Genetics Lec 44: Patterns of Inheritance and GeneticDisorders
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
22
how many pairs of autosomes do we have?
1
how many pairs of sex chromosome do we have?
dominant allele
the ________ determines the organism's phenotype
recessive allele
the ____________ has no noticeable effect on phenotype
alleles
The different forms of one gene
phenotype
outward appearance of an individual
genotype
genetic make up of an individual
Law of Segregation
The two alleles for a phenotype separate during gamete formation, and end up in different gametes:
Law of Dominance
Genes exist in pairs. In F1 hybrid, dominant allele determines the organism’s appearance(phenotype). The recessive allele is responsible for the recessive phenotype and masked by dominant allele in F1, which shows up in later generations.
Law of Independent Assortment
Genes at different locations in the genome (loci) are transmitted independently
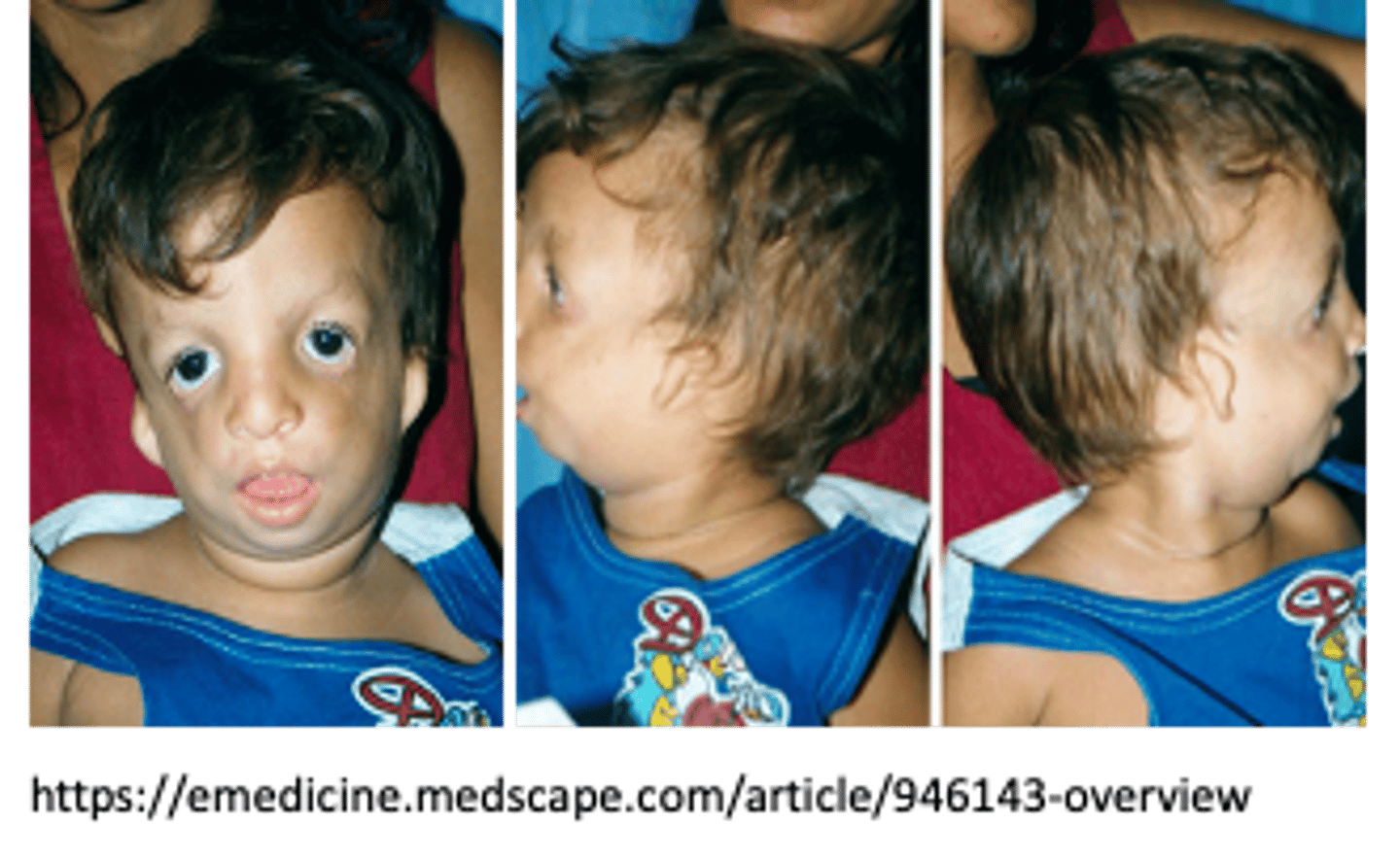
Treacher Collins syndrome
TCOF1 gene mutations, decreased amount of neural crest cells in the first & second pharyngeal arch, causing mandibulofacial dysostosis.
Ellis-van Creveld syndrome
•Mutations in the EVC or EVC2 gene
•Dwarfism, Polydactyly, Heart defect, Dental abnormalities
1/2
in autosomal dominant inheritance, if one parent is has one gene for a disease and mates with an unaffected mate, what is the probability that they will have an affected child?
3/4
in autosomal dominant inheritance, if one parent is has one gene for a disease and mates with another affected mate, what is the probability that they will have an affected child?
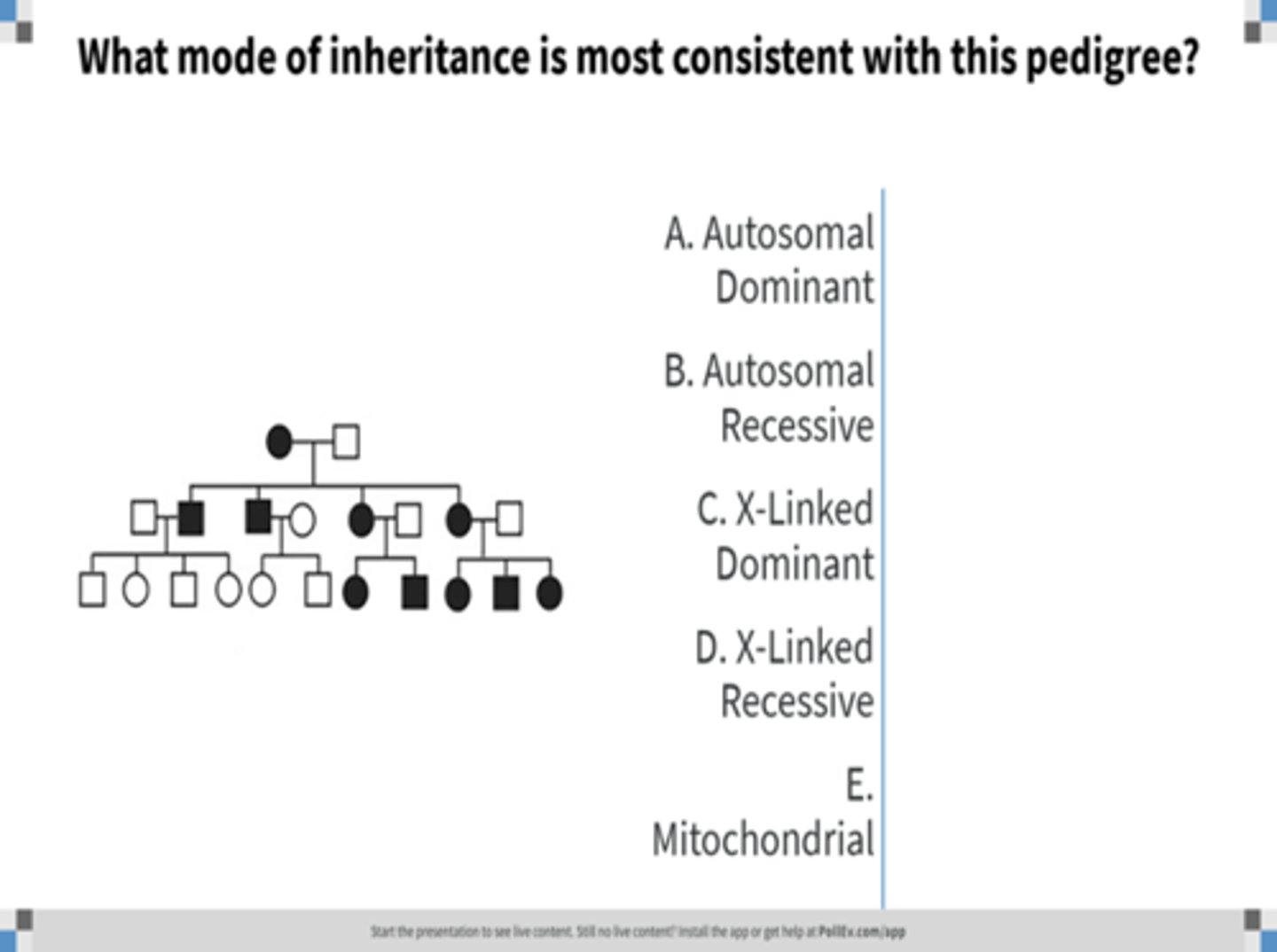
autosomal dominant inheritance
Identify the pattern of inheritance:
•Only one mutated gene copy is necessary for expression of trait
•Multiple generations are affected (vertical transmission)
•Males and females are equally likely to be affected
•Male to male transmission is observed
Unaffected individuals have unaffected children
autosomal dominant inheritance
Treacher Collins syndrome has what pattern of inheritance?
0
in autosomal recessive inheritance, if one parent is affected and mates with an unaffected mate, what is the probability that they will have an affected child?
1/2
in autosomal recessive inheritance, if one parent is affected and mates with a carrier mate, what is the probability that they will have an affected child?
1/4
in autosomal recessive inheritance, if one parent is a carrier and mates with another carrier mate, what is the probability that they will have an affected child?
1/1
in autosomal recessive inheritance, if both patents are affected, what is the probability that they will have an affected child?
autosomal dominant inheritance
Identify the pattern of inheritance:
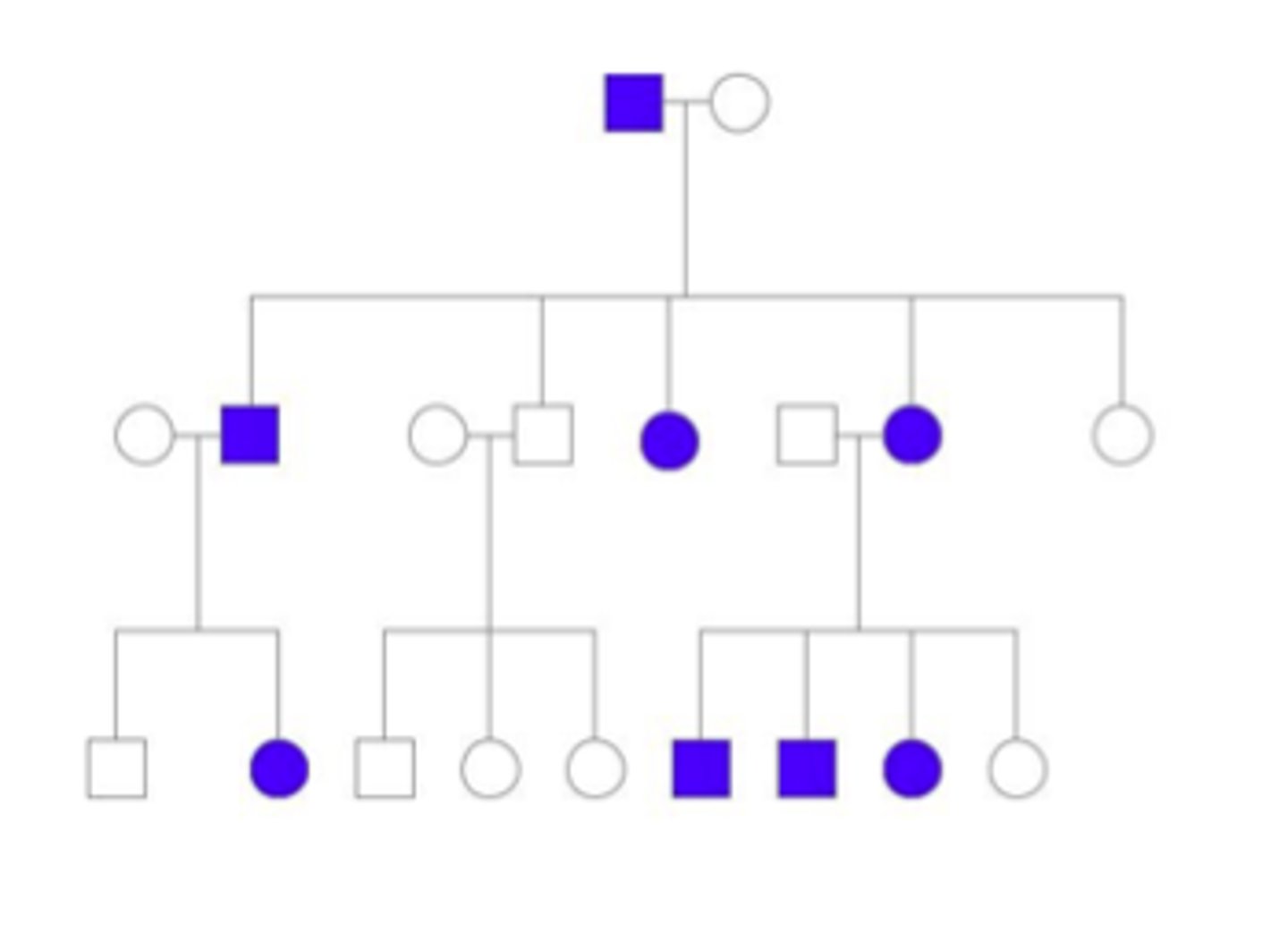
autosomal recessive inheritance
Identify the pattern of inheritance:
