chapter 2 Comprehensive Guide to Chemistry of Life: Atoms, Bonds, Water, Organic Molecules, and Energy
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
Matter
Anything that takes up space and has mass
Mass
Amount of matter contained in a substance; Determines weight
Atom
Building block of all matter; Smallest stable unit
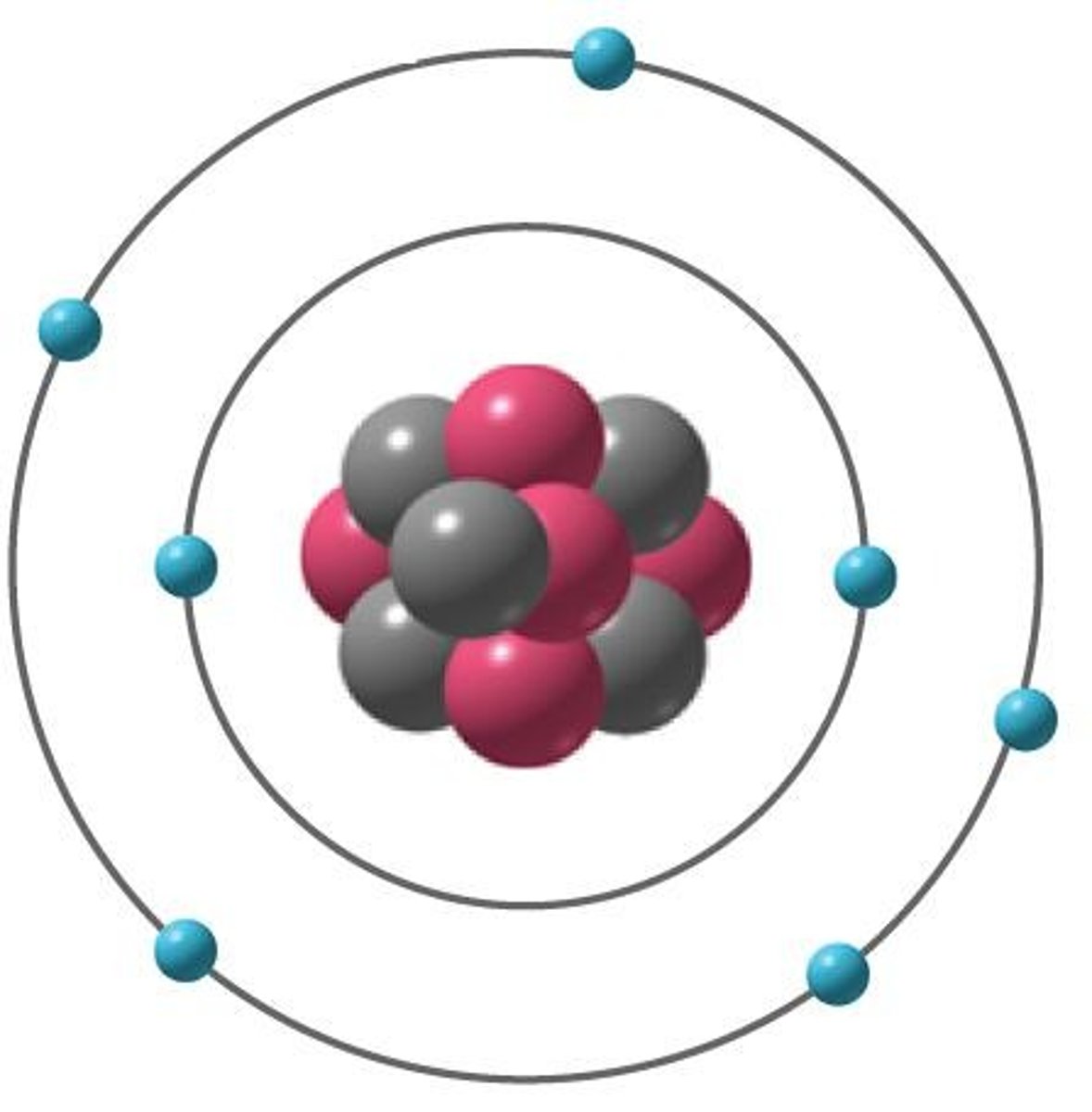
Proton
Found in nucleus; Mass: one amu; Charge: +1
Neutron
Found in nucleus; Mass: one amu; Charge: 0
Electron
Orbits nucleus; Mass: ~1/1800th amu; Charge: -1; Arranged into electron shells (energy levels)
Element
Simplest matter with unique chemical properties; Possess only one kind of atom; Identified by unique symbols
Minerals
Inorganic elements extracted from soil by plants; Significant to body structure and physiology
Atomic Number
# of protons
Atomic Mass
# protons + neutrons
Atomic Weight
Average mass of all elemental isotopes
Isotopes
Same # of protons, but different # of neutrons
Chemical Stability
Full valance shell = chemical stability; Atom is inert
Chemical Bonds
Ionic, Covalent, Hydrogen
Molecule
Two or more atoms held together by a bond; May be identical or different elements
