Biology 7th precomp
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
137 Terms
Characteristics of Living Things
Reproduction, Growth & Development, Cells, Energy, Sense & Respond to Change, DNA, Homeostasis
Reproduction
One or two organisms create a new organism via sexual reproduction (2 organisms) or asexual reproduction (1 organism)
Growth and Development
The organism goes through some change in their body, like growth of lung size for instance.
Cells
The organism has at least one cell
Energy
The organism is able to gain and use energy
Sense and Respond to Change
If the environment were to change, the organism would be able to tell and react to the change accordingly. For instance, if the temperature dropped from 100ºF to 50ºF, the organism would notice and react to the change (probably) by moving to someplace warmer.
DNA
Genetic material located inside a/the cell; contains the information need to make a replica of the organism whose DNA was used
Homeostasis
An organism's ability to change its internal environment in order to maintain equilibrium
homeo, Greek for similar, like, or equal; stasis, Greek for balance, or stable; thus homeostasis = equal balance
equi, latin for equal, or same; (libr)ium, latin for balance, or stability; thus equilibrium = equal balance
Necessities of Life
1. Food
2. Water
3. Air
4. A place to live
Scientific Method
1. Ask a question/Recognize a problem
2. Form a hypothesis
3. Test the Hypothesis/Do the experiment
4. Analyze the results/data
5. Form conclusions
6. Communicate results
Ask a question/Recognize a problem
Find a question whose answer you have been pondering for eternity
Form a hypothesis
Make an educated guess at the possible answer (you have been pondering it for eternity)
Test the Hypothesis/Do the experiment
Now is your chance! Work hard! FIND THE ANSWER!!
Analyze the results/data
What has the experiment told us?
Form conclusions
Write down that info yo
Communicate results
TELL EVERYONE THAT YOU HAVE SOLVED THE ETERNAL QUESTION! (and the results)
Macromolecules
Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids, Nucleic Acids
Carbohydrates
Cell wall= Cellulose; Made of sugar; provides short term energy; contains either fructose or glucose (Glucose used by animals)
Proteins
Made by amino acids; speeds up chemical reactions; makes up cobwebs, hair, feathers, etc.; transports hemoglobin (red blood cells) & O₂
Lipids
Ex.: fats, oils, wax, etc.; Made of CHO (carbon hydrogen oxygen); used for long term energy; composed of a hydroPHILIC head (loves water) & a hydroPHOBIC tail (hates water); when groups of them come together like in the picture given, they are called the PHOSPHOLIPID BILAYER
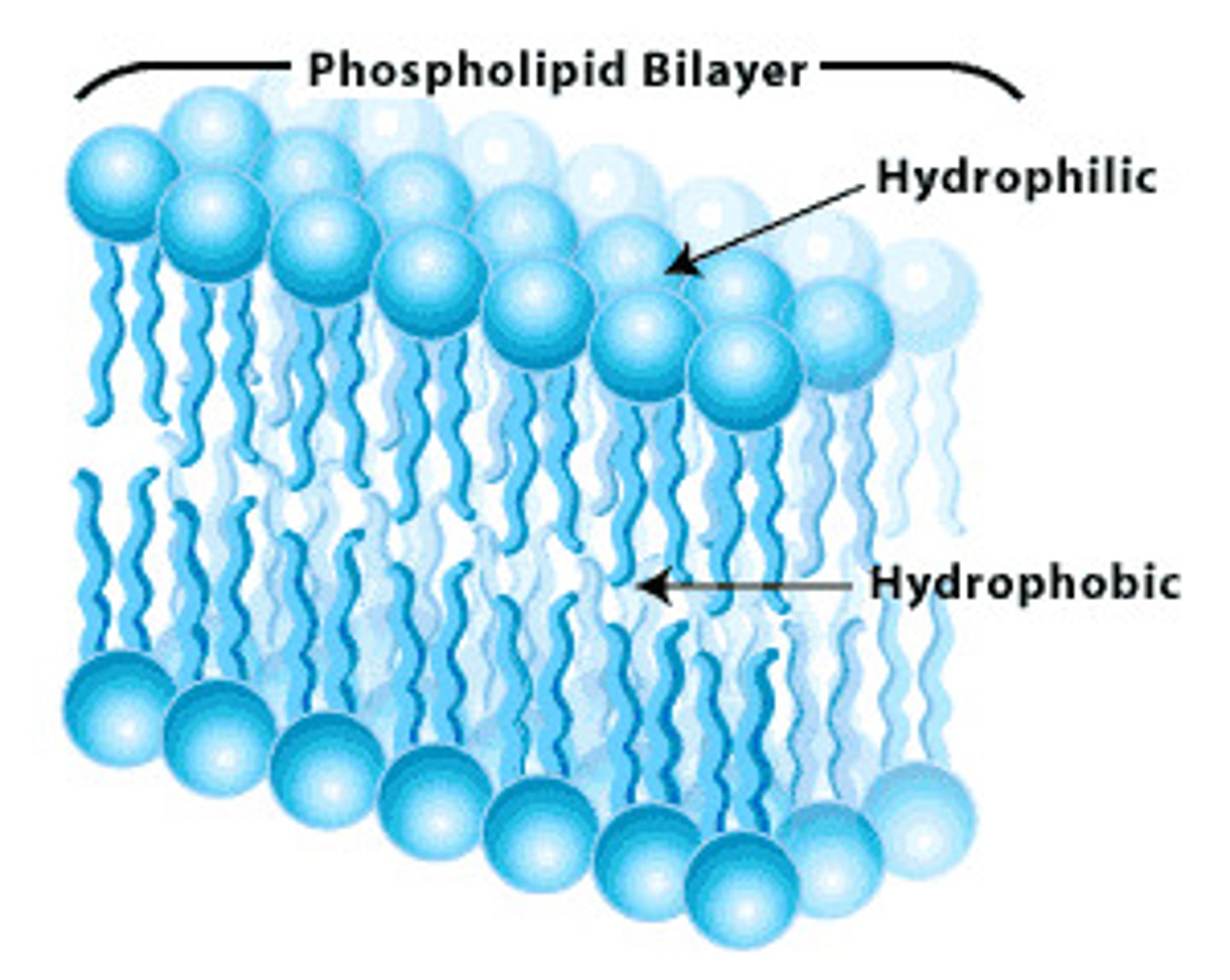
Nucleic Acids
Made of CHONPS (6 elements that make body) (carbon hydrogen nitrogen phosphate and sulfur); Made of 5 nucleotides (cyosine-guanine Adenine-thymine); Blueprints of life; Have instructions to make protiens. DNA and RNA
ATP
Adenosine triphosphate; Energy carrying molecule in cells (fuels all life) energy from carbohydrates turned into ATP. Used by ALL life; NOT A MACROMOLECULE
T-Chart of Differences between Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes
Prokaryotes | Eukaryotes
No membrane bound organelles | MBO
No nucleus (Nucleoid) | Nucleus
Single celled | Single-or-Multi-cellular
Bacteria+Archaea | Eukarya
Asexual Reproduction | Asexual & Sexual Reproduction
Similarities between Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes
Contain genetic material; can be single celled; belong in Domains, kingdoms, etc.; have RIBOSOMES; reproduce
Cells and Macromolecules
Macromolecules literally mean big molecules, and they refer to the (who knew) big molecules in cells, which are Proteins, Carbohydrates, Lipids, & Nucleic Acids
Cell Structure and Function
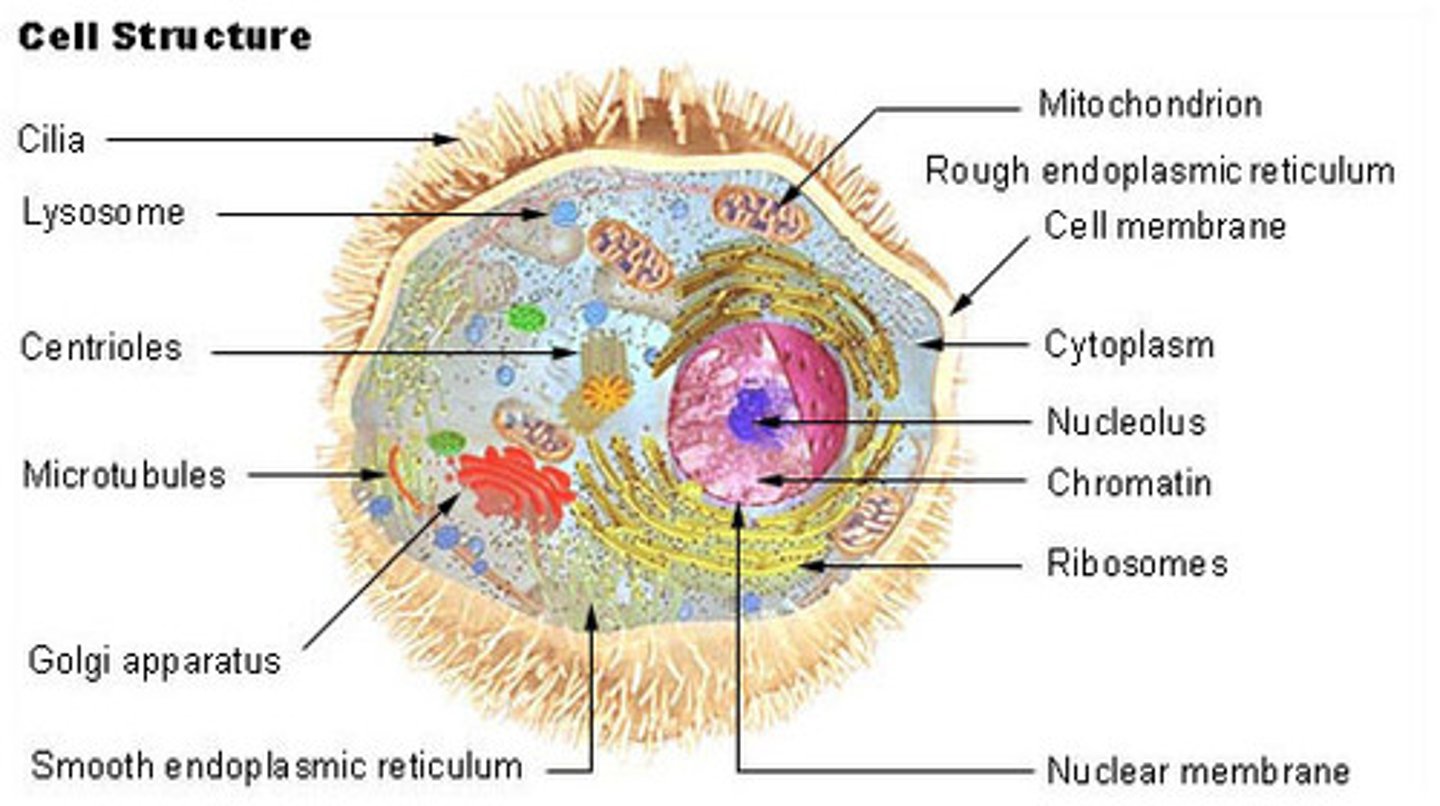
Cell Theory
All cells originate from other cells; the basic unit of life is the cell
Cell
A microscopic blob of stuff that carries out functions necessary for life to be lived (digestion, breathing, and EVERYTHING ELSE YOU COULD POSSIBLY IMAGINE (maybe))
Cell Membrane
Contains the innards of the cell and allows stuff to enter and exit the cell
Nucleus
Contains the DNA; brain of cell
Cytoplasm
Jello-like substance in the cell
Mitochondria
Power-house of cell; generate the cell's ATP, which is the major energy source of the cell
Golgi Apparatus
Sorts and ships proteins from the ER
Nucleolus
Begins assembly of ribosomes
Ribosomes
Assembles amino acids into proteins
Lysosomes
Digests food particles
Central Vacuole
Stores excess water; gives plants their shape; only in plant cell
Cell Wall
Protects cell (in plant cells)
Chloroplasts
Does photosynthesis in cell
Smooth ER
Breaks down toxins and makes lipids; located close to the membrane
Rough ER
Transports proteins
Vesicle
Transport pod for ribosomes, lipids, etc.
Cilia
Hair-like projections on ciliates that allow the ciliate to move
Flagella
Tail thing on flagellates that spin around to allow the flagellate to move
Nucleoid
In prokaryotic cells; contains genetic material; it is different from a nucleus (eukaryotic cell) because it doesn't have a nuclear membrane
Prokaryote
No membrane bound organelles, No nucleus; single-celled; contains neucleoids; contains ribosomes; some have flagella; Contains cell wall; NOT A CELL PART
Eukaryote
Membrane bound organelles; nucleus; can be either single and multi cellular; has ribosomes; protists, fungi, plants, & animals; NOT A CELL PART
Evolution
Change over a LONG period of time
Natural Selection
Nature selects the which of two+ species is more likely to survive
Speciation
The making of a new species
Species
A group of similar organisms that can produce VERITABLE OFFSPRING
Mechanisms of Change
Mutation, Migration, Natural Selection, Artificial Selection
Genetic Variation
Variation of DNA
Mutation
A sudden & random change in the genetic makeup of an organism; if the mutation is beneficial, the organism will survive and reproduce; may create a new species
Migration
When a species goes from one region to another region, often to escape unfavorable conditions in the first region's environment or to complete a certain step in their reproductive cycle.
Artificial Selection
Mankind selects which of two+ species gets to survive and reproduce; examples of its effects: dogs, cats, dogs, dogs, and dogs. Ooh, and dogs too. Did I mention dogs? I don't think I mentioned dogs. Don't forget dogs. NEVER forget dogs. Dogs are superior in EVERY way.
Darwin
Discovered (NOT invented) evolution on the galapagos islands
Adaptation
The process by which a species adjusts to its environment; usually occurs after a migration
Homologous Structures
Same structure, different function (homo-same, logous-correspondence or relation (i.e. related structures)); derived for common ancestor
Analogous Structures
Different structure, same function
Common Ancestor
A group of species share common descent if they have a common ancestor; they are kind of like the great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-great-grandparent of different species (or something)
Peppered Moth Simulation
2 moths one black one white, hide and blend in with the trees, when trees black, black moth survive, trees turn white (because of humans) white moth survives. May be artificial selection because human caused the change in trees, but could also be natural because humans didn't specifically breed the moths, nature selected it based on our human impact
Classification
From Domain to Species (DKPCOFGS)
Darling King Phillip Came Over For Good Spaghetti
Dumb Kids Play Chase On Freeway Get Splat.
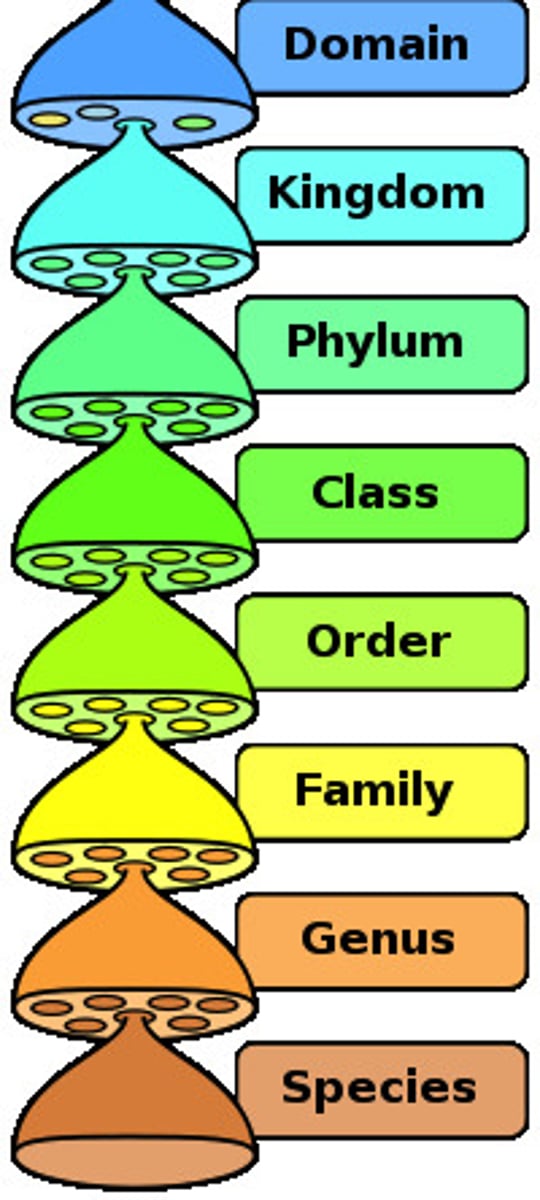
Domain
Right now, you are being as general as you possibly can under terms of classification
~ Bacteria
Prokaryotic; made up of kingdom Eubacteria; Use binary fission; shapes: bacilli, cocci, & spirilla
~ Archaea
Prokaryotic; Extremophiles; Oldest lifeforms on earth; made up by kingdom archaebacteria
~ Eukarya
Eukaryotic; Made up of kingdoms Animalia, Protista, Plantae, & Fungi
Kingdom
2nd most general; 7th most specific
~ Archaebacteria
Prokaryotic; under domain Archaea
Extremophiles: Live in harsh environments
3 types: Heat lover, salt lover, and methane maker
~ Eubacteria
Prokaryotic; AKA "True bacteria"; Can be heterotrophs or autotrophs; under domain Bacteria
~ Protista
Eukaryotic; Get energy via photosynthesis and/or consumption; mostly unicellular except for algae; under domain Eukarya
~ Fungi
Eukaryotic; Get energy via decomposition, mutualism, and/or parasitism; reproduce with spores; heterotrophs (unless the fungi is using mutualism or parasitism); multicellular EXCEPT FOR YEASTS; under domain Eukarya
~ Plantae
Eukaryotic; Get energy via photosynthesis; multicellular; autotrophs; under domain Eukarya
~ Animalia
Eukaryotic; Get energy via consumption; multicellular; heterotrophs; under domain Eukarya
Phylum
3rd most general; 6th most specific
Class
4th most general; 5th most specific
Order
5th most general; 4th most specific
Family
6th most general; 3rd most specific
Genus
7th most general; 2nd most specific; ALWAYS capitalized and ALWAYS italicized (or underlined when writing instead of typing)
Species (Classification)
You are now as specific as you can be under terms of classification; NEVER capitalized and ALWAYS italicized (or underlined when writing instead of typing)
Scientific Name
A given name for an organism that you can refer to with scientists around the world
Binomial Nomenclature
A system of nomenclature in which two terms, the genus name and the species name, are used to classify a species of living organism.
How is life categorized or classified?
Taxonomy (a taxon is any of the taxonomic categories, which are Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Family, Genus, & Species)
Bacteria and Archaea
Prokaryotic; Oldest life-forms on Earth (starting with Archaea)
Eubacteria Characteristics
AKA "True bacteria"; Prokaryotic; Can be heterotrophs or autotrophs; under domain Bacteria
Archaebacteria Characteristics
Extremophiles: Live in harsh environments
3 types: Heat lover, salt lover, and methane maker
Prokaryotic; under domain Archaea; oldest living things on Earth
Cocci
Circular shaped bacteria, can absorb the most liquids for a longer time
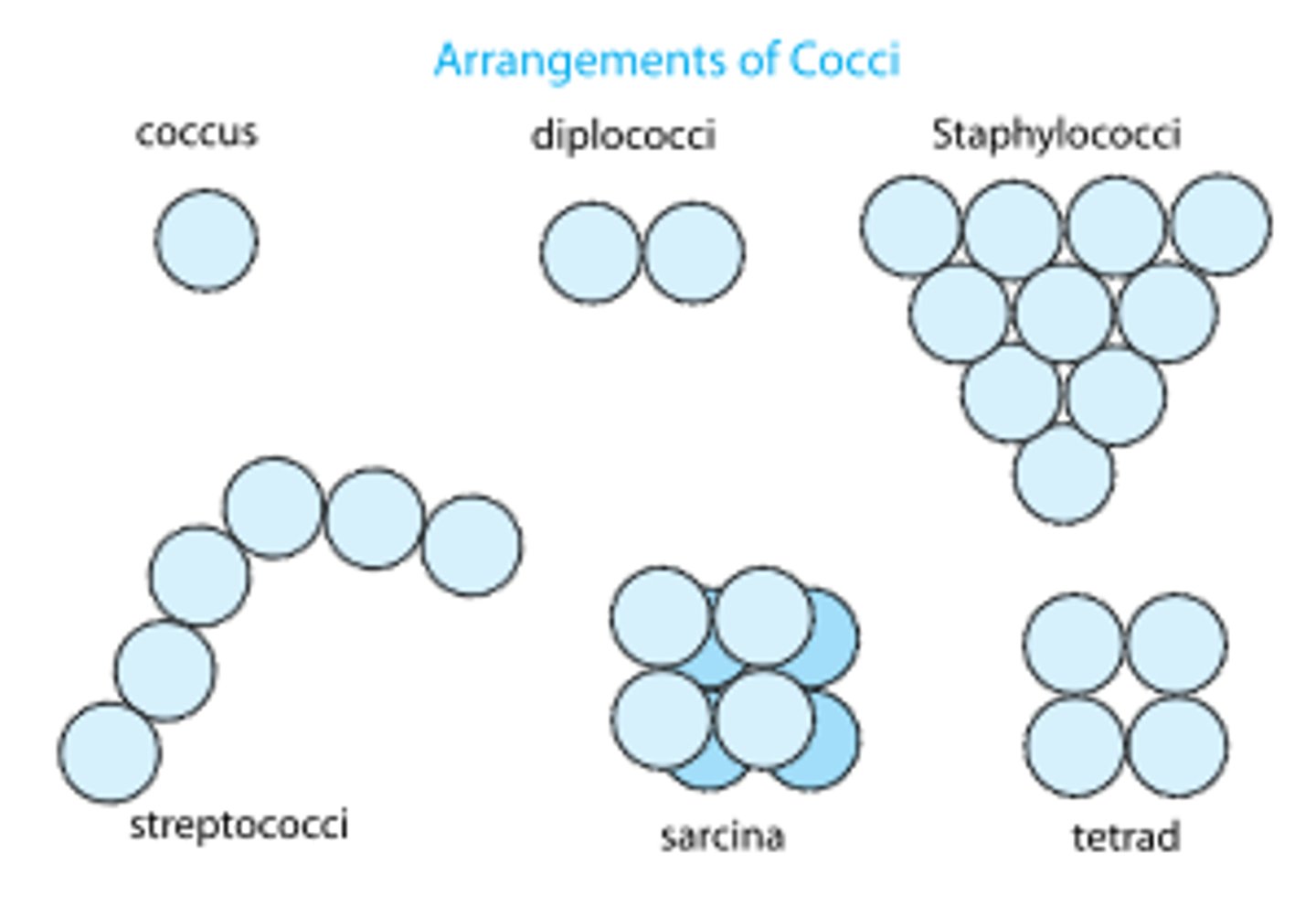
Bacilli
Fat long rod shapes that have the largest surface area but dry out very easily
Spirilla
Twirly rods that move the fastest of the three
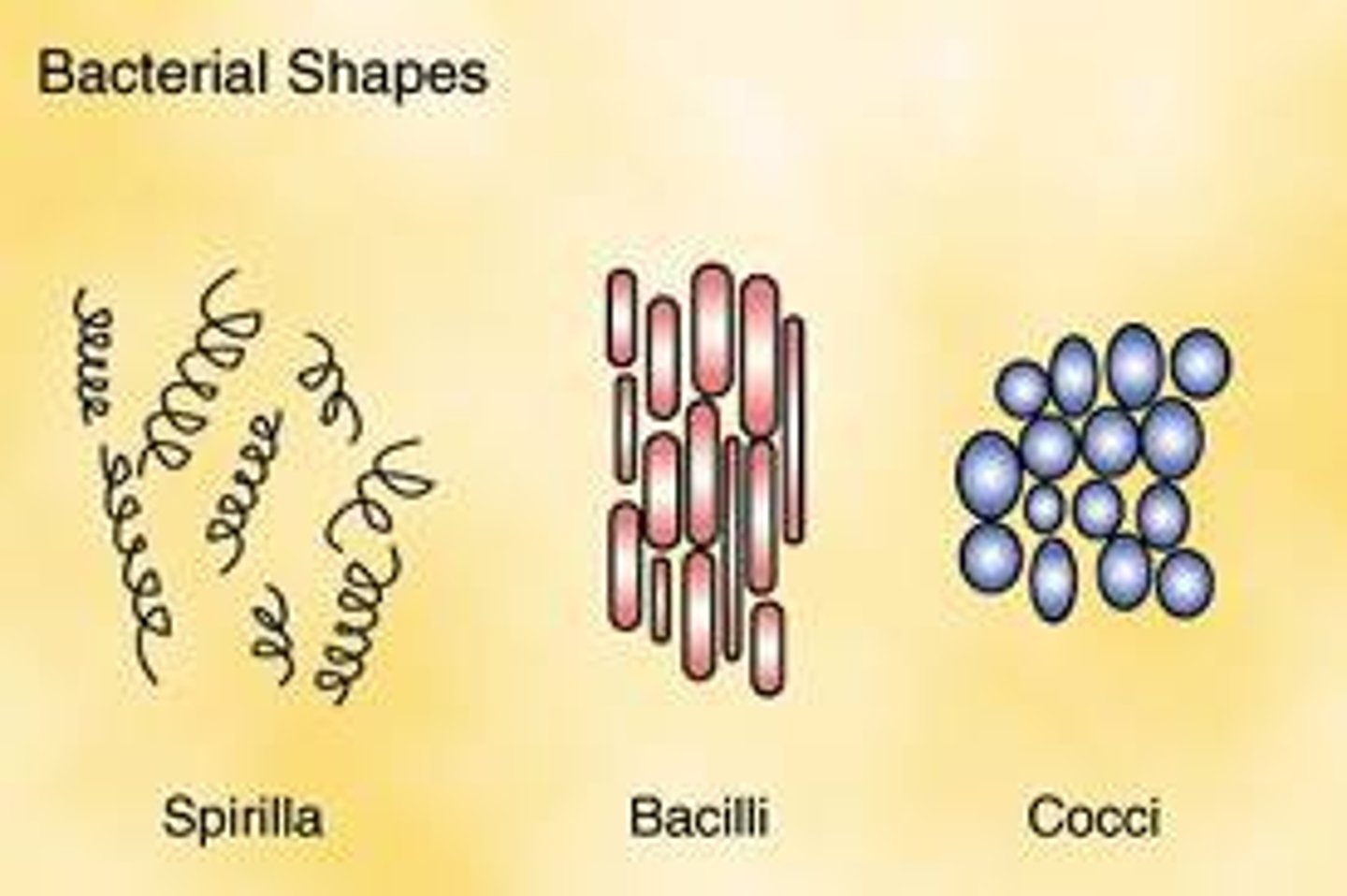
Advantages each shape give the bacteria
Cocci: Can absorb the most liquids & for a longer time
Bacilli: Largest surface area
Spirilla: Greatest speed
Binary Fission
1. Cell grows
2. DNA replicates itself
3. Cell elongates
4. Cell splits into two
Endospore
A shell created by the bacteria itself when outside conditions become unfavorable that allows the bacteria to be dormant until conditions are right
Bacteria's role in the environment
Nitrogen-fixing, recycling, & cleaning up
Nitrogen Fixation
Converting nitrogen into a form plants and animals can use. N2 to NH3 (ammonia)
Bioremediation
Changing of toxic materials to non-toxic. Also cleansing, such as an oil spill
Decomposers/Recyclers
Help decompose dead organic matter, and recycle them back into nature
Bacteria's role in food & medicine
In food they are amble to make cheese, bread, sourdough. For people with diabetes, E. coli bacteria help produce insulin.
Harmful bacteria
Pathogenic bacteria cause diseases
Viruses
Microscopic particles that invade and often destroy cells
Shapes + What disease each shape can cause
1. Crystal: Polio virus 2. Sphere: Influenza 3. Cylinder: Mosaic virus 4. Bacteriophage T4: Only attack bacteria