OCR A-Level Chemistry
1/225
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
226 Terms
Acid
A species that releases H+ ions in aqueous solution
Acid Dissociation Constant Ka
The equilibrium constant that shows the extent of dissociation of a weak acid
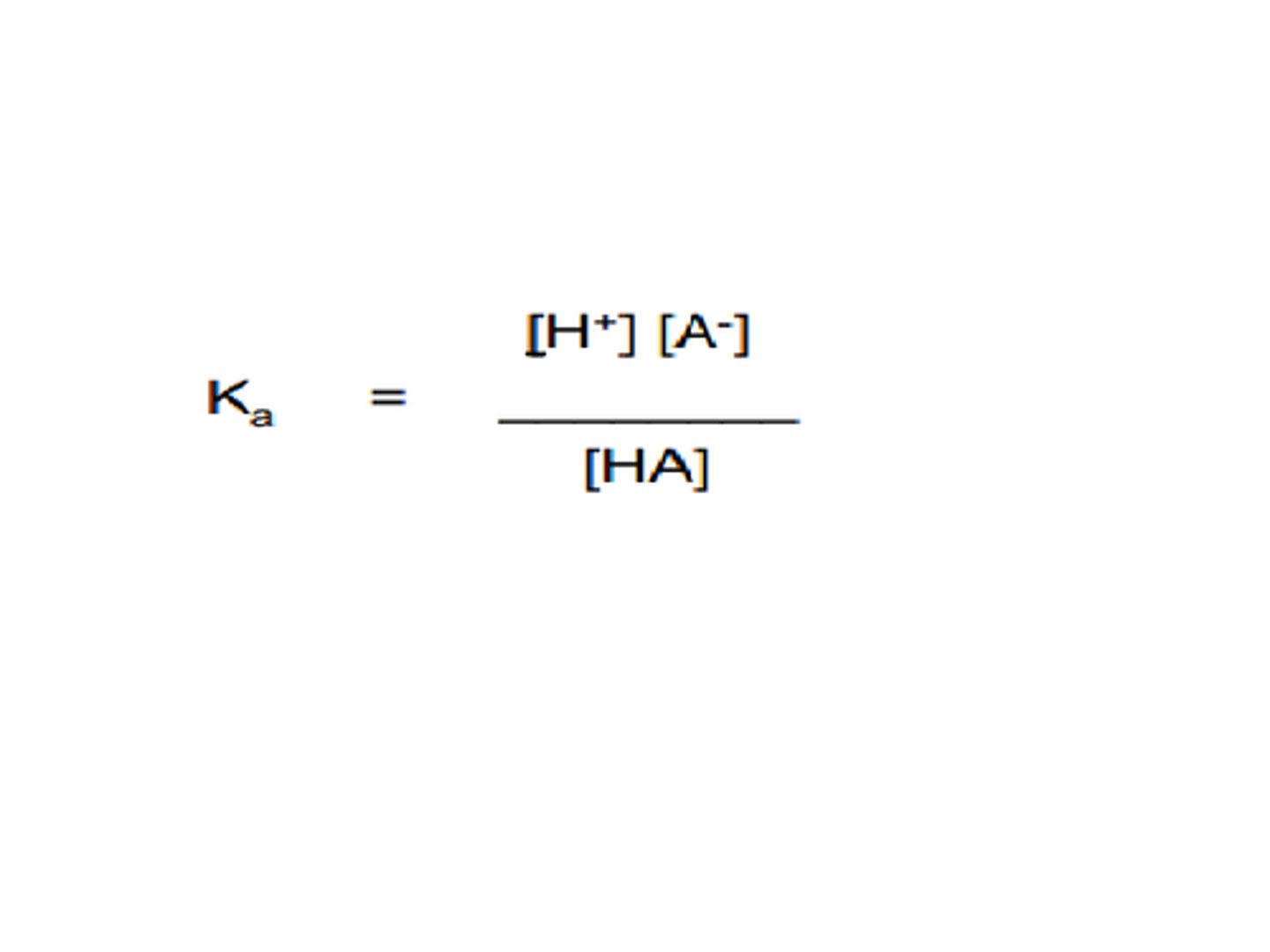
Acid-Base Pair
A pair of two species that transform into each other by gain or loss of a proton
Activation Energy
The minimum energy required to start a reaction by the breaking of bonds
Actual Yield
The amount of product obtained from a reaction
Addition Polymerisation
Formation of a very long molecular chain, by repeated addition reactions of many unsaturated alkene molecules (monomers).
Addition Reaction
A reaction in which a reactant is added to an unsaturated molecule to make a one saturated molecule
Adsorption
The process that occurs when a gas or liquid or solute is held to the surface of a solid.
Alicyclic
Containing carbon atoms joined together in a ring that is not aromatic
Aliphatic
Containing carbon atoms joined together in straight or branched chains.