Compound
Atoms of two or more elements held together by a bond; Held together by chemical bonds
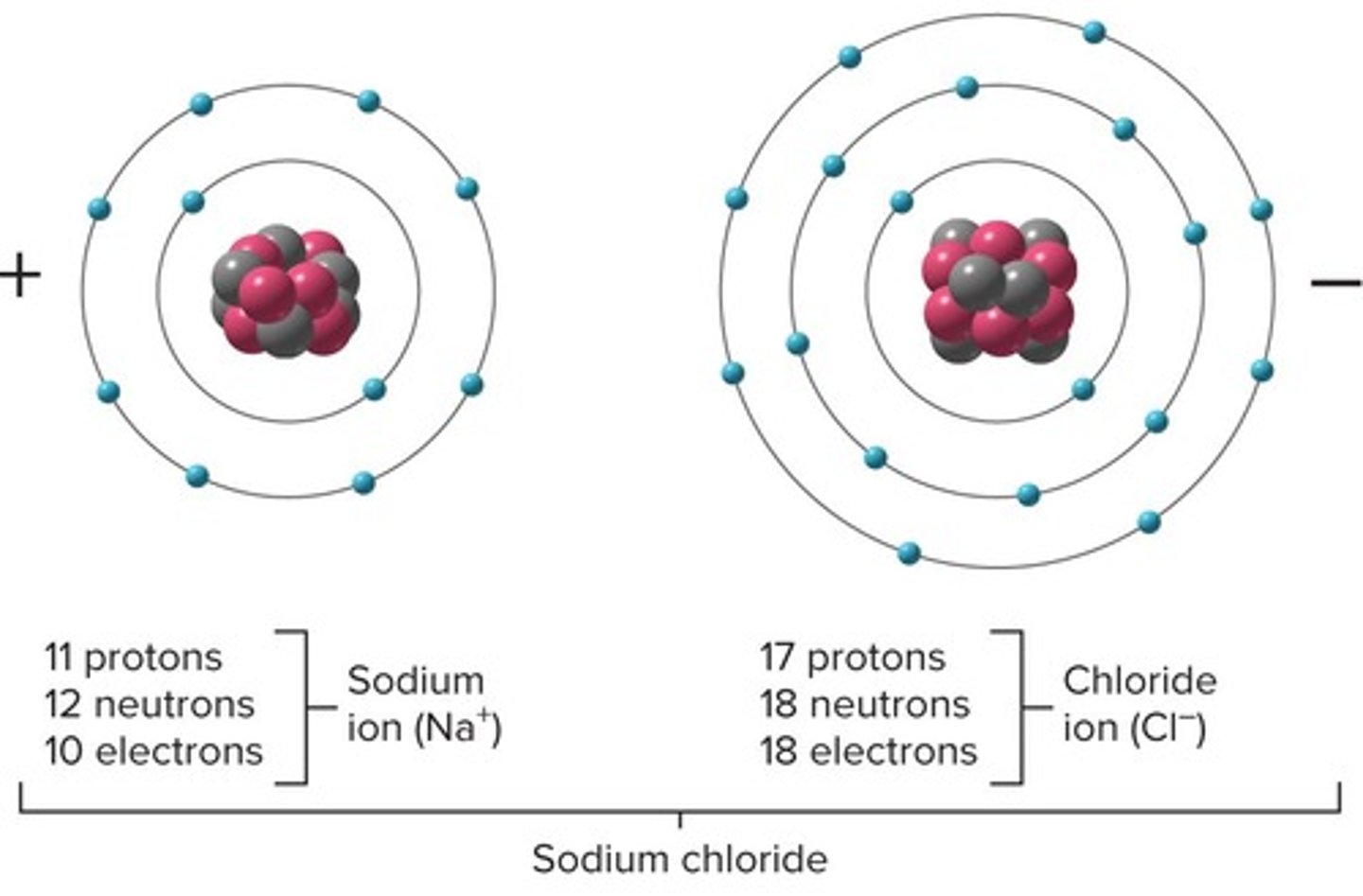
Ions
Charged particles; # protons ≠ # electrons; Formed when atoms gain or lose electrons
Cations
Lost one or more electrons; Positive charge; Atoms with 1 - 3 valence electrons
Anions
Gained one or more electrons; Negative charge; Atoms with 4 - 7 valance electrons
Electrolytes
Salts that ionize in water; Form solutions capable of conducting electricity
Free Radicals
A particle with an unpaired electron; Harmful and highly reactive
Ionic Bonds
Formed between two or more atoms; Results in ionic compound; Weaker than covalent bonds
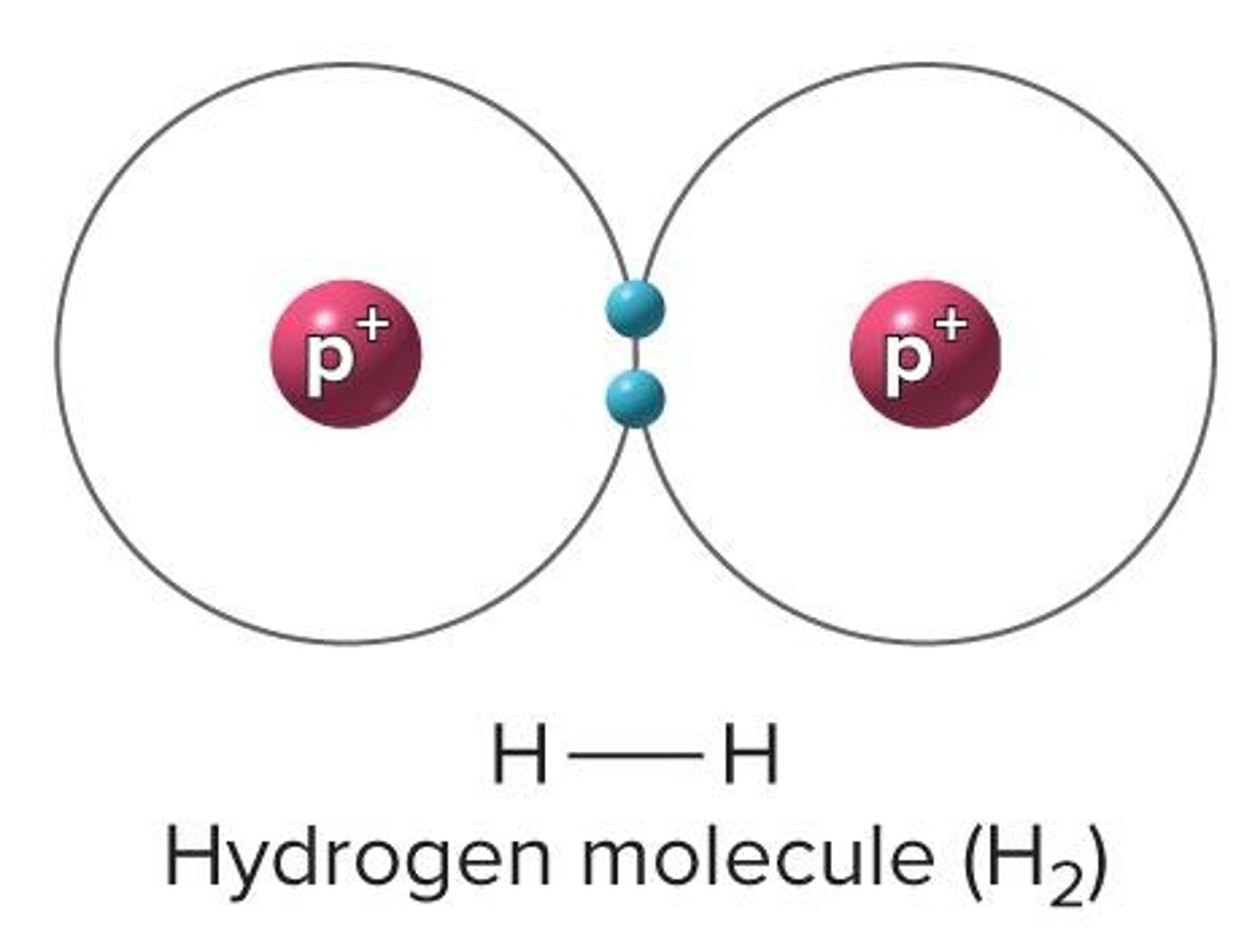
Covalent Bonds
Atoms share electrons; Common and strong; Atoms can share multiple e- pairs
Polar Covalent
Electrons shared unequally
Nonpolar covalent
Electrons shared equally
Electronegativity
"Pull" an atom has on electrons
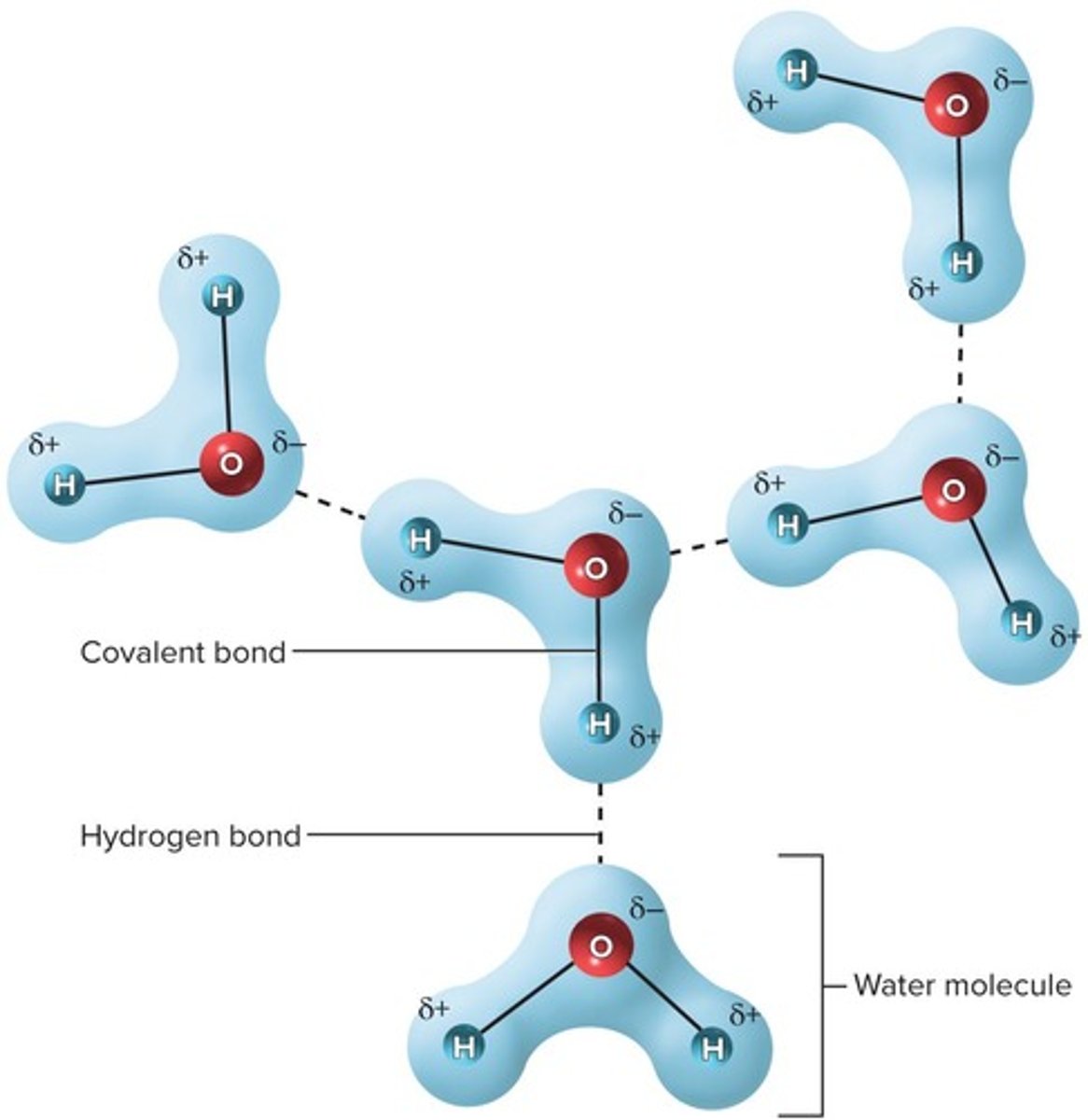
Hydrogen Bonds
Attraction between a δ+ H and a δ- N or O
Basic Water Facts
Around 50 - 75% of body weight
Water Formula
H2O
