CE3300 Ch.1: Introduction to Structural Analysis
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Structural analysis
Is the prediction of the performance of a given structure under prescribed loads and/or other external effects, such as support movements and temperature changes in the interest of 1. stresses or stress resultants, such as axial forces, shear forces, and bending moments; 2. deflections; and; 3. support reactions.
Structural engineering
Is the science and art of planning, designing, and constructing safe and economical structures that will serve their intended purposes.
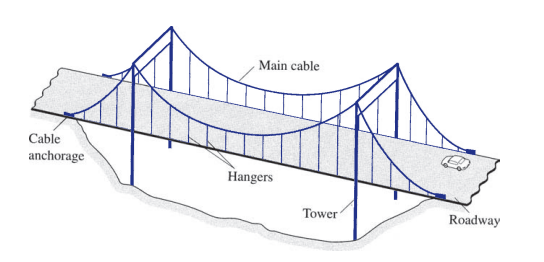
Tension Structures
Are subjected to pure tension under the action of external loads. (eg. steel cables in suspension bridges)
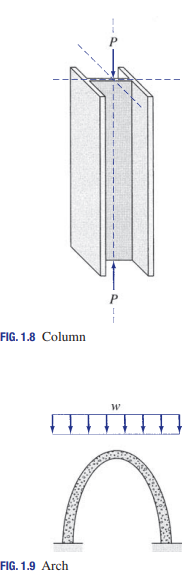
Compression structures
Develop mainly compressive stresses under the action of external loads. (eg. columns & arches)
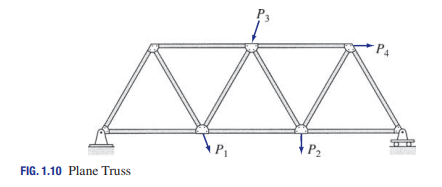
Trusses
Are composed of straight members connected at their ends by hinged connections to form a stable configuration that are put under uniform tension or uniform compression (eg. roofs)
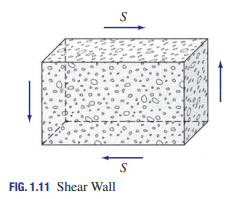
Shear structures
Used in multistory buildings to reduce lateral movements due to wind loads and earthquake excitations. They develop mainly in-plane shear, with relatively small bending stresses under the action of external loads.
Bending structures
Develop mainly bending stresses under the action of external loads. (eg. beams, rigid frames, slabs, and plates)
Beam
Straight member that is loaded perpendicular to its longitudinal axis
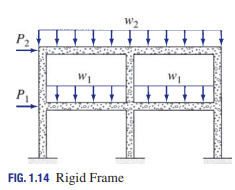
Rigid frames
Are composed of straight members connected together either by rigid (moment-resisting) connections or by hinged connections to form stable configurations
Framed structure
Is frequently used to refer to any structure composed of straight members, including a truss
Rigid connection
Prevents relative translations and rotations
Hinge connection
Prevents only relative translations