Learning & Memory
1/133
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
134 Terms
Learning
relatively permanent change in behaviour or knowledge in response to experience
learning can be intentional, unintentional, active or passive
active learning
learning for which the learner is required to do something intentional to engage in their learning
eg. studying for exam
passive learning
learning that involves listening and observing
behaviourist approach to learning
an approach to learning that describes behaviours learnt through interaction with the environment
eg. classical conditioning and operant conditioning
Social-cognitive approach to learning
a perspective that stresses the importance of social interactions and cognitive process in shaping human learning and behaviour
eg. observational learning
Holistic
an approach that considers the whole system rather than analysing or focusing on its individual parts in isolation
Classical conditioning
a behaviourist approach to learning where an individual forms an association between two stimuli to produce a learnt response
learning to elicit an involuntary behaviour to a stimulus you usually wouldn’t respond to. Eg: blinking, salivation, vomiting
involves pairing two stimuli tgt (one that elicits reflex and one that doesn’t) so that association formed between two stimuli. eg: food aversions
association
two or more stimuli are paired together to produce learnt response
Phase 1: Before Conditioning
Must identify neutral stimulus (NS) and say it does not producing any response naturally
Must identify unconditioned stimulus (UCS) and the unconditioned response that it produces (UCR) INVOLUNTARILY
neutral stimulus
stimulus that does not evoke the reflex (UCR), eg: whistle
unconditioned stimulus
stimulus that evokes reflex naturally, eg: food
unconditioned response
reflex that occurs INVOLUNTARILY when UCS is presented, eg: salivation
Phase 2: During conditioning
Present UCS IMMEDIATELY AFTER NS (NS before UCS)
UCS evokes the reflex (UCR)
→ Must Mention stimuli are presented together (timing) and repeated many times
Phase 3: After conditioning
AN ASSOCIATION HAS FORMED BW NS AND UCS
The NS becomes the Conditioned stimulus (CS)
The CS then produces the Conditioned response (CR) on it’s own
Conditioned stimulus (CS)
Previously neutral stimulus that has through conditioning acquired capacity to evoke automatic reflex
→ SAY : association between two stimuli have formed
Conditioned response (CR)
a learned response (sim to automatic reflex) is produced on presentation of conditioned stimulus alone (CS → CR)
Stimulus Generalisation after conditioning
another stimulus similar to conditioned stimulus, may also trigger a conditioned response. eg: child may fear all dogs, not just type that bit them
Extinction (stop or decrease after conditioning)
after, if CS alone presented repeatedly without UCS, the strength of conditioned response reflex decreases over time
eg: child repeatedly walks past friendly dogs (no bite). gradually static reflex will reduce
Stimulus discrimination after conditioning
only the conditioned stimulus and no similar stimulus triggers the conditioned response, eg: child shows fear to only one breed of dog, not all
Spontaneous recovery (stop or decrease after conditioning)
even if CR extinguished, CR may occasionally and temporarily reappear
eg: after extinction, child who doesn’t show static reaction to dogs, may occasionally out of habit
Operant conditioning
a behaviourist approach to learning in which an individual learns through associating a behaviour with a consequence
consequence to VOLUNTARY behaviour can influence the likelihood of the behaviour occurring again
3 components
Antecedent
Voluntary behaviour
Consequence
Antecedent
this is an event or stimulus that is present just before the target behaviour occurs.