Alkali
A type of base that dissolves in water forming hydroxide ions, OH- (aq) ions.
Alkanes
The hydrocarbon homologous series with single carbon-to-carbon bonds
and the general formula: CnH2n+2.
Alkenes
The hydrocarbon homologous series with at one double carbon-to-carbon
bonds and the general formula: CnH2n.
Alkyl Group
A side chain formed by removing a hydrogen atom removed from an
alkane parent chain, for example, CH3, C2H5; any alkyl group is often shown
as R.
Alkynes
The hydrocarbon homologous series with one triple carbon-to-carbon bonds and the general formula: CnH2n-2.
Amount of Substance
The quantity whose unit of the mole, used as a means of counting any species such as atoms, ions and molecules.
Anhydrous
Containing no water molecules
Anion
A negatively charged ion with more electrons than protons
Aromatic
Containing one or more benzene rings
Atom Economy
((sum of molar masses of desired products)/(sum of molar masses of all products)) x 100%.
Atomic (Proton) Number
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
Atomic Orbital
A region around the nucleus that can hold up to two electrons with opposite spins
Average Bond Enthalpy
The average enthalpy change that takes place when breaking by homolytic fission 1 mol of a given type of bond in the molecules of a gaseous species.
Avogadro's Constant
The number of atoms per mole of the carbon-12 isotope. (6.02 × 10^23 mol-1 ).
Base
A compound that neutralises an acid to form a salt
Binary Compound
A compound containing 2 elements only
Bond Angle
The angle between 2 bonds at an atom
Bond Dissociation Enthalpy
The enthalpy change that takes place when breaking by homolytic fission 1 mol of a given bond in the molecules of a gaseous species.
Bonded Pair
A pair of electrons shared between 2 atoms to make a covalent bond
Brønsted-Lowry acid
A species that is a proton, H+, donor
Brønsted-Lowry base
A species that is a proton, H+, acceptor
Buffer Solution
A system that minimises pH changes on addition of small amounts of an acid or a base.
Carbocation
An ion that contains a positively charged carbon atom
Catalyst
A substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being used up in the process; a catalyst provides an alternative route for the reaction with lower activation energy.
Cation
A positively charged ion with fewer electrons than protons
Chain Reaction
A reaction in which the propagation steps release new radicals that continue the reaction
Chemical Shift δ
A scale, in ppm, that compares the frequency of an NMR absorption with the frequency of the reference TMS at δ = 0 ppm
Chiral Carbon
A carbon atom attached to four different atoms or groups of atoms.
Chromatogram
A visible record showing the result of separation of the components of a mixture by chromatography.
Cis-Trans Isomerism
A special type of E/Z isomerism in which there are two non-hydrogen groups and two hydrogen atoms around the C=C double bond: the cis isomer (Z isomer) has H atoms on each carbon on the same side; the trans isomer (E isomer) has H atoms on each carbon on different sides.
Closed System
A system isolated from its surroundings
Collision Theory
Two reacting particles must collide for a reaction to occur, and must be in the correct orientation and have sufficient energy to overcome the
activation energy of the reaction.
Complex Ion
A transition metal ion bonded to ligands by coordinate bonds (dative covalent bonds).
Concentration
The amount of solute, in moles, dissolved in 1 dm^3 (1000cm^3) of solution
Condensation Reaction
A reaction in which two small molecules react together to form a larger molecule with elimination of a small molecule such as water
Conjugate Acid
A species that releases a proton to form a conjugate base
Conjugate Base
A species that accepts a proton to form a conjugate acid
Coordinate Bond
A shared pair of electrons in which the bonded pair has been provided by one of the bonding atoms only; also called a dative covalent bond.
Coordination Number
The total number of coordinate bonds formed between a central metal ion and its ligands
Covalent Bond
The strong electrostatic attraction between a shared pair of electrons and the nuclei of the bonded atoms
Dative Covalent
A shared pair of electrons in which the bonded pair has been provided by one of the bonding atoms only; also called a coordinate bond.
Dehydration
An elimination reaction in which water is removed from a saturated molecule to make an unsaturated molecule.
Delocalised Electrons
Electrons that are shared between more than 2 atoms
Desorption
Release of an adsorbed substance from a surface
Dipole
A separation in electrical charge so that one atom of a polar covalent bond, or one end of a polar molecule, has a small positive charge δ+ and the other has a small negative charge δ-.
Displacement Reaction
A reaction in which a more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from an aqueous solution of the latter's ions.
Displayed Formula
A formula showing the relative positioning of all the atoms in a molecule and the bonds between them
Disproportionation
A redox reaction in which the same element is both oxidised and reduced
Dynamic Equilibrium
The equilibrium that exists in a closed system when the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction and concentrations do not change
E/Z Isomerism
A type of stereoisomerism in which different groups attached to each carbon of a C=C double bond may be arranged differently in space because of the restricted rotation of the C=C bond.