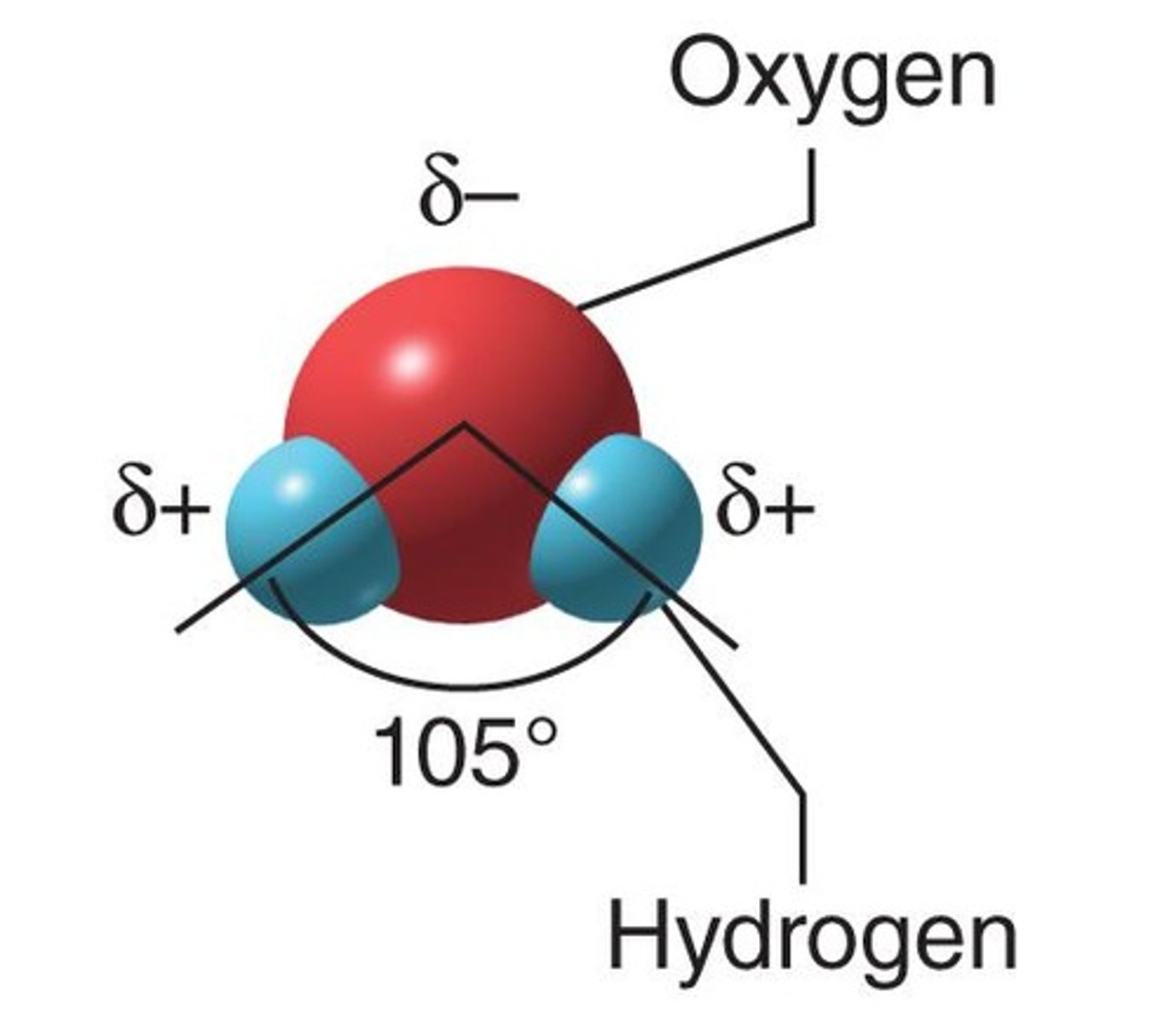
Polar molecule
A molecule with a V-shaped structure that contributes to polarity.
Chemical reactivity
Participates in chemical reactions and disassociates into H+ and OH-.
Thermal stability
Stabilizes body temperature due to high heat capacity from hydrogen bonds.
Cohesion
Water molecules cling to each other, contributing to surface film and surface tension.
Adhesion
Water molecules cling to other substances, reducing friction.
Solvency
Ability to dissolve other chemicals.
Hydrophilic
Substances that will dissolve in water.
Hydrophobic
Substances that won't dissolve in water.
Amphipathic molecules
Molecules that have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions.
Suspension
Particles settle when mixture stands, scatters light, and is cloudy/opaque.
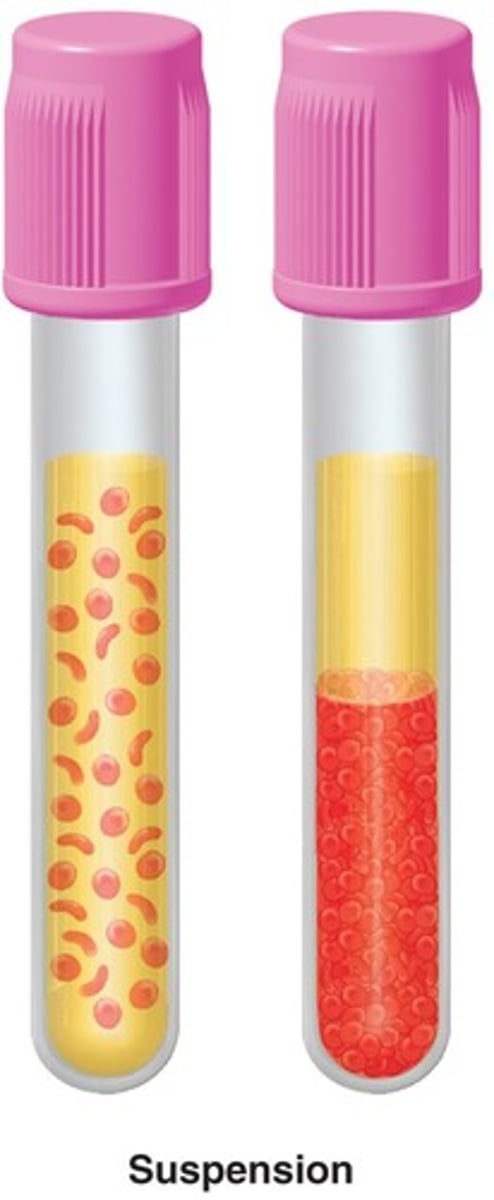

Colloid
Remains mixed when mixture stands, scatters light, and is cloudy/opaque.
Solution
Remains mixed when mixture stands, is a homogenous mixture of solute and solvent.
Emulsion
Suspension of one liquid in another.
Neutralization
Mixing acids and bases can form water and salts, bringing pH to 7.
Buffer
Solutions which resist changes in pH and assist with maintenance of body fluid pH.
Acidosis
Abnormally low blood pH.
Alkalosis
Abnormally high blood pH.
Denaturation of enzymes
H+ ions disrupt bonds and chemical structure
Energy
Capacity to do work (move something)
Potential energy
Energy of position (stored energy)
Kinetic energy
Energy of motion
Chemical Reactions
Forming new bonds or breaking old bonds
Reactants
Substances present at start of reaction
Products
Substances present at end of reaction
Metabolism
Sum of all chemical reactions in a cell or organism
Activation energy
Energy required for a chemical reaction to begin
Enzymes
Lower the energy cost for starting a reaction and act as catalysts: increase reaction rate
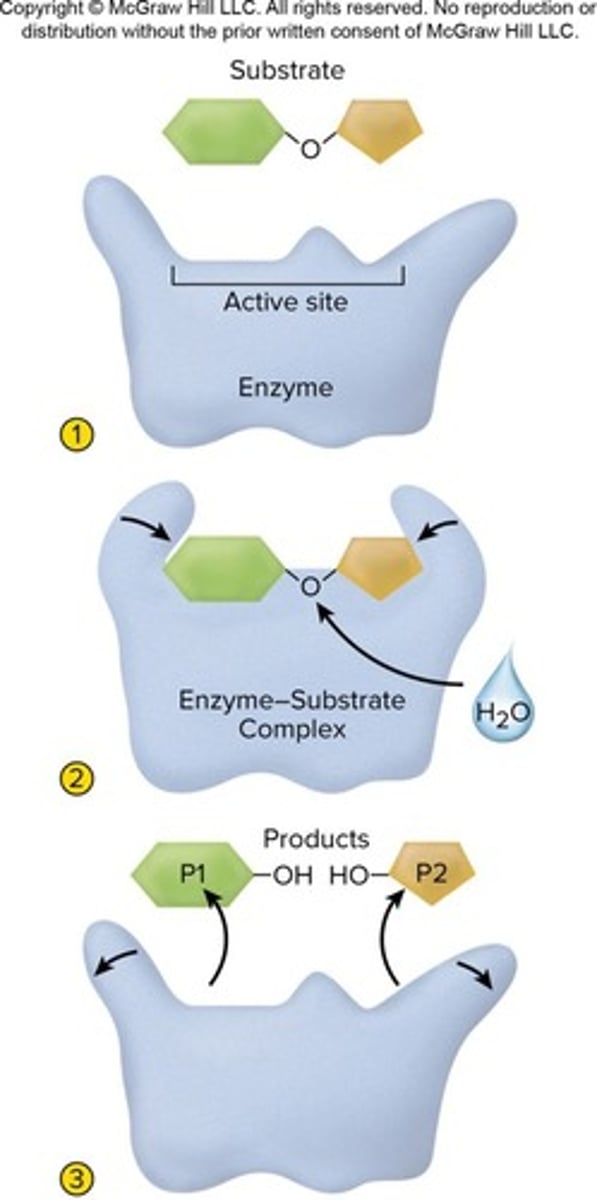
Specificity
Matched to specific substrate; active site only fits substrate
Saturation Limits
All enzymes busy = saturation; need to add more enzyme to increase rate
Regulation
Functional if active site is open; can be 'turned off' by adding inhibitors
Cofactors
Many enzymes require a non-protein 'partner' to function
