLU
More Content Words; Fewer Function Words
Fewer Subordinate Clauses
discourse features of IDS
More Repetition
More Questions
Attendance to Social Partners
phase 1 of joint reference and attention
Emergence & Coordination of Joint Attention
phase 2 of joint reference and attention
Transition to Language
phase 3 of joint reference and attention
caregiver responsiveness
caregivers’ attention and sensitivity to infants’ vocalizations and communicative attempts
intraindividual differences
Differences or variations within the same individual — how a person’s performance, behavior, or characteristics vary across time, situations, or domains
interindividual differences
Differences or variations between different individuals — how people compare to each other in a particular trait or ability
expressive language
The language a person produces spontaneously, without imitating another person’s verbalizations. Includes content, form, and use.
receptive language
The language people comprehend
early talkers
children between ages 11 and 21 months who score in the top 10% for vocabulary production for their age on the MacArthur–Bates CDI. Producing an average of 475 words compared to the “typical” 200 words
late talkers
produces fewer than 50 words by age 2. about 13.4% of the general population. does not necessarily mean a child will have a language delay or impairment; however, it can be an important predictor of being diagnosed with a delay or impairment at a later age
informal language screens
checklists of common early language milestones that clinicians and parents can use to check off whether or not an infant exhibits each behavior in question
parent-report measures
having parents report directly on their infant’s development