Microbe Mission Science Olympiad
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
Microbe
A microscopic form of life including bacterial, archaeal, fungal, and protozoal cells.
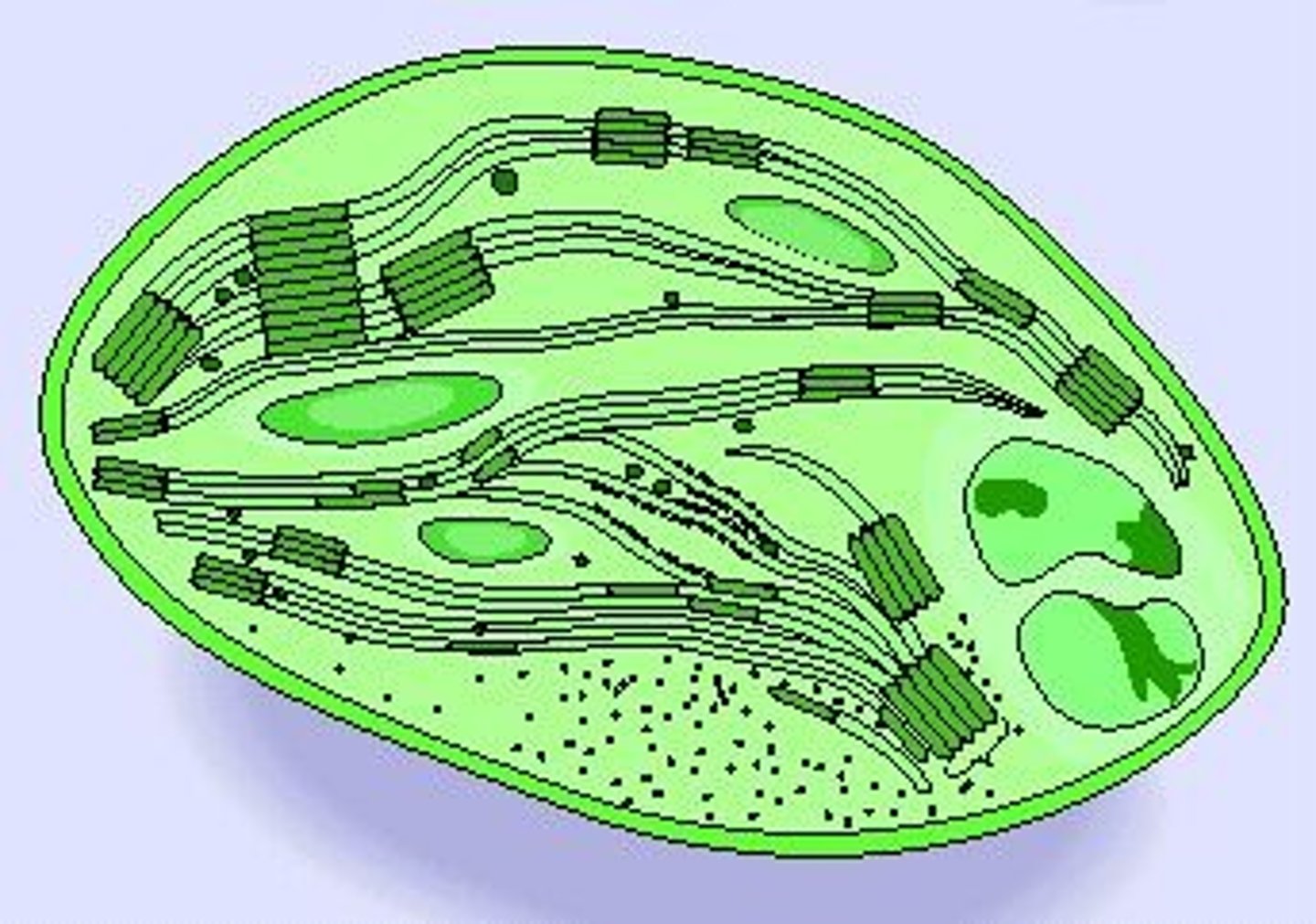
Eukaryotic Cell
A complex cell in which the genetic material is organized into a membrane-bound nucleus or nuclei.

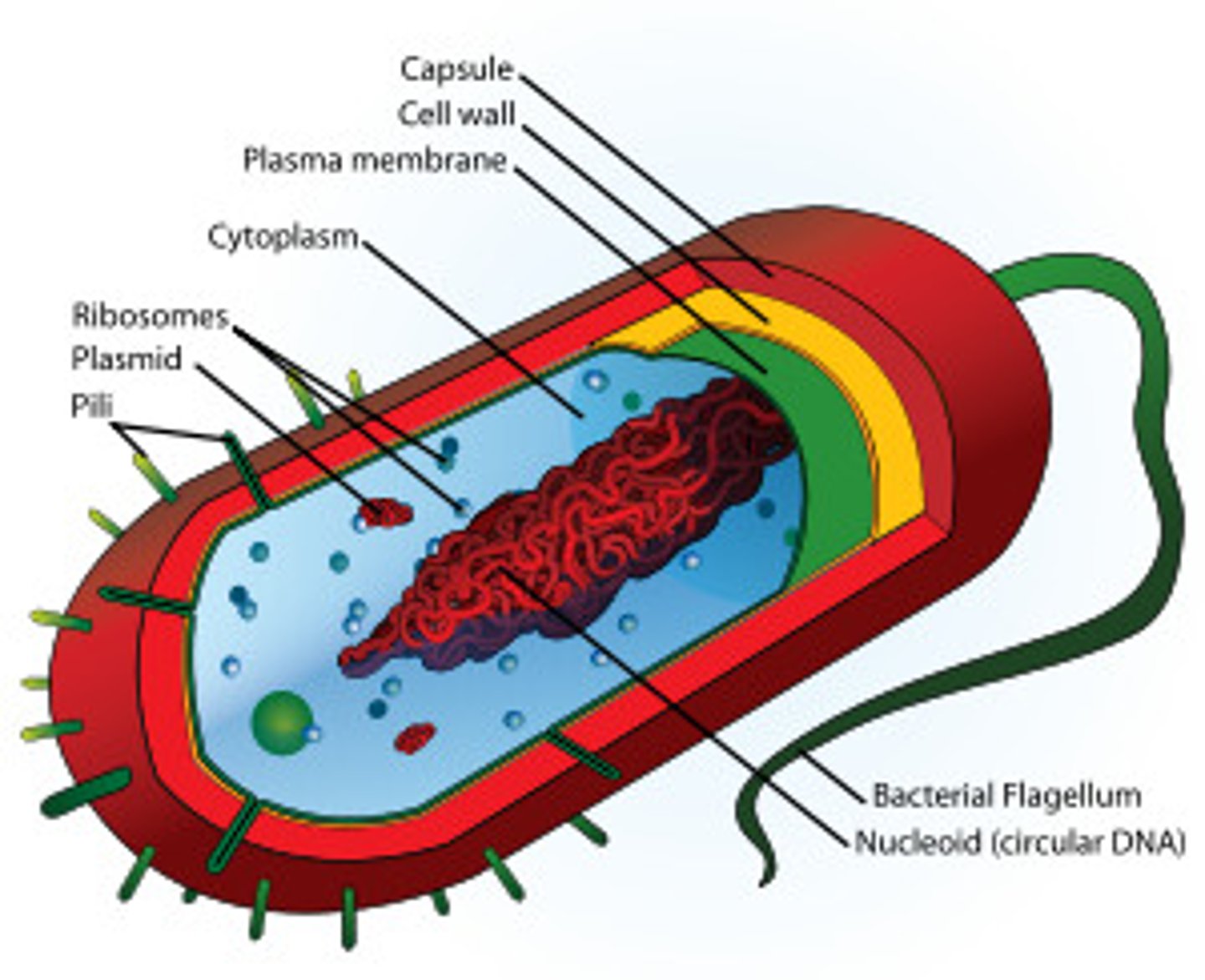
Prokaryotic Cell
An organism that lacks a membrane-bound nucleus, mitochondria, or any other membrane-bound organelle.
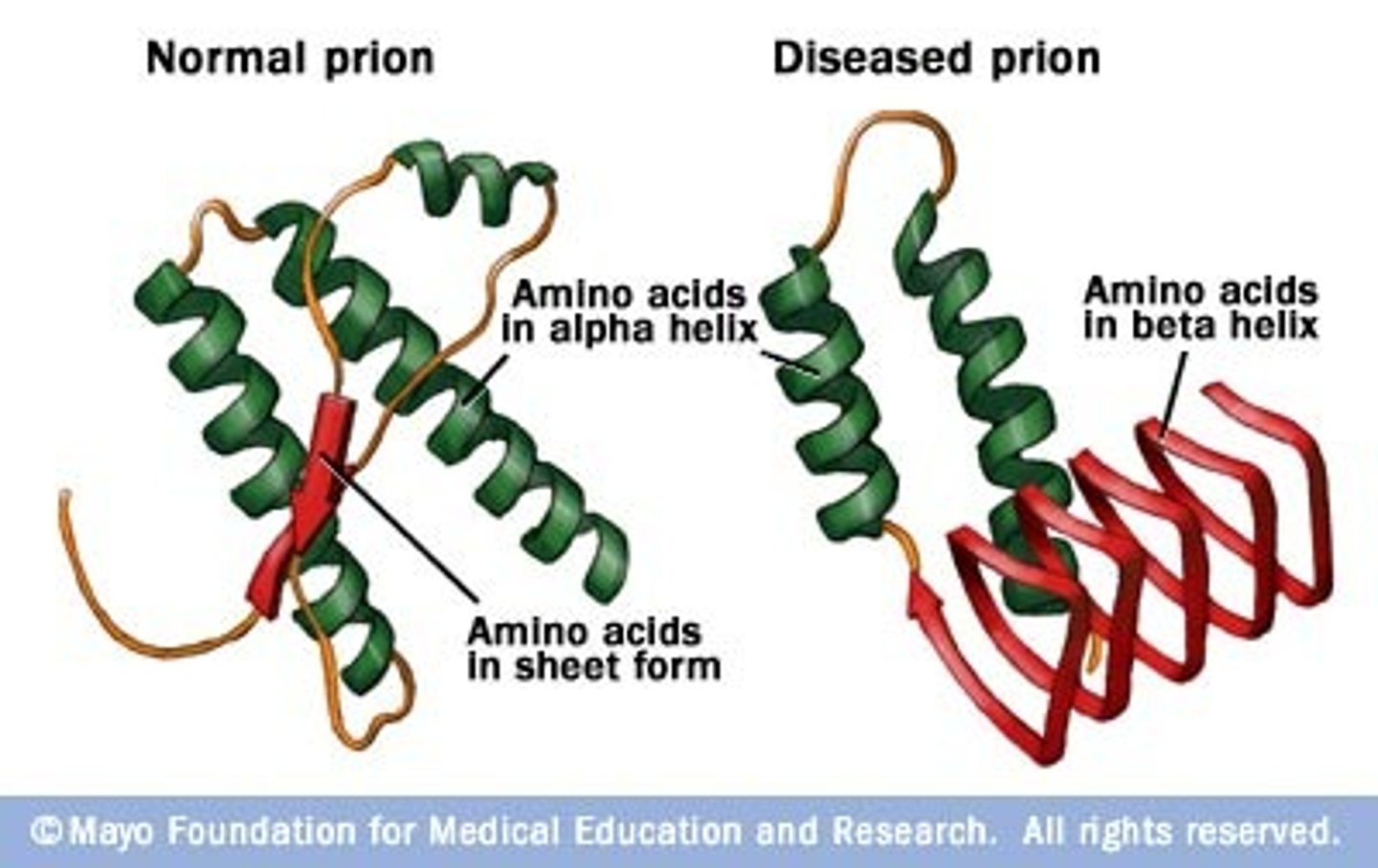
Prion
An infectious agent composed entirely of protein material, that can fold in multiple, structurally distinct ways, at least one of which is transmissible to other proteins, leading to disease that is similar to viral infection.
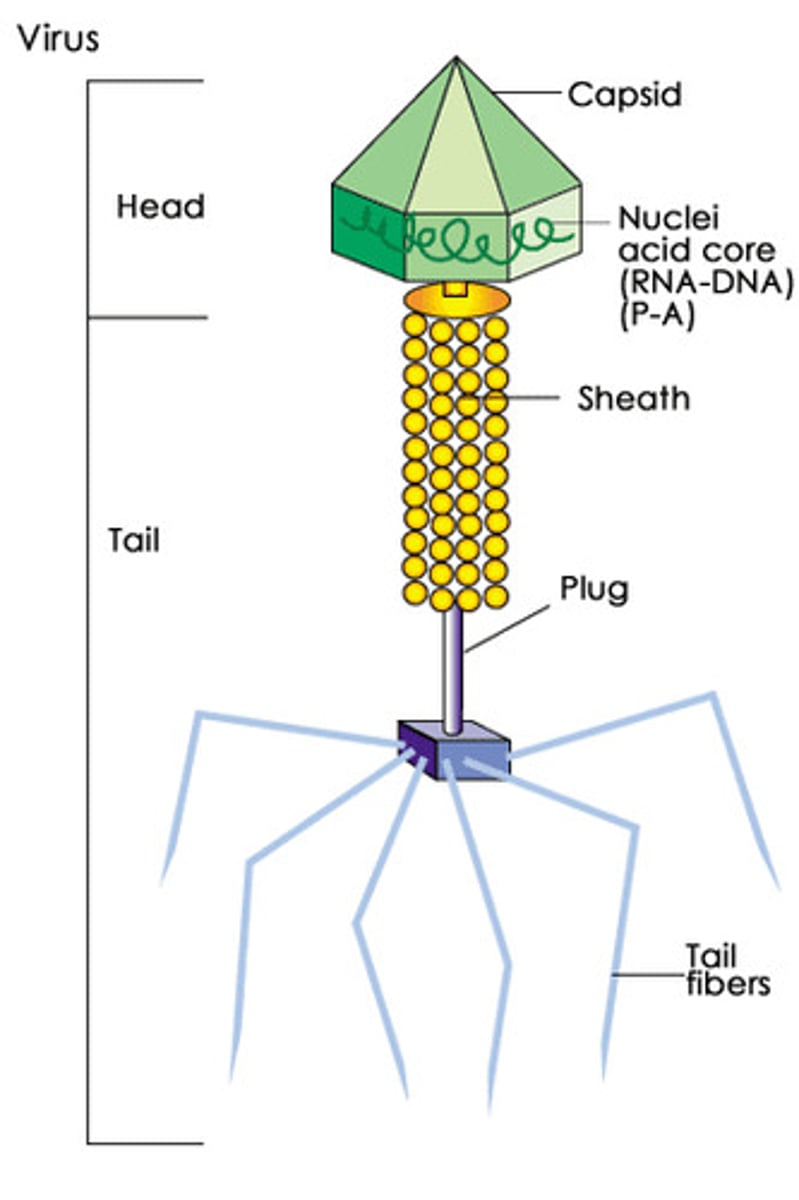
Virus
A microorganism that is smaller than a bacterium that cannot grow or reproduce apart from a living cell. It invades living cells and uses their chemical machinery to keep itself alive and to replicate itself. It may reproduce with fidelity or with errors (mutations). It is non-living.
Bacteria
Single-celled microorganisms that can exist either as independent organisms or as parasites. They are prokaryotes. The entire organism consists of a single cell with a simple internal structure.
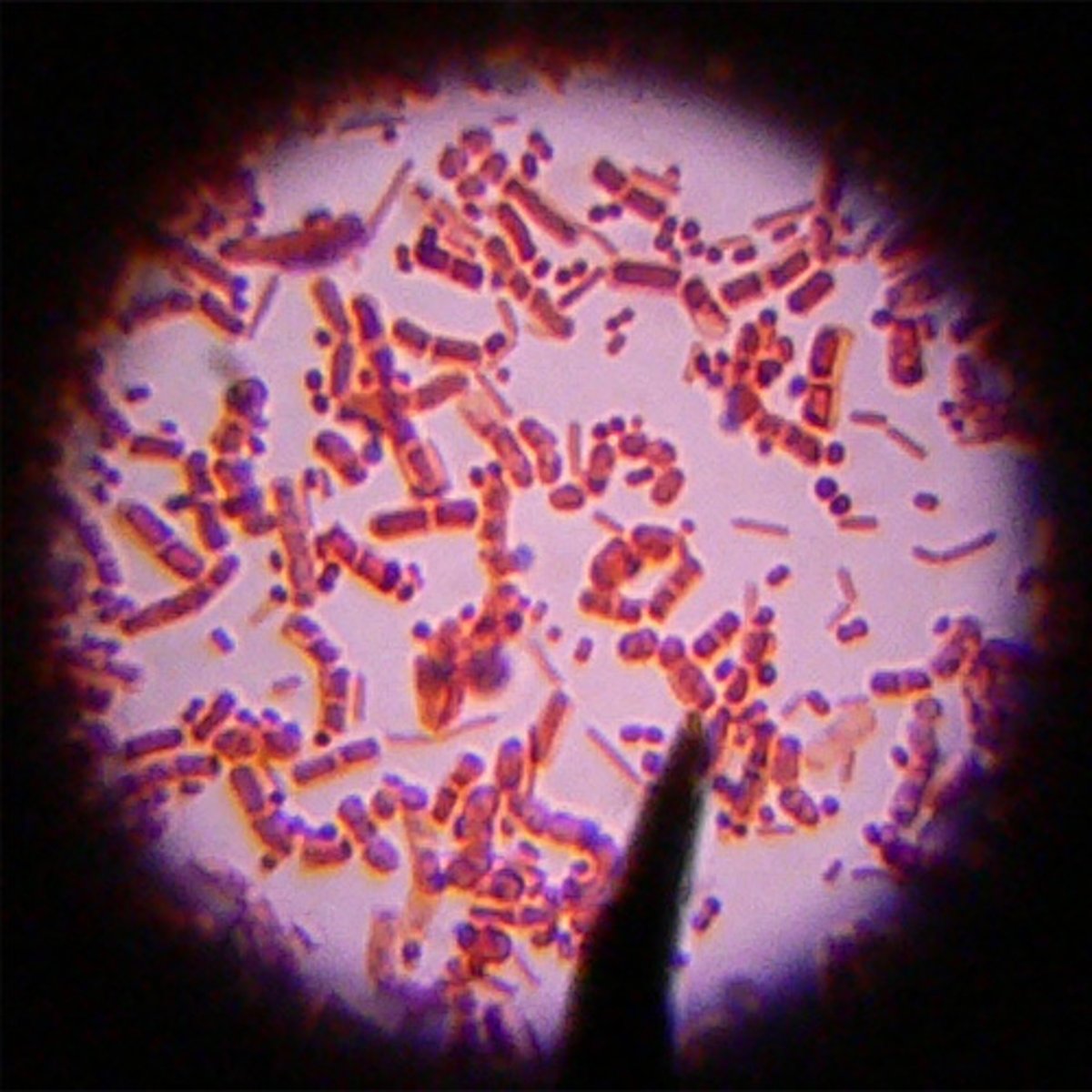
Archaeabacteria
A unique group of microorganisms that are called bacteria but are genetically and metabolically different from all other known bacteria. They appear to be living fossils, the survivors of an ancient group of organisms that bridged the gap in evolution between bacteria and eukaryotes. They are prokaryotes.
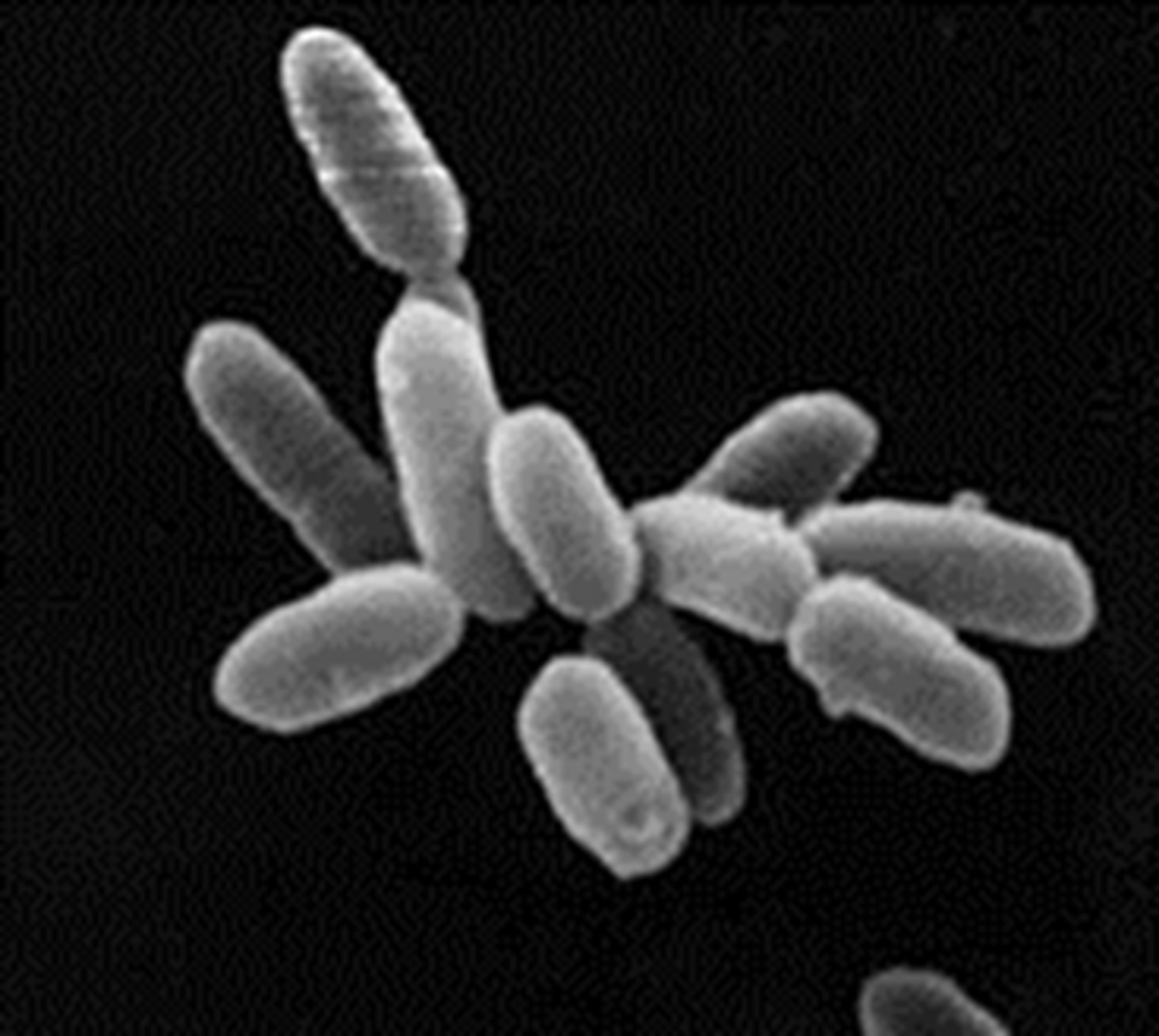
Fungi
A kingdom of eukaryotic organisms that grow in irregular masses, without roots, stems, or leaves, and are devoid of chlorophyll or other pigments capable of photosynthesis. Each organism (thallus) is unicellular to filamentous, and possesses branched somatic structures (hyphae) surrounded by cell walls containing glucan or chitin or both, and containing true nuclei. They reproduce sexually or asexually (spore formation), and may obtain nutrition from other living organisms as parasites or from dead organic matter as saprobes (saprophytes).
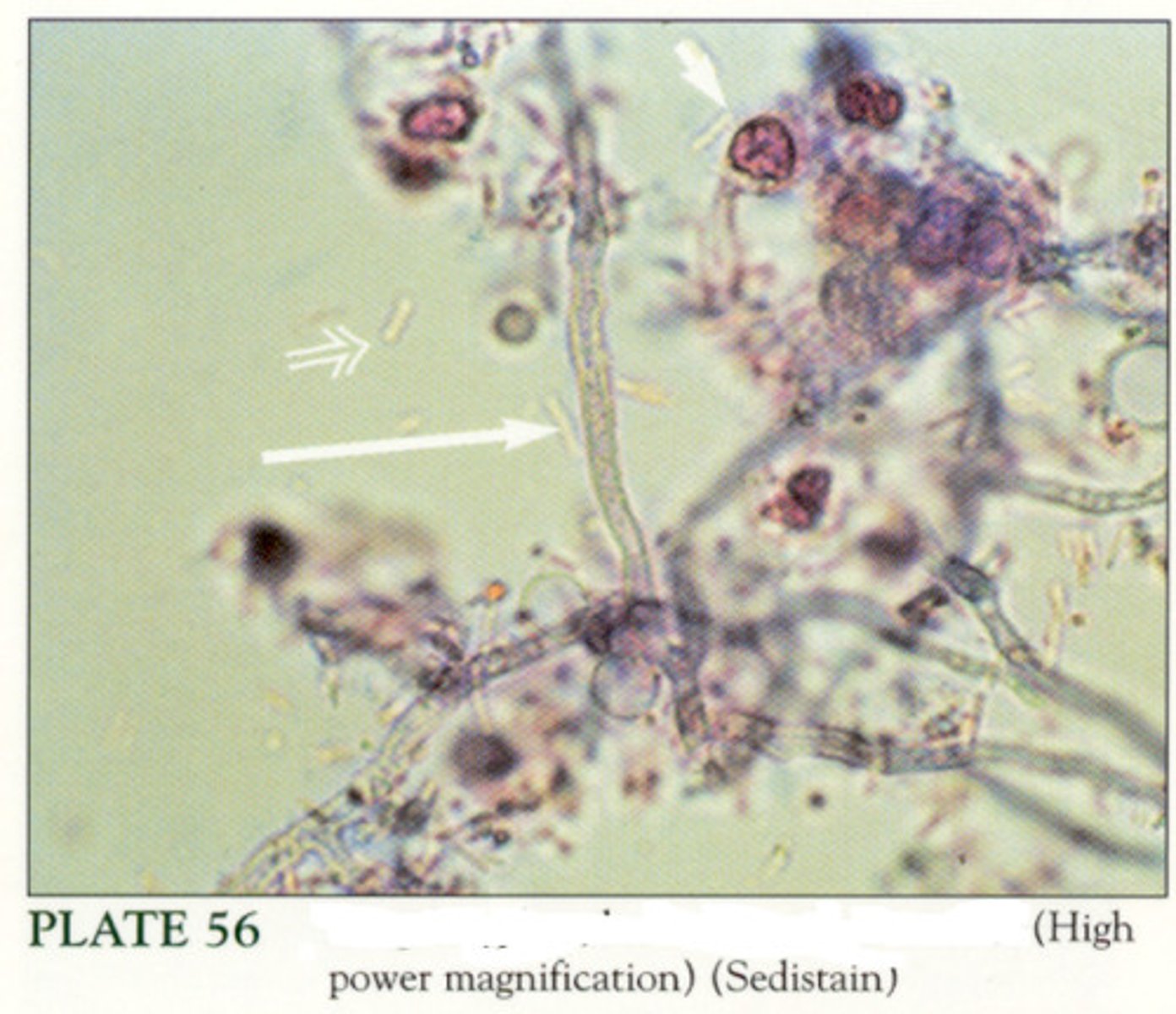
Protists
Members of an informal grouping of diverse eukaryotic organisms that are not animals, plants or fungi. They do not form a natural group, or clade, but are often grouped together for convenience, like algae or invertebrates.
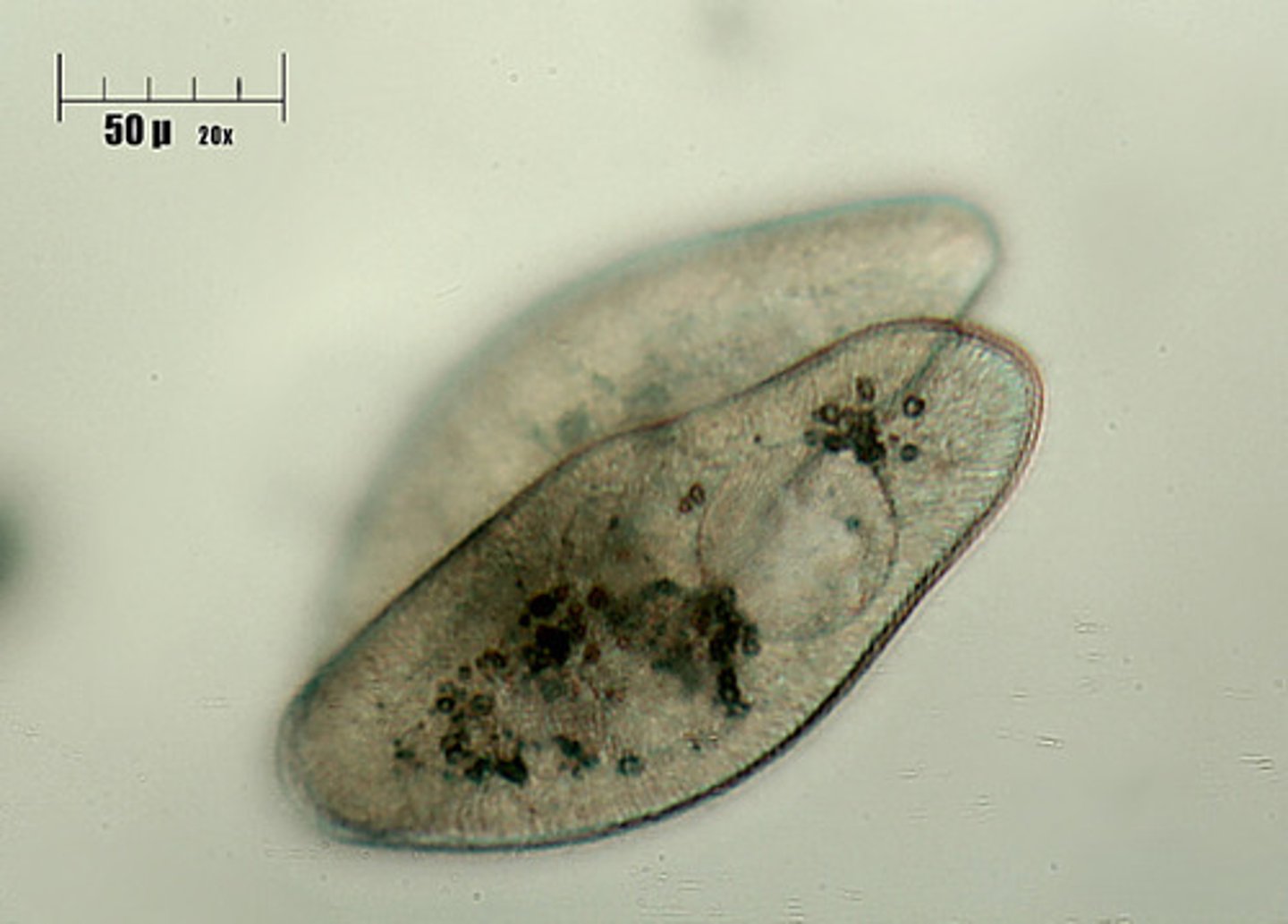

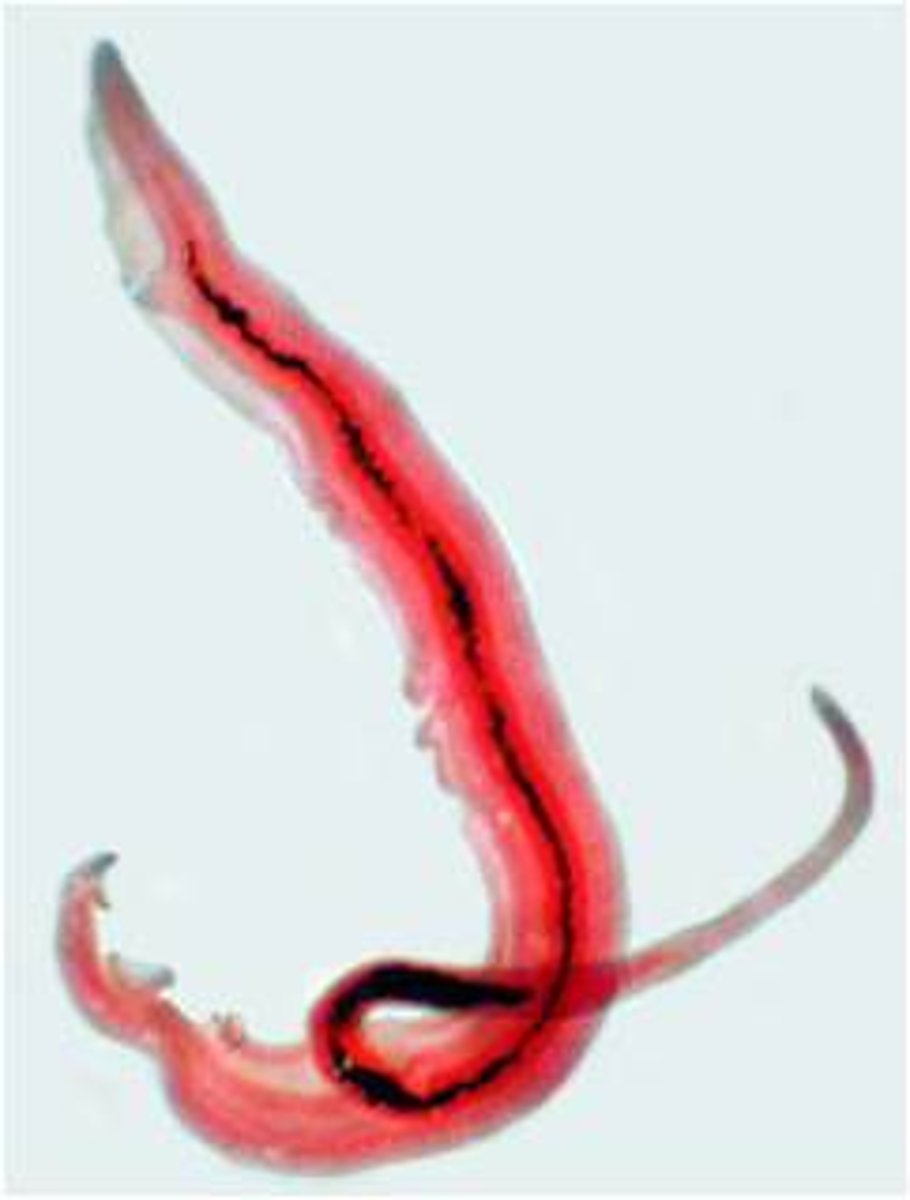
Parasitic Worms
Feed on a living host to gain nourishment and protection, while causing poor nutrient absorption, weakness and disease in the host.
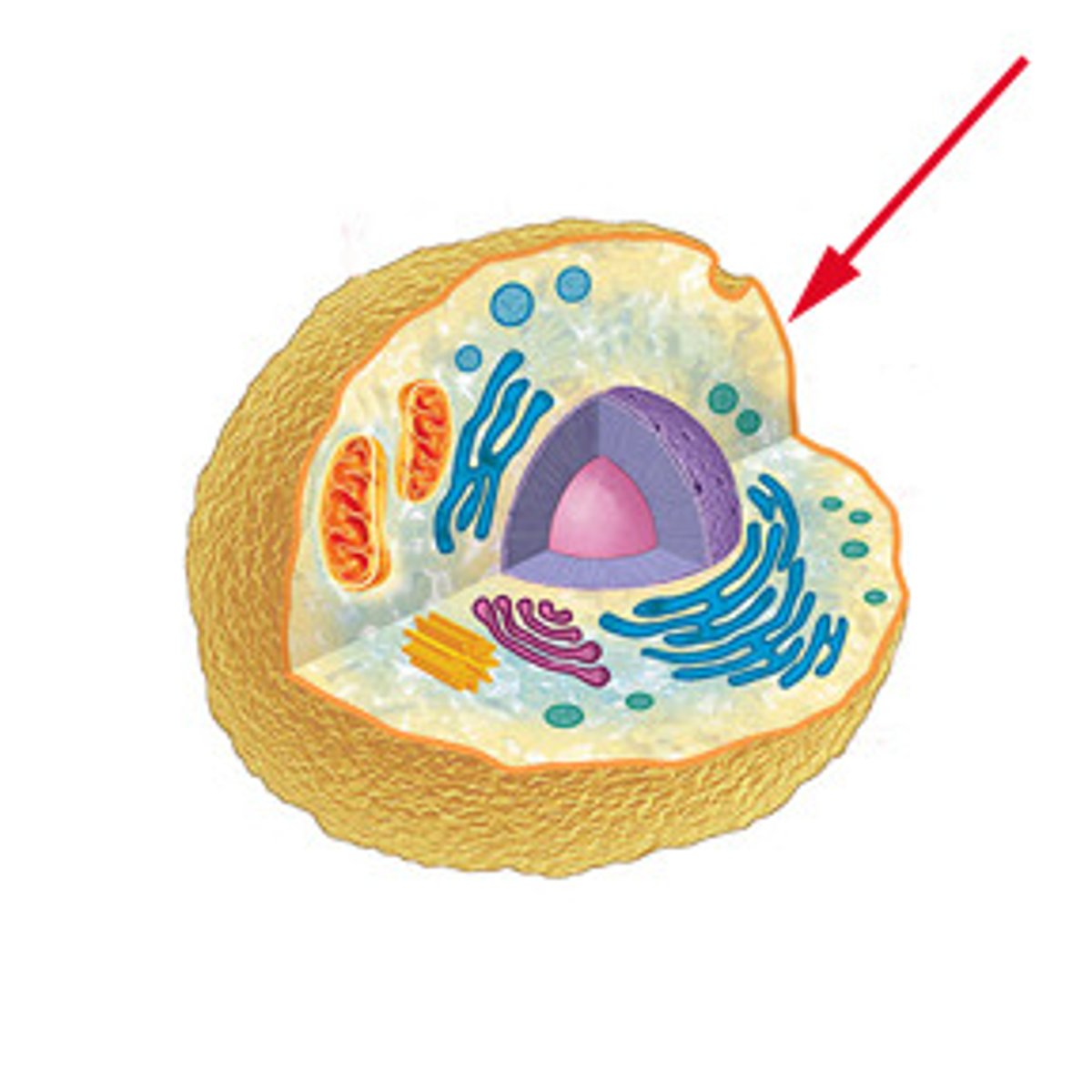
Plasma Membrane
Regulates what can enter and exit the cell.
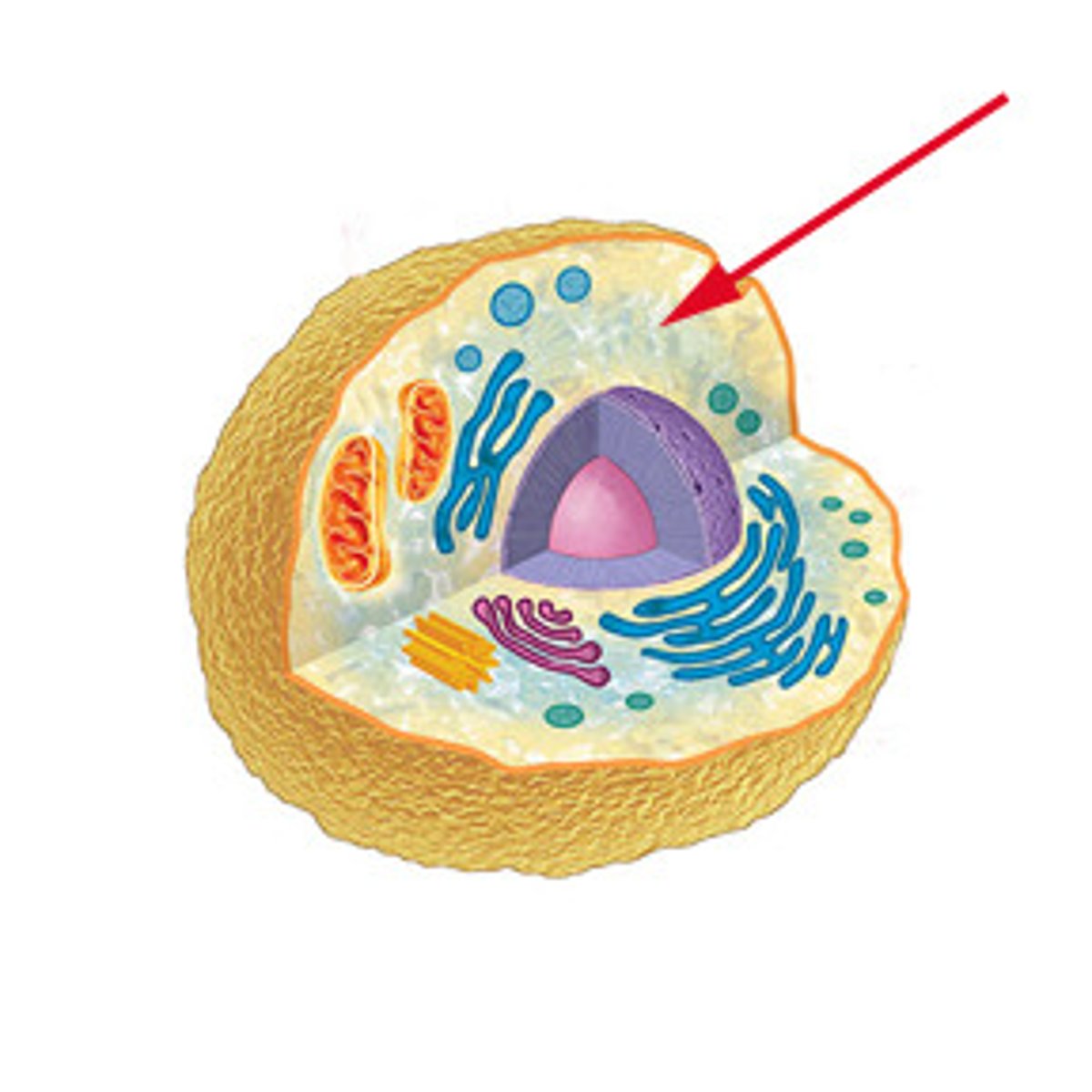
Cytoplasm
The fluid that is the filling of the cell.
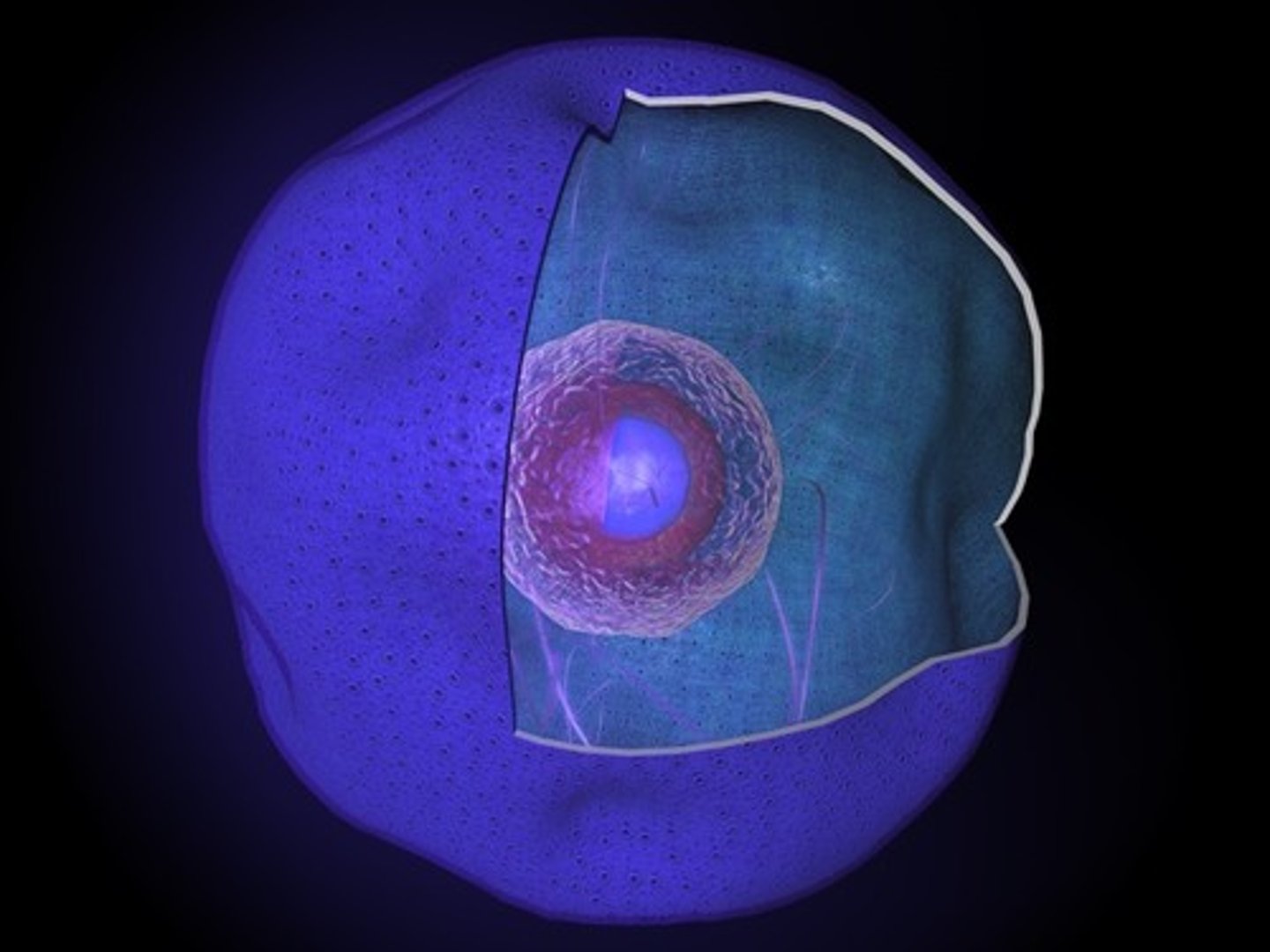
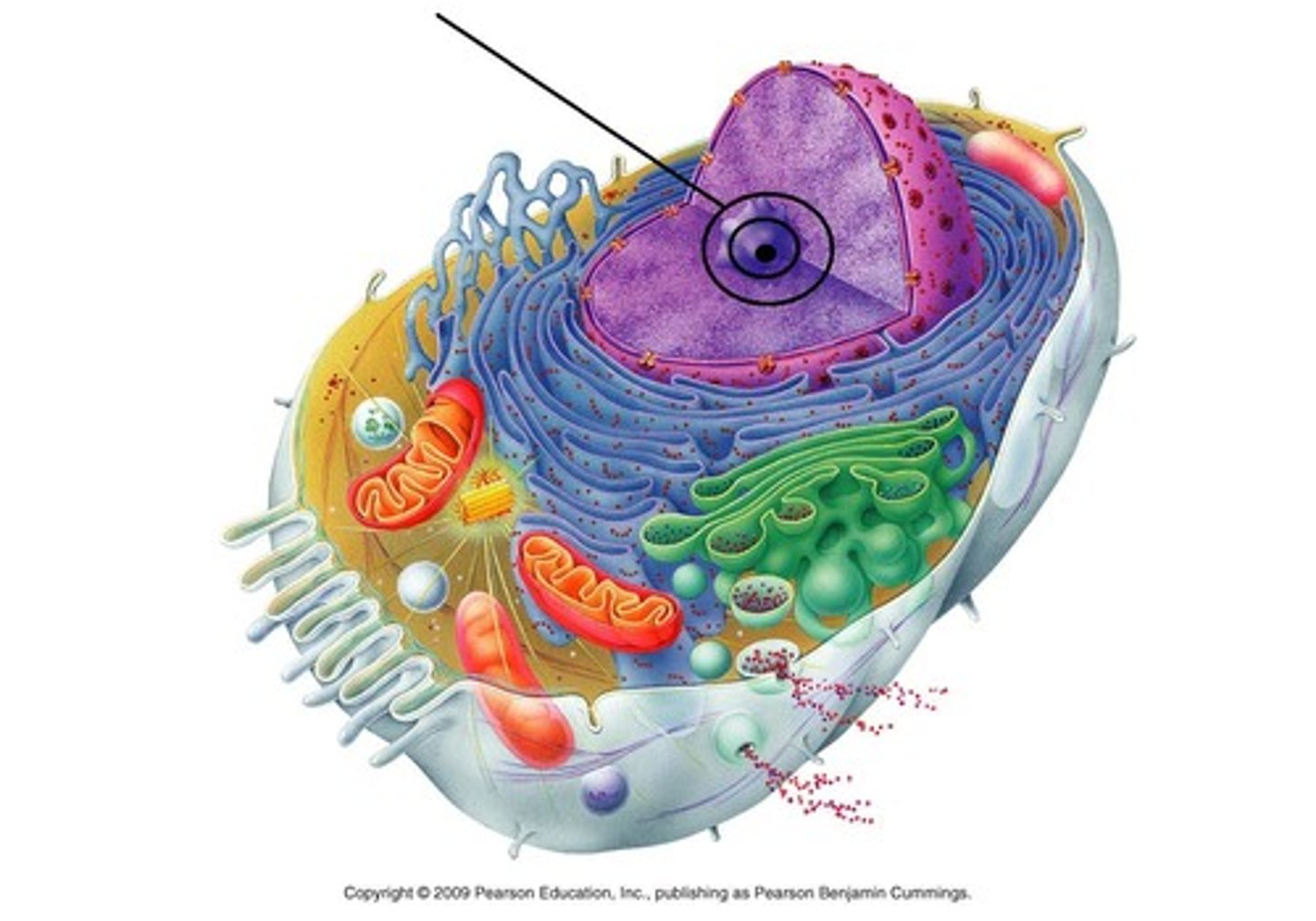
Nucleus
Control center of the cell because it is responsible for the regulation of consumption, movement, and reproduction.
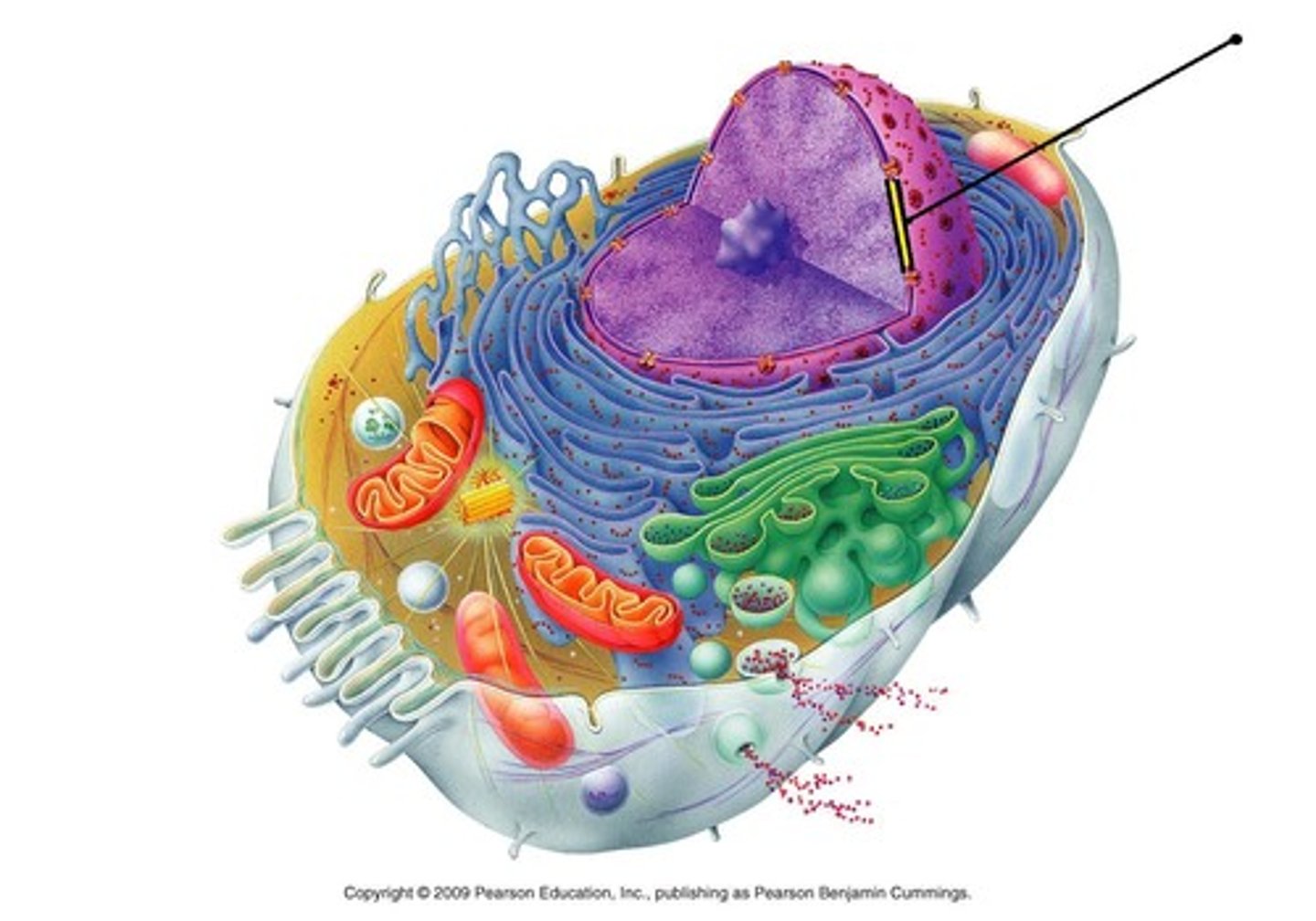
Nuclear Envelope
Encases the nucleus and acts in a similar way as the cell membrane.

Pores (in the nucleus)
Allow RNA and proteins to pass through, but the nucleolus and chromatin remain inside.
Nucleolus
Made of RNA and protein. This is where ribosomes are synthesized and created.
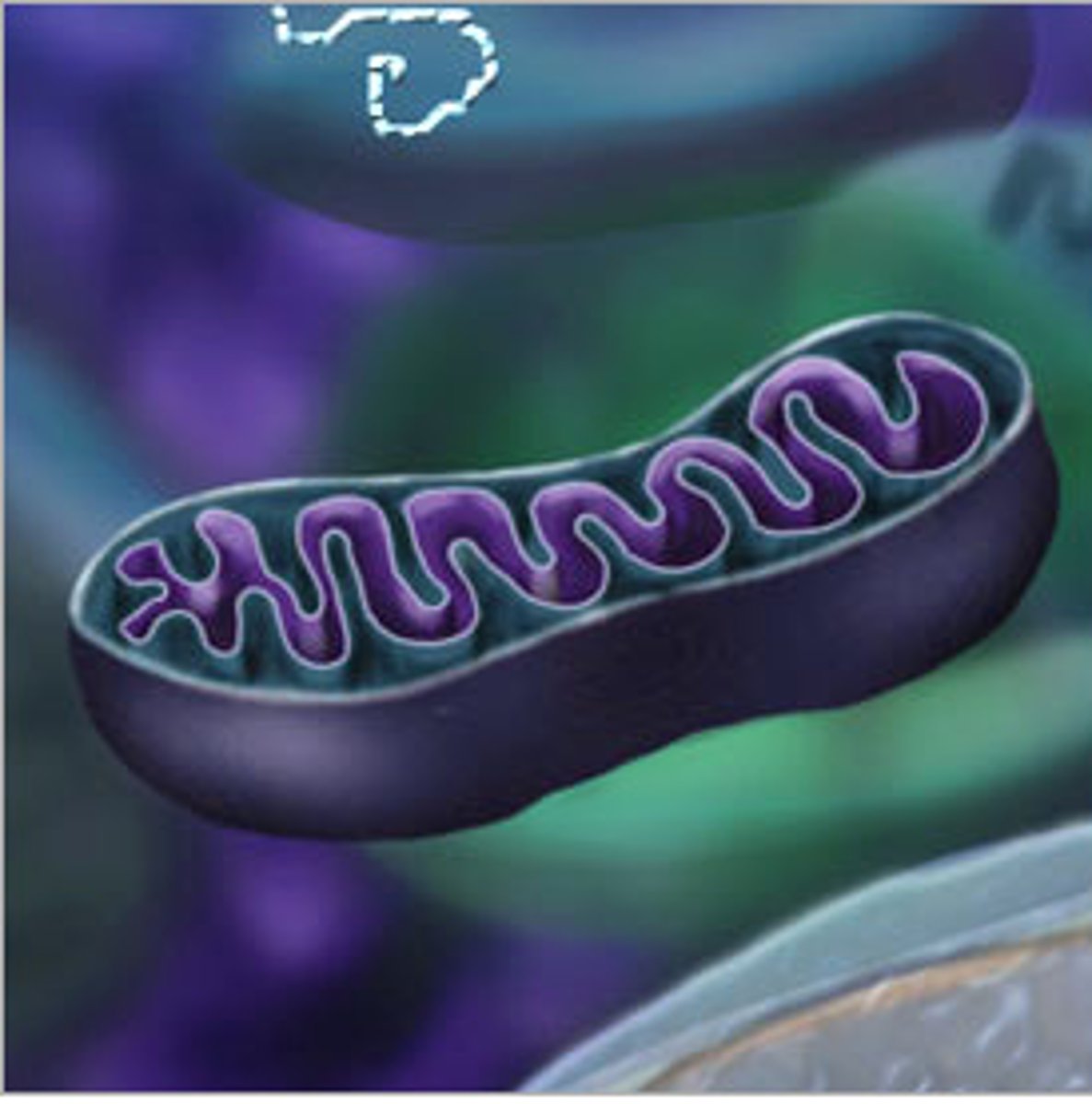
Mitochondria
Consume nutrients and create energy for the cell by breaking down the nutrients.
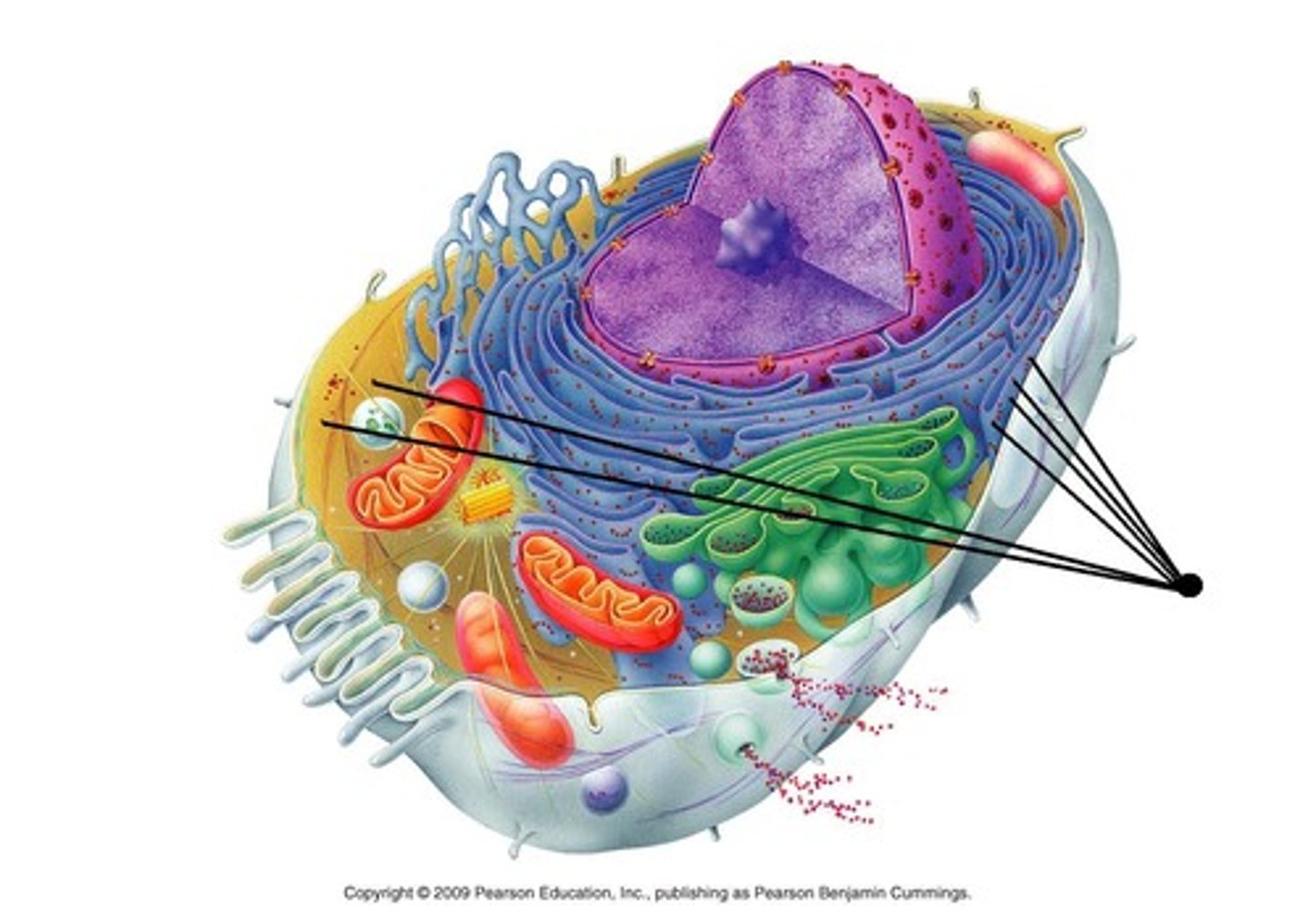
Ribosome
Creates protein for the cell.
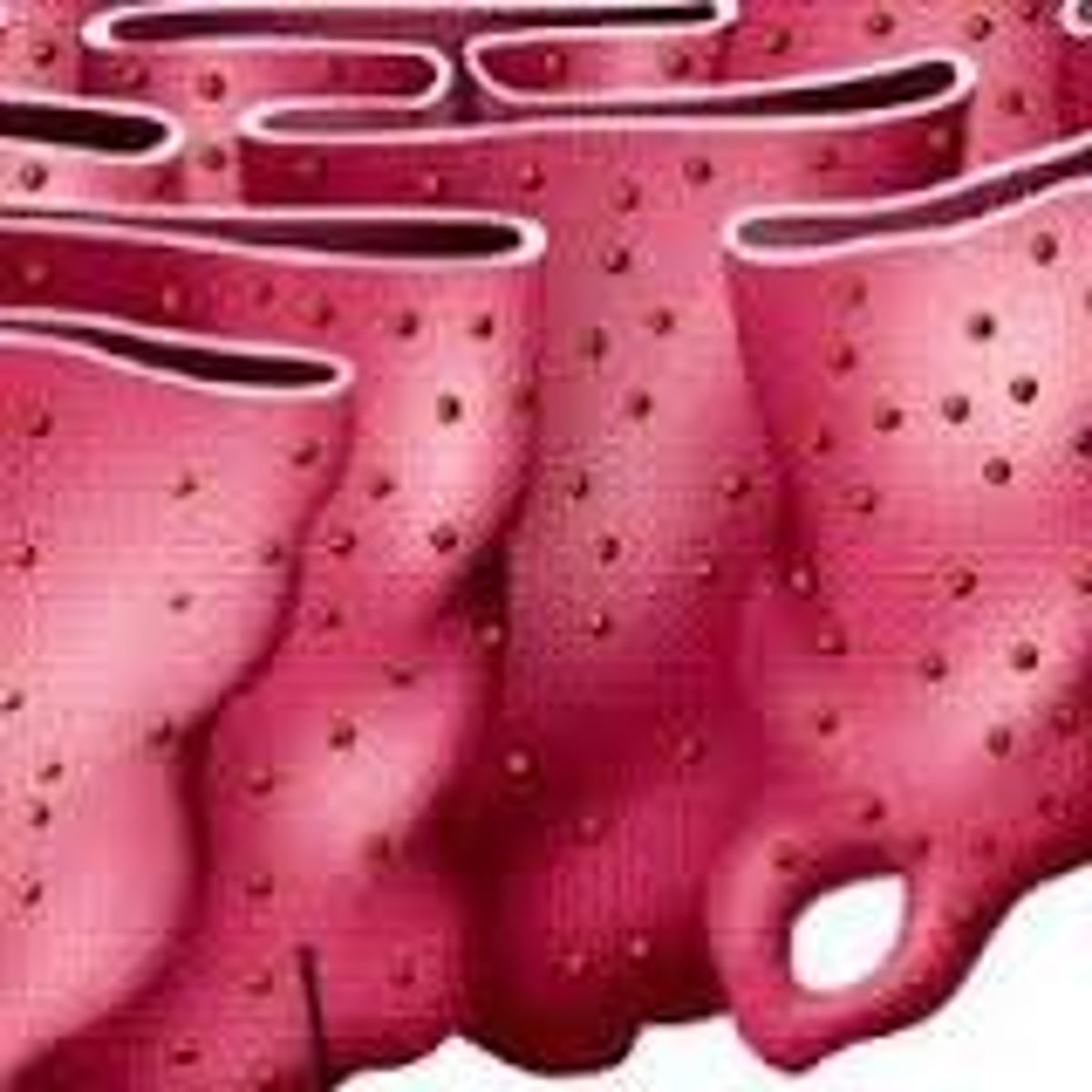
Rough ER (Endoplasmic Reticulum)
Packages and synthesizes proteins.
Smooth ER (Endoplasmic Reticulum)
Stores and creates lipids.
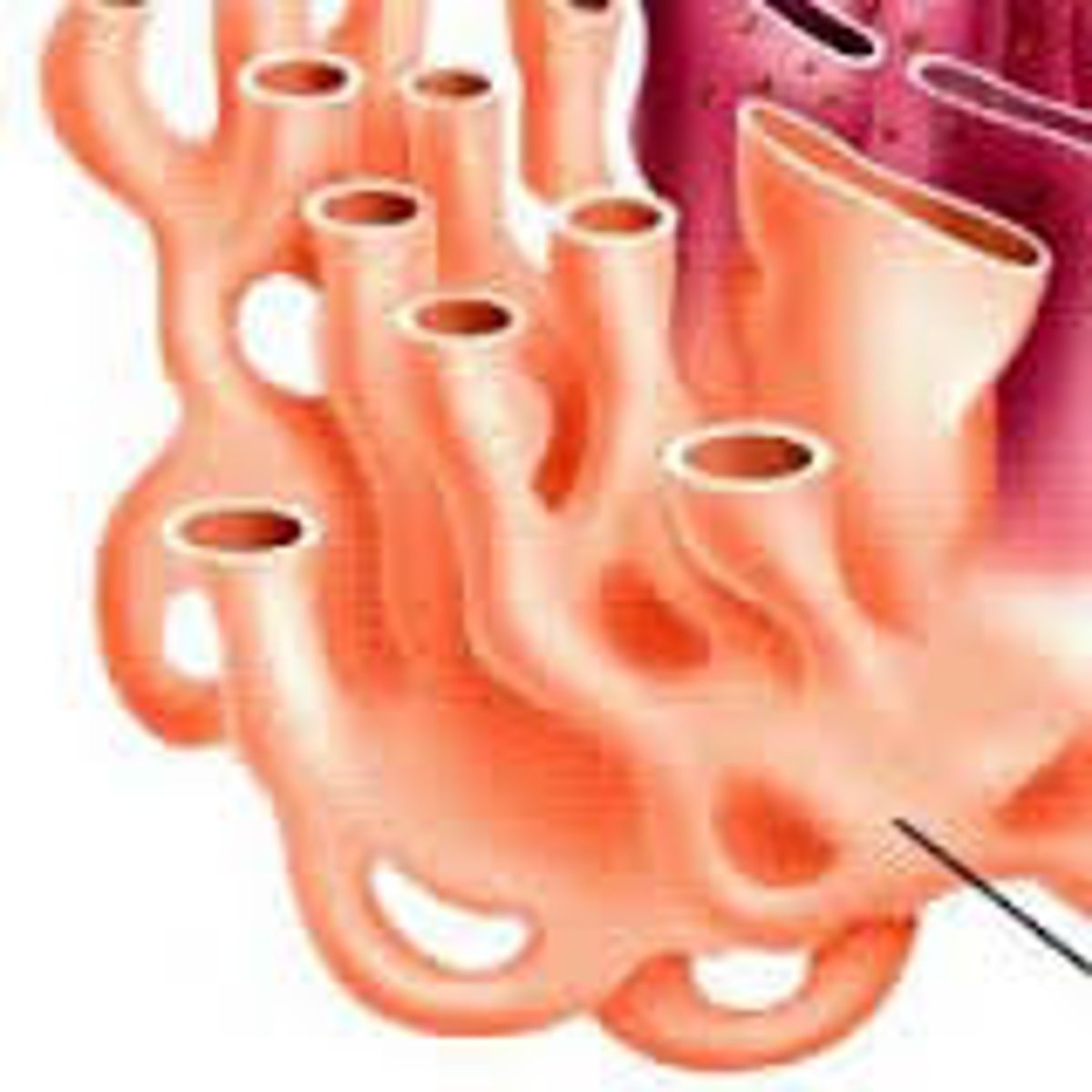
Golgi Apparatus
Takes in simple molecules to create complex molecules.
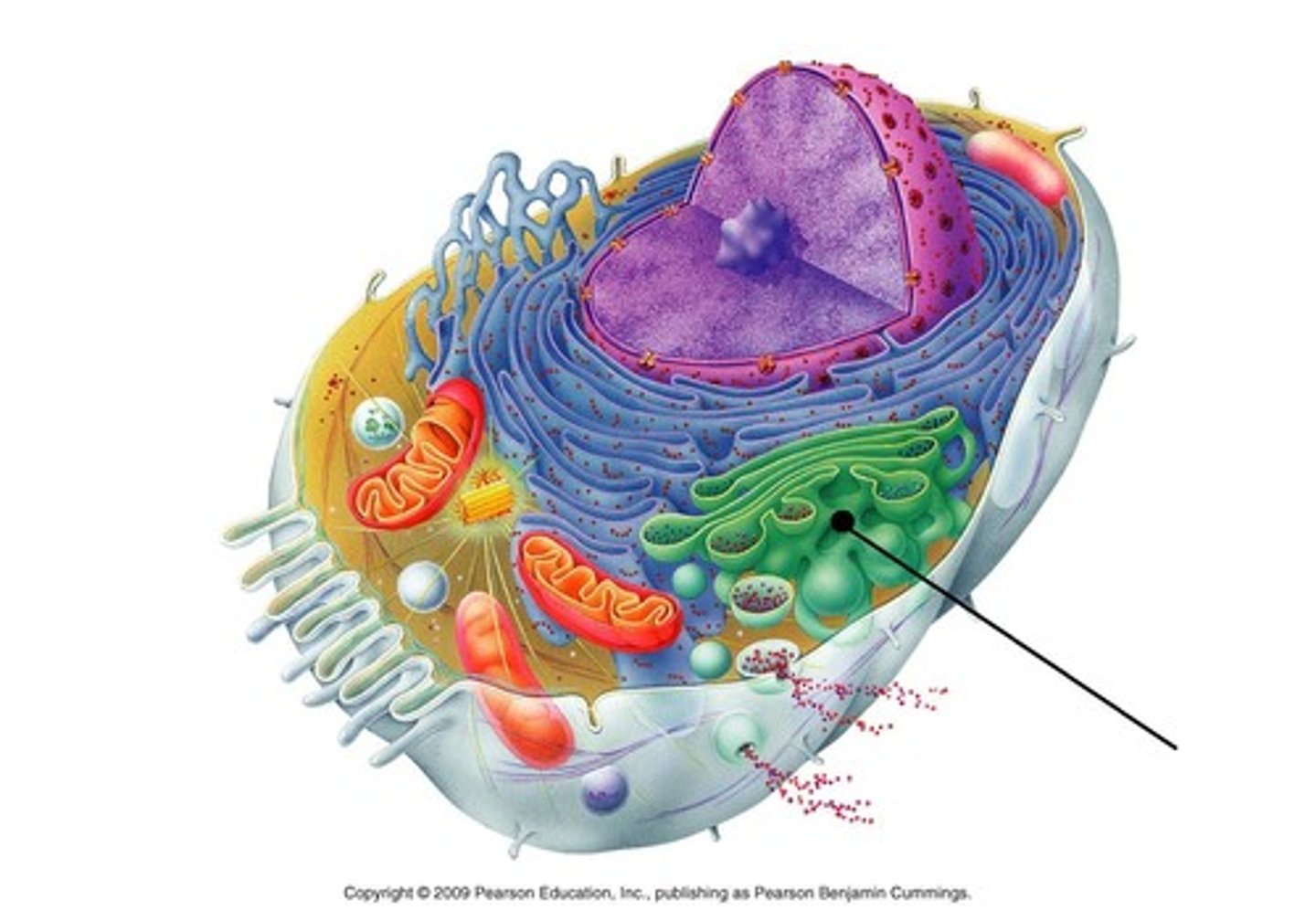
Vesicle
Store and transport substances around the cell.
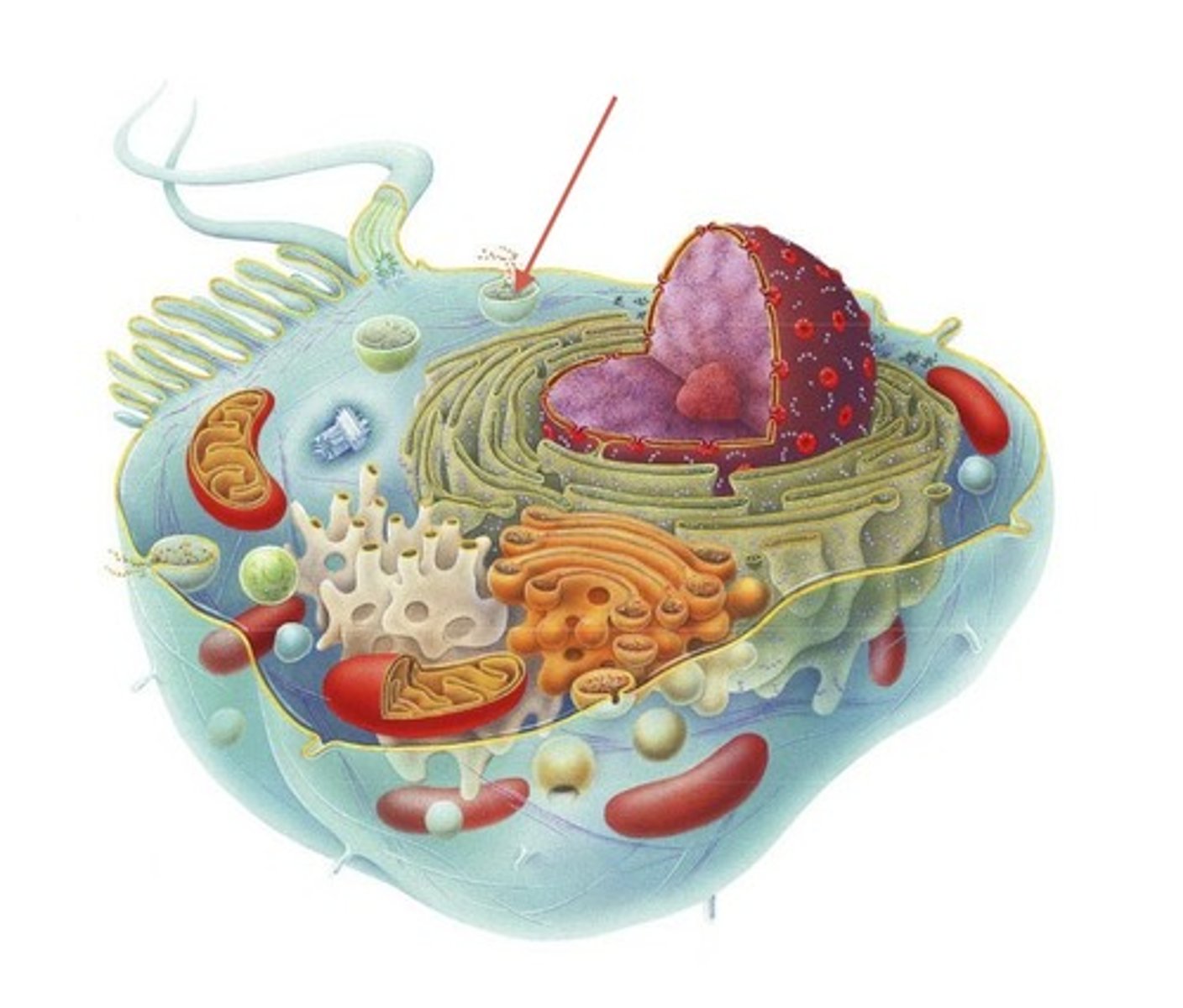
Vacuole
Storage pockets in the cell.
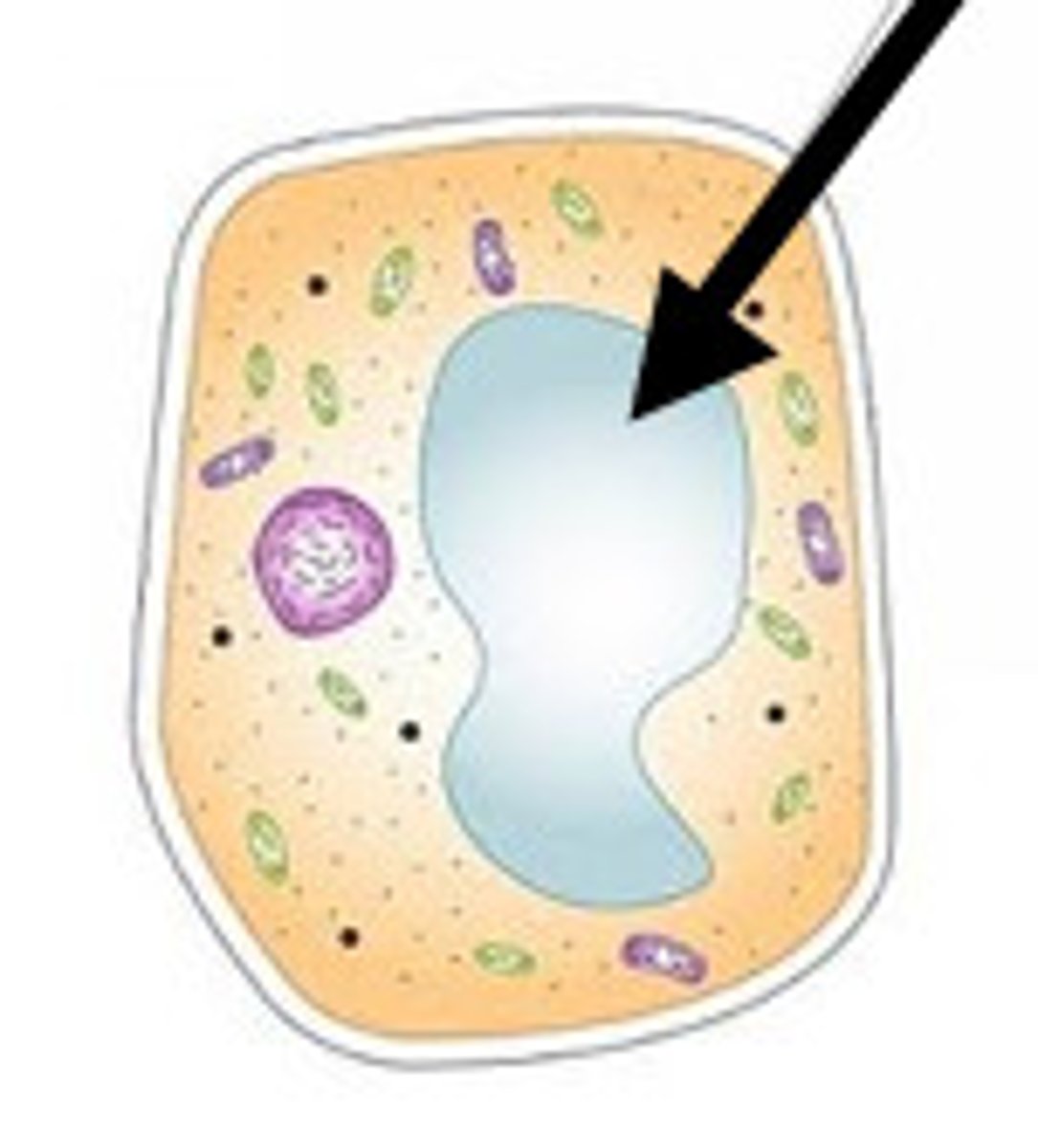
Cell Wall
Support the plant cells and allow them to be very sturdy.
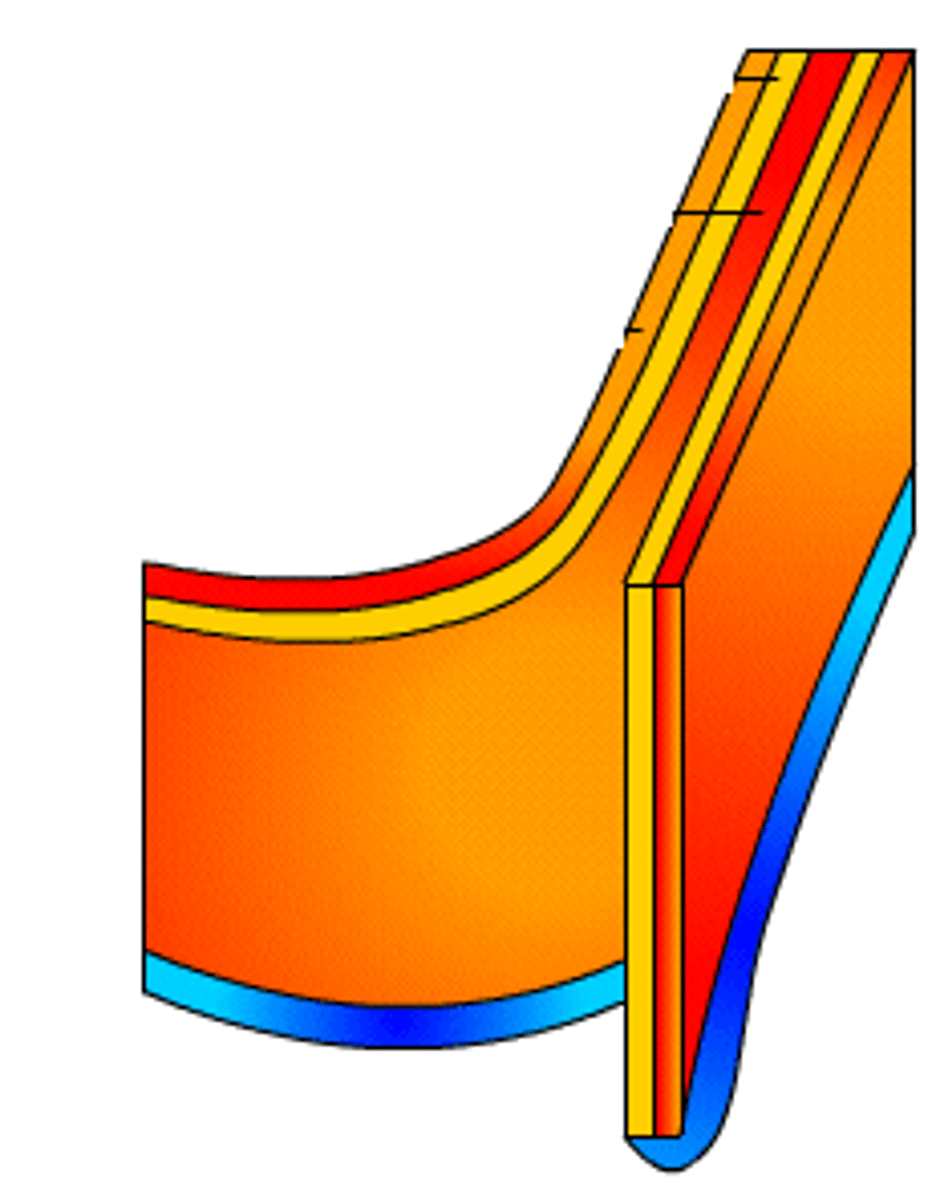
Chloroplast
A type of plastid that allow photosynthesis to occur.
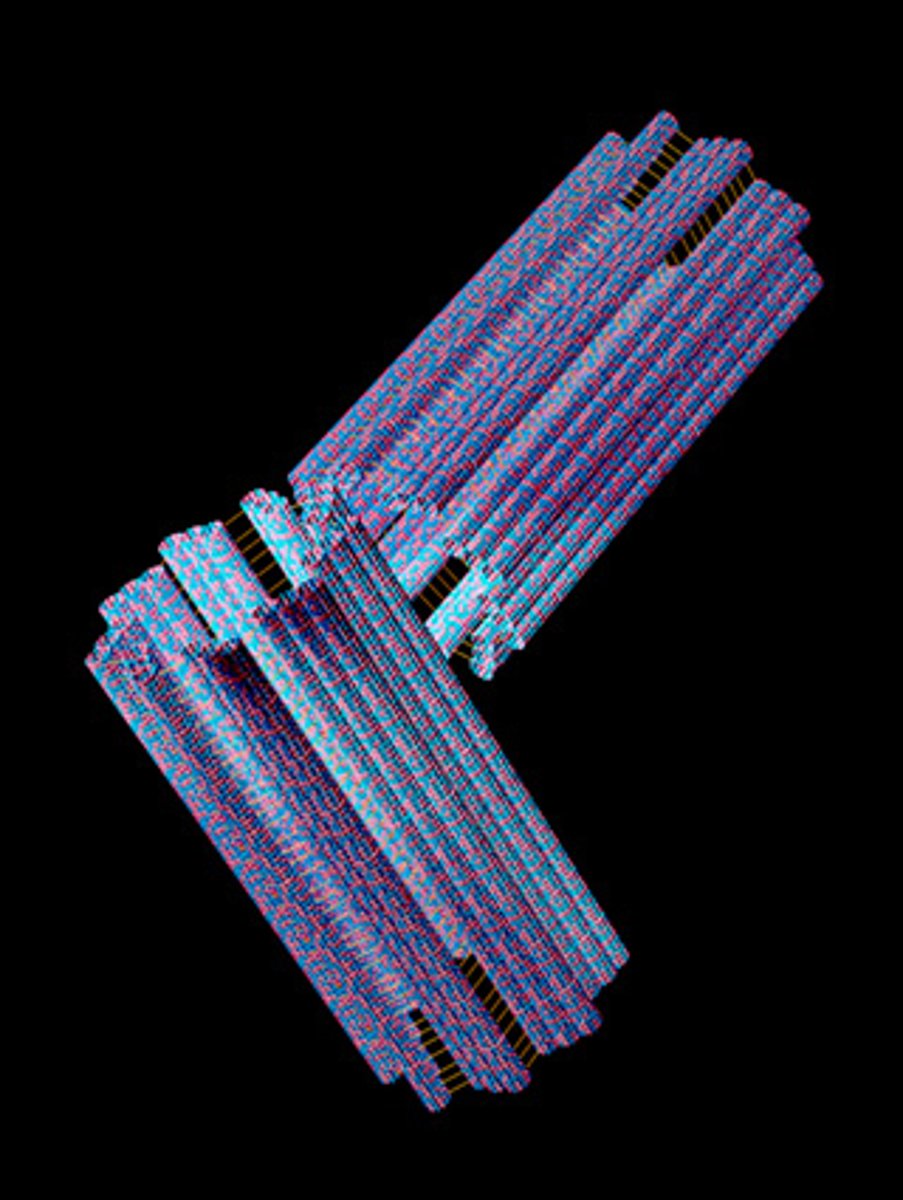
Centriole
Involved in cell division by using mitosis and meiosis.
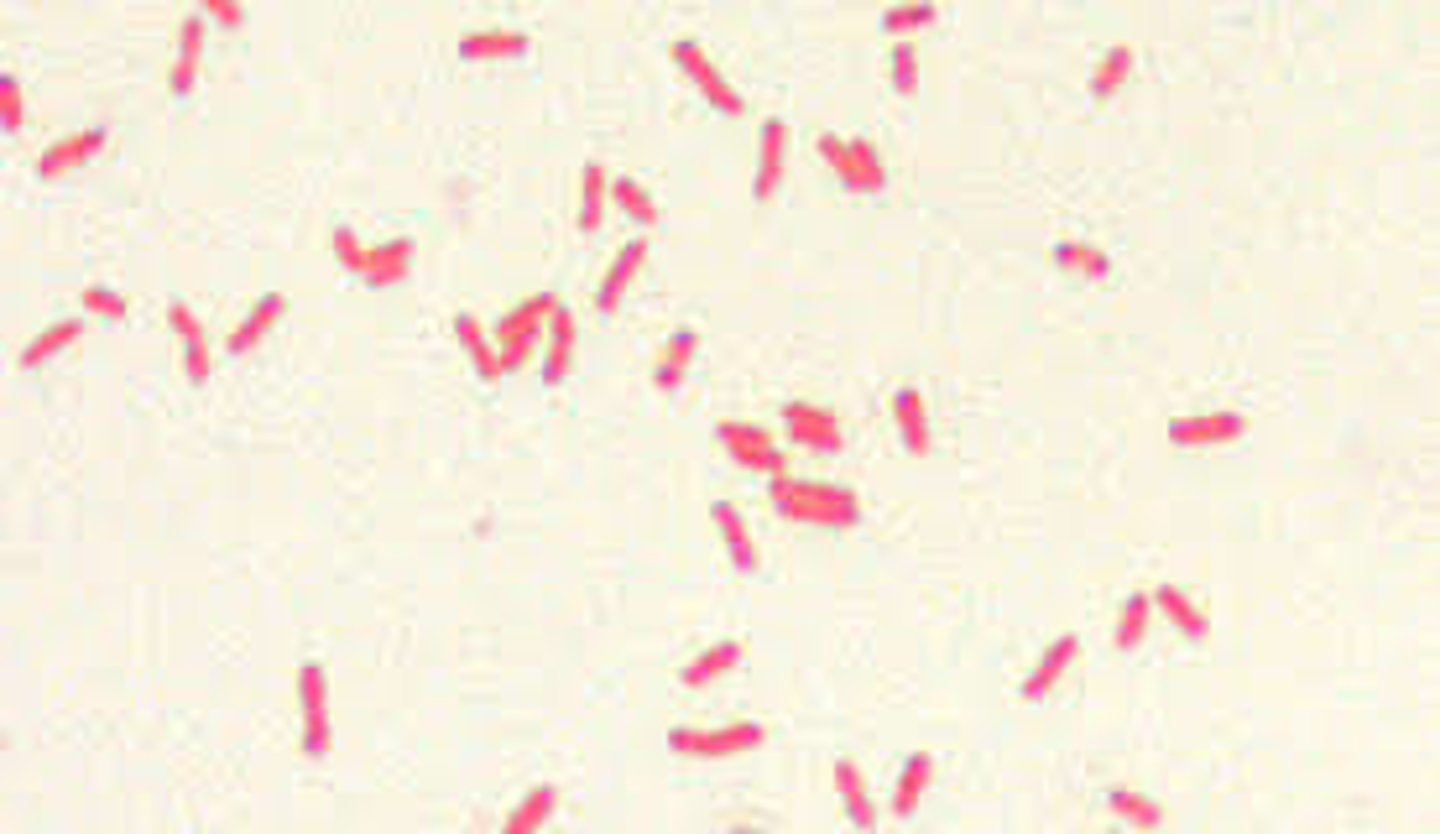
Anaerobic Bacteria
These are the bacteria who do not use oxygen to produce food. They are much like those at the beginning of Earth's history.
Aerobic Bacteria
These are the bacteria who do use oxygen to produce food. They are the present day bacteria.
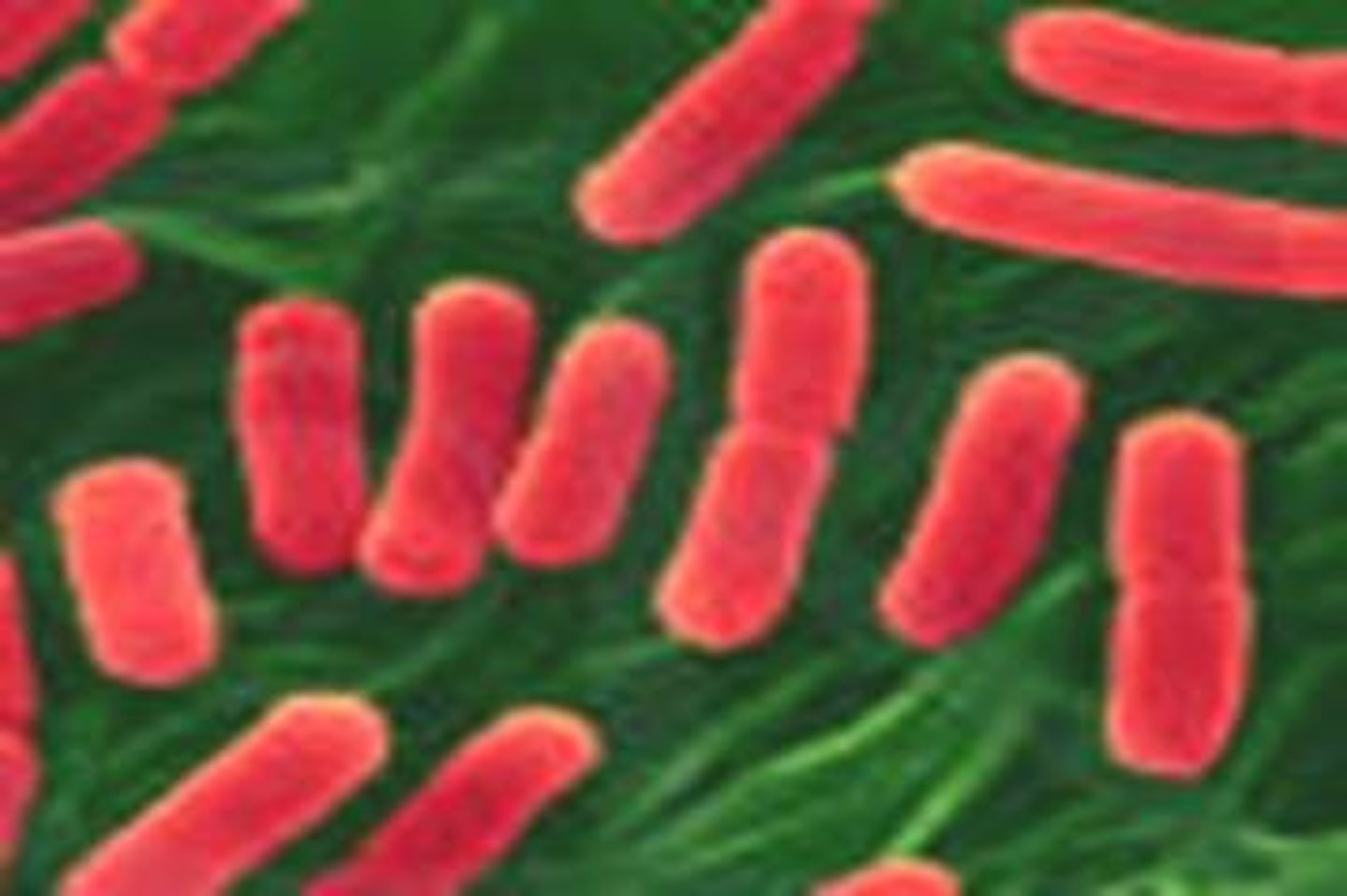
Photosynthetic Bacteria
These are the bacteria who use photosynthesis to produce their food. They use the sun's energy to do their food processing. They are living with the Aerobic Bacteria- and have been living after the Anaerobic Bacteria.
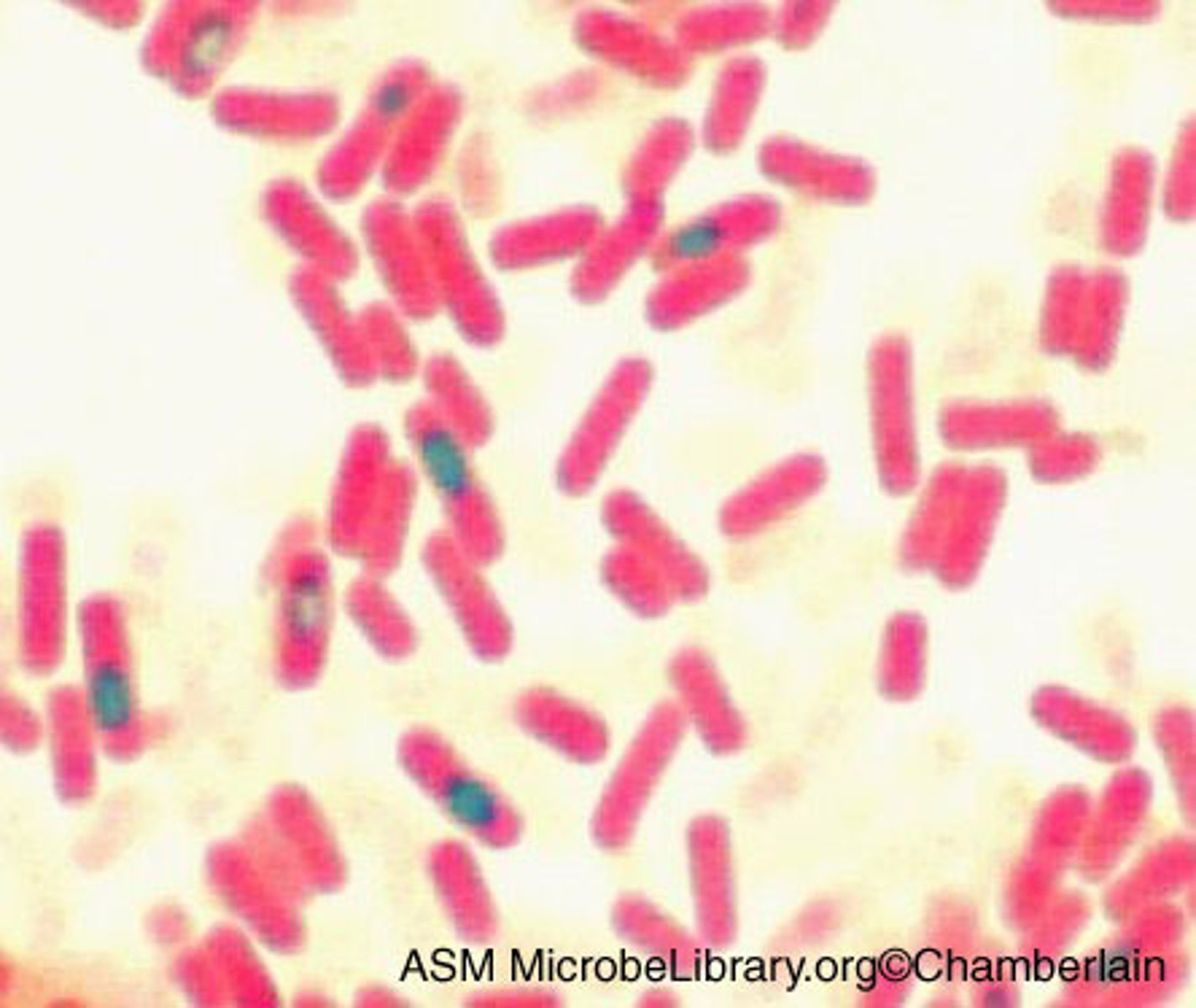
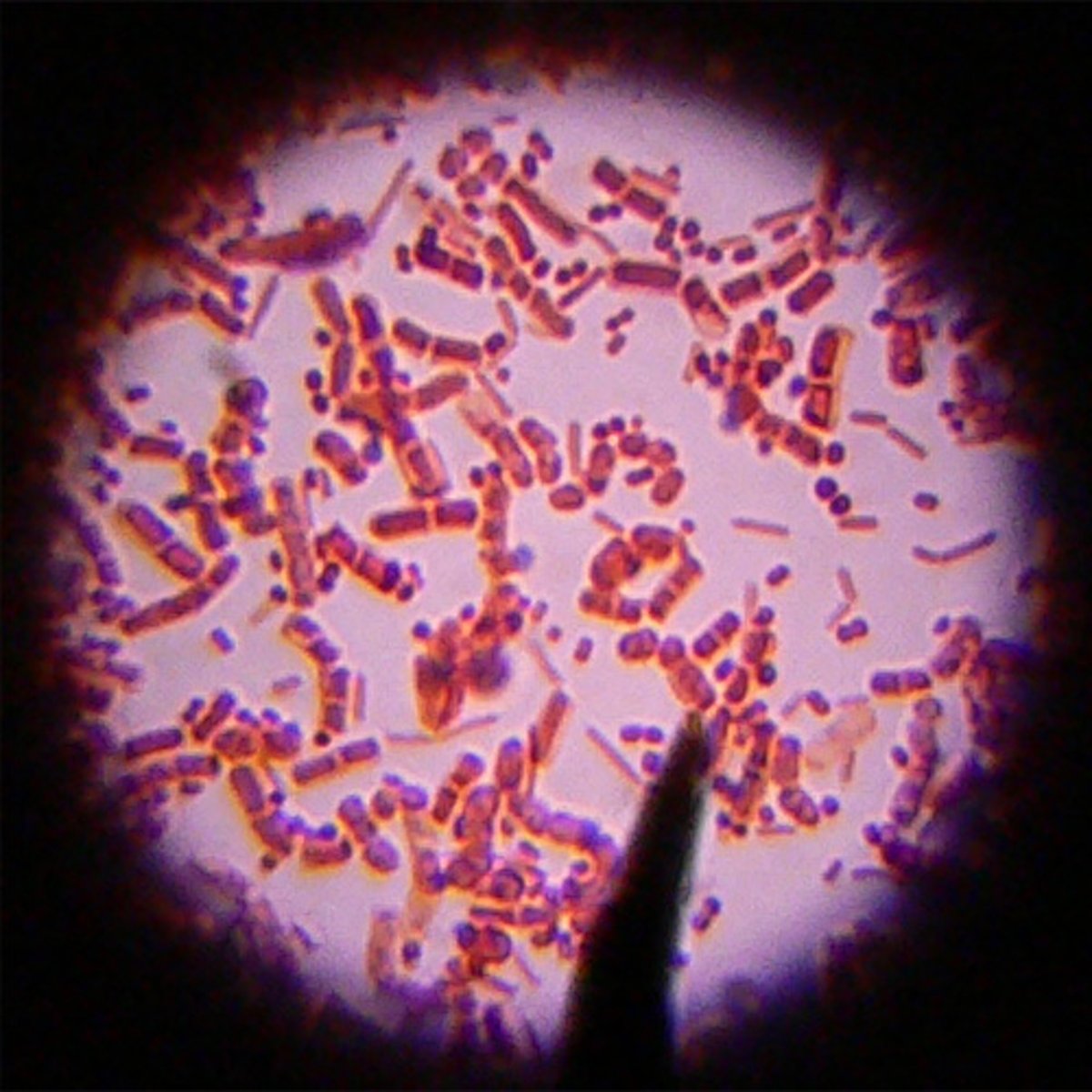
Bacilli Bacteria
Anaerobic, Rod-shaped bacteria that is mainly found in soil and water. May cause Food Poisoning, and Anthrax.
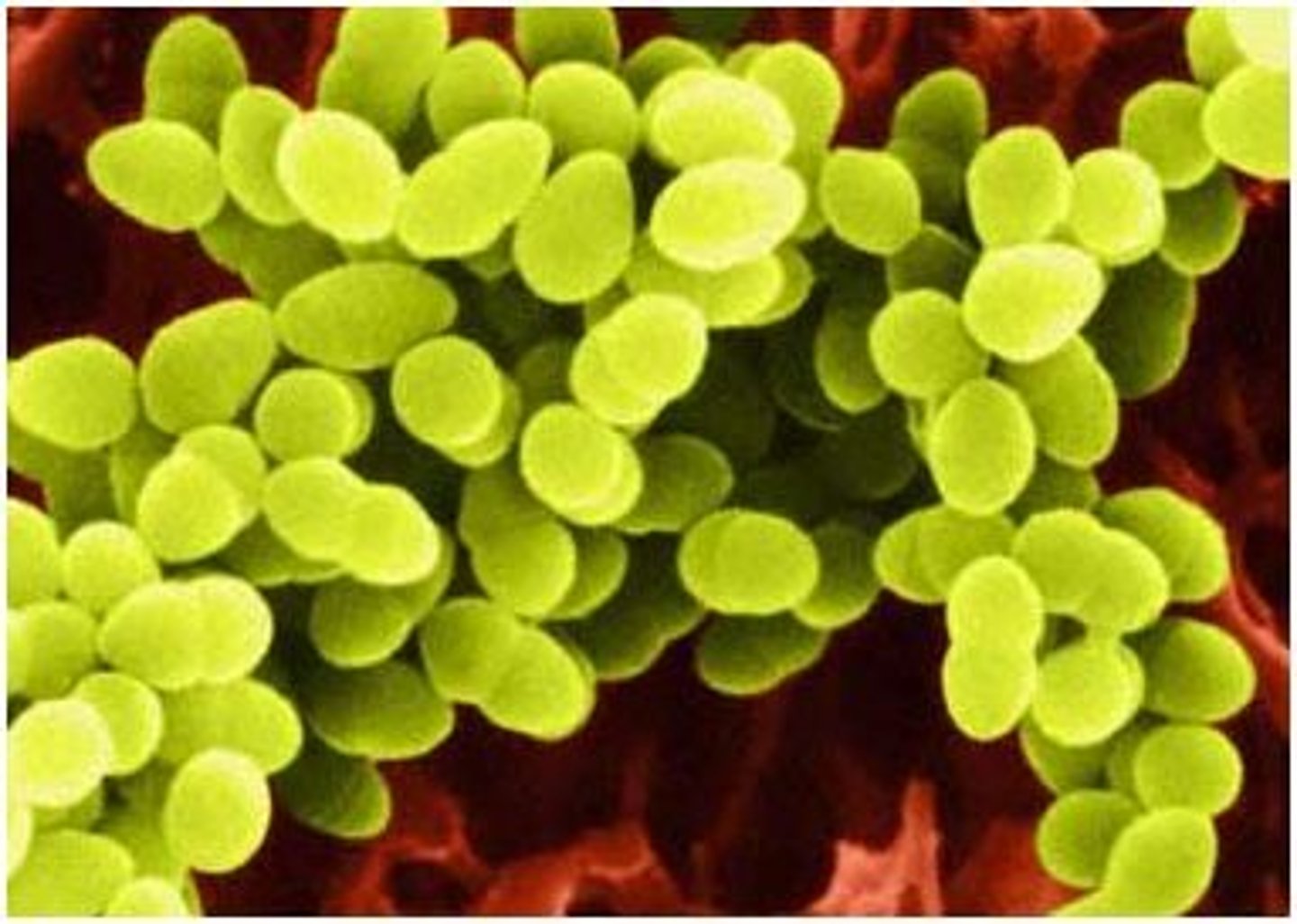
Cocci Bacteria
Any bacteria that is rounded, circular. Can be found almost anywhere, and many good types are found in humans. It may cause skin irritations, and sometimes serious diseases.
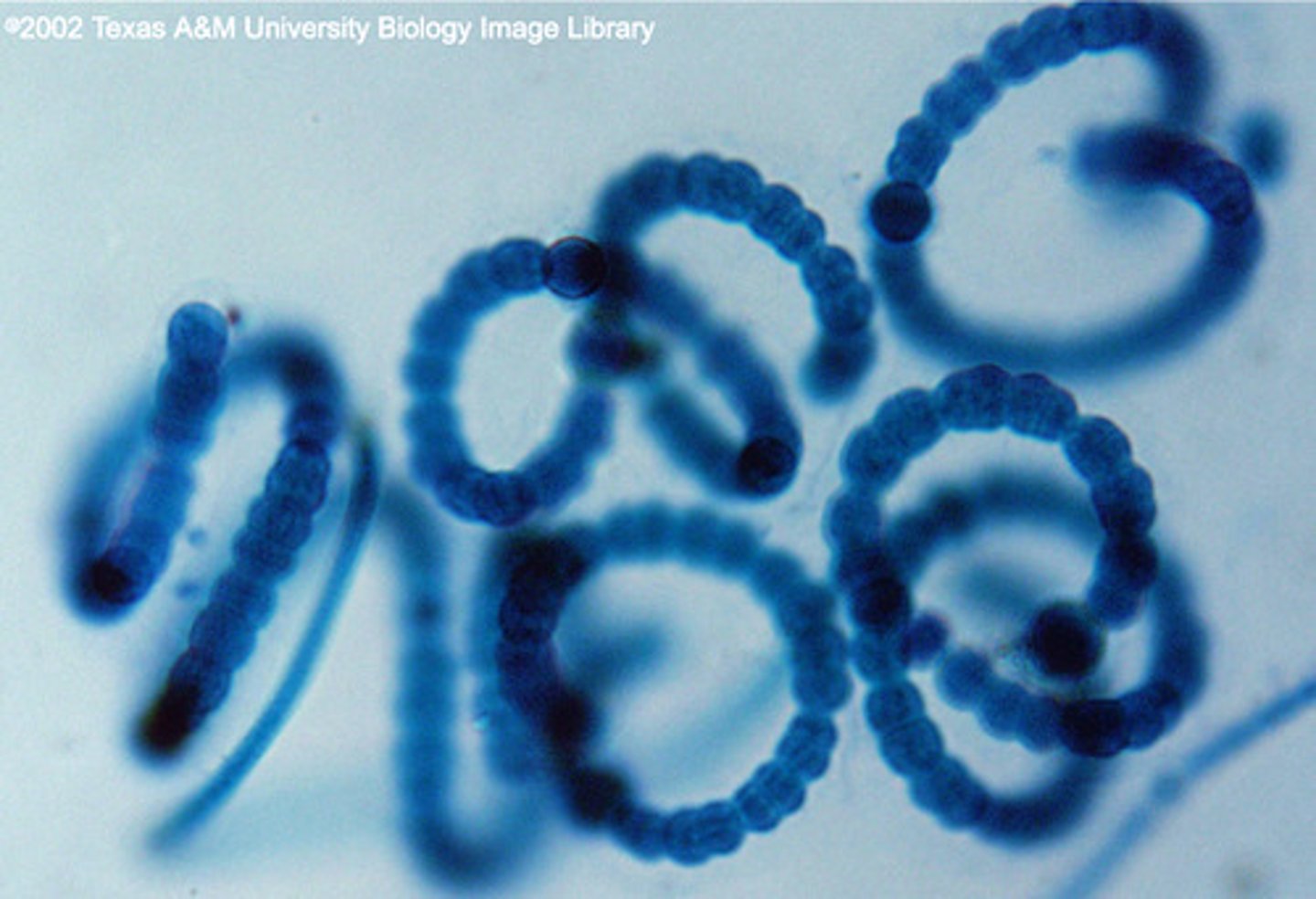
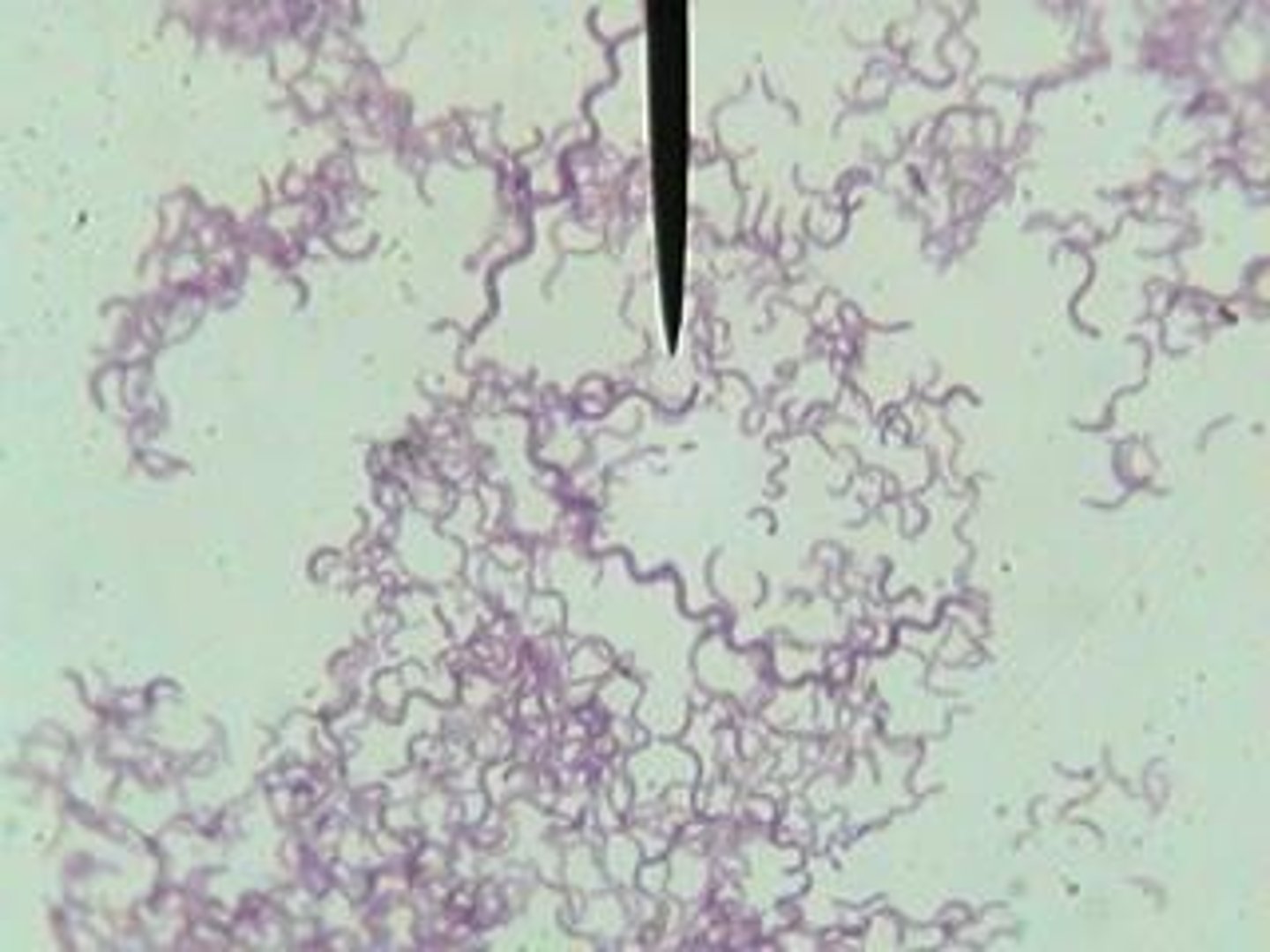
Spirillum Bacteria
Corkscrew-shaped, lives mainly in water due to it's shape. May cause rat-bite infection.
Animalia
Includes mammals, reptiles, birds, and is one of the 5 kingdoms of life.