Organic compounds
Contain carbon and hydrogen; primarily covalent bonds; often large, complex
Inorganic molecules
Typically do not contain carbon; includes water, oxygen, and carbon dioxide
Polymers
Molecules made of repeating subunits called monomers
Carbohydrates
Source of chemical energy; short-term, easy access; converted into glycogen or fat for storage
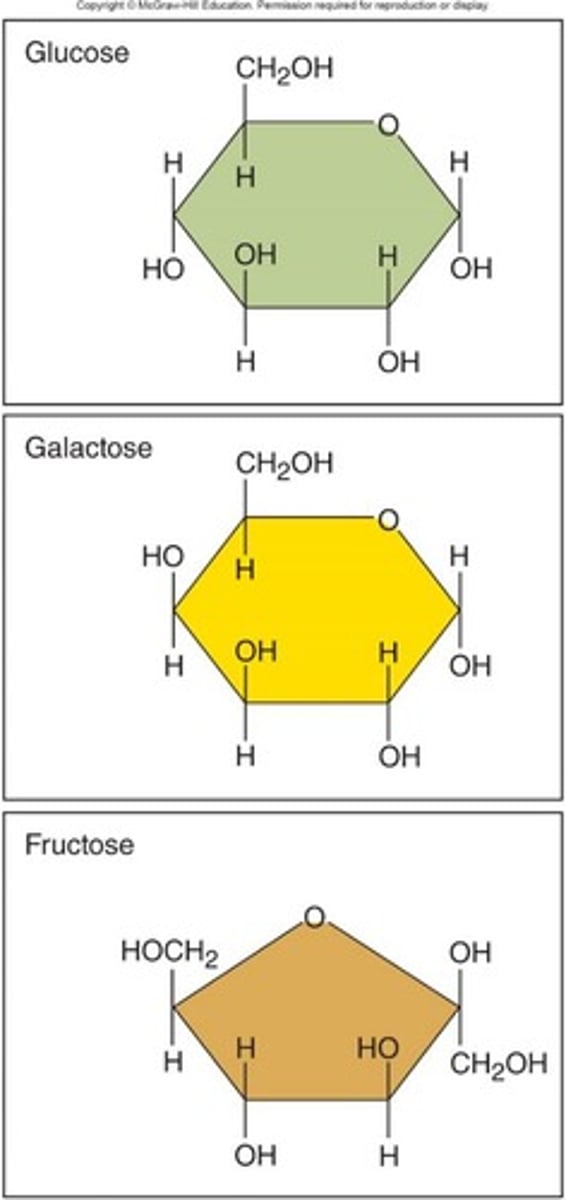
Monosaccharides
Simple sugars; primary cellular energy source
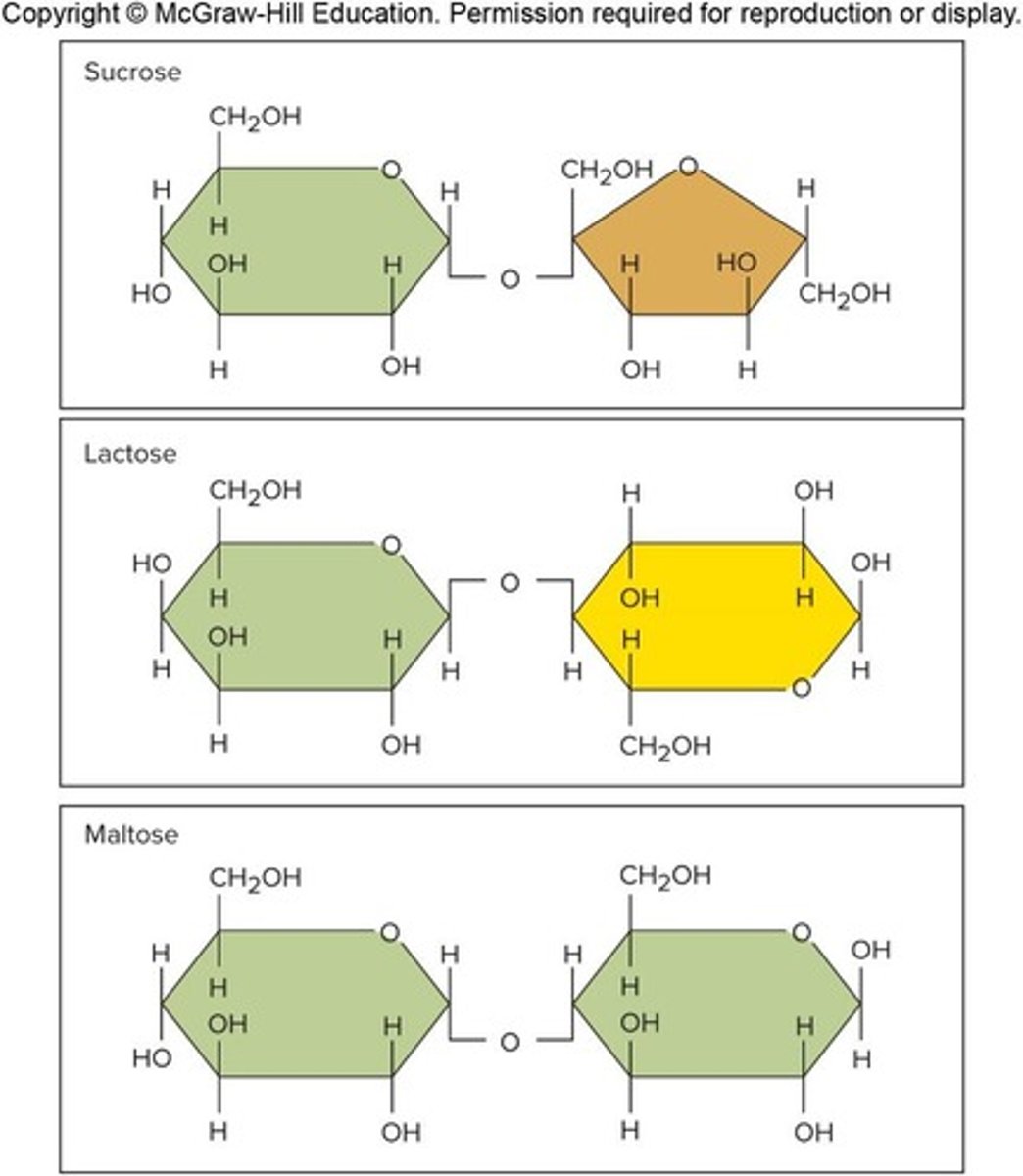
Disaccharides
Composed of two joined monosaccharides
Polysaccharides
Long chains of monosaccharides
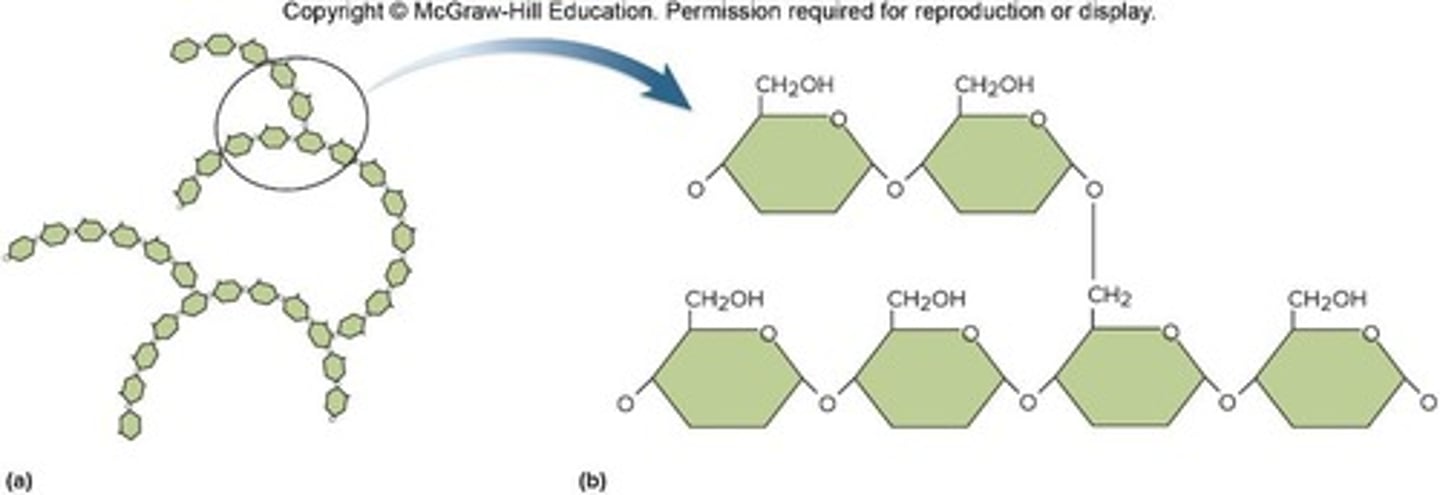
Glycogen
Animal storage form of glucose; produced by liver, muscles, etc.
Cellulose
Structural polysaccharides for plants; indigestible by humans (lack enzyme)
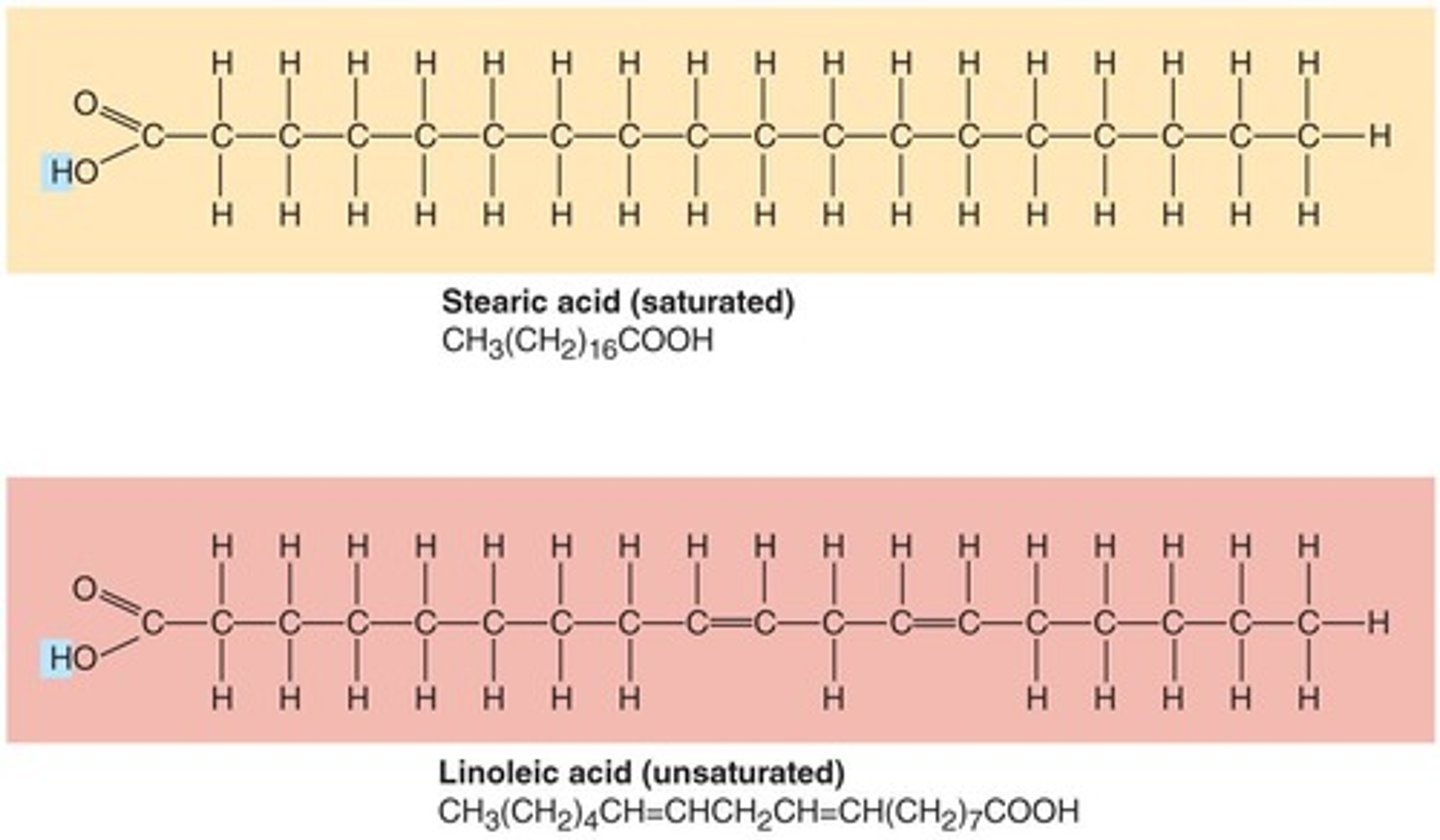
Lipids: Fatty Acids
Hydrocarbon chains with a 'Head' end possessing a carboxyl group (-COOH) that is hydrophilic and a 'Tail' that is a chain of 4 -24 carbons, where saturated means no double bonds and unsaturated means one or more double bonds.
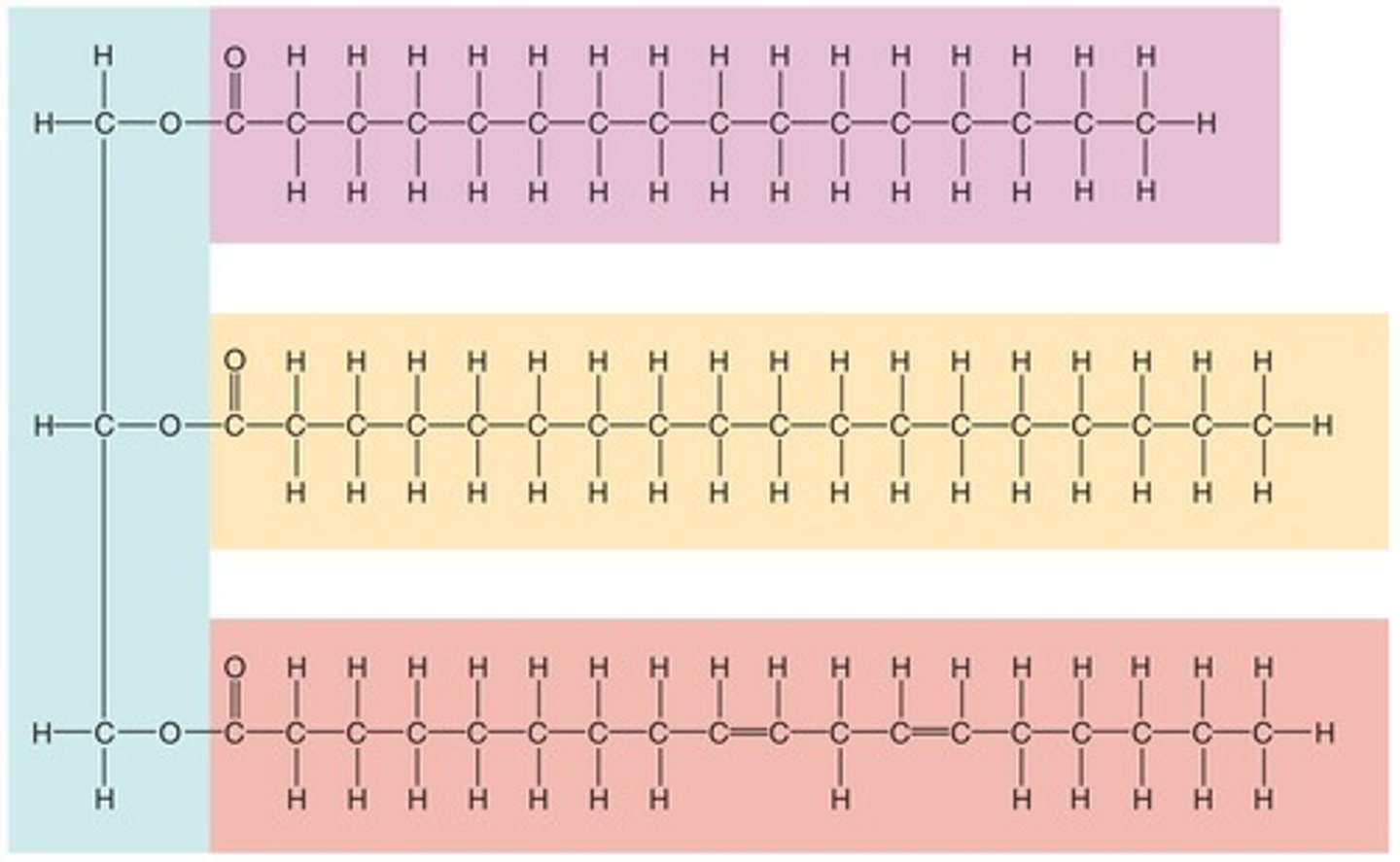
Lipids: Triglycerides
Combination of glycerol, a three-carbon alcohol, and three fatty acid chains, serving functions such as energy storage, insulation (adipose tissue), and protection (adipose tissue).
Lipids: Phospholipids
Combination of glycerol, two fatty acid chains, and a phosphate group, making them amphipathic with hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails, serving as structural components of the plasma membrane.
Lipids: Eicosanoids
Derived from arachidonic acid and act as local signaling molecules.
Prostaglandins
Coordinate/direct local cell activities, produced in most tissues, with roles in pain sensation, labor, inflammation, clotting, etc.
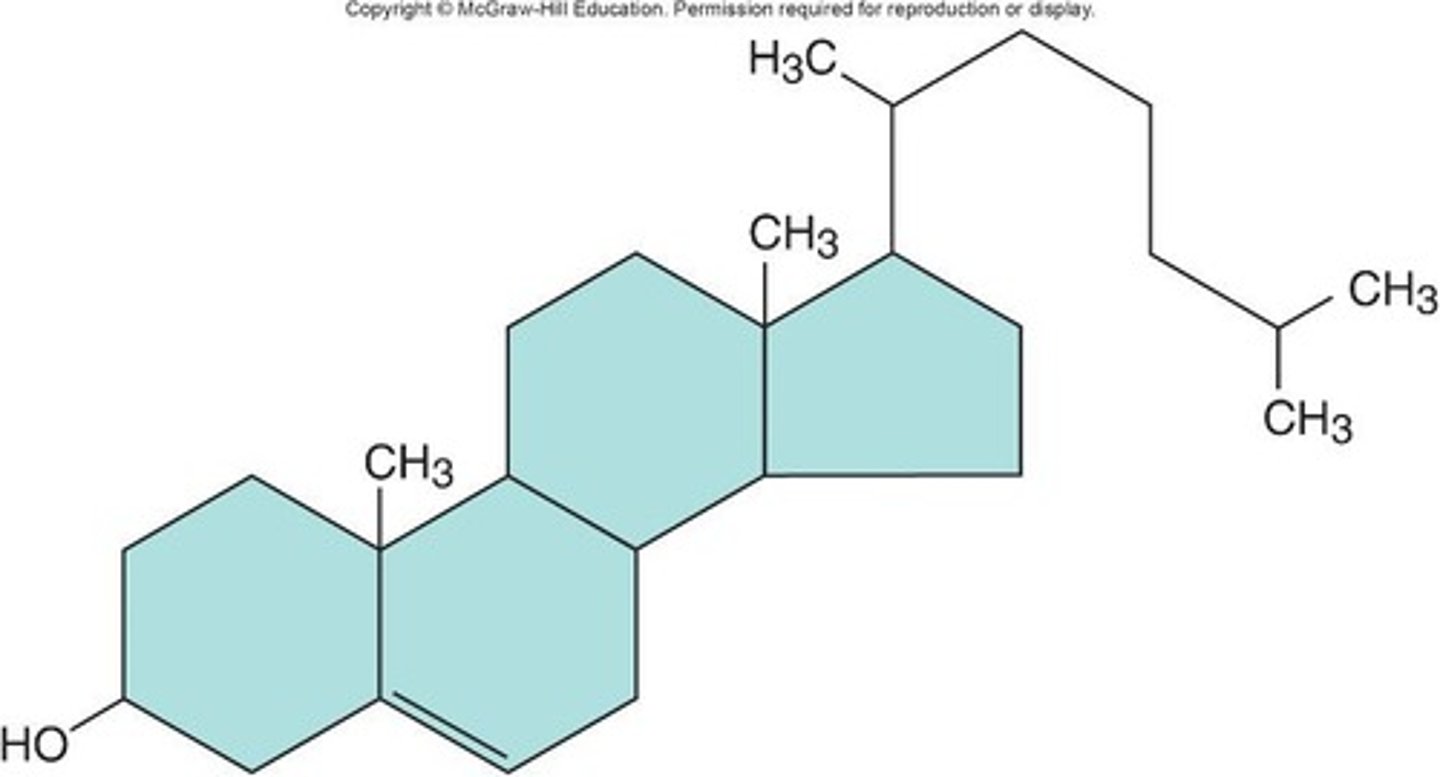
Lipids: Steroids
Contain four hydrocarbon rings, derived from cholesterol, serving as chemical messengers between cells, and can be ingested from animal products or synthesized.