eg: messy room
Voluntary behaviour
observable target behaviour
eg: do chores (clean)
Consequence
occurs as a result of behaviour to increase or decrease its likelihood of happening the next time the antecedent occurs
eg. given pocket money
To increase / decrease likelihood of behaviour
reinforcement
punishment
reinforcement
an event or a stimulus that increases the likelihood of a behaviour occurring again
punishment
an event or a stimulus that decrease the likelihood of a behaviour occurring again
positive reinforcement
the addition of a reward or positive stimulus that encourages a behaviour to occur again
negative reinforcement
the removal of an unpleasant stimulus that encourages a behaviour to occur again
positive punishment
the addition of an unpleasant stimulus that discourages a behaviour from occurring again
negative punishment
the removal of a pleasant stimulus that discourages a behaviour from occurring again
acquisition
the initial learning stage, when an individual associates a neutral stimulus or behaviour with specific outcome or consequence
association
where two or more stimuli are paired together to produce a learnt response
Classical vs Operant Acquisition (v)
Claasical : learns to link to two stimuli (involuntarily)
Operant: volntary behaviour strengthened or weakened by association W consequence
Classical / Operant Association (a)
classical: association of NS to UCS through repeated pairing
Operant: organism learns to associate a behaviour w a consequence
Observational learning
a type of learning that occurs by observing and imitating the behaviours of others
learning that occurs when a learner observes someone else’s actions and the consequences that follow to guide their own future actions
Attention
observer must actively watch the model closely (actively focus) in order to observe the behaviour and notice technique and any consequences of the models behaviour
more likely to repeat if model is perceived more positively and has higher status/ similar to ourselves/successful
Retention
observer must be able to remember the behaviour of the model and store it in their memory as a mental representation
Reproduction
when models behaviour attended to and retained in memory, observer can only attempt to reproduce it if he or she has the physical or mental ability to do so
Motivation
learner must want to imitate the behaviour
Reinforcement
influences the motivation to reproduce the observed behaviour and increases the likelihood of reproduction in the future
self-reinforcement: internal factors (eg. how you perceive yourself)
external reinforcement: external factors (eg. reward)
vicarious reinforcement: seeing someone else be reinforced
People (single)
single geo-cultural community with ATSI (Aboroginal Torres Strait Islanders)
Peoples (Plural)
wider region + diversity of Aboroginal + Torres Strait Islander Peoples + cultures connected to lands across Australia
Aboriginal ways of knowing buzzwords
passed on from generation to generation
holistic
interconnected → spiritual, physical, emotional ties (to land)
learner is part of a system of knowledge - structured and interconnected framework for understanding
multimodal
8 ways of learning
Aboriginal perspectives come from indigenous processed of knowledge transmission, rich overlap between these and best mainstream pedagogies
Story sharing
learning maps
Non-verbal
Symbols + Images
Land links
Non-linear approaches
Deconstruct and Reconstruct
Community Links
Story sharing
approaches to learning through narrative
yarning circles: circles where everyone is at an equal level to share without judgement
Learning Maps
explicitly mapping/visualising processes + ideas
Non-verbal
using movement to share, connect or express knowledge
Symbols +Images
using images art, symbols, metaphors, dance to understand concepts and content
creating meaningful or representative drawings, paintings, icons and metaphorical examples
Land links
place based learning, linking content to local land, place and environmental events - connecting to country
Non-linear approaches
innovatively understanding ideas by thinking laterally or combining systems
Deconstruct and reconstruct
looking at a concept as a whole before breaking it down into parts to study in detail
Community links
involves a learner centering local viewpoints and applying learning to benefit their mob or community
Memory
the process of receiving, encoding, storing and retrieving information
Encoding
process of converting raw, sensory information into a form that can be processed by the brain
Storage
process of maintaining information in a memory store
Memory store
site where information can be stored temporarily or permanently → allow info to be easily attended to or accessed when required
Retrieval
process involving accessing and diverting info from long-term memory to short-term memory so it can be used and/or manipulated
Atkinson-Shiffrin multi-store model of memory
suggests that human memory consists of more than one type of memory store.
sensory memory
short-term memory
long-term memory
Each memory store has a specific function, capacity and duration.The three memory stores work together to encode, store and retrieve information.
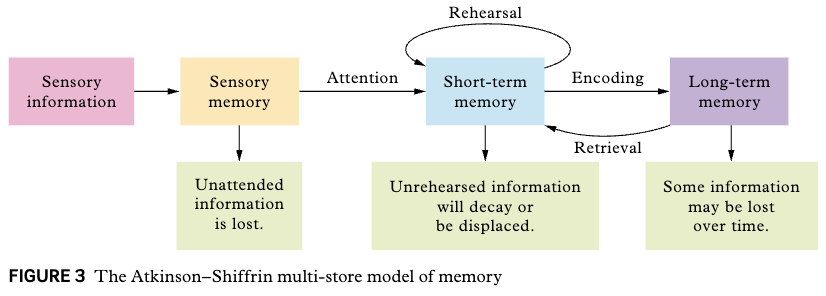
Capacity (general):
no.of items that memory store holds
duration (general):
length of time it can hold them for
Sensory memory
a memory store for incoming sensory info that is held for a short time (0.2 - 4 seconds)
brain filters out irrelevant info, allowing us to focus on essential components of our experiences
sensory memory: capacity
unlimited for both echoic + iconic
sensory memory: duration
0.2 - 0.5 for iconic and 3-4 for echoic
iconic memory
a part of sensory memory where visual info held for 0.2-0.5 secs
echoic memory
a part of sensory memory where auditory info can be held for a short time (3 - 4 secs)
Short-term memory
a memory store that receives information from sensory memory stores and has a limited capacity of 5 to 9 items and a limited duration of 12 to 30 secs
STM acts as bridge after transferring sensory memory into LTM
“working memory” → manipulation and working with memory occurs here
STM capacity
7± 2 items (5-9) at a time
rehearsal
a mental process of repeating / manipulating info in short-term memory to enhance length of time it is held in short-term memory and to increase the likelihood of it being transferred to long term memory
can be used to extend the duration of STM (in a broad sense)
maintenance rehearsal
repeating info to keep it in your attention (does not go into LTM)
elaborative rehearsal
meaning is added to piece of info to connect it to other items or ideas held in LTM (assign purpose) → send to LTM
decay
fading and removal of an item from a memory store due to inattention or lack of use (eg. when elaborative rehearsal doesn’t occur)
chunking
grouping or combining small units of information to increase the likelihood of retaining information in short-term memory
can be used to expand the capacity of STM
displacement
when information held in short-term memory is pushed out and replaced by new, incoming information
STM Pairs
duration + decay
capacity + displacement
Long tem Memory
a memory store for information that has been encoded from short-term memory that has potentially unlimited capacity and duration
stores, encodes and organises a large amount of information
strength and accessibility of memories can vary → factors such as physical changes to brain, retrieval cues and passing time can affect retrieval
retrieval cue
a prompt or stimulus that improves the ability to recall info from long-term memory
LTM capacity
potentially unlimited
difficult to determine bc how dyk why smth is forgotted (eg. irrelevance?)
LTM duration
relatively permanent
after encoding, memory has potential to be available and recalled over extended periods
Explanatory power of Atkinson-Shiffrin Model
Strengths
provides clear framework and how memory is organised + processes involved
explains 3 diff memory stores vary in capacity and duration
Weaknesses
does not consider factors such as motivation + incentive can influence encoding of info from STM to LTM
does not account for individual differences in memory processes, storage duration and capacity (eg. ppl with photographic memory vs amnesia)
Implicit Memory
a memory of a skill, an emotion or a disposition that is unconscious and automatically retrieved
eg. riding a bike → initially needs conscious retrieval of info and concentration but after enough practice, info on how to ride bike is in long term memory
procedural memory
an aspect of implicit memory that concerns our memory of how to perform particular tasks, skills or actions
physically carry out action, initially requires conscious effort but once info about “how to” perform skill stored in long-term memory, retrieval process requires little to no effort
eg: handwriting
classically conditioned memory
aspect of implicit memory that concerns our memory of association between stimuli and responses
eg. classically conditioned emotional responses occur automatically and without conscious retrieval
Explicit Memory
a memory of knowledge, facts and personal experiences that can be retrieved consciously
eg. when asked abt favourite movie, you consciously retrieve info abt movies from LTM
Semantic memory
an aspect of explicit memory that concerns memory of facts and general knowledge
eg. time tables or ingredients for cake
episodic memory
an aspect of explicit memory that concerns memory of personal life experiences
personal memories often accompanied by associated emotions + sensory details
more prone to being forgotten compared to semantic memories due to large volume of info
eg. sensation of scariest roller coaster
Hippocampus
curved structure in the brain responsible for consolidation of explicit memories and aids in transferring explicit memories to parts of the neocortex for storage
forms connections with frontal lobe, thalamus and amygdala
involved in the encoding, consolidation and retrieval of explicit memories
Consolidation
series of neurological changes to the brain that results in short-term memory being stored in LTM
consolidation process ensures that info can be easily retrieved later with help of retrieval cues
Role of hippocampus in explicit memory
helps encode info from STM to LTM
also transfers newly encoded explicit memory to relevant parts of brain for storage → consolidation process ensures that info can be easily retrieved later with help of retrieval cues
Amygdala
almond shaped structure in each cerebral hemisphere in temporal lobe that serves multiple functions that relate to our memory of emotionally arousing events
located near hippocampus
Amygdala Role in explicit memory
works with hippocampus to encode + consolidate the emotional component of explicit memories → adds emotional significance which makes easier to recall
when explicit memory retrieved from LTM, hippocampus helps recall factual details while amygdala retrieves emotional component linked to that memory
Amygdala Role in implicit memory
classically conditioned responses have an emotional component
amygdala contributes to formation + retrieval of implicit conditioned emotional responses
emotional reactions + associations automatically retrieved from LTM when encountering similar stimuli
classically conditioned emotional responses
an emotional response (eg. fear) that becomes associated with a neutral stimulus as a result of classical conditioning
When amygdala damaged
difficulty encoding + retrieving emotional component of implicit and explicit memories and difficulty establishing emotional association bw stimuli
Neocortex
largest section of the cerebral cortex that is responsible storing explicit memories
Neocortex Role in explicit memory
serves as storage site for information related to our conscious memories
encoded by the hippocampus, info is distributed across the neocortex and sent to different regions of the neocortex for storage
location influenced by function of cortical lobes
Damage to neocortex
Damage to the neocortex can impair both short-term and long-term memory, affecting the ability to learn new information and recall old memories.
Basal Ganglia
Group of subcortical nuclei that are responsible for motor control, learning and memory.
Main roles is the encoding, consolidation, and retrieval of implicit procedural memory, specifically habits.