Plantae
Includes plants, and is one of the 5 kingdoms of life.

Fungi (Kingdom)
Includes Fungi and is one of the 5 kingdoms of life

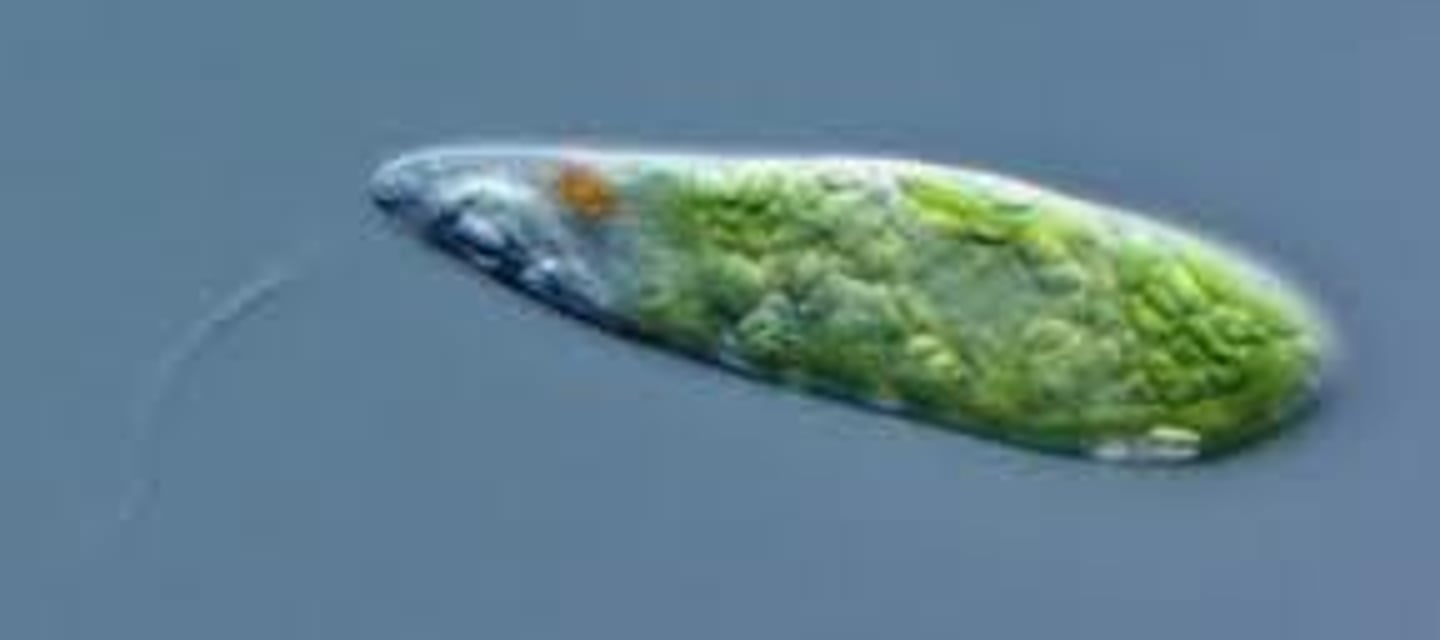
Protista
Includes Protozoans, and any single-celled eukaryotes. It is one of the 5 kingdoms of life.

Monera
Includes Bacteria, and unicellular organisms, in is one of the 5 kingdoms of life.
Bright Field Microscope
Uses the visible light source under the stage to produce a clear image. The Diaphragm adjusts the amount of light entering the stage. It consists of three objectives- the scanning power(usually 4x-6x), the low power(10-12x), and high power(40x).
Dark Field Microscope
Illumination comes from the sides, thus making the background appear dark, and the organism on the slide appear light(bright).
Phase Contrast Microscope
An optical-microscopy technique that converts phase shifts in light passing through a transparent specimen to brightness changes in the image. Phase shifts themselves are invisible, but become visible when shown as brightness variations.
Differential-Interference Microscope
Optical Microscopy used to enhance or create contrast in transparent, unstained organisms.
Fluorescence Microscope
An optical microscope that uses fluorescence and phosphorescence instead of, or in addition to, reflection and absorption to look at organisms on a slide.
Up to 2000x magnification.
Confocal Microscope
A microscope used for increasing the optical resolution and contrast that eliminates out-of-focus light.
Up to 2000x magnification.
Transition Electron Microscope (TEM)
A form of electron microscopy in which an image is derived from electrons that have passed through the specimen, in particular one in which the whole image is formed at once rather than by scanning.
Up to 100,000x magnification.
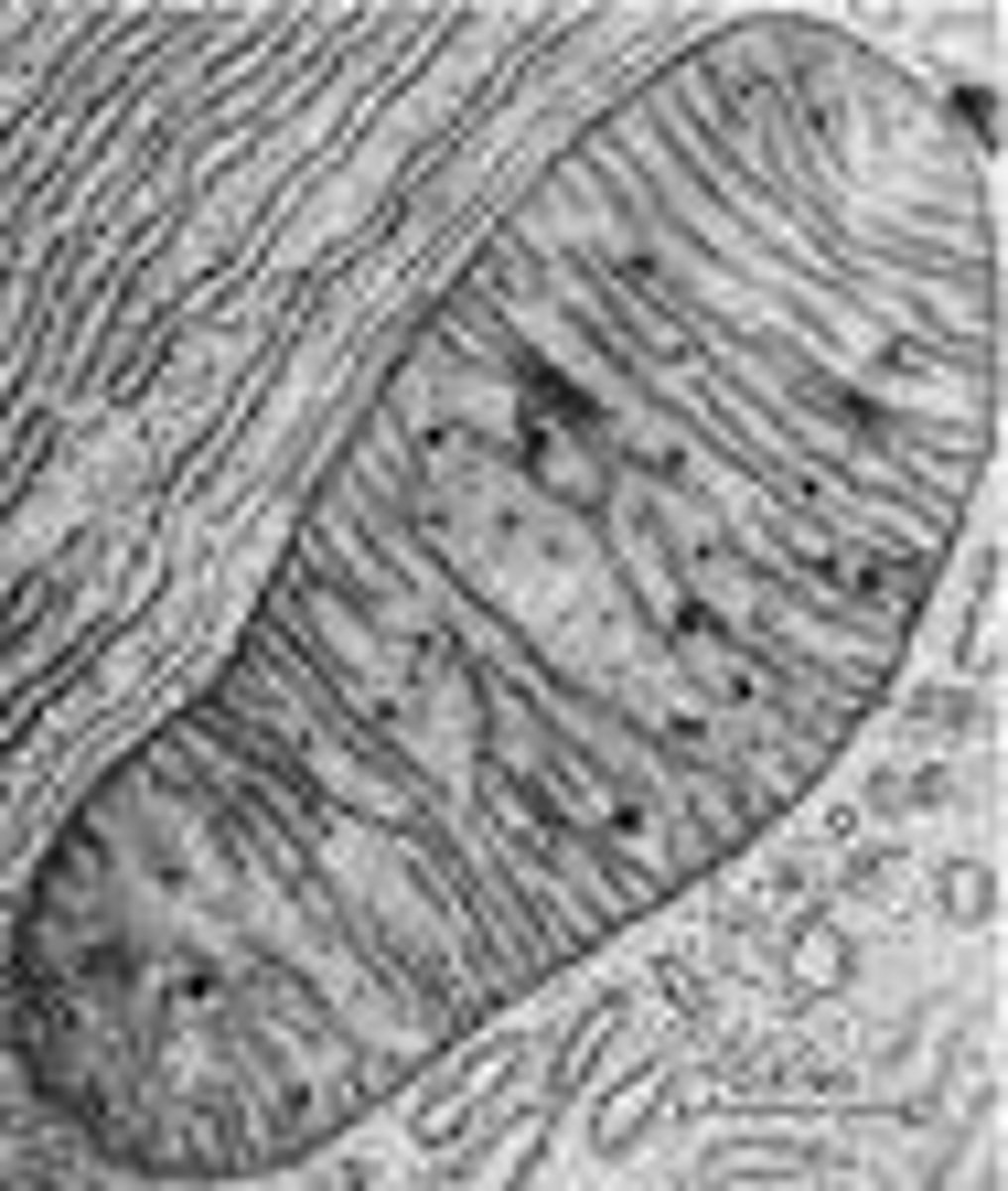
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
An electron microscope in which the surface of a specimen is scanned by a beam of electrons that are reflected to form an image.
An instrument that bounces electrons off objects to create a three-dimensional image that is more highly magnified than possible through a light microscope.
up to 650,000x magnification.