Bile acids
Aid in digestion and absorption of lipids.
Proteins
Monomers made of amino acids, composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and often sulfur, with numerous functions.
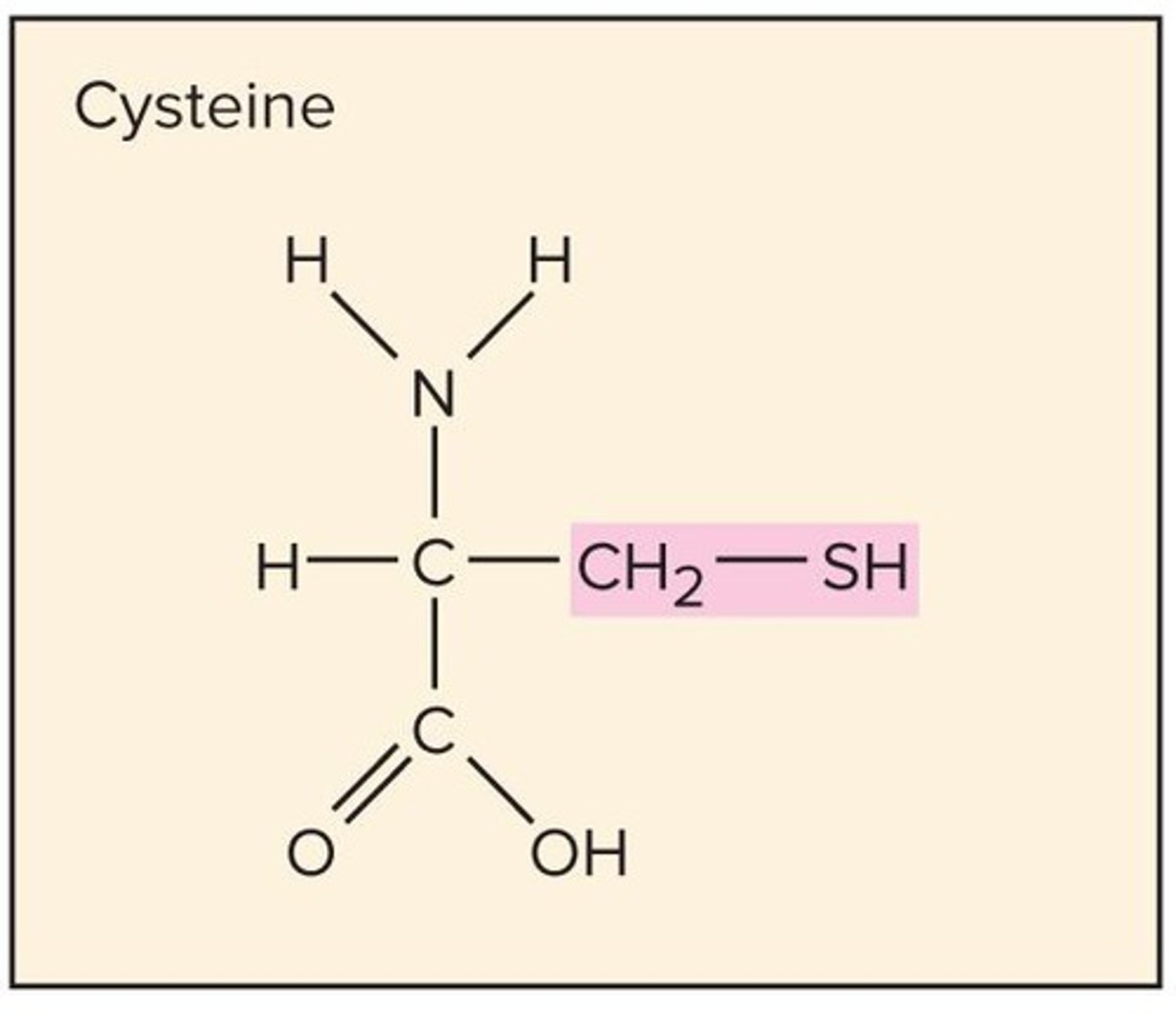
Conformation
The 3D shape of proteins that varies with function and can denature when exposed to extreme pH or heat.
Peptide
Two or more amino acids joined by peptide bonds, with the name depending on the number of amino acids present.
Amino Acids
20 found in humans, each with a distinctive structure including an amine group (-NH2), a carboxyl group (-COOH), and a variable group (R group) that determines unique properties.
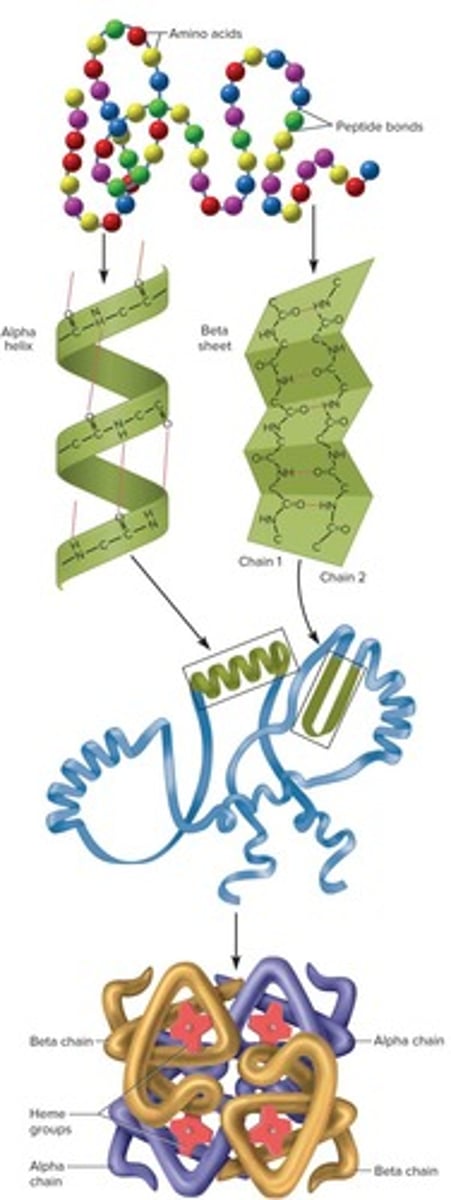
Protein Structure: Primary
Sequence of amino acids joined by peptide bonds.
Protein Structure: Secondary
Coiled or folded 3D shape held together by hydrogen bonds, with the most common forms being alpha helix or beta sheet.
Protein Structure: Tertiary
Result of hydrophobic/hydrophilic side chain interactions, typically resulting in globular or fibrous shapes.
Protein Structure: Quaternary
Association of two or more polypeptides with each other due to ionic bonds and R group interactions; not all proteins have this structure.
Protein Function: Structure
Proteins serve as structural components of cells and tissues, providing strength, durability, and flexibility.
Protein Function: Communication
Proteins serve as hormones and local signaling molecules and act as receptors for chemical messengers.
Protein Function: Membrane transport
Proteins form channels in cell membranes and act as carriers for other substances.
Protein Function: Catalysis
Enzymes participate in metabolic reactions.
Protein Function: Recognition and protection
Glycoproteins serve as cell identification molecules and participate in immunity, especially antibodies.
Protein Function: Movement
Proteins provide the basis for movement through contractile and motor proteins.
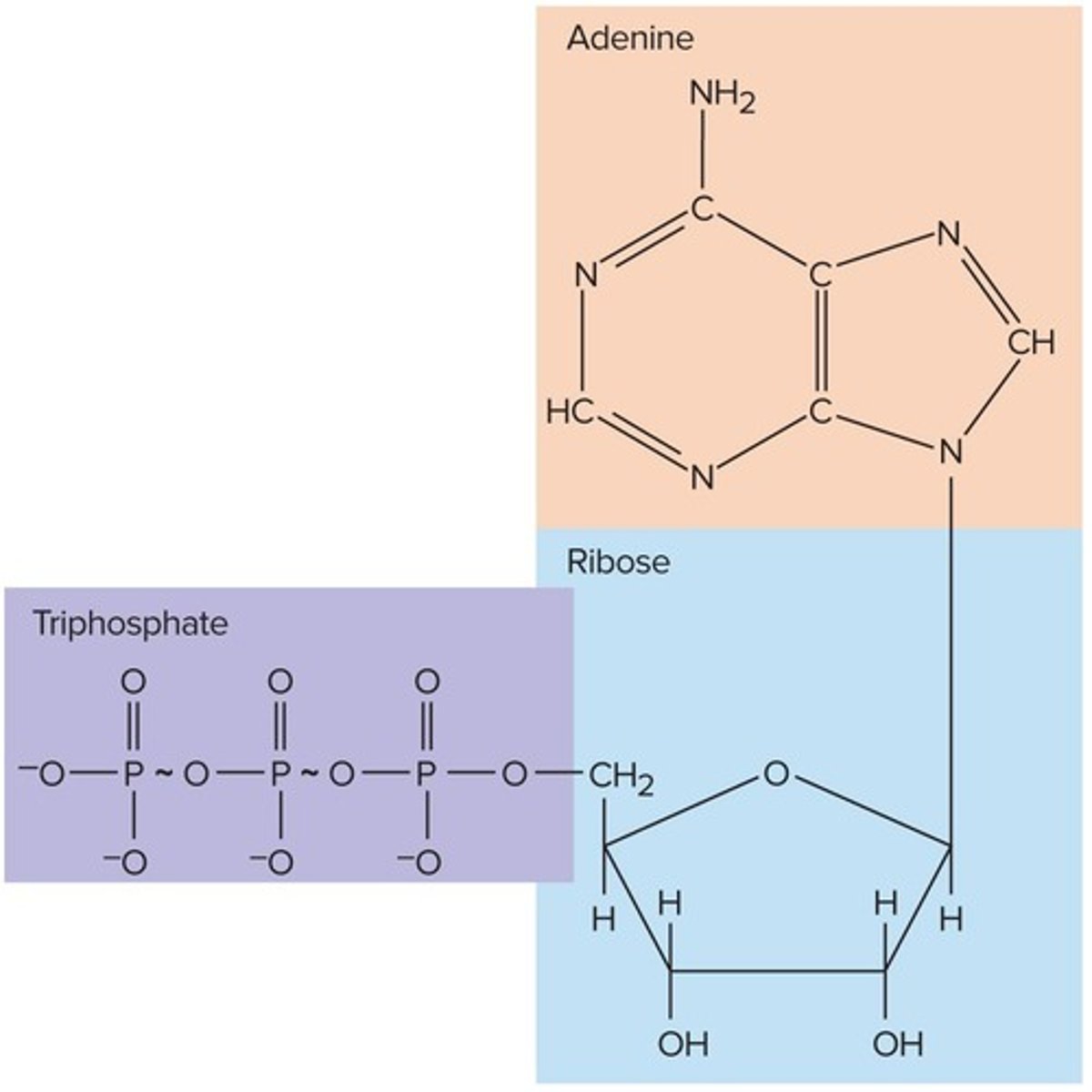
Nucleic Acids
Composed of nucleotide monomers including a pentose sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), a phosphate functional group, and a nitrogenous base.
Nucleic Acids: DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid, stores genetic information directing protein synthesis, double stranded, uses AGCT only, found in the nucleus.
Nucleic Acids: RNA
Ribonucleic acid, participates in protein synthesis, single stranded, uses AGCU only, found in nucleus and cytoplasm.
Nucleotide: Adenosine Triphosphate
Primary energy-transfer molecule required to perform most of the body's work, with the reaction ATP + H2O → ADP + Pi + energy.
Producing ATP
Requires glucose or other fuel and involves a multi-stage process including anaerobic fermentation and aerobic respiration.
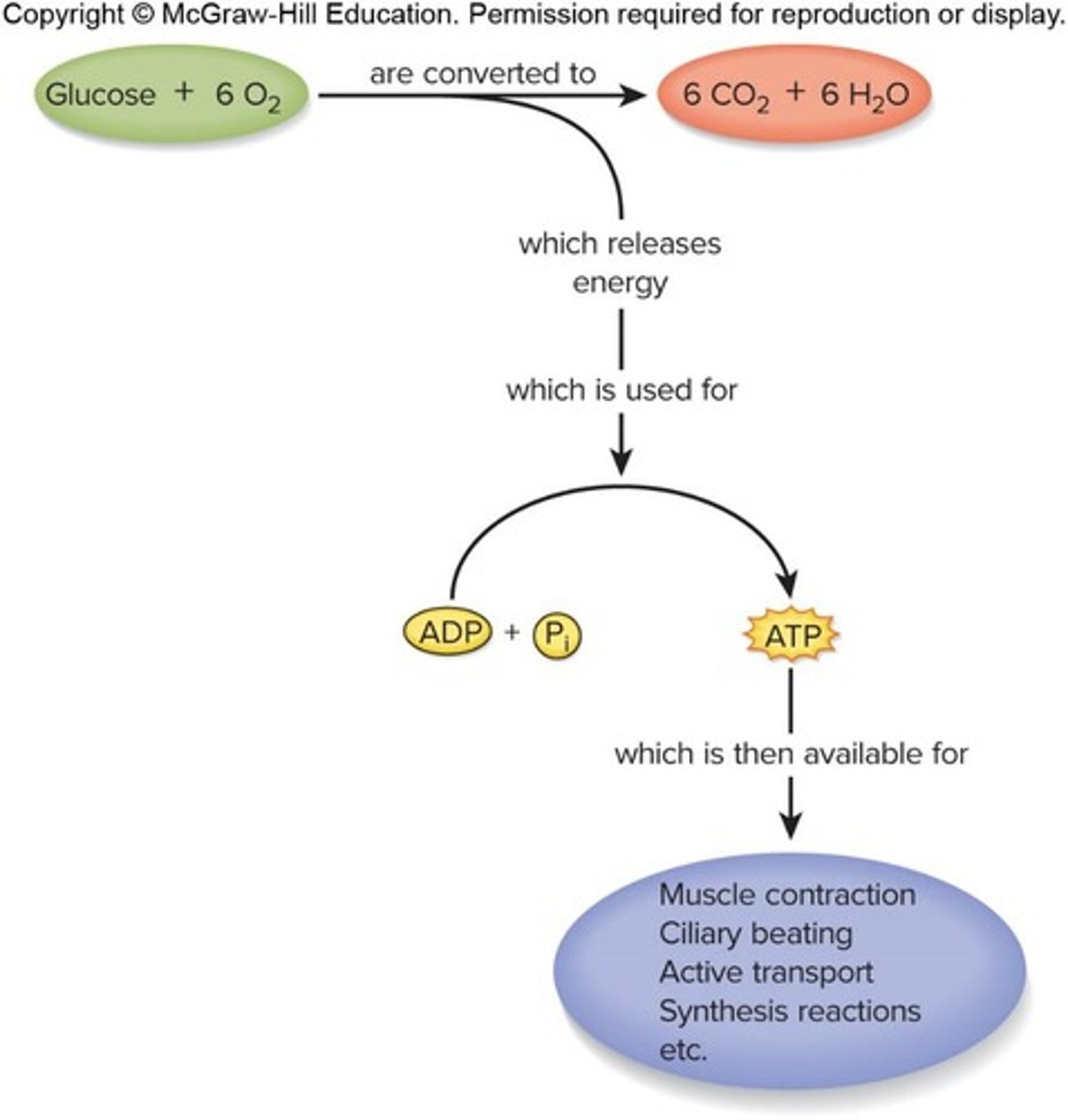
Anaerobic fermentation
Does not require oxygen, produces fewer ATP, occurs in cytoplasm, and produces lactate.
Aerobic respiration
Requires oxygen, produces more ATP, and is more efficient, occurring in mitochondria.