Electron Configuration
A shorthand representation that shows how electrons occupy sub-shells in an atom
Electronegativity
A measure of the attraction of a bonded atom for the pair of electrons in a covalent bond
Electrophile
An atom (or group of atoms) that is attracted to an electron-rich centre or atom, where it accepts a pair of electrons to form a new covalent bond.
Electrophilic Addition
An addition reaction in which the first step is attack by an electrophile on a region of high electron density
Electrophilic Substitution
A type of substitution reaction in which an electrophile is attracted to an electron-rich centre or atom, where it accepts a pair of electrons to form a new covalent bond.
Elimination Reaction
The removal of a molecule from a saturated molecule to make an unsaturated molecule
Empirical Formula
The formula that shows the simplest whole-number ratio of atoms of each element present in a compound
Enantiomers
Stereoisomers that are nonsuperimposable mirror images of each other; also called optical isomers
End Point
The point in a titration at which an indicator changes colour; the end point indicates when the reaction is just complete
Endothermic reaction
A reaction in which the enthalpy of the products is greater than the enthalpy of the reactants, resulting in heat being taken in from the surroundings (∆H is positive).
Enthalpy H
The heat content that is stored in a chemical system
Enthalpy change ΔH
The difference between the enthalpy of the products and the enthalpy of the reactants
Enthalpy Cycle
A diagram showing alternative routes between reactants and products which allows the indirect determination of an enthalpy change from other known enthalpy changes using Hess' law.
Enthalpy Profile Diagram
A diagram for a reaction to compare the enthalpy of the reactants with the enthalpy of the products.
Entropy
The measurement used for the dispersal of energy and disorder within the chemicals making up the chemical system
Equilibrium Constant Kc
A measure of the position of equilibrium; the magnitude of an equilibrium constant indicates whether there are more reactants or more products in an equilibrium system.
Equivalence Point
The point in a titration at which the volume of one solution has reacted exactly with the volume of the second solution
Esterification
A reaction in which a carboxylic acid reacts with an alcohol to form an ester and water.
Exothermic Reaction
A reaction in which the enthalpy of the products is smaller than the enthalpy of the reactants, resulting in heat loss to the surroundings (ΔH is negative)
Fingerprint Region
An area of an infrared spectrum below 1500cm-1 that gives a characteristic pattern for different compounds
First Electron Affinity
The enthalpy change that takes place when one electron is added to each atom in one mole of gaseous atoms to form one mole of gaseous 1- ions
First Ionisation Energy
The energy required to remove one electron from each atom in one mole of gaseous atoms of an element to form one mole of gaseous 1+ ions
Fractional Distillation
The separation of components in a liquid mixture by their different boiling points into fractions with different compositions
Fragment Ions
Ions formed from the breakdown of the molecular ion in a mass spectrometer
Fragmentation
The process in mass spectrometry that causes a positive ion to split into pieces, one of which is a positive fragment ion.
Free Energy Change ΔG
The balance between enthalpy, entropy and temperature for a process given by ΔG = ΔH − TΔS. A process is feasible when ΔG < 0.
Functional Group
The part of the organic molecule responsible for its chemical reactions.
General Formula
The simplest algebraic formula of a member of a homologous series. For example, the general formula of the alkanes is CnH2n+2
Giant Covalent Lattice
A three-dimensional structure of atoms, bonded together by strong covalent bonds.
Giant Ionic Lattice
A three-dimensional structure of oppositely charged ions, bonded together by strong ionic bonds.
Giant Metallic Lattice
A three-dimensional structure of positive ions and delocalised electrons, bonded together by strong metallic bonds.
Group
A vertical column in the periodic table. Elements in a group have similar chemical properties and their atoms have the same number of outer shell electrons
Half-Life
The time taken for the concentration of a reactant to decrease by half
Hess's Law
If a reaction can take place by more than one route and the initial and final conditions are the same, the total enthalpy change is the same for each route.
Heterogenous Catalysis
A reaction in which the catalyst has a different physical state from the reactants; frequently reactants are gases whilst the catalyst is a solid.
Hetergenous Equilibrium
An equilibrium in which the species making up the reactants and products have different physical states.
Heterolytic Fission
The breaking of a covalent bond with both of the bonded electrons going to one of the atoms, forming a cation and an anion
Homoegenous Catalysis
A reaction in which the catalyst and reactants are in the same physical state, which is most frequently the aqueous or gaseous state
Homogenous Equilibrium
An equilibrium in which all the species making up the reactants and products are in the same physical state
Homologous Series
A series of organic compounds with the same functional group but with each successive member differing by CH2