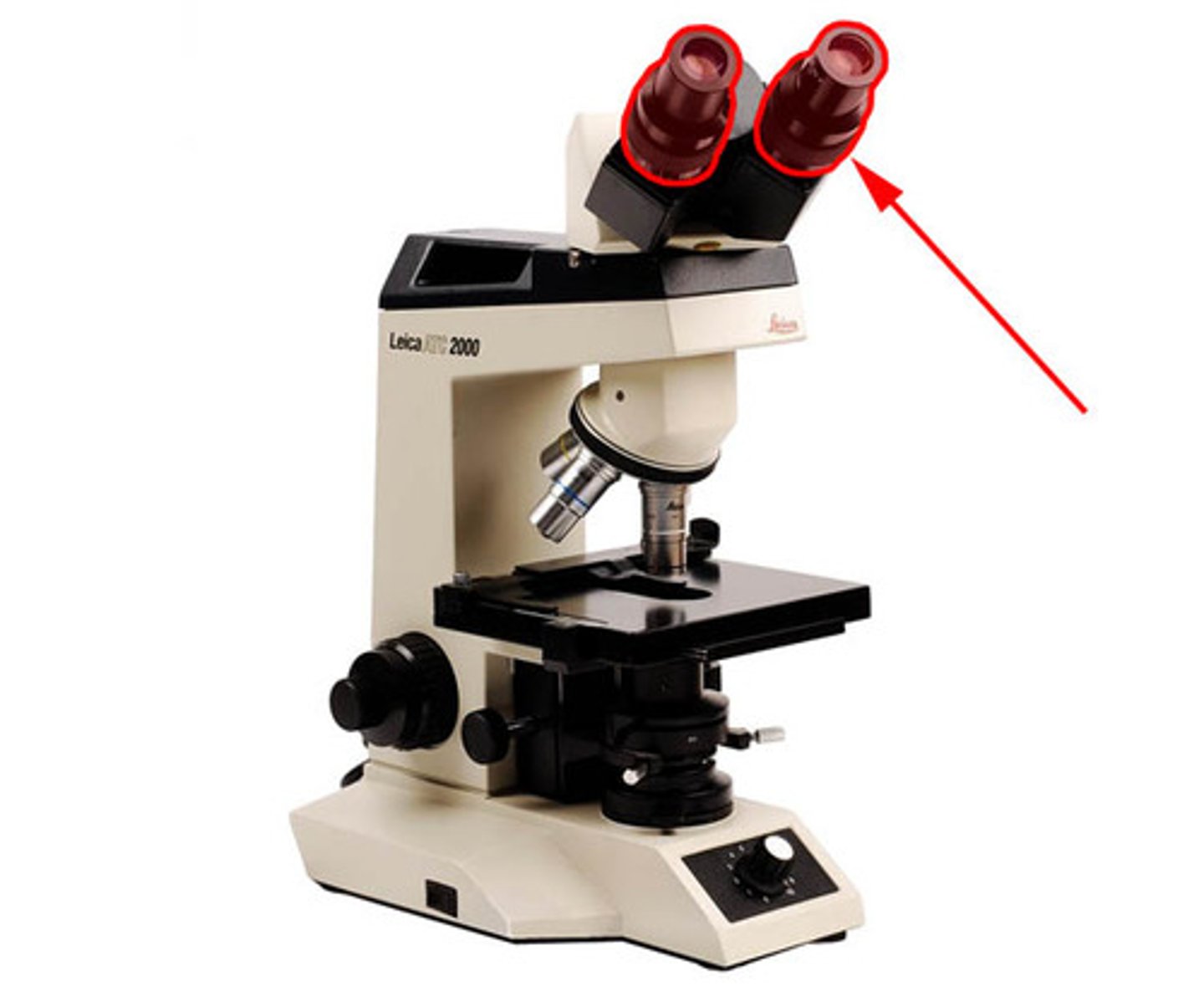
Ocular
The eyepiece in which you see through. This has a magnification of 10x.
magnifies the image formed by the objective.
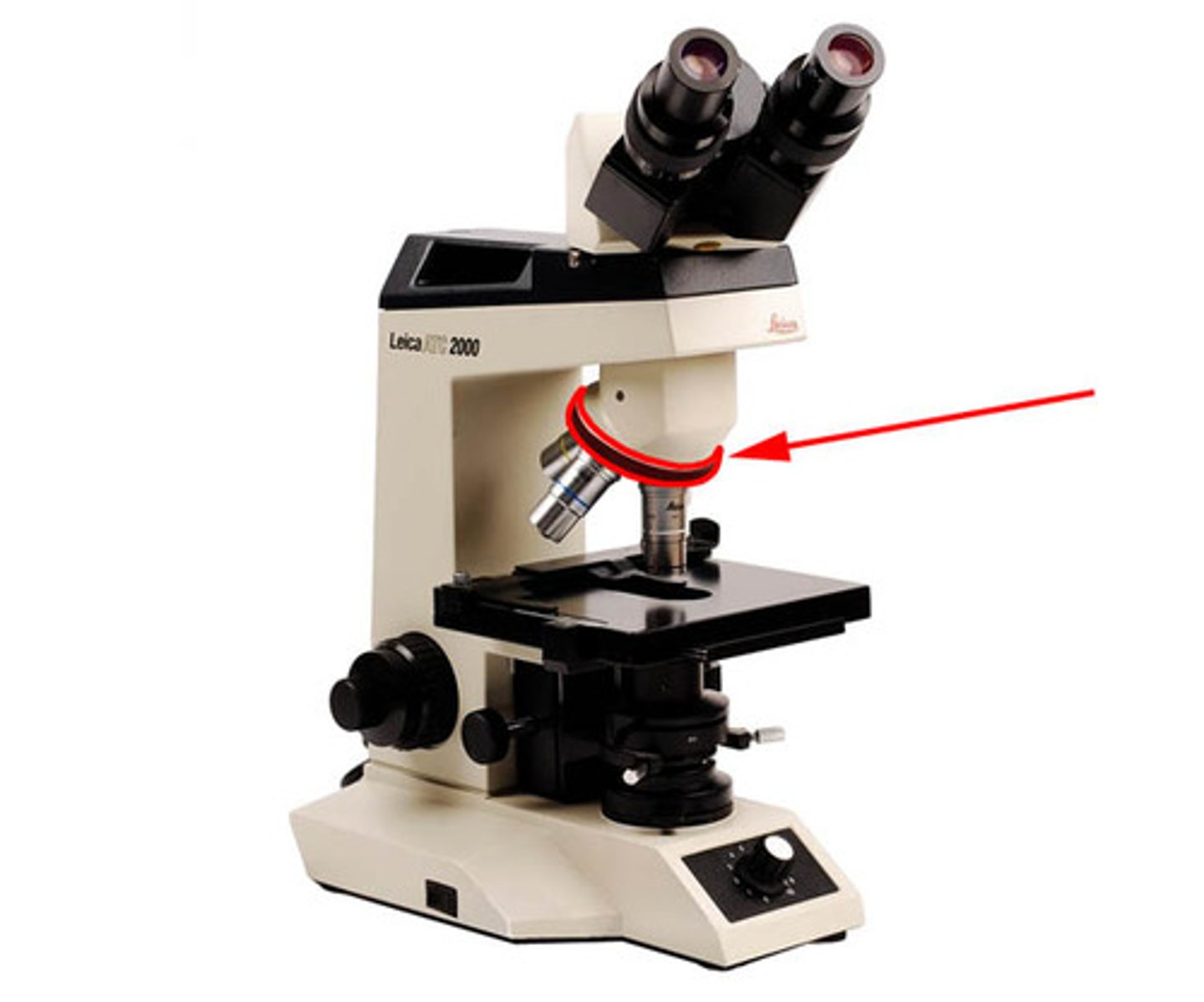
Nosepiece
Supports and holds the objectives.
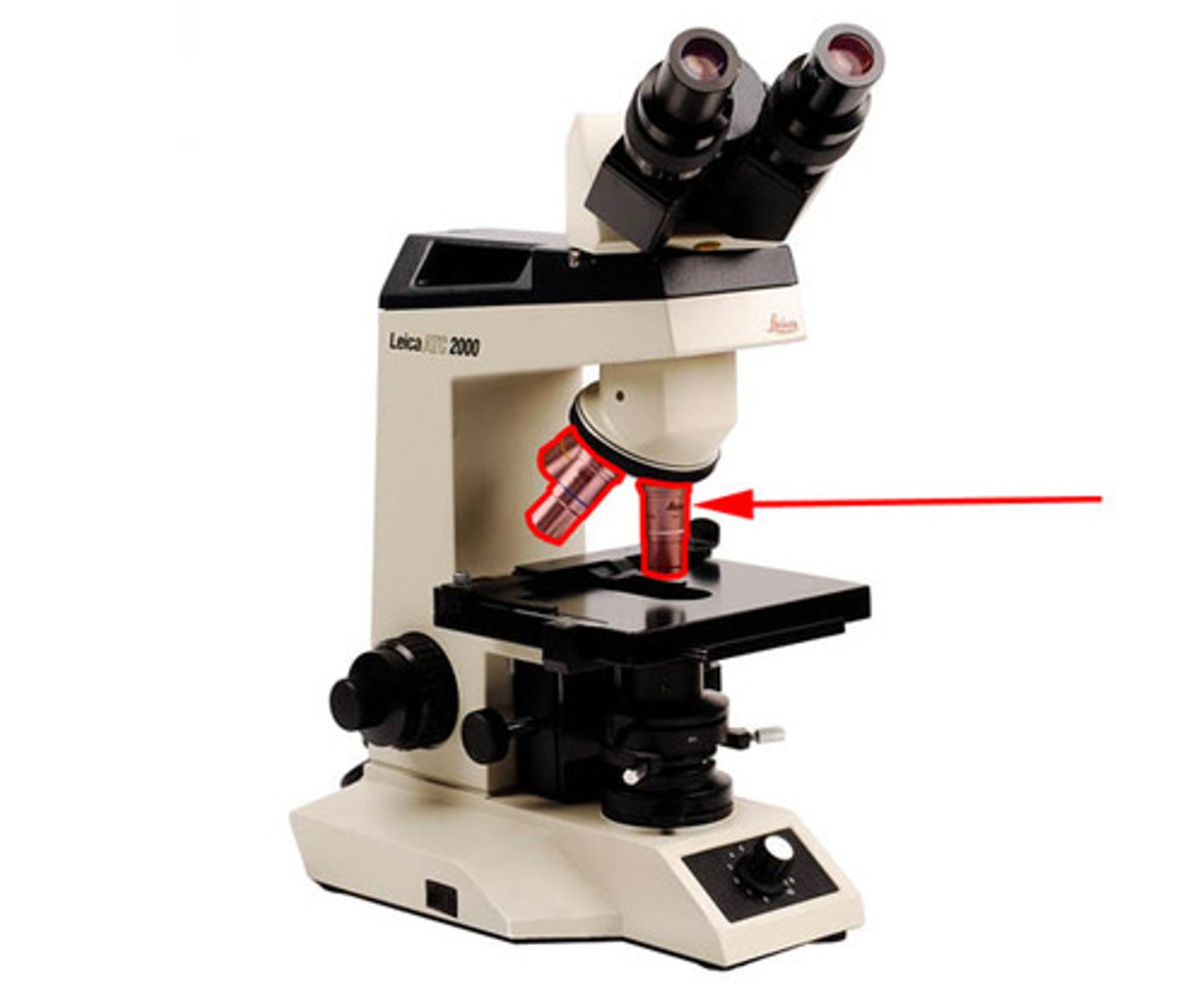
Objectives
Magnify the item on the slide either: A. Scanning power, which usually ranges from 4x to 6x; B. Low power, which usually ranges from 10x to 12x; C. High power, which usually is 40x
lenses that receive the light from the field of view and form the first image.
Stage Clips
Holds the slide down to the stage.
supports the slide and the specimen.
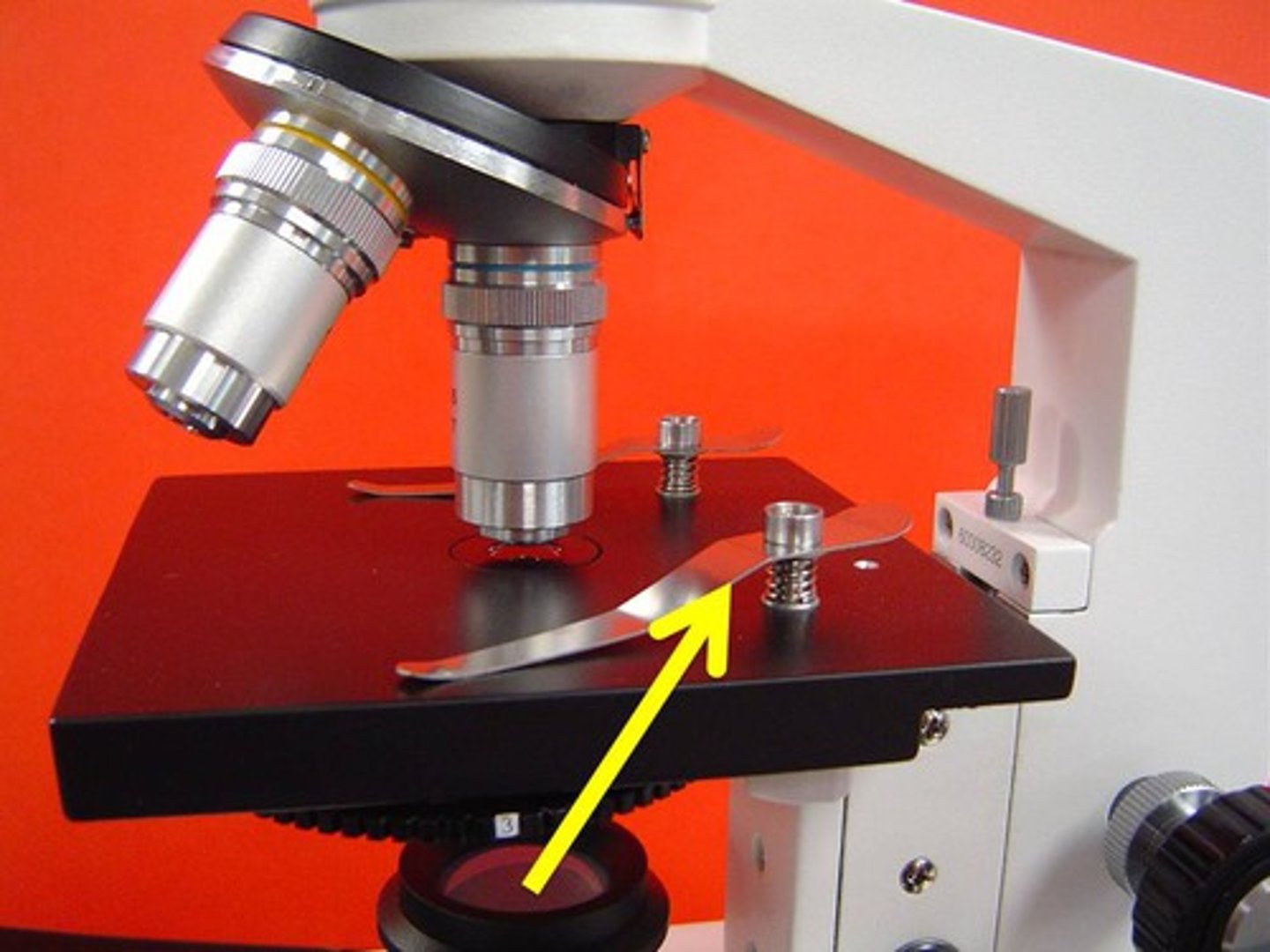

Stage
Holds the slide.
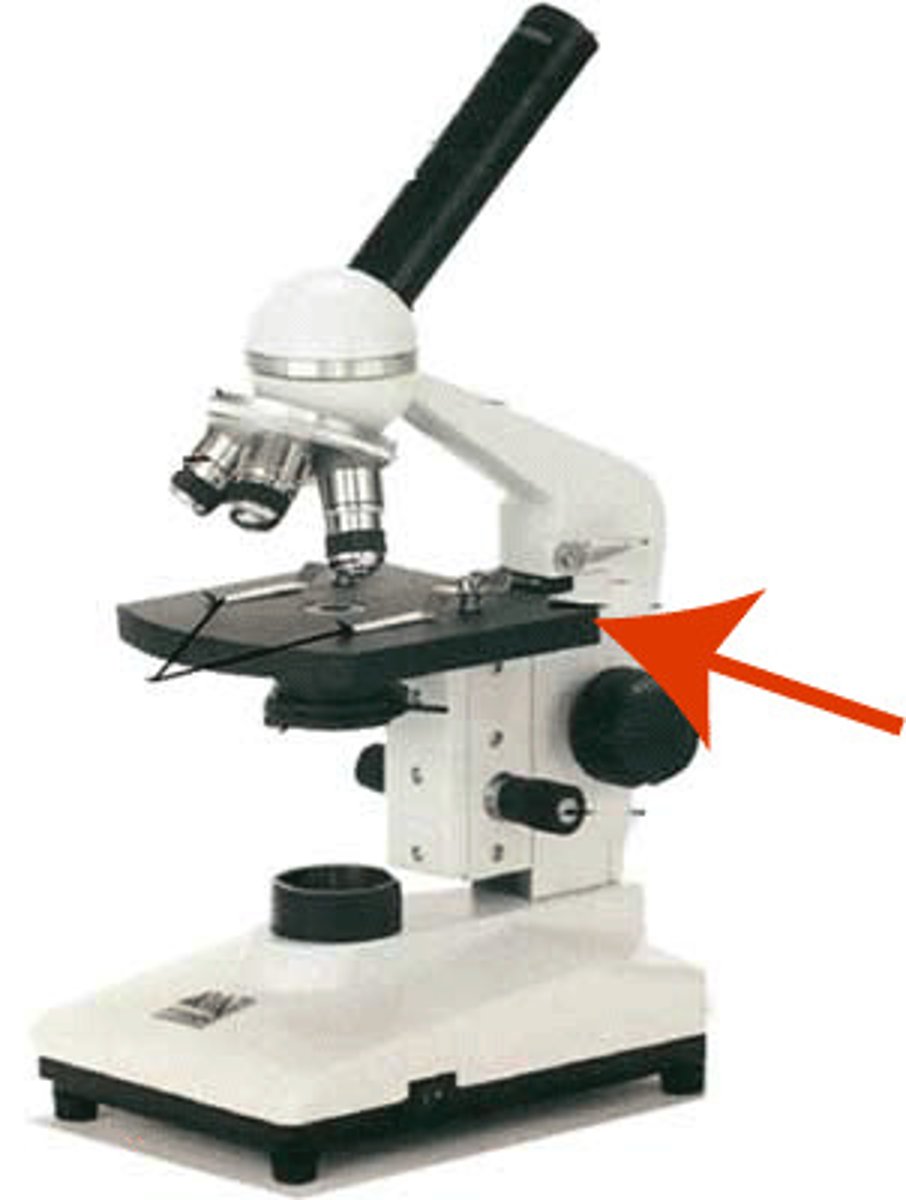
Coarse Adjustment
Used for initial or low power adjustment.
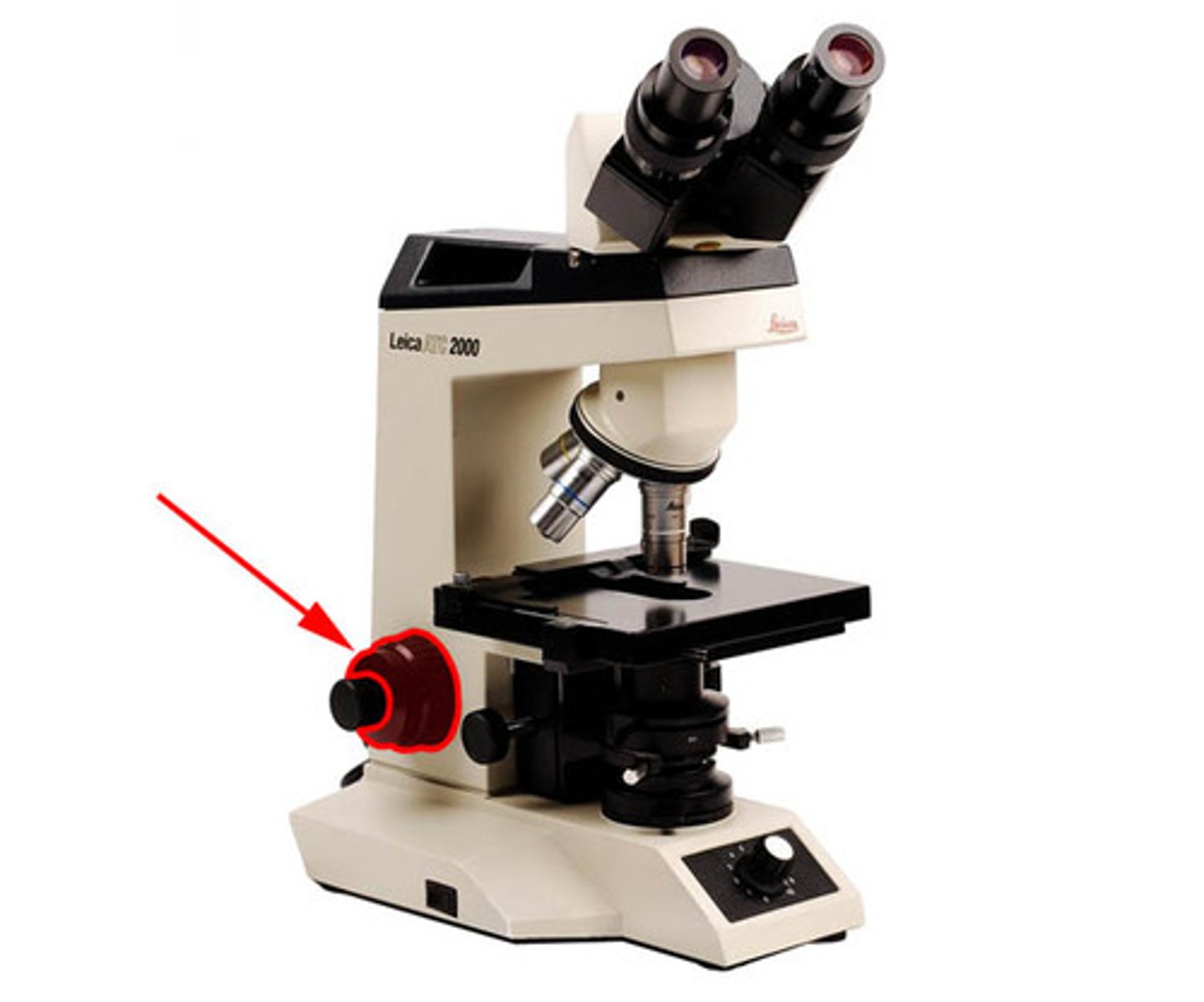
Fine Adjustment
Used for fine tuning & high power focusing.
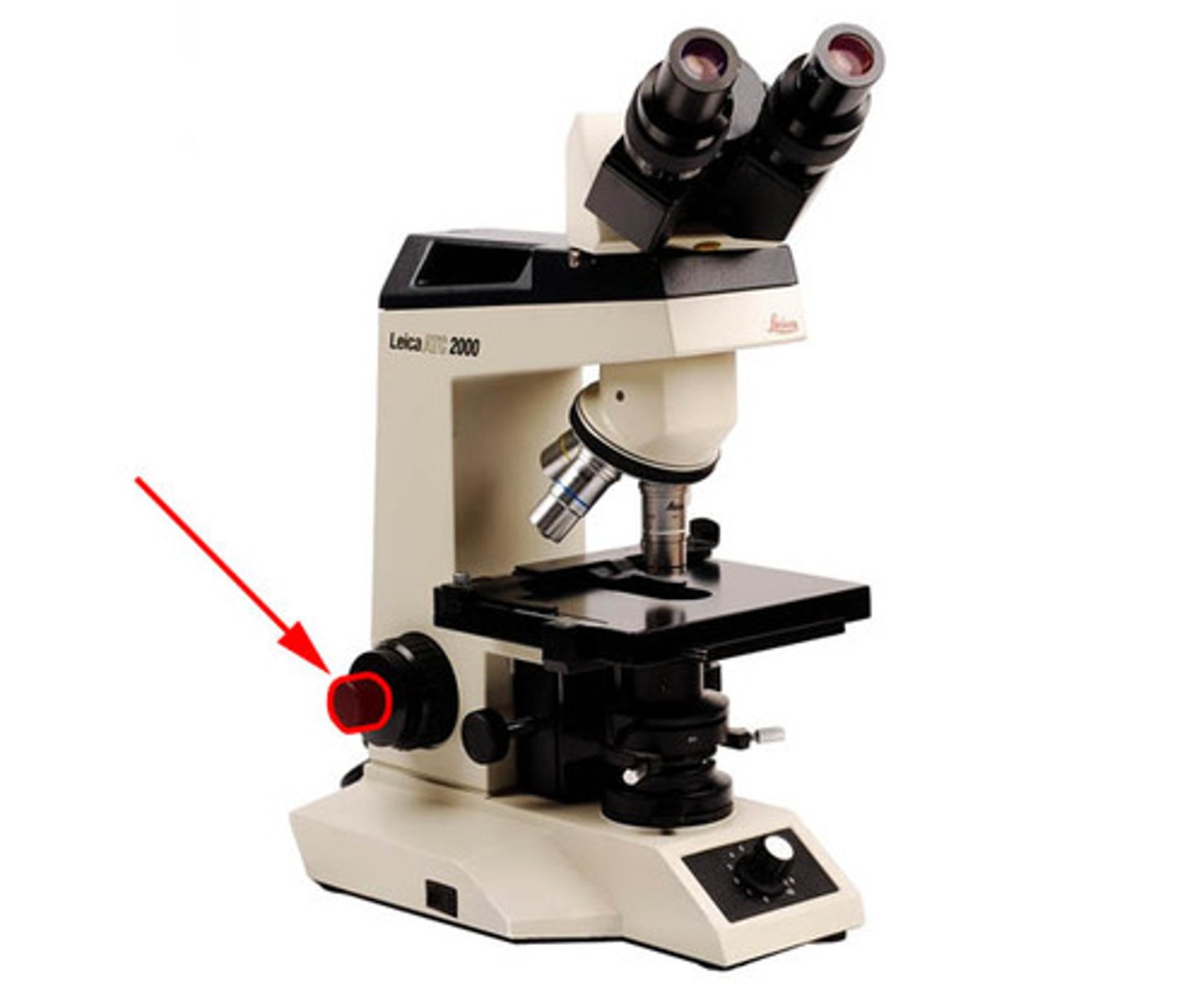
Base
Foundation which supports the scope & keeps it stable.

Diaphragm
Controls how much light illuminates the organism/slide.
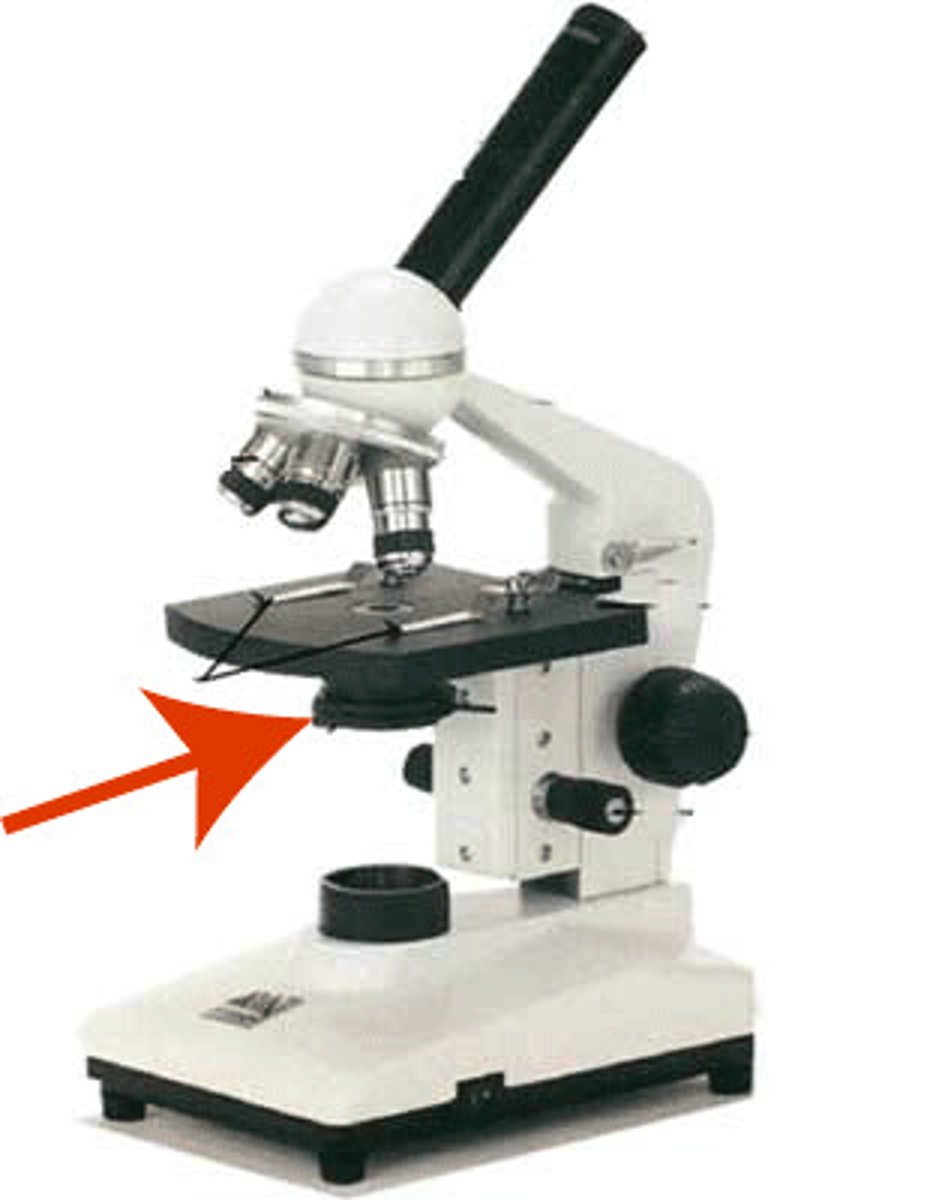
Light Source
It is the light source that lights up the specimen.

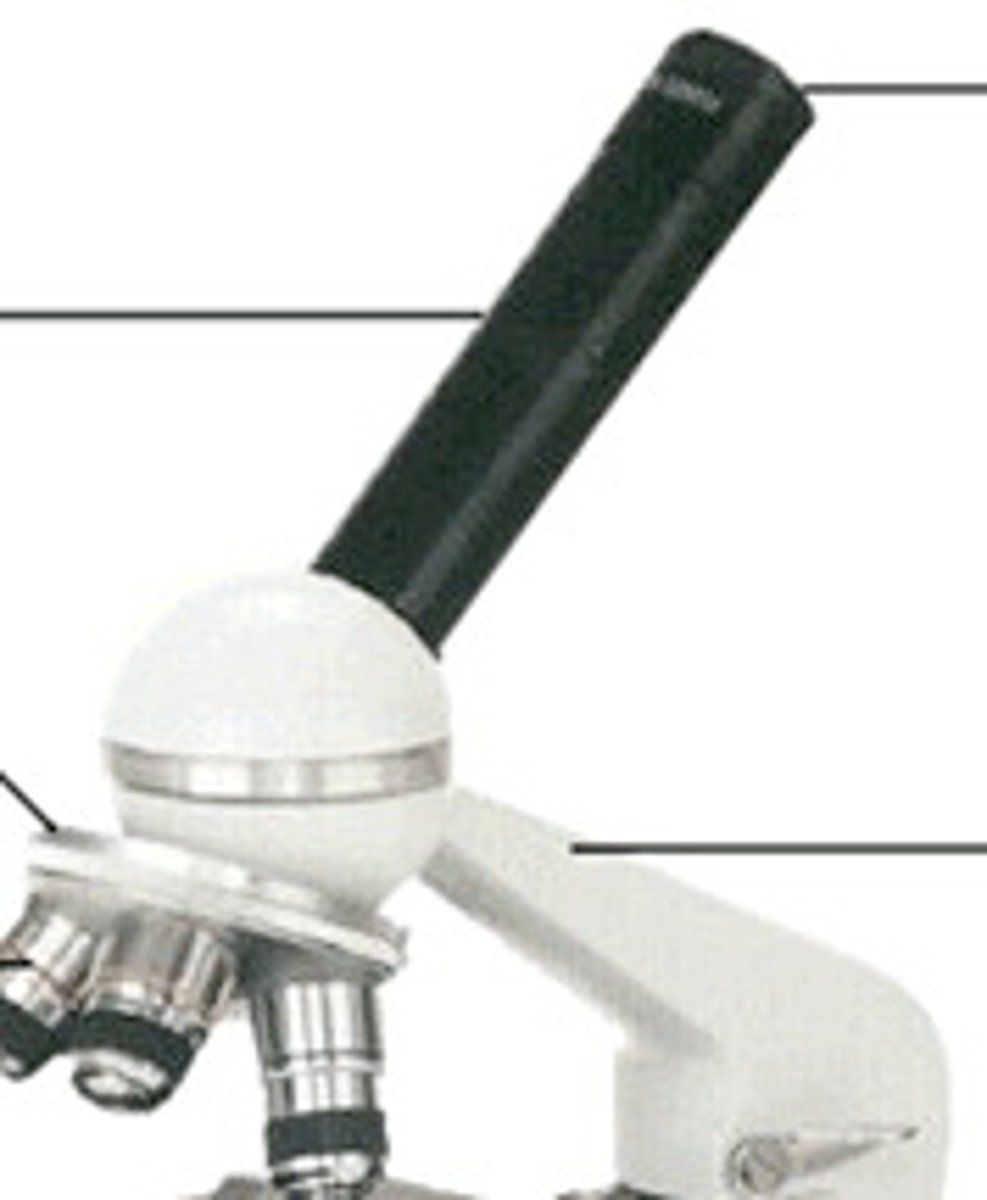
Arm
Holds the Objectives, the Nosepiece, the Ocular, and the Body Tube.
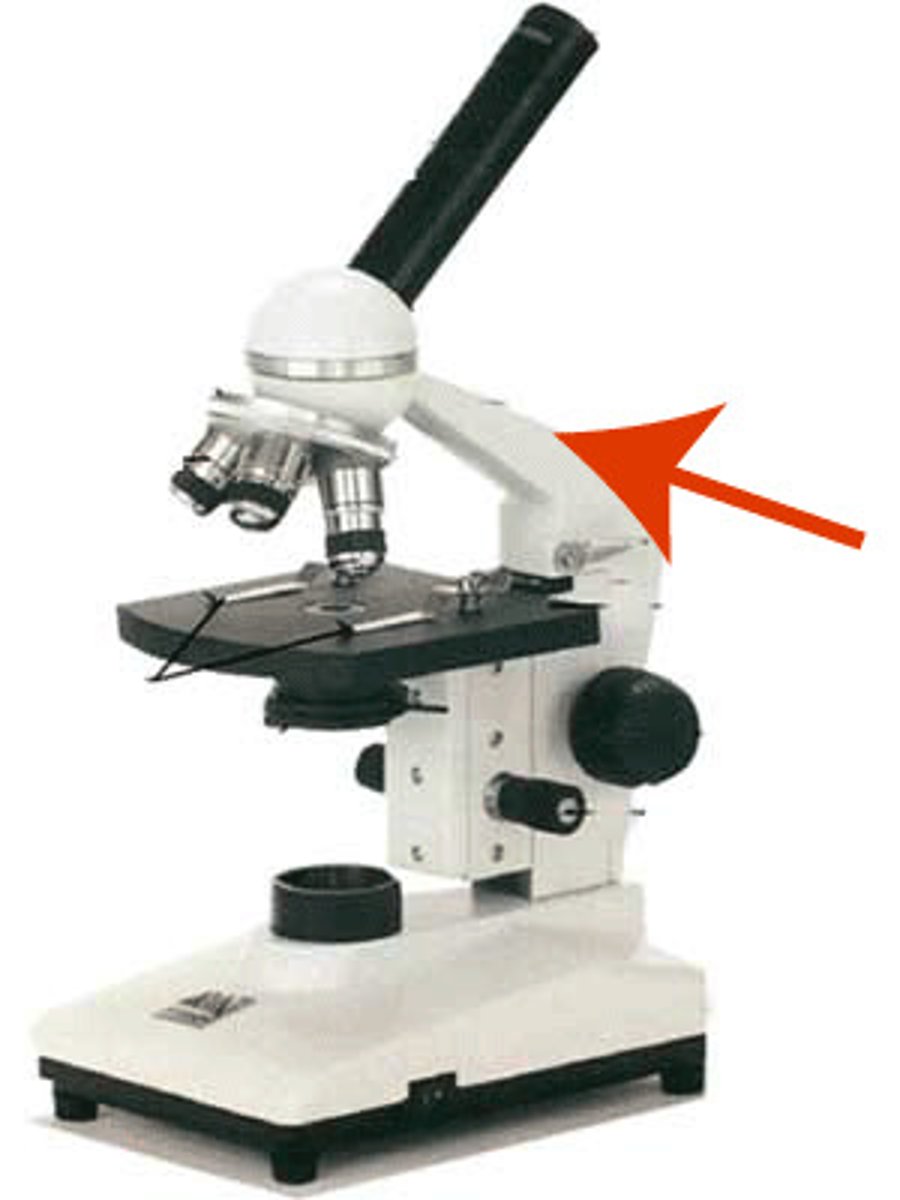
Body Tube
The tube between the ocular and the nosepiece/objectives.

Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, and Species
The Classification of Organisms (put in order)

Acellular
Does not have any cellular components; they may not metabolize, or reproduce by themselves. A virus is this because they must invade a host cell to reproduce, and cannot grow on it's own.
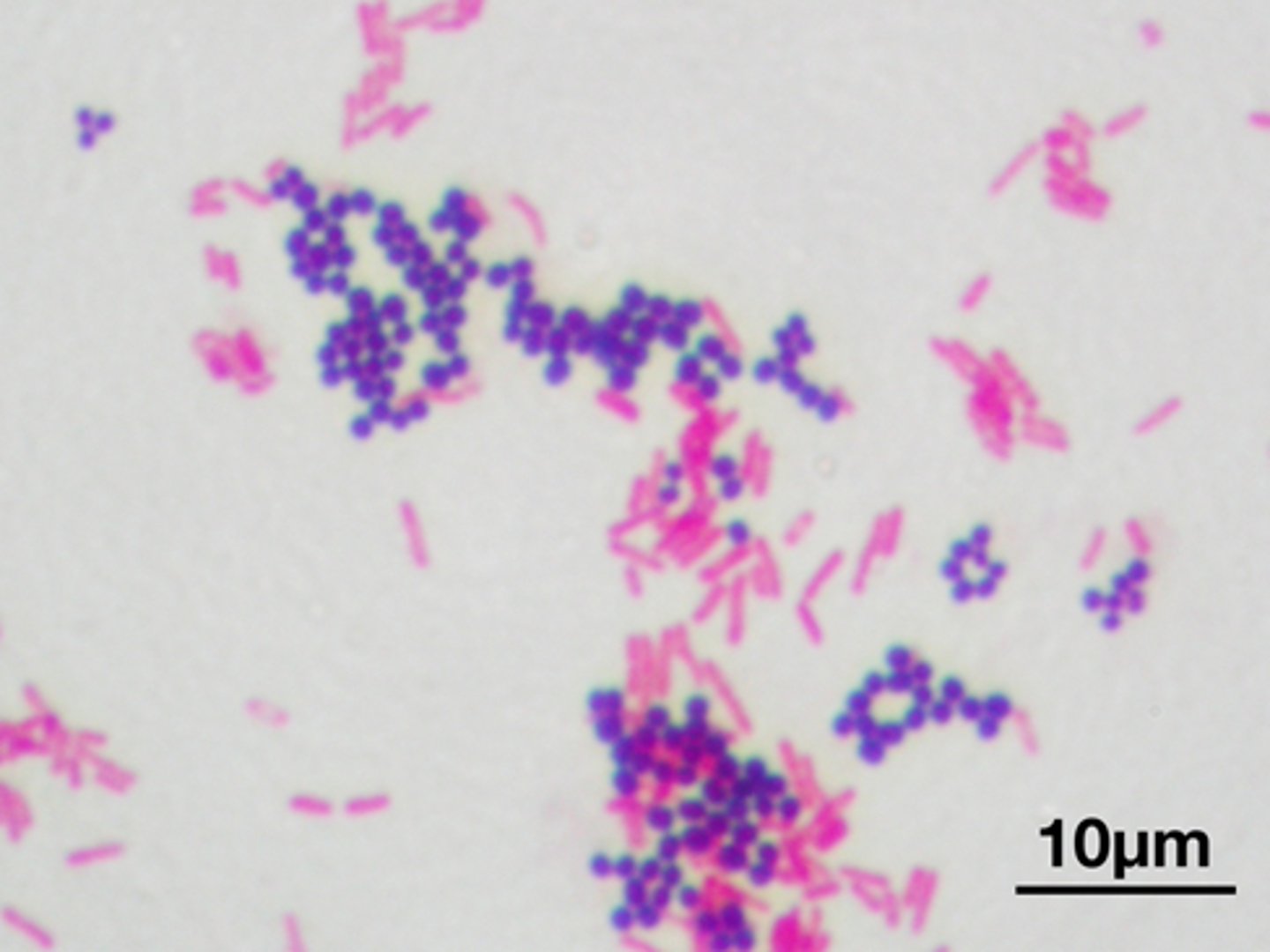
Gram-Positive Bacteria
After being stained with the violet dye, these bacteria look to be purple. This is because they have a thick cell wall composed of peptidoglycan.
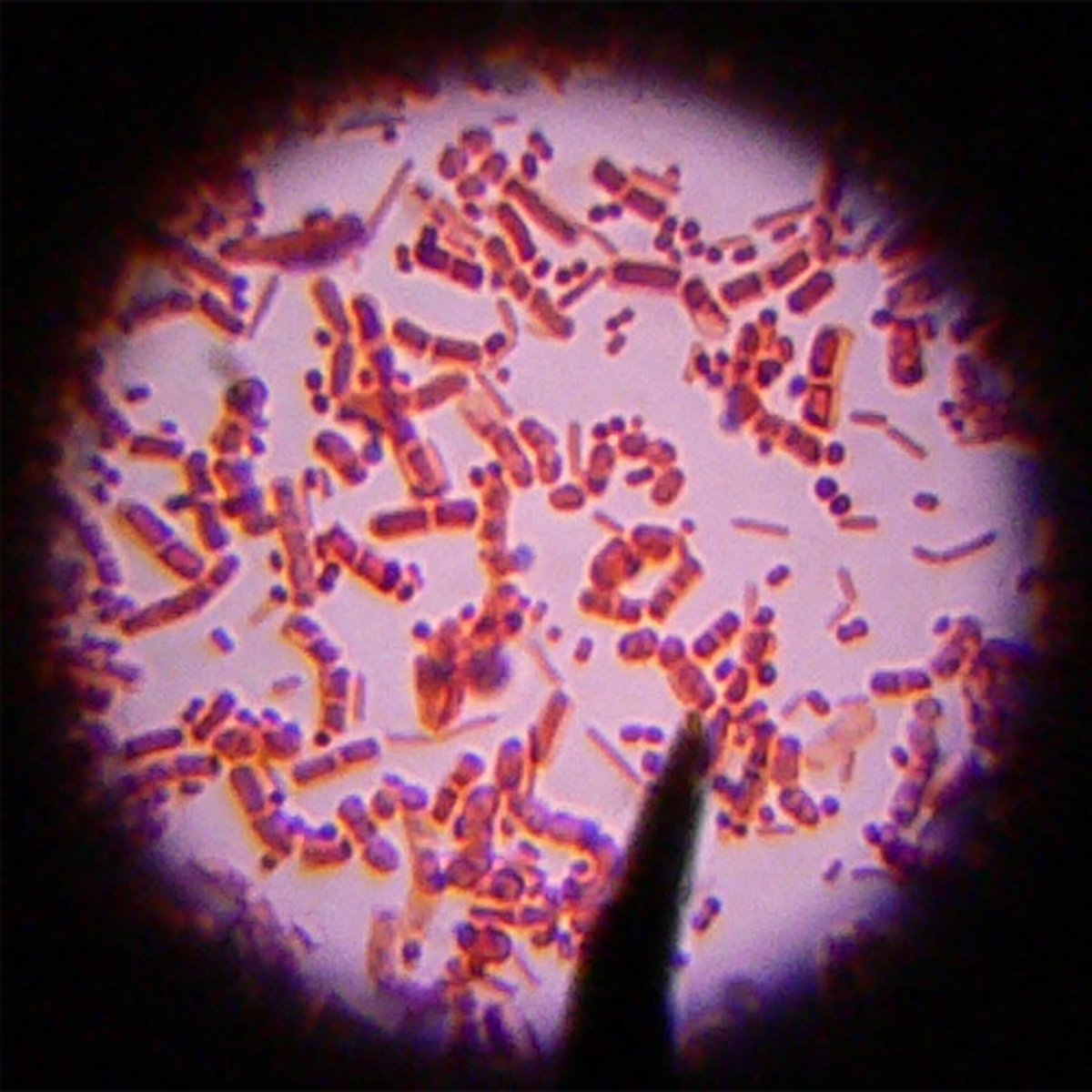
Gram-Negative Bacteria
Bacteria that retain a red-pink color. These bacteria have a thin membrane of peptidoglycan, sandwiched between an outer membrane and an inner membrane.
AIDS
Caused by human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), spreads by bodily fluid contact, treatment is Antiretroviral Therapy, no Vaccines.
Chicken Pox
Caused by the Varicella zoster virus, airborne, Treatments are painkillers, itch-relievers, fever-relievers, varicella vaccine.
Shingles
Caused by varicella zoster virus, spread by direct contact to rash, treatment is painkillers, antivirals, and there is a vaccine. (Only if a person has had chicken pox).
Common Cold
Can be caused by rhinoviruses, respiratory syncytial virus, parainfluenza virus, airborne, people can usually recover own their own within two weeks, there is no vaccine.
Dengue Fever
Caused by Dengue Virus, spread by infected mosquito, treatments include pain-relievers, and fluids, no vaccine.
Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever
Virus belongs to the Family Filoviridae, genus Ebolavirus, spreads though contaminated surfaces and bodily fluid contact, treatments are fluids and supportive(hospital) care, no vaccine.
Hepatitis
Caused by hepatits A virus(HAV): fecal-oral transmission, hepatitis B virus(HBV): spread by bodily fluid contact, and hepatitis C virus(HCV): spread by bodily fluid contact, treated with antiviral medication, Hepatitis B&A vaccines available.
Influenza
Caused by the influenza virus, airborne, treatment includes bedrest and fluids and antiviral medication, there is a vaccine.
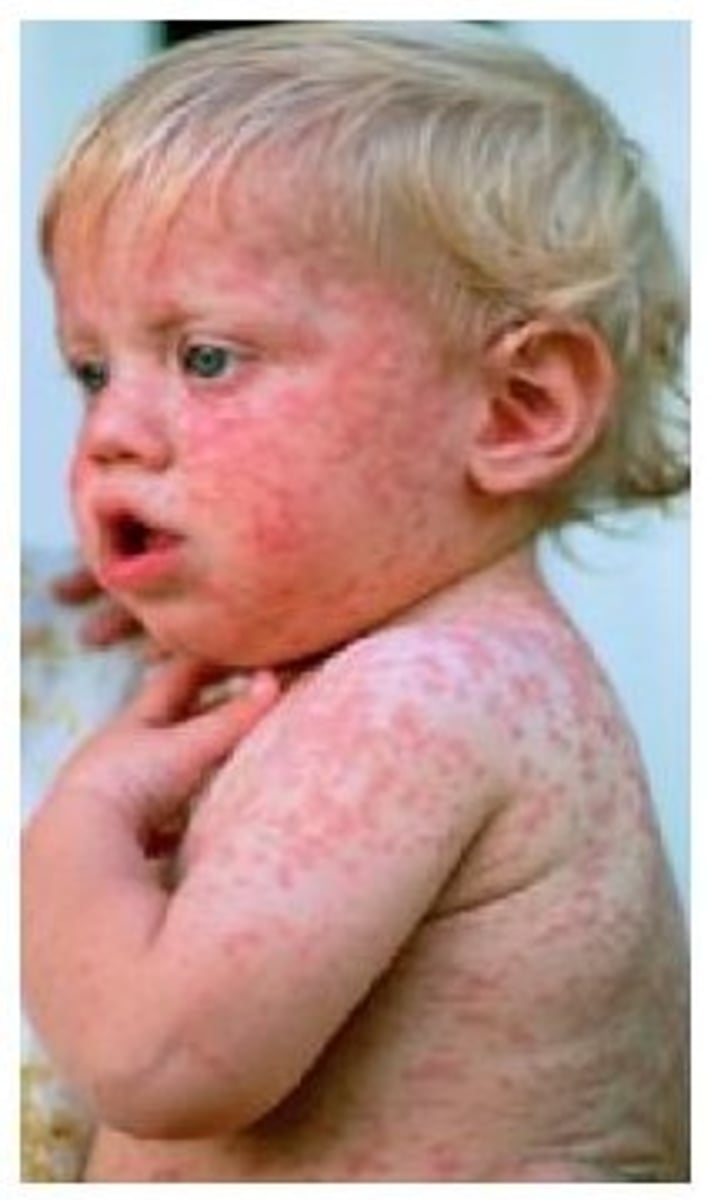
Measles
Caused by the morbillivirus, airborne, no treatment, MMR vaccine.
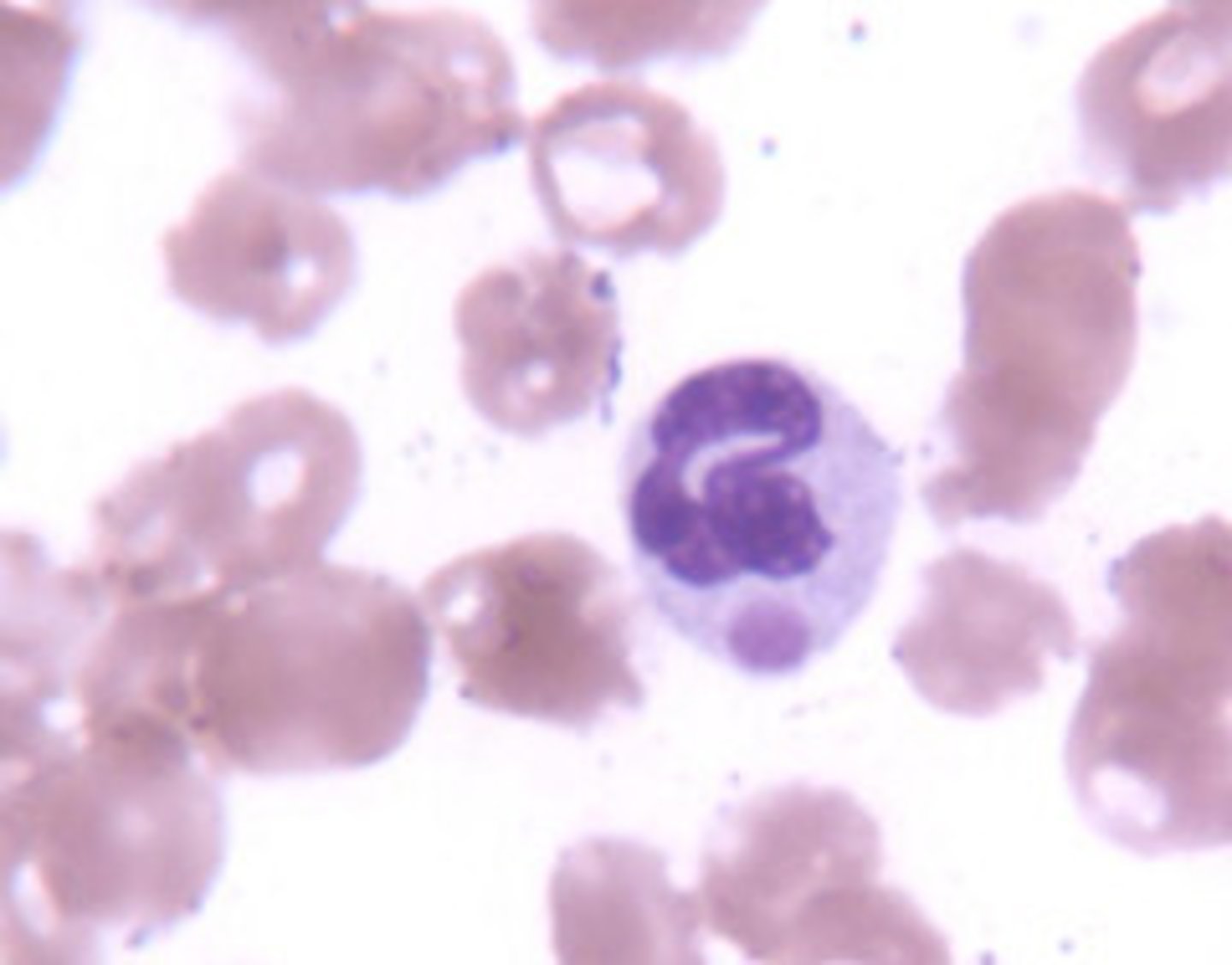
Mumps
Caused by the paramyxovirus, spread by saliva, no treatment, MMR vaccine.
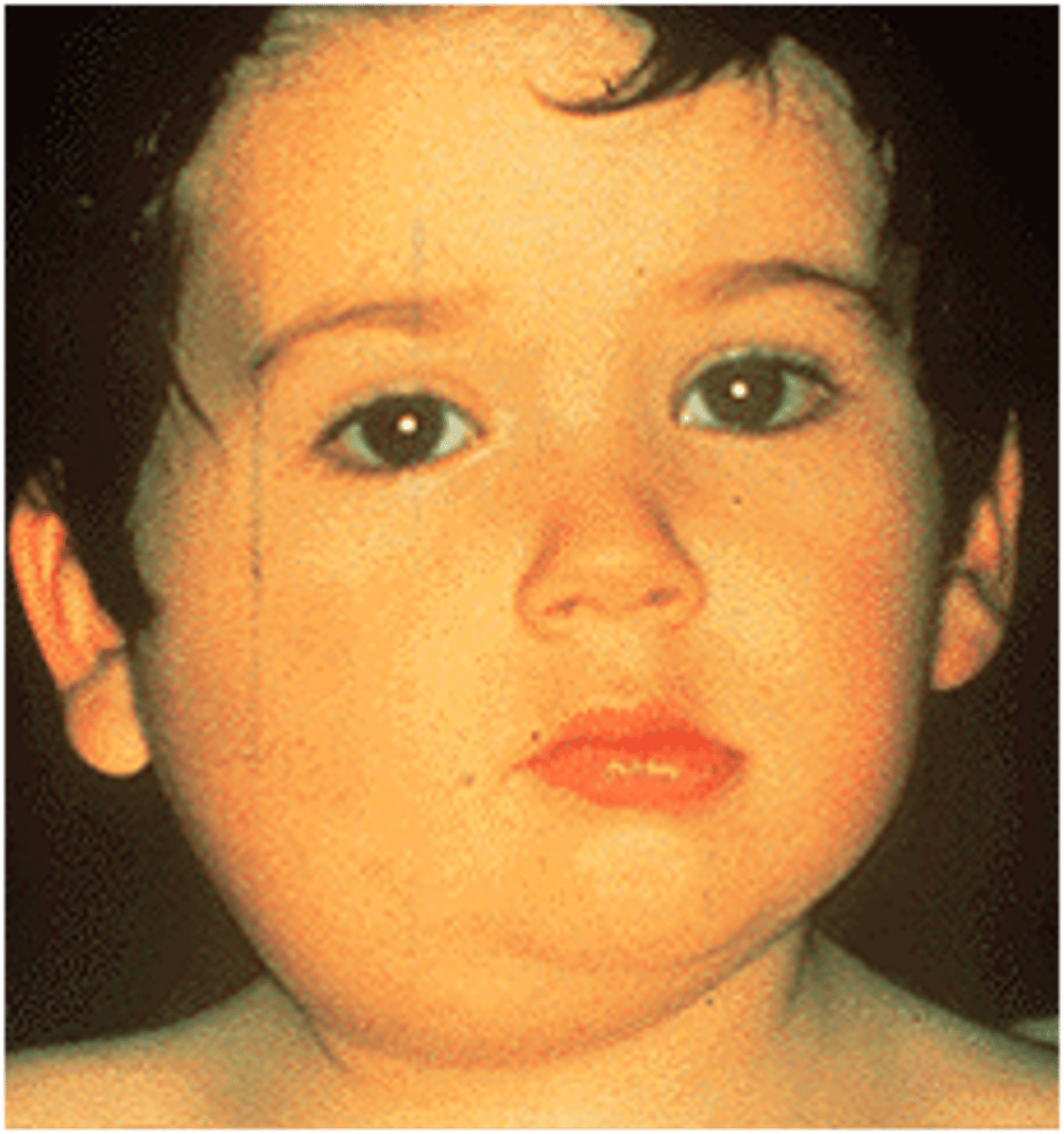
Rubella
Caused by the rubella virus, airborne, no treatment, MMR vaccine.
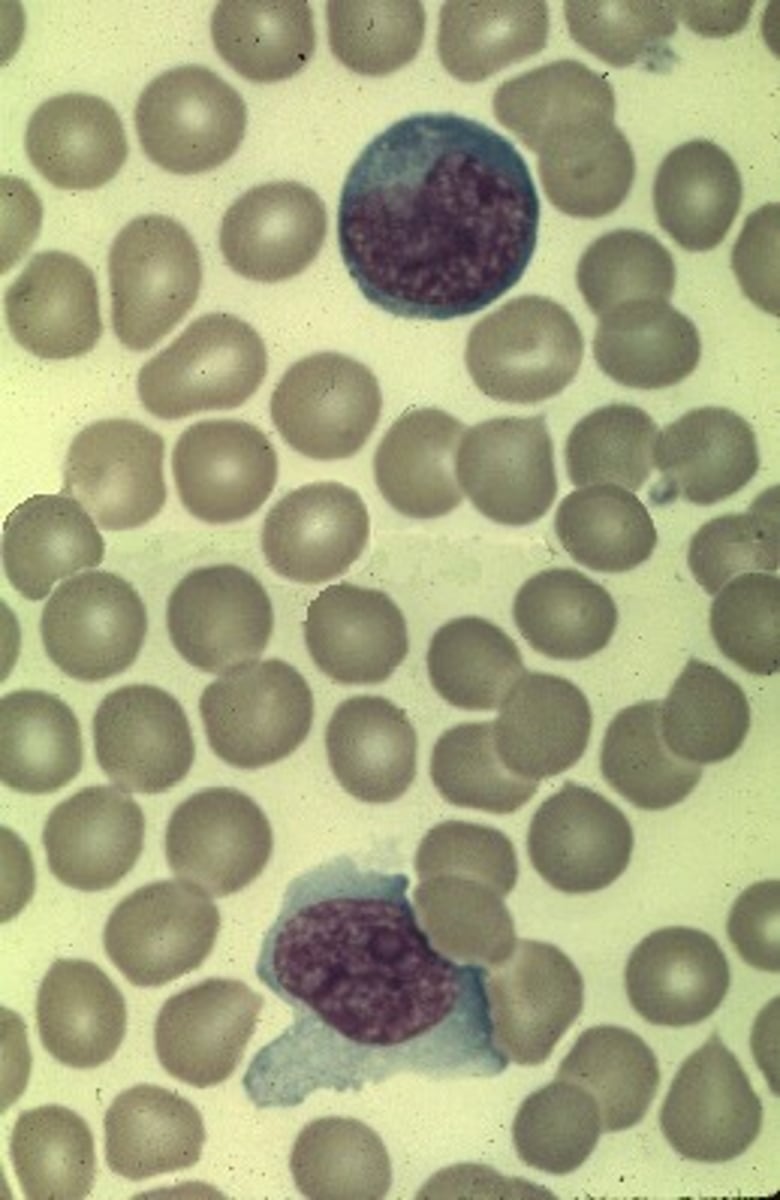
Mononucleosis
Caused by the Epstein-Barr virus, spread by saliva, no treatment, no vaccine.
Polio
Caused by the poliovirus, spread by fecal-oral transmission, no treatment, there is a vaccine.

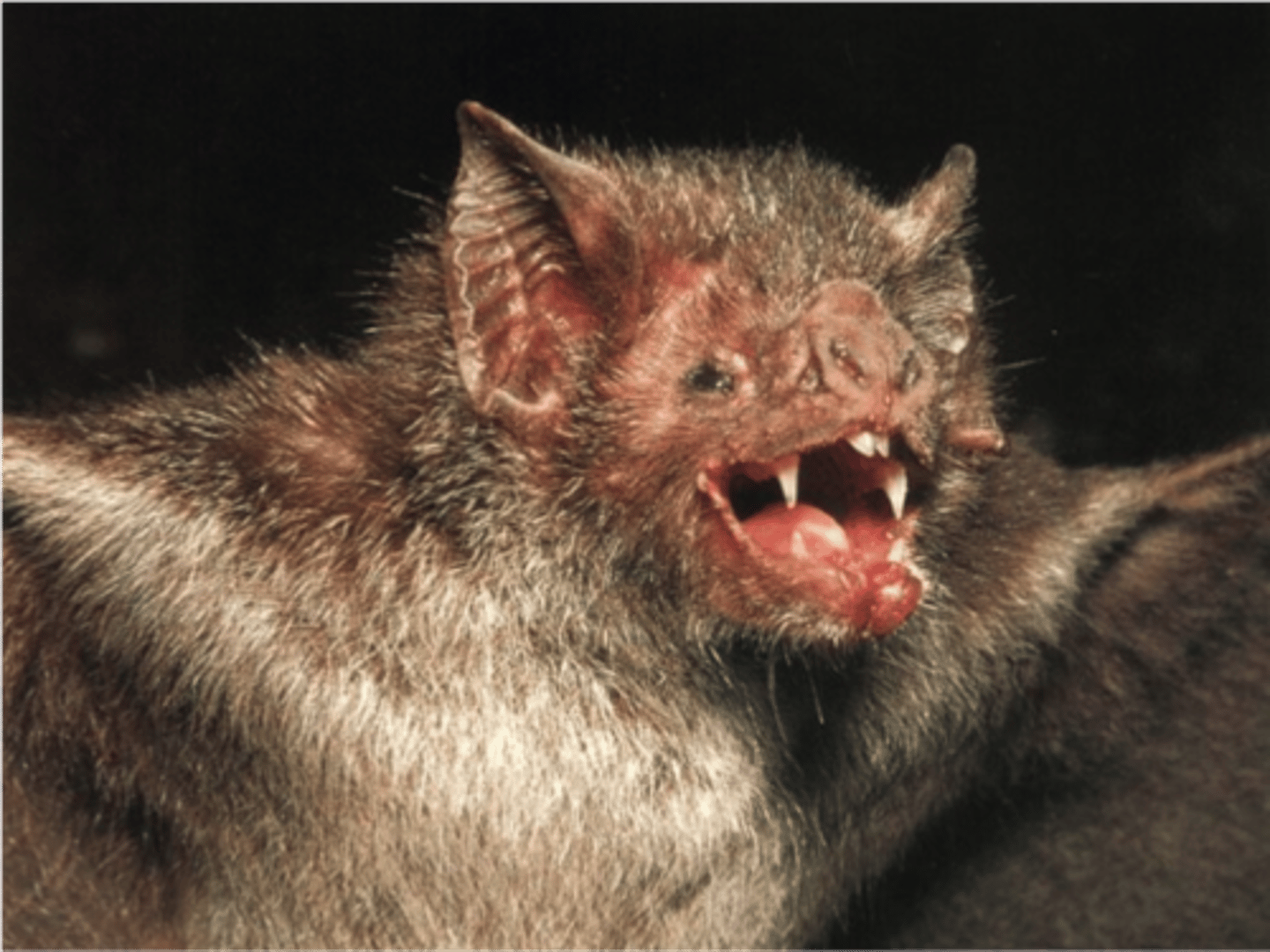
Rabies
Caused by the rabies virus, spread by the bite of an infected animal, blood transfusion and antiviral medication are ways to treat it, there is a vaccine.

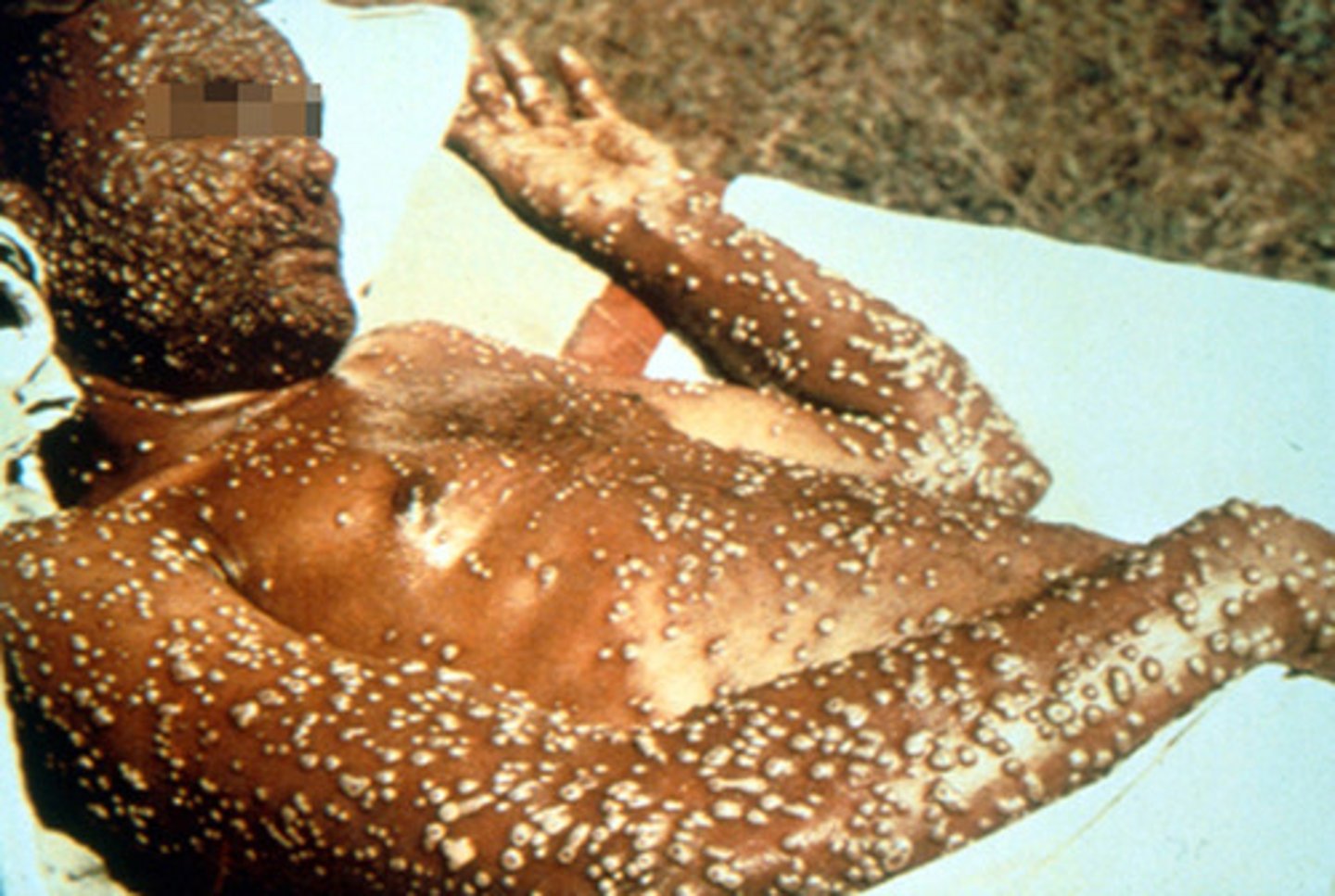
Small Pox
Caused by the variola virus, contact with person or item spreads the virus, there is no treatment, there is a vaccine.

West Nile Fever
Caused by the flaviviridae virus, spread by infected mosquitos, no treatment, no vaccine.
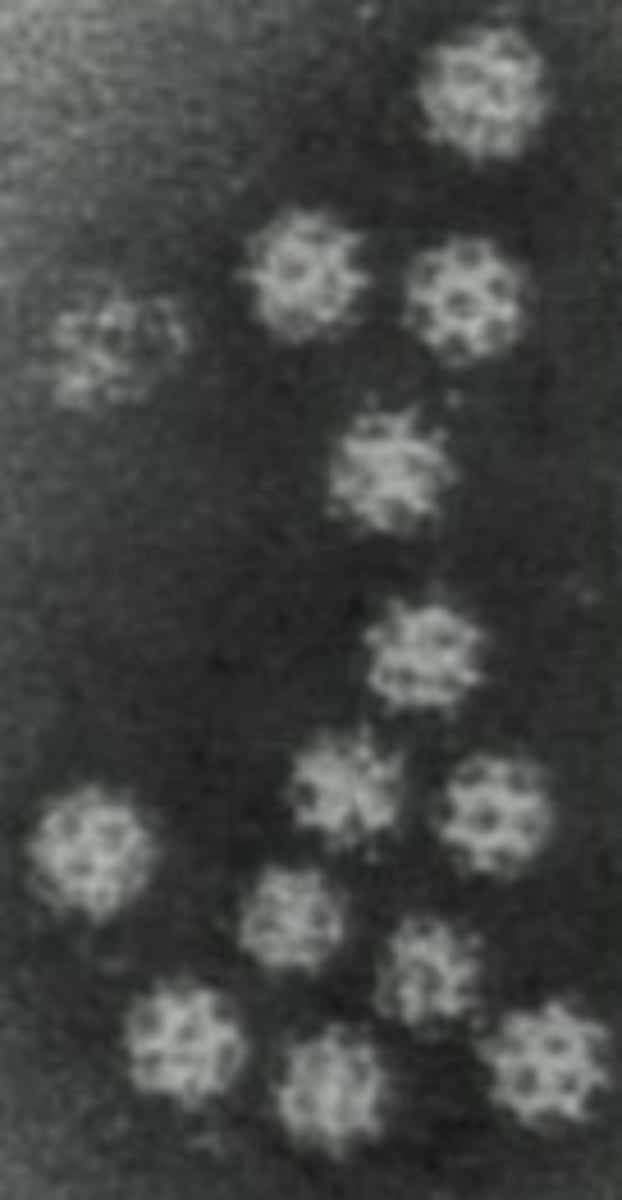
Yellow Fever
Caused by the yellow fever virus, spread by infected mosquitos, no treatment, vaccine available.
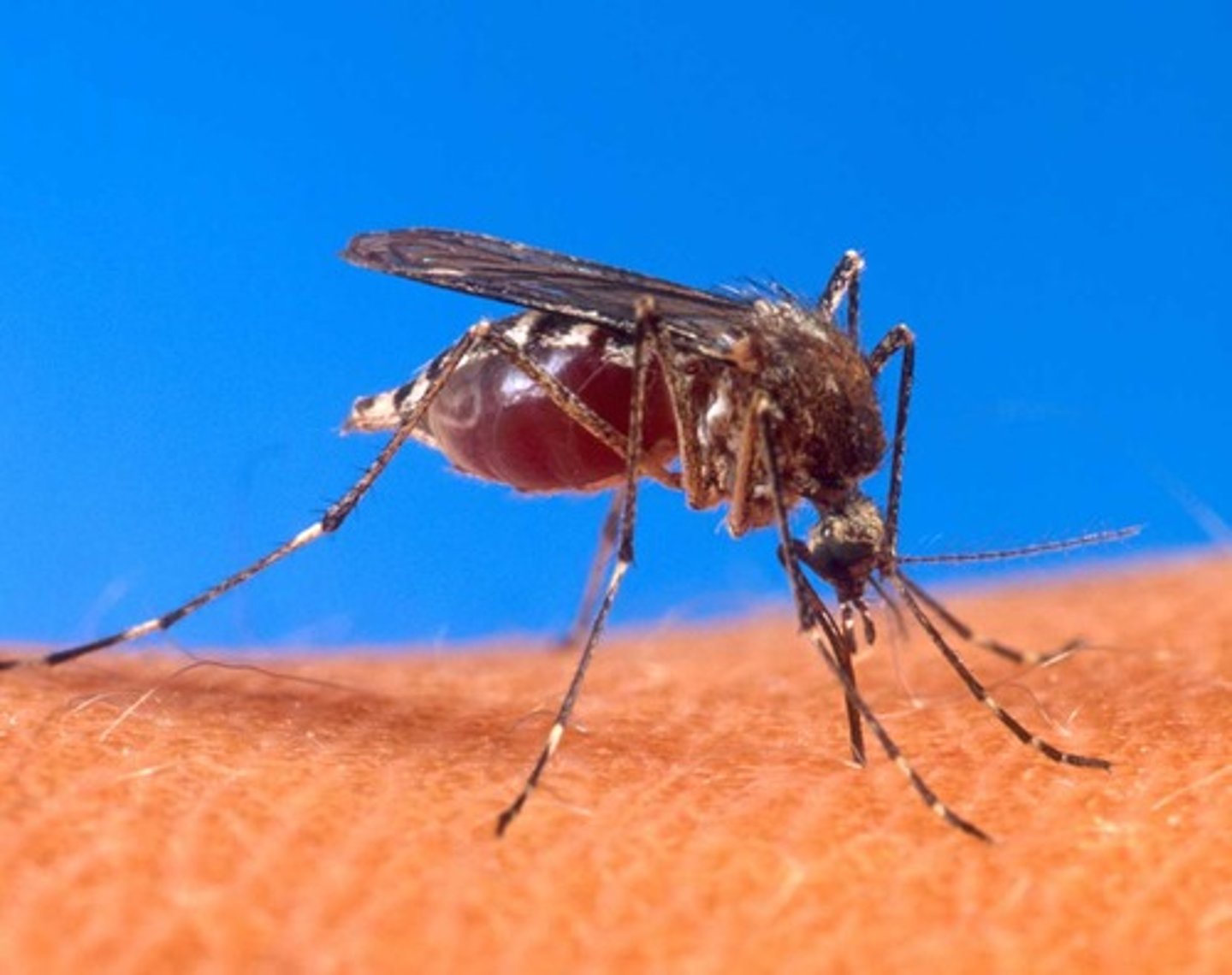
Anthrax
Caused by the gram-postive bacillus anthracis, spread by infected spores, penicillin is used to treat it, if exposed to spores, antibiotics are used as prevention.
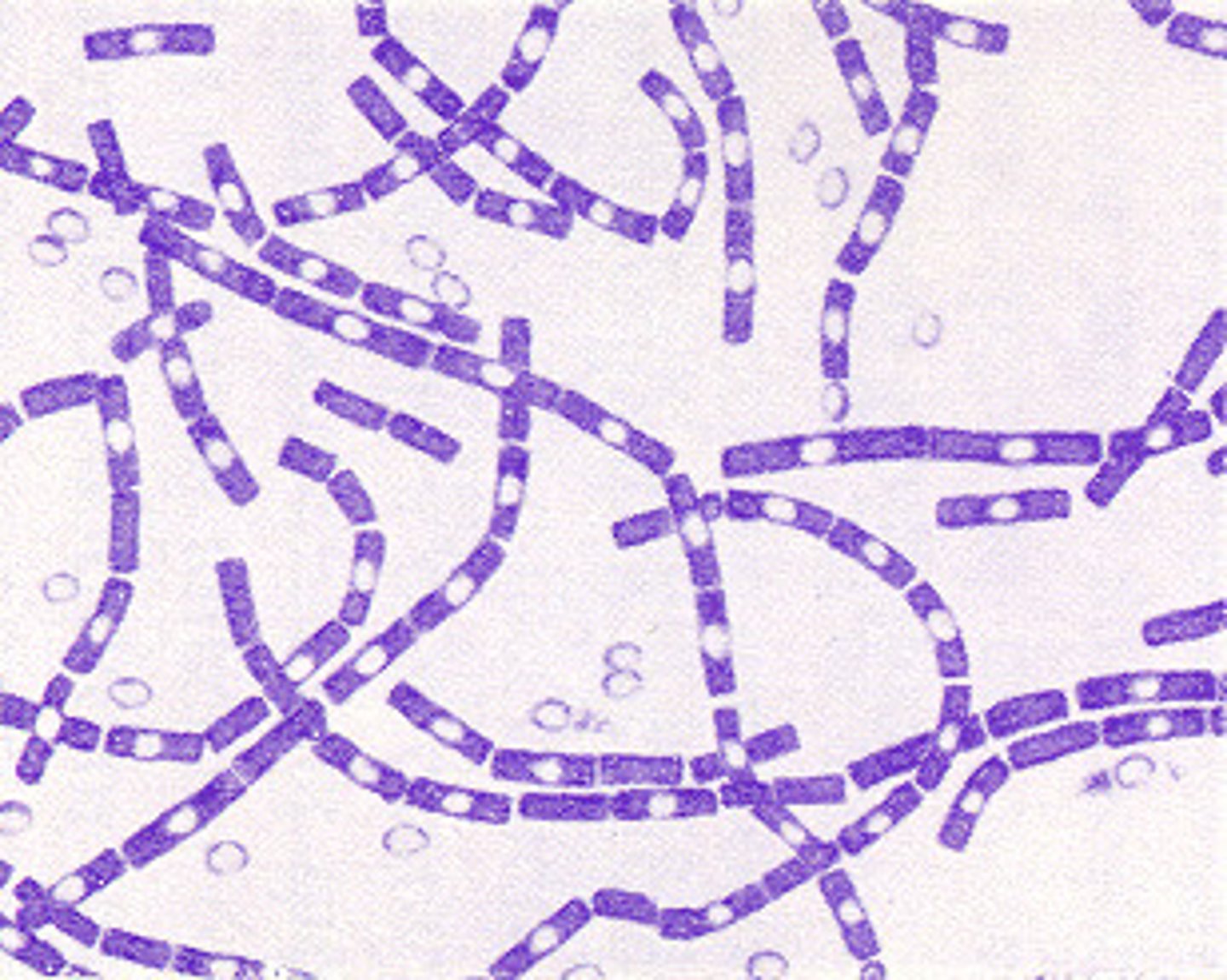
Botulism
Caused by gram-positive clostridium botulinum, spread by contaminated food, an antitoxin injection and breathing support treat it, and use strict-hygienic procedures when canning food.
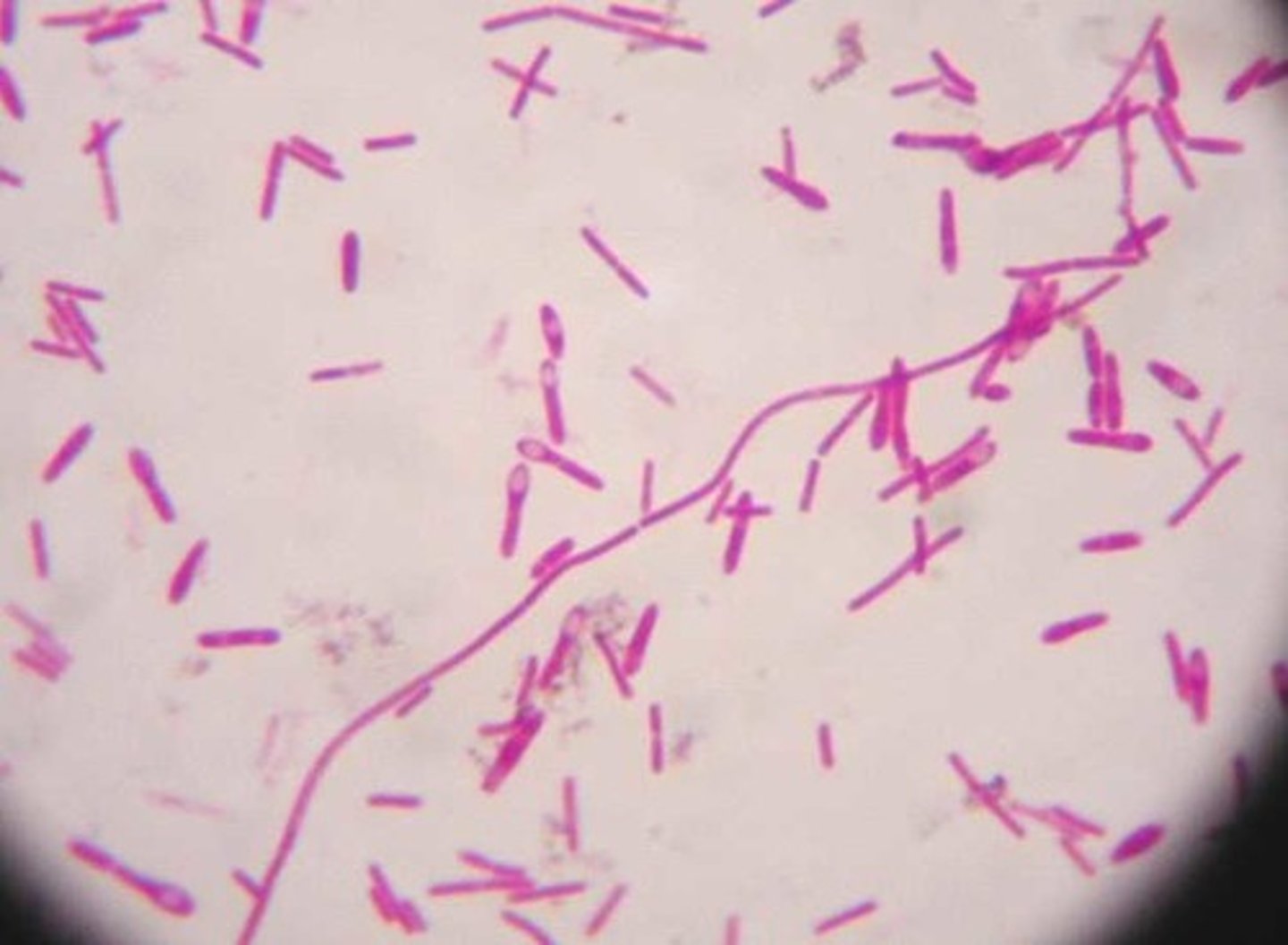
Cholera
Caused by gram-negative vibrio cholerae, spread by contaminated food or water, antibiotics are used to treat it, preventing it includes cooking food well and using clean water.
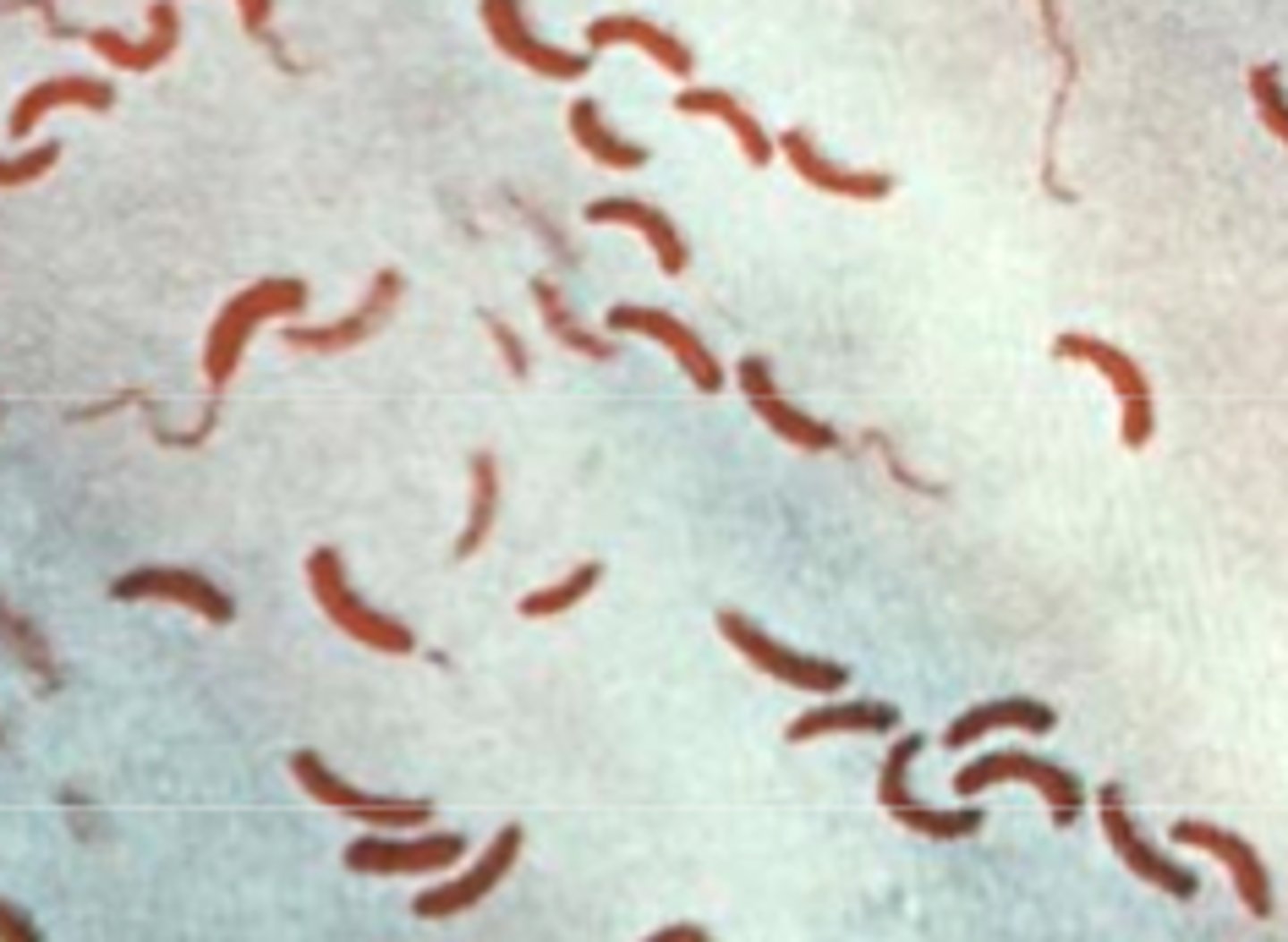
Chlamydiasis
Caused by gram-negative chlamydia trachomatis, spread by infected bodily fluids, antibiotics are used as treatment, prevention includes use of condoms and limiting number of sexual partners.
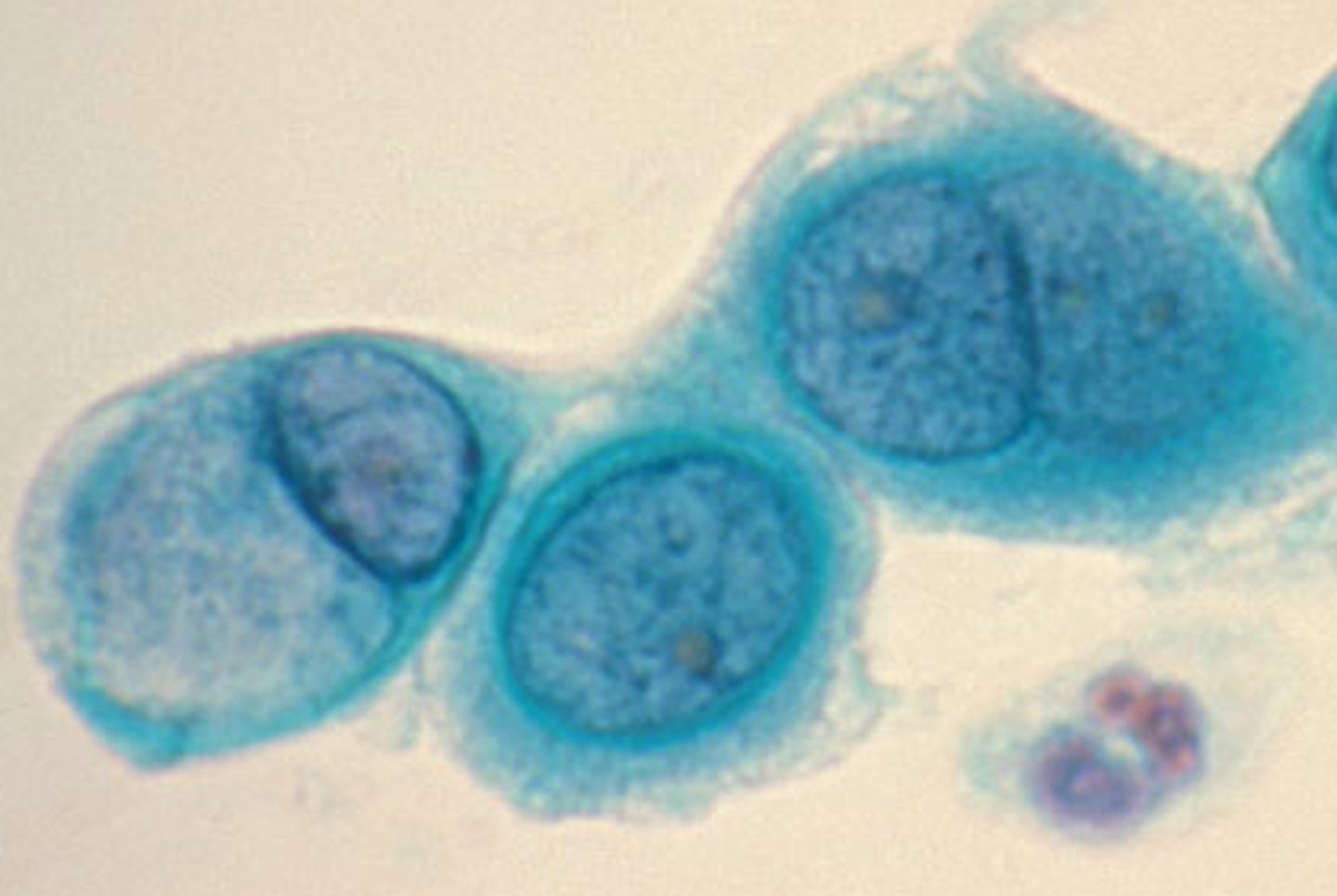
Dental Caries (tooth decay)
Caused by gram-positive streptococcus mutans and lactobacillus, happens when sugars react with the bacteria on the dental biofilm, fillings and pulp capping and root canals, prevention it to maintain good oral hygiene.
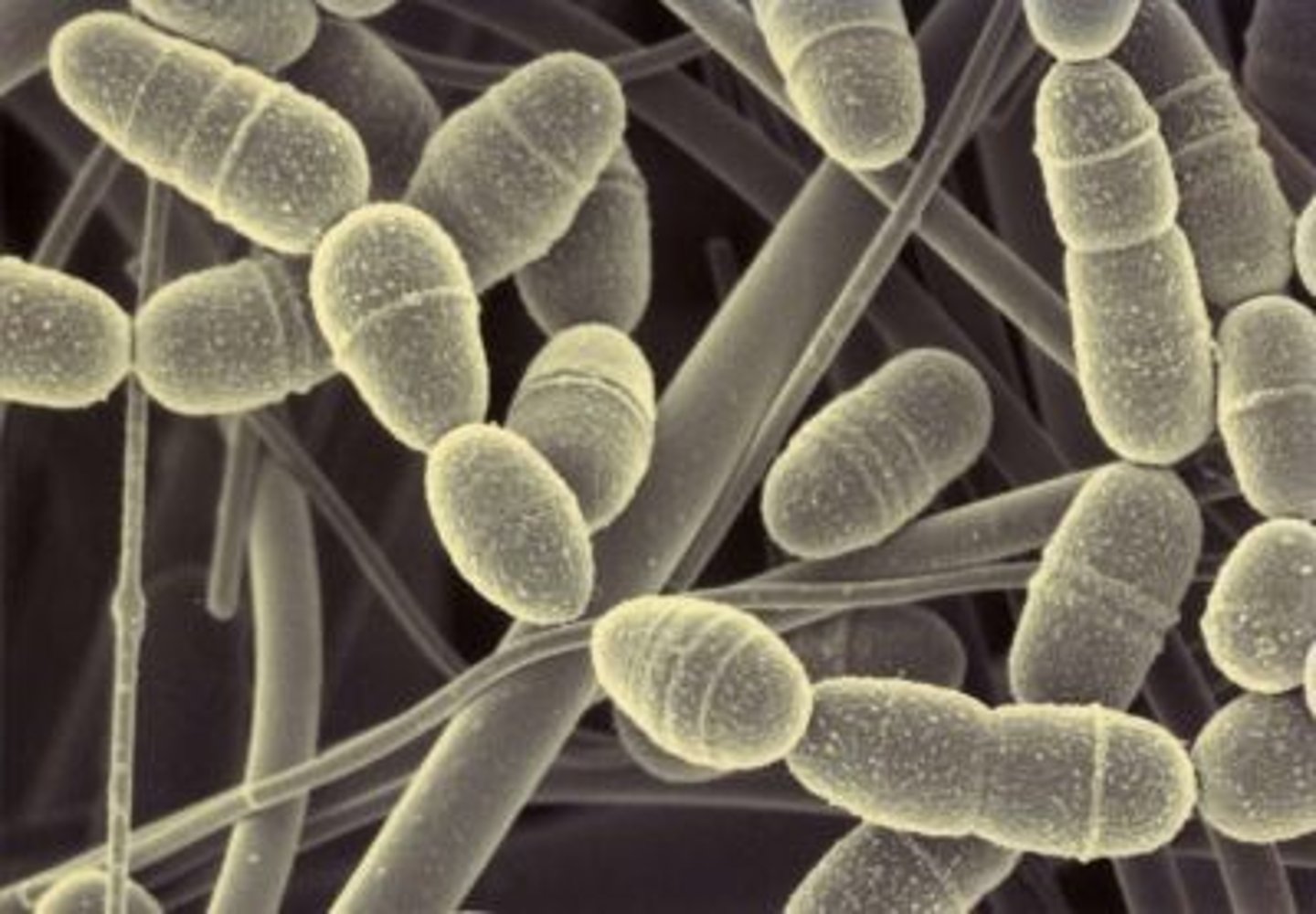
Legionnaire's Disease
Caused by gram-negative legionella bacteria, airborne, antibiotics are used to treat, avoiding smoking and frequent disaffecting of water systems.
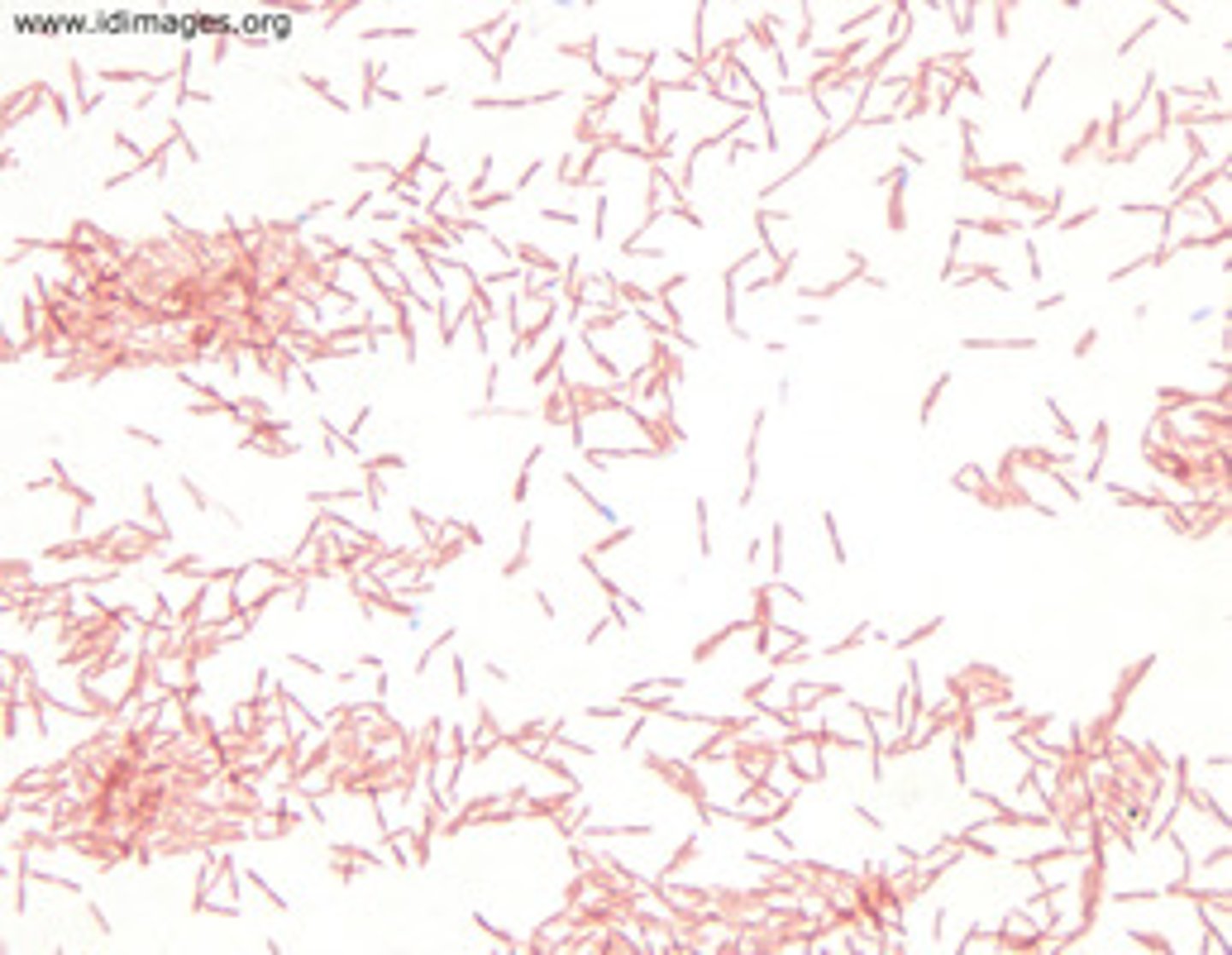
Lyme Disease
Caused by gram-negative borrelia burgdorferi bacteria, transmitted by the bite of infected black-legged ticks, antibiotics are used to treat, avoid areas where deer ticks live as prevention.
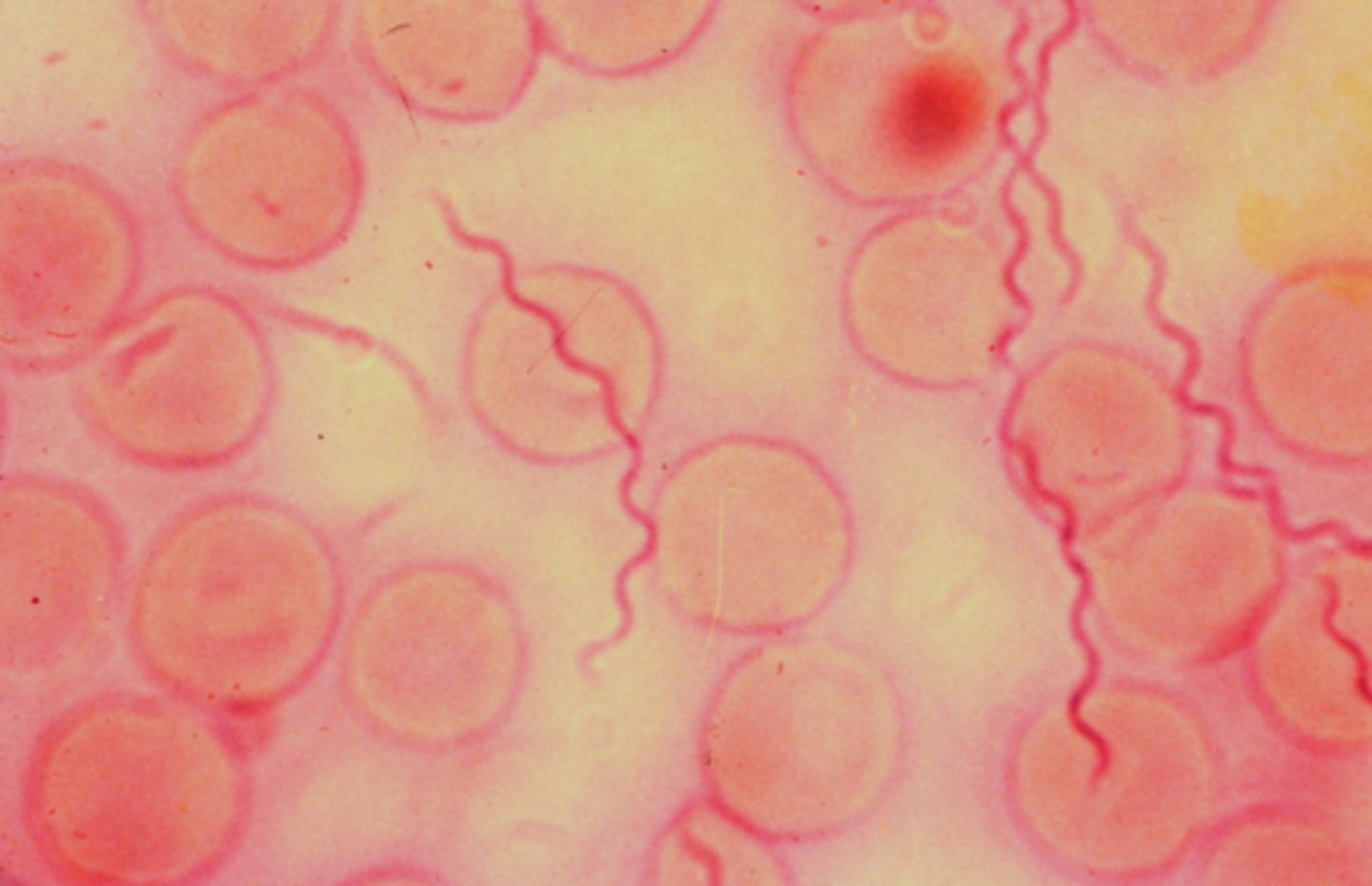
MRSA
Caused by gram-positive staphylococcus aureus bacteria, airborne and direct contact, antibiotics are used as treatment, scrubbing hands with soap and water many times throughout the day prevents it.
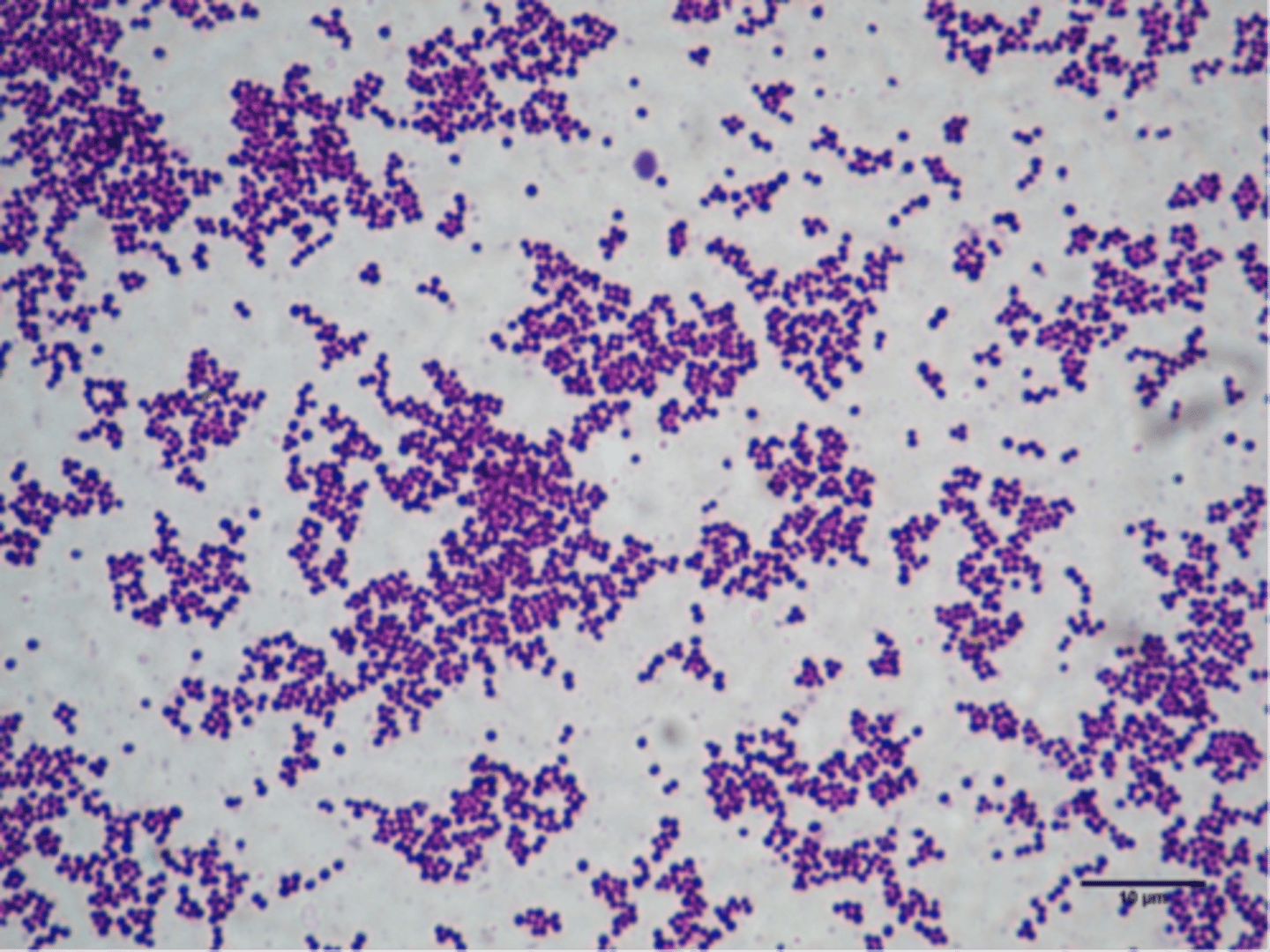
Peptic Ulcer Disease
Caused by the gram-negative helicobacter pylori, transmitted person-to-person by saliva or by fecal contamination of food or water, good hygiene is aa way to prevent it, and antibiotics are used as treatment.
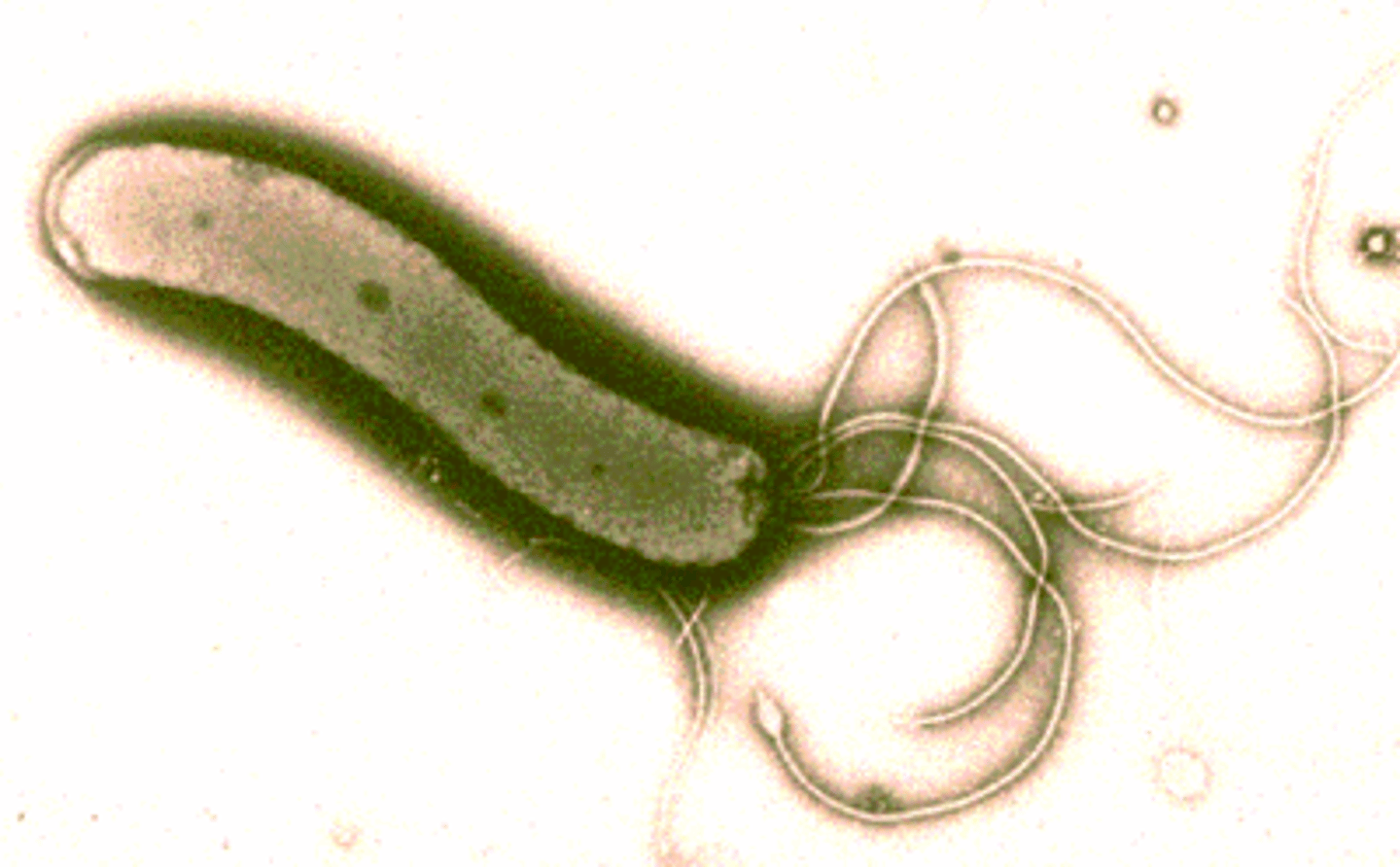
Pertussis (whooping cough)
Caused by the gram-negative bordetella pertussis, airborne, frequent hand washing can prevent it, and antibiotics are used as treatment.

Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
Caused by the gram-negative rickettsia rickettsii, spread by the bite of an infected tick, avoid tick bites as prevention, antibiotics are used as treatment.
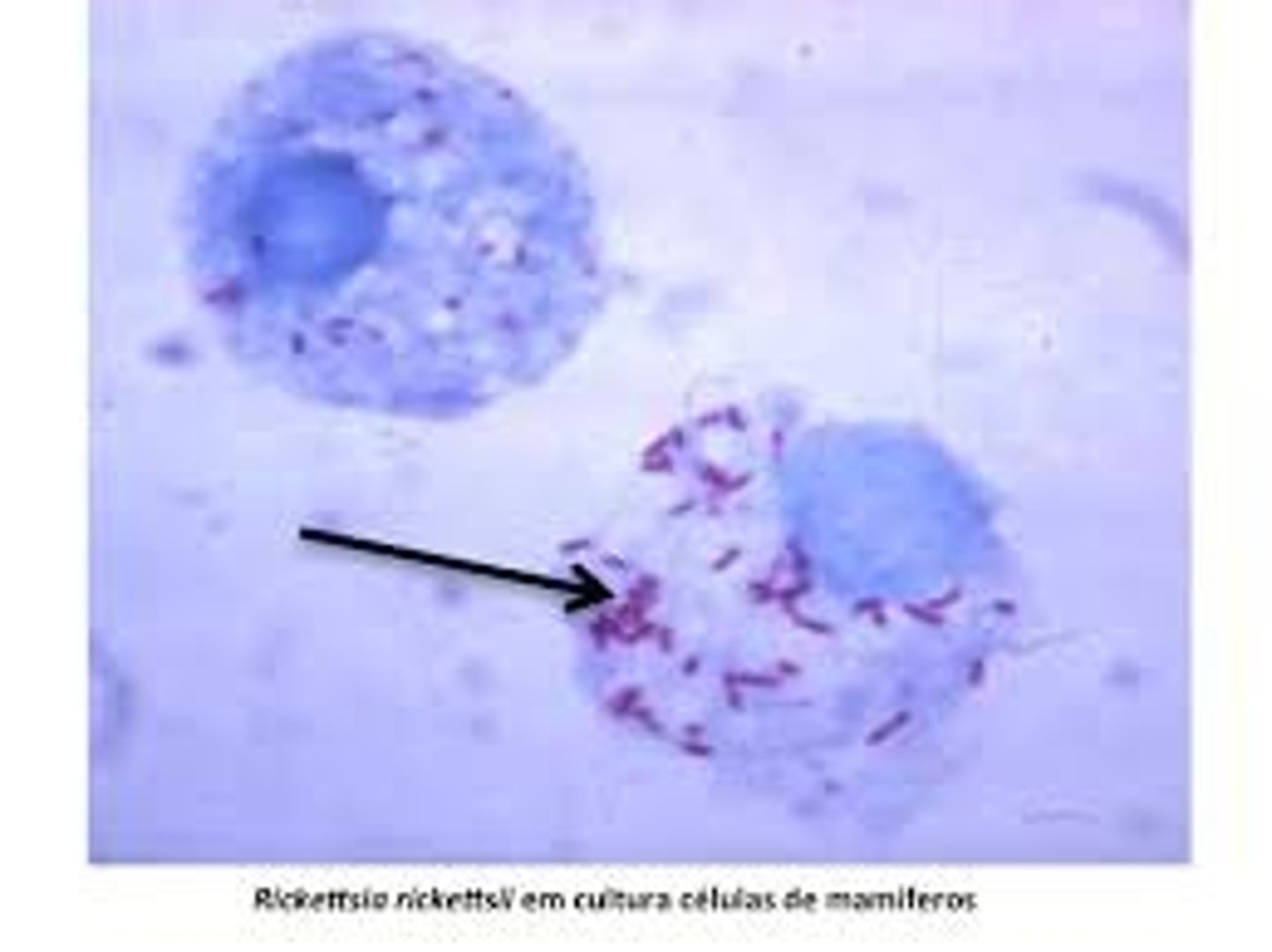
Strep Throat
Caused by the gram-positive streptococcus pyogenes, airborne or spread by shared drinks, prevent by washing hands frequently and not sharing eating utensils, antibiotics are used as treatment.
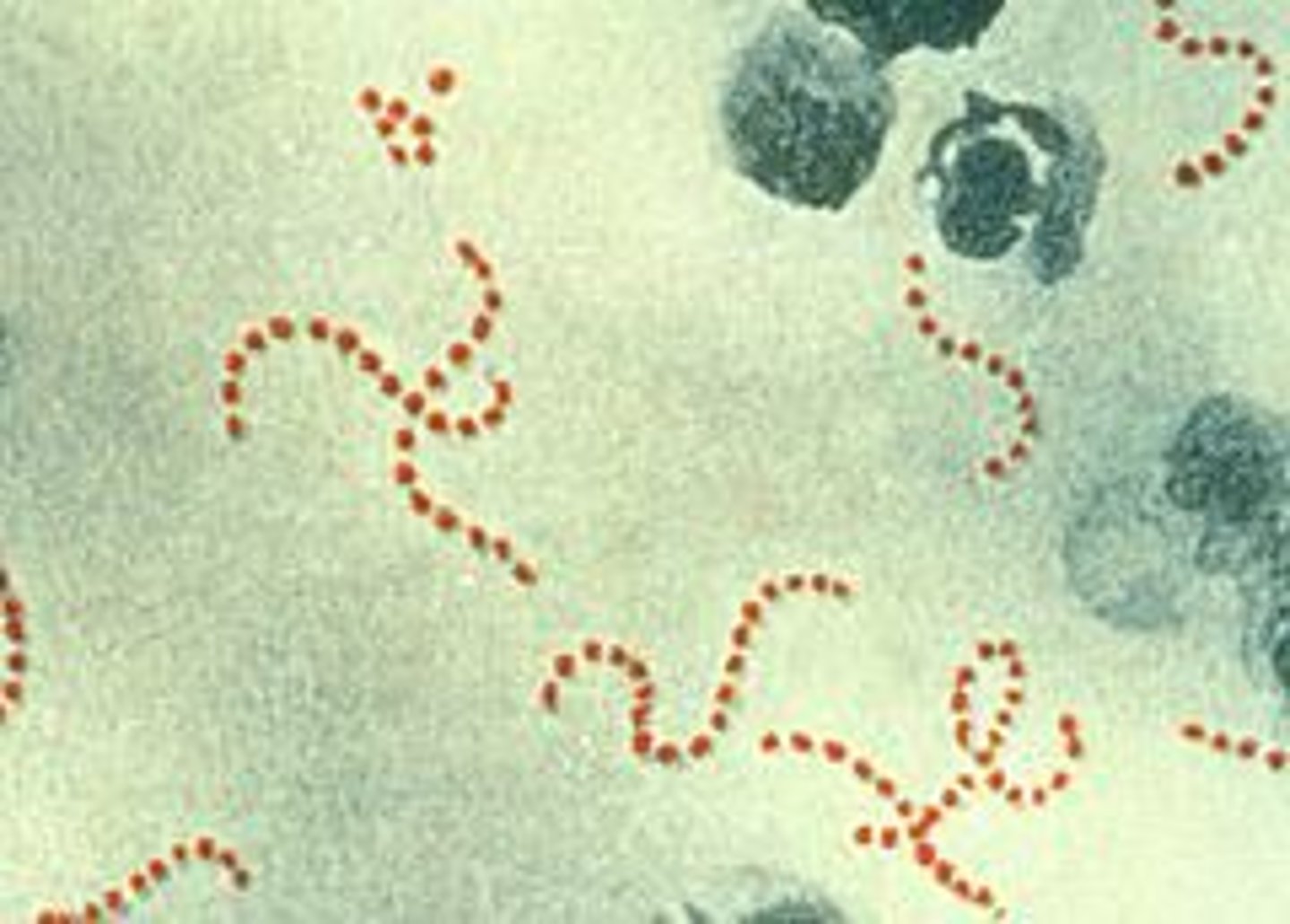
Syphilis
Caused by the gram-negative treponema pallidum, sexually transmitted, practice safe sex and monogamous relationships in order to prevent, antibiotics are used to treat.
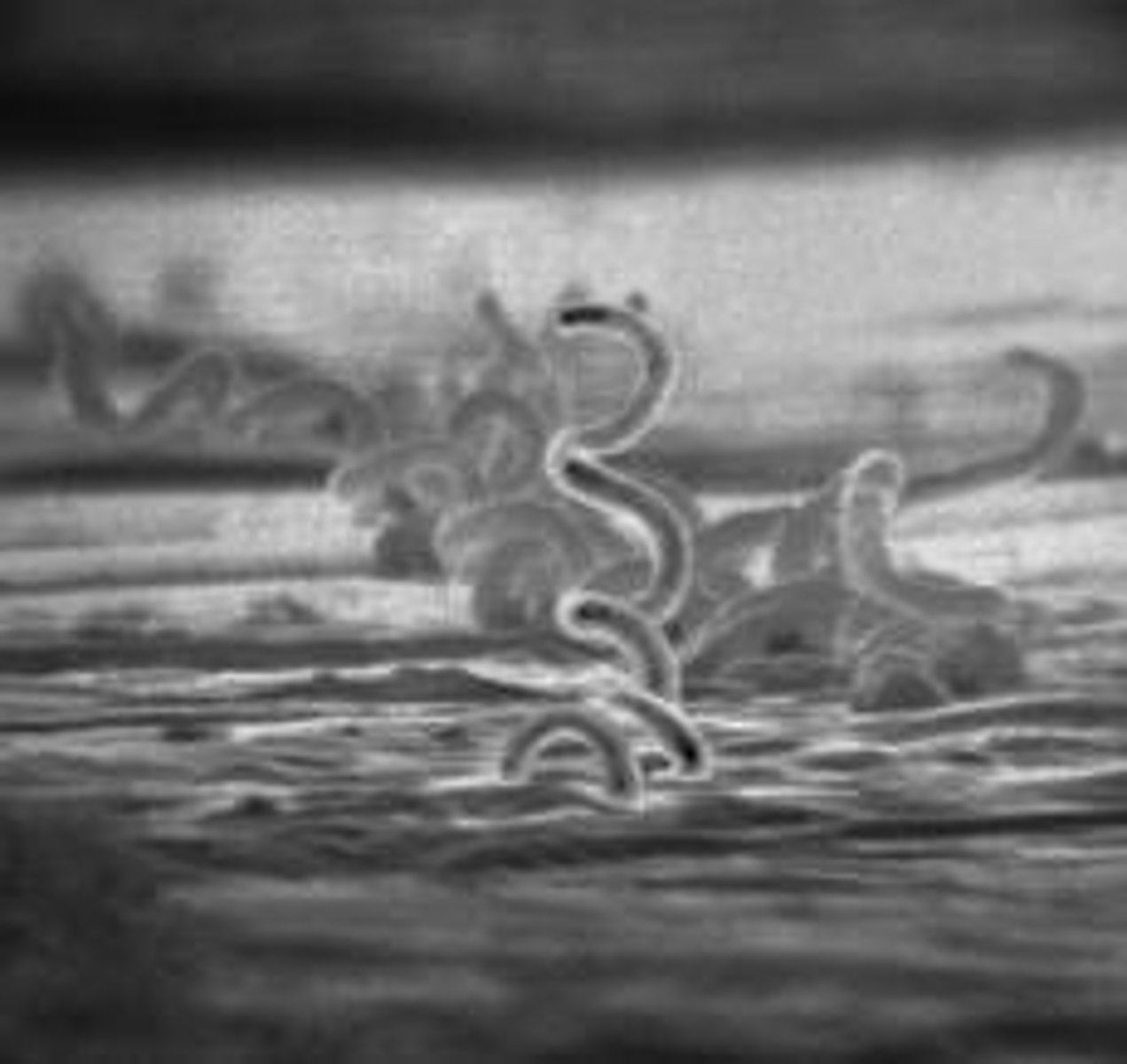
Tetanus
an acute and potentially fatal infection of the central nervous system caused by a toxin produced by the tetanus bacteria
Tuberculosis
Communicable lung disease caused by an infection by mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria; airborne transmission bacteria remain dormant until a later time
Athlete's Foot
Another terms for Tinea Pedis ringworm of the foot. A fungal infection that can occur on the bottom of the feet and often appear as a red itchy rash in the spaces between the toes, most often between the fourth and fifth toe.
Dutch Elm Disease
a fungal disease of elm trees that is spread by elm bark beetles
Ergotism
Gangrene, nervous spasm, burning sensations, hallucinations, and temporary insanity in humans caused by rye plants containing ergots that were milled into flour
Histoplasmosis
This infectious disease is caused by a fungus found in the soil infested with bird/bat droppings. It is transmitted by inhalation.
Potato Blight
A destructive fungal disease of potatoes resulting in dry brown rot of the tubers, resulted in Irish Potato Famine
Ringworm
Skin disorders: fungal infection involving hair, skin or nails and form ring shaped patches
Thrush
infection of the oral cavity caused by Candida albicans yeast. White coating on the tongue, yeast infection of the mouth