Epidemiology Midterm (Weeks 1, 2, & 3)
1/363
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
364 Terms
Observational studies
Define the type of studies:
- One or more groups are observed.
- Characteristics about the observed are recorded described and analyzed.
Experimental/Intervention Studies
Define the type of studies:
- Investigator controlled intervention/exposure allocation such as treatment, procedure or drug therapy.
- Investigator analyzes effect of intervention/exposure on the study outcome.
Descriptive
Analytical
What are the 2 types of observational studies?
Descriptive studies
Define the type of studies:
Investigator observes the patterns of the exposure and the other variables in the study.
Descriptive
Are case studies/case reports considered descriptive or analytical observational study designs?
Descriptive
Are case series considered descriptive or analytical observational study designs?
Descriptive
Are cross-sectional studies (without comparison) considered descriptive or analytical observational study designs?
Analytical
Are case-control studies considered descriptive or analytical observational study designs?
Analytical
Are cohort studies considered descriptive or analytical observational study designs?
Analytical
Are cross-sectional (with comparison) considered descriptive or analytical observational study designs?
True
T/F: Cross-sectional studies can be descriptive as well as analytical
Descriptive studies
What type of study has the following characteristics?
- Helpful in observing trends or patterns for the main variables of interest as well as in relation to covariates.
- Helpful in generating research hypotheses for larger studies.
- Investigator observes and collects information on the variables of interest in the study.
- Investigator does not change any of the study aspects.
Descriptive studies
What type of study has the following characteristics?
- Typically used to describe and characterize who? (exposure group), where? (population source or location), and when? (time period) in relation to the what (outcome)
- Used to measure the relationship between exposure and outcome
- Direction of relationship cannot be determined
Experimental/interventional studies
What type of study has the following characteristics?
1. Controlled trials (parallel controls or self-controlled)
- Trials that include an experimental group and a control or comparison group
- Examples:
- - Randomized versus non-randomized
- - Design variations - Cross-over, split mouth
2. Trials with no controls or external controls
Human subjects
In-vitro experiments
Animal studies
What are 3 types of subjects in study designs?
1. Systemic reviews and meta-analyses
2. Randomized controlled trials
3. Cohort studies
4. Case-control studies
5. Cross-sectional studies
6. Case reports/series
7. Expert opinion
8. Anecdote
What is the hierarchy of evidence? (8) from most valid → least
Exposure
Define the following:
- Characteristic of the individual (age, gender, weight) or a variable related to environment (air pollution), lifestyle (smoking, exercise), social status (poverty or income level) or participant's background (education level, race/ethnicity).
- AKA a 'risk factor'.
Outcome
Define the following:
- Term representing the result or effect of interest in the study.
- Ex: Presence of disease, health status, success of treatment.
- Some studies may have multiple outcomes and multiple exposures.
Cases
Define the following:
- Main group of interest in a study
- In observational studies referred to as ___________
- In experimental studies referred to as treatment or intervention group
Controls
Define the following:
- Comparison group
- Sometimes referred to as non-cases.
- In experimental studies this is referred to as non-treatment or ____________ group.
Case study
What type of study has the following characteristics?
- Characteristics of a patient is recorded and published in a report (ex: case reports)
- No control is used
- Usually short duration of study
- Precursor to future studies (hypothesis generating)
B. Present
Which of the following time frames do case studies take part in?
A. Past
B. Present
C. Future
Case-series
What type of study has the following characteristics?
- Characteristics of a series of patients are recorded and published in a report (ex: case reports)
- Looking at same condition or treatment in a series of patients
- To observe trends or patterns
- No controls used (rarely comparison set of patients included)
- Short duration of study
- Precursor to larger studies (hypothesis generating)
Easy to conduct
Short duration
Inexpensive
Useful for generating hypotheses for larger studies
4 advantages of case report + series
We cannot evaluate associations
Generalizability is an issue
2 disadvantages of case report + series
B. Present
Which of the following time frames do case series take part in?
A. Past
B. Present
C. Future
Descriptive cross-sectional study
What type of study has the following characteristics?
- Useful in describing the characteristics of a population at one point in time (a slice of time to see what is happening).
- Useful in describing the characteristics such as knowledge, attitude and practices in the population.
Cross-sectional study
In this sample say you want to evaluate the prevalence of children wearing eye-glasses. Then you add up the number of kids wearing glasses and divide by the total. In this case it would be 4/6 = 60%. What type of study is this?
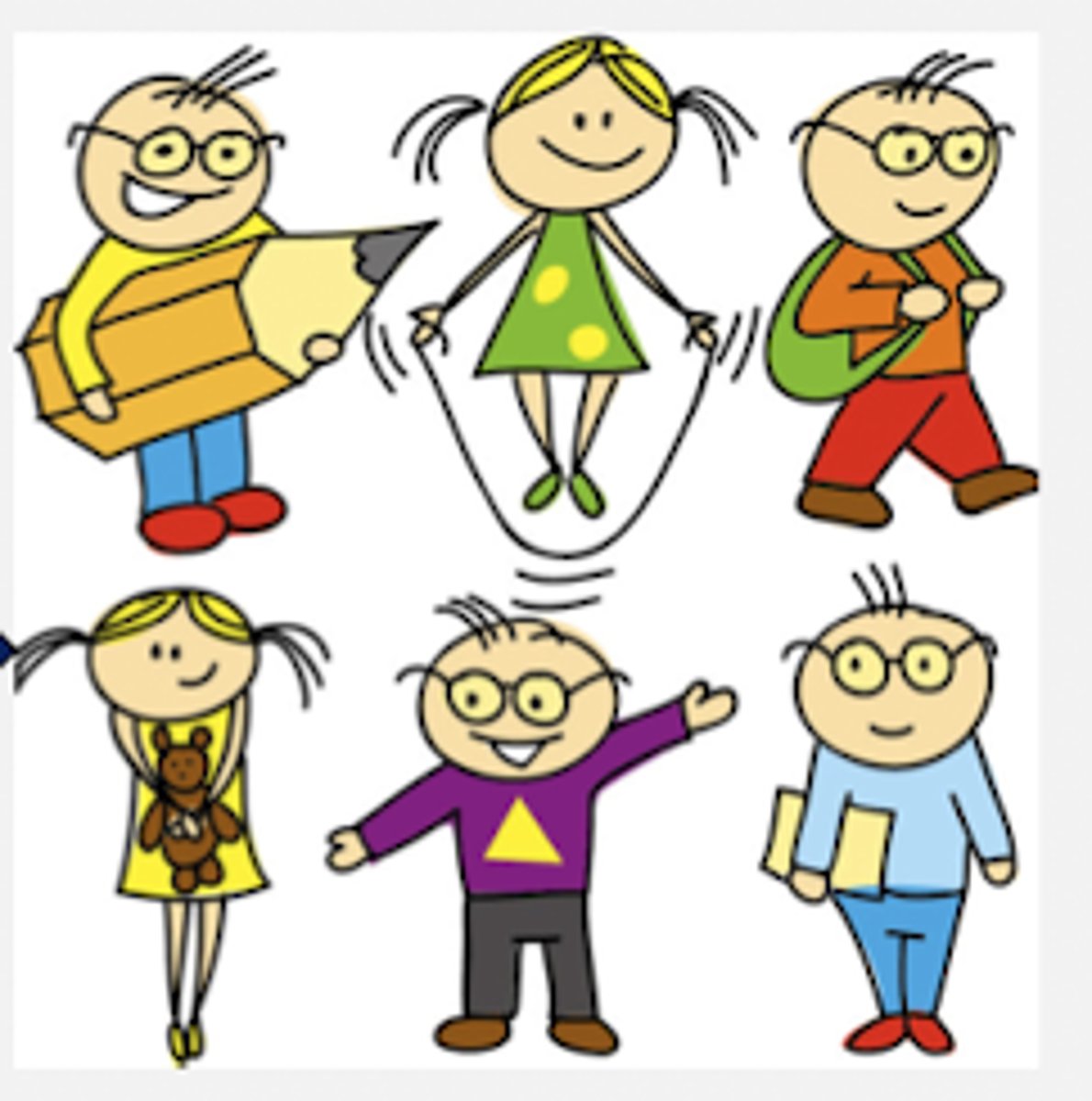

Cross-sectional study
What type of study does this image show?
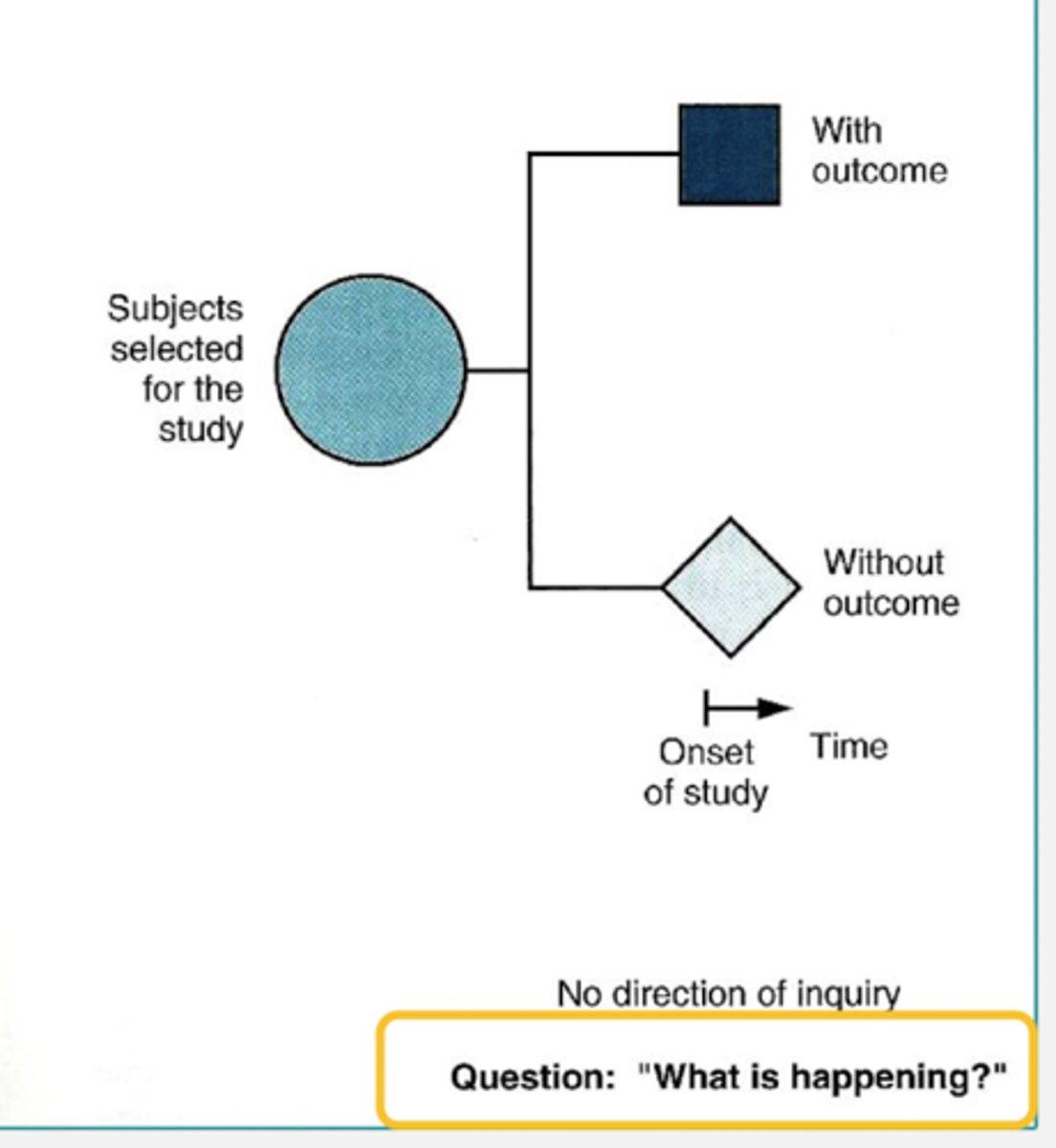
Descriptive cross-sectional study
What type of study has the following characteristics?
- Sometimes referred to as prevalence studies as they can be used to examine prevalence of a disease or condition Ex: Surveys, Epidemiologic studies
- Can be short or long duration.
- Can be precursor to cohort and case-control studies.
True
T/F: You can use cross-sectional study design to study...
- Incidence patterns or mortality rates over a period of time.
- Make comparisons by race/ethnicity or time period.
- Estimate overall incidence rates and adjusted rates
Convenient
Less time consuming
Large samples
Can be done with limited resources
4 advantages of descriptive cross-sectional studies
Cannot evaluate causal associations as we cannot determine direction of association.
Participation bias in studies that use surveys and interviews.
Interview or reporting bias can also occur.
Investigation conducted at a slice of time --> this may not be representative of the full picture
4 disadvantages of descriptive cross-sectional studies
B. Present (fixed slice of time)
Which of the following time frames do descriptive cross-sectional studies take part in?
A. Past
B. Present
C. Future
Analytical
What type of study has the following characteristics?
- Analytical studies test the research hypothesis about the exposure-outcome relationship that is under investigation.
- We can measure the association between the exposure and outcome.
- We can evaluate the magnitude of the association between exposure and outcome.
- Ex: Does smoking status (never, past and current) have an effect on periodontal disease status (yes/no)
Analytical
Cross sectional, case control and cohort studies are all examples of what type of study?
Analytical cross-sectional study
What type of study has the following characteristics?
- Association between exposure and outcome at one point in time is evaluated.
- Magnitude of relationship estimated but not direction
Descriptive
Descriptive or analytical cross-sectional study?
- Overall disease burden can be described in large populations.
Descriptive
Descriptive or analytical cross-sectional study?
- Disease patterns can be described with this design.
Descriptive
Descriptive or analytical cross-sectional study?
- Can be utilized to generate research question or hypothesis for future studies.
Analytical
Descriptive or analytical cross-sectional study?
- In addition to describing disease burden, disease patterns and trends, relationship between exposure and outcome can be analyzed.
Analytical
Descriptive or analytical cross-sectional study?
- Research hypothesis/research question can be evaluated statistically
Analytical
Descriptive or analytical cross-sectional study?
- Odds ratios for the relationship between exposure and outcome can be estimated
Easy to conduct.
Commonly used to describe burden of disease, disease trends, behavioral patterns etc.
Correlation between variables can be determined and cross-sectional relationships can be analyzed.
3 advantages of analytical cross-sectional studies
Requires a large sample size.
Requires time, money and resources.
Cannot establish causal association.
Cannot establish time sequence or temporality.
4 disadvantages of analytical cross-sectional studies
Case-control study
What type of study has the following characteristics?
- Compares diseased individuals to non-diseased individuals - in relation to exposure status
- Cases - have the outcome of interest
- Controls or non-cases - do not have the outcome
- Retrospective in nature
- Start in present time and go back in time to evaluate risk factor exposure
- Analyze factors/exposures related to outcome in cases and controls
- We measure the odds of disease among exposed versus odds of exposure among those with disease versus those without disease
Case-control study
What type of study has the following characteristics?
- At the start of the study, the disease or outcome has already occurred, and cases and controls are grouped based on the outcome/disease status.
- Exposure variables of interest are identified among cases and controls.
- Information on contributing factors and exposure(s) is obtained retrospectively (review of medical/dental charts, interviews or surveys).
Cases
In a case control study, will the cases or the controls have the outcome of interest?
- Controls can be selected from the same community, location or hospital.
- Similar characteristics as cases except for disease status
- Evaluate exposure information in controls in the same manner as cases
What is some of the criteria for selecting controls in a case-control study?
Case-control study
What type of study does this image show?
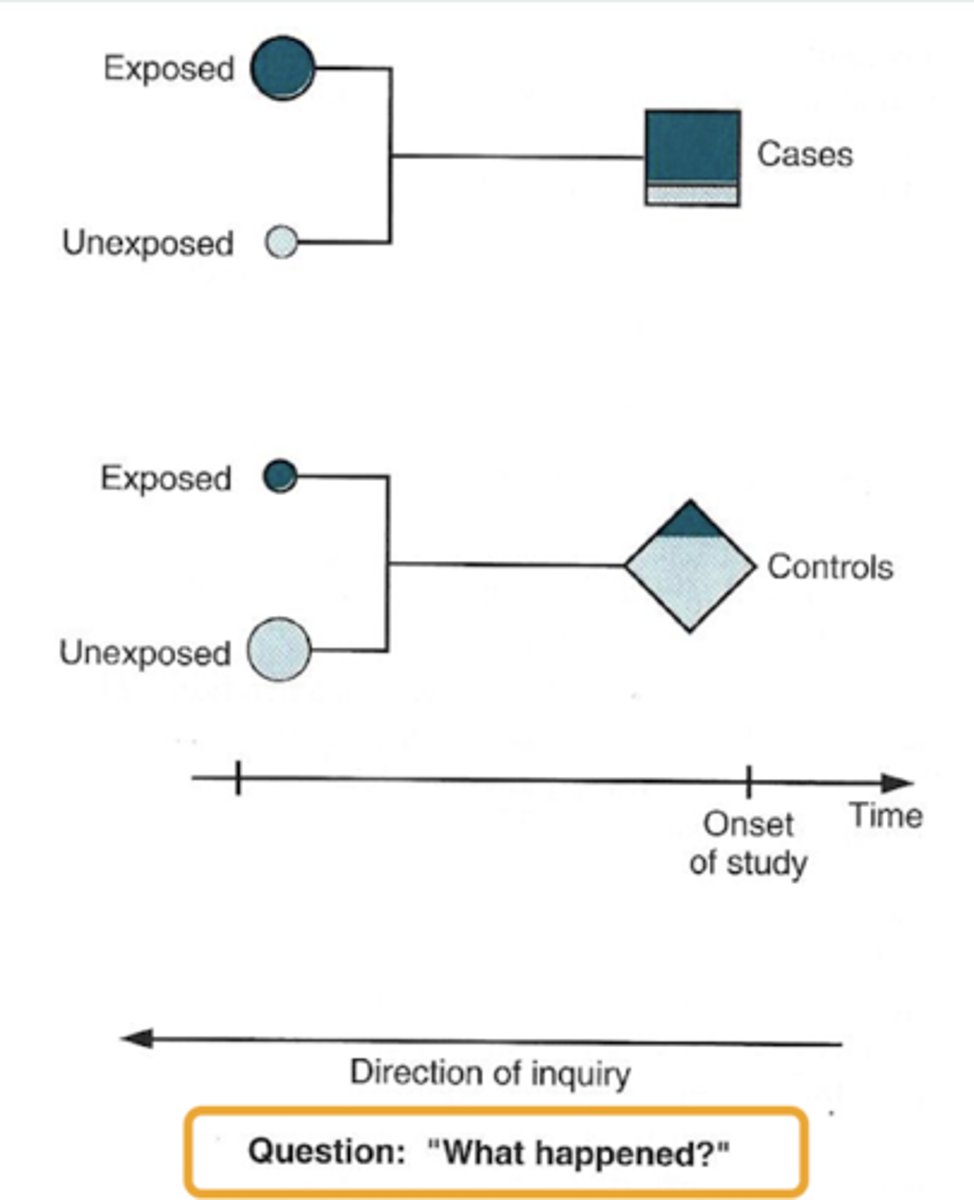
Case-control study
In this sample say you want evaluate the variables that may have contributed to children wearing eye-glasses. So we can compare the children with eye-glasses to children not wearing eye-glasses. We can retrospectively collect information like family history, medical history, tv-watching, etc. We can then evaluate the odds of these possible risk factors to the outcome of children wearing eye-glasses (outcome could be astigmatism, myopia). What type of study is this describing?
Present and past (retrospective)
Which of the following time frames do case-control studies take part in?
A. Past
B. Present
C. Future
Odds ratios
Association between exposure-outcome can be evaluated by estimating ____________
Odds ratios
____________ are estimated based on the probability of disease among exposed individuals relative to the probability of disease among unexposed individuals.
Efficient in design
Shorter duration
Less expensive
Convenient for studying many exposures
Efficient for rare diseases and for diseases with long latency period
Measures of association can be calculated to evaluate exposure-outcome relationship (Odds ratio)
6 advantages of case-control studies
Retrospective nature of the study
Difficult to establish time sequence of the exposure-outcome relationship
Retrospective nature of the design leads to potential biases
3 disadvantages of case-control studies
Recall bias
Define the following:
Cases recall information differently when compared to controls
Recall bias (Cases remember and report their previous exposure experience differently from controls)
What is the most common type of bias in case-control studies?
Recall bias
What type of bias is this?
Moms of children with orofacial clefts recall risks more accurately
True
T/F: Recall bias can occur in cross-sectional studies
Interviewer bias
Define the following:
Differences that occur in the recording or interpretation of information from participants
Interviewer bias
In cross-sectional, case-control and cohort studies, knowledge of a subject's disease status or exposure status may lead to increased questioning by the interviewer. This is known as _____________
Interviewer bias
What type of bias is this?
Those with periodontal disease are examined more frequently to evaluate oral health status versus those without
Interviewer bias
What type of bias is this?
Those who smoke are interviewed more to evaluate oral health status versus those who do not smoke
Reporting bias
What type of bias is this?
- Cross-sectional, Case-control and cohort studies: Under-reporting of socially undesirable behaviors (Smoking, drinking)
- Over-reporting (Exposure to chemicals, fluoride in water)
- Cases may refuse to answer sensitive questions (Substance abuse)
Case-control studies
Misclassification bias is most common in what type of studies?
Misclassification bias
What type of bias is this?
- Inaccurate case definitions or inclusion/exclusion criteria
- Participants are incorrectly 'assigned' or categorized into the wrong exposure or outcome group
- Can lead to diluted or exaggerated effects
Cross-sectional
Cross-sectional or case-control study?
Assessed at a point in time (slice of time)
Cross-sectional
Cross-sectional or case-control study?
Trends and relationships between exposure and outcome variables described and analyzed.
Cross-sectional
Cross-sectional or case-control study?
Temporality cannot be established.
Case-control
Cross-sectional or case-control study?
Assessed retrospectively.
Case-control
Cross-sectional or case-control study?
Association between exposure and outcome can be estimated.
Case-control
Cross-sectional or case-control study?
If information is available about exact time period of exposure and date of diagnosis it is possible to establish temporality.
Cohort study
What type of study has the following characteristics?
- Prospective or longitudinal studies.
1. Start with a group of people and identify an exposure.
2. Divide the cohort into exposed and unexposed groups (Smokers versus non-smokers).
3. Follow them over a period of time to observe the outcome (periodontal disease).
4. At the end of the study determine incidence of outcome among exposed versus unexposed.
Cohort
Define the following:
Any designated group of individuals
Cohort study
What type of study does this image show?
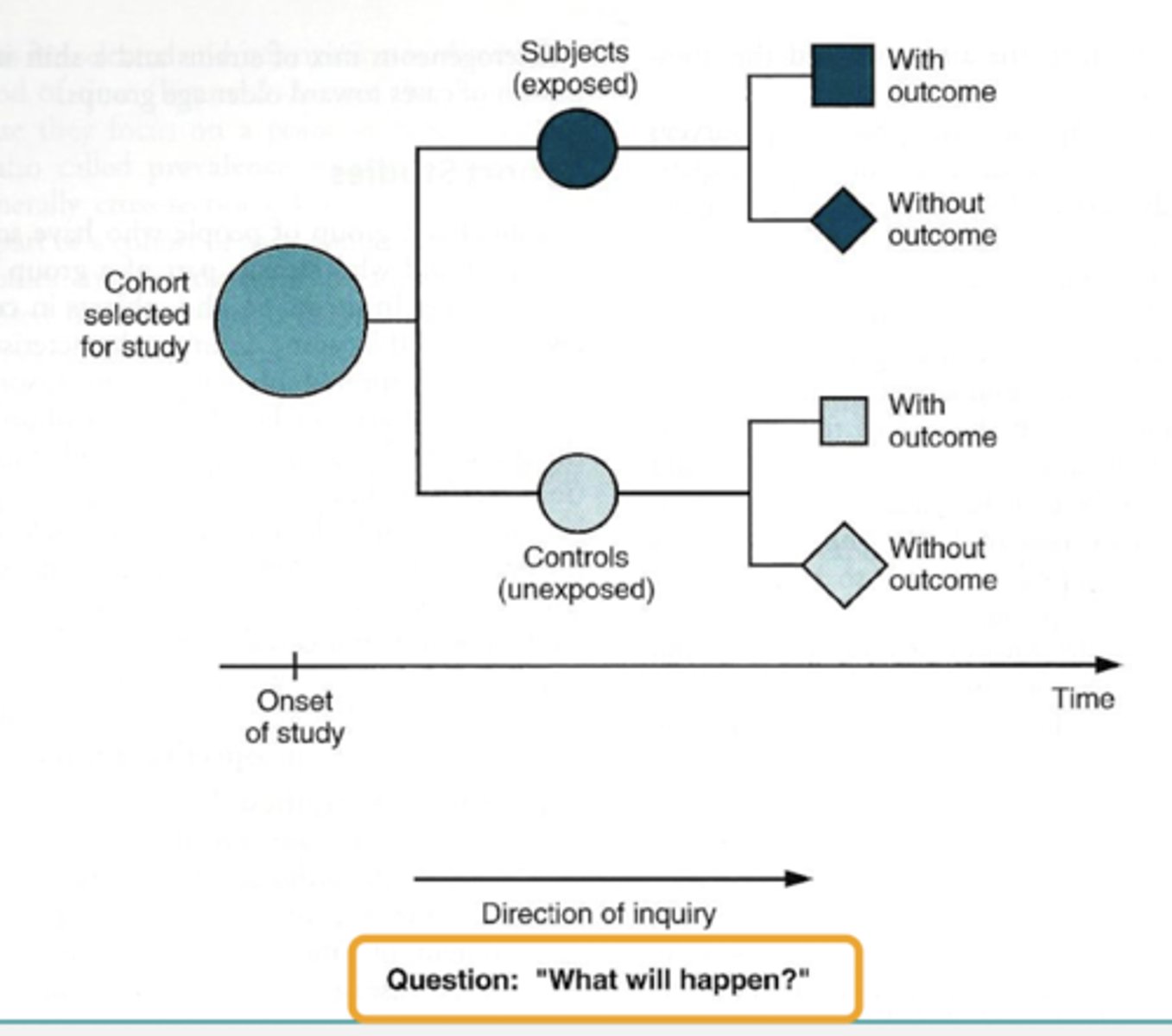
Cohort study
What type of study has the following characteristics?
- Compare disease rates among exposed vs. unexposed
- Record newly developed cases during follow-up
- Can calculate incidence (proportions) + incidence rates
- Due to prospective nature time sequence of events can be established
Present and future
Which of the following time frames do cohort studies take part in?
A. Past
B. Present
C. Future
In terms of efficiency most similar to randomized clinical trials
Can be more ethical in certain cases than clinical trials
Good for rare exposures
Agriculture pesticide and cancer
Can look at multiple outcomes due to single exposure
Can estimate incidence rates over time as we have time information
Can be used to establish temporality and causality
7 advantages of cohort studies
Not efficient for rare diseases
Long duration can cost time and money
Need additional resources
Exposure status may change over time (smoking or drinking patterns)
Prone to loss to follow-up bias
5 disadvantages of cohort studies
Case control
Case control or cohort study?
Participants are grouped by disease status
Case control
Case control or cohort study?
Utilizes less time and money
Case control
Case control or cohort study?
Can be used for rare diseases
Case control
Case control or cohort study?
Multiple exposures can be studied
Case control
Case control or cohort study?
Does not work well for rare exposures
Case control
Case control or cohort study?
Prone to recall bias/information bias
Cohort study
Case control or cohort study?
Participants are grouped by exposure status
Cohort study
Case control or cohort study?
Long duration of follow-up so utilizes more time and resources
Cohort study
Case control or cohort study?
Can be used for rare exposures
Cohort study
Case control or cohort study?
Multiple outcomes can be evaluated
Cohort study
Case control or cohort study?
May not work well for rare diseases
Cohort study
Case control or cohort study?
Prone to loss to follow-up bias due to dropouts
Systemic reviews and meta analysis
What is at the top of the hierarchy of evidence?
Anecdote
What is at the bottom of the hierarchy of evidence?
Systematic reviews
Define the following:
Seek to collate evidence that fits pre-specified eligibility criteria in order to answer a specific research question. They aim to minimize bias by using explicit, systematic methods documented in advance with a protocol.
Systematic reviews
What type of study has the following characteristics?
- A detailed review of published articles on a particular research question
- Search criteria, inclusion and exclusion criteria, and time period are defined clearly
- Multiple study design types can be included
- All types of analytical observational studies
- Summarize the evidence from the included studies
Efficient way to summarize information from different sources
Results can be more broadly generalized
Most reliable than individual studies as we are summarizing information from multiple studies
Quality of information highest (recall hierarchy of evidence pyramid)
4 advantages of systematic reviews
Laborious
Time consuming
May be difficult to combine information when methods and measures vary across studies
3 disadvantages of systematic reviews
Meta-analysis
Define the following:
Quantitative, formal epidemiological study design used to systematically assess previous research studies to derive conclusions about that body of research
Meta-analysis
What type of study has the following characteristics?
- Data from different studies are extracted, pooled and analyzed
- - Specific analytical methods are utilized
- - Specific software available to conduct the analysis
- The summarized data is used to make interpretations or causal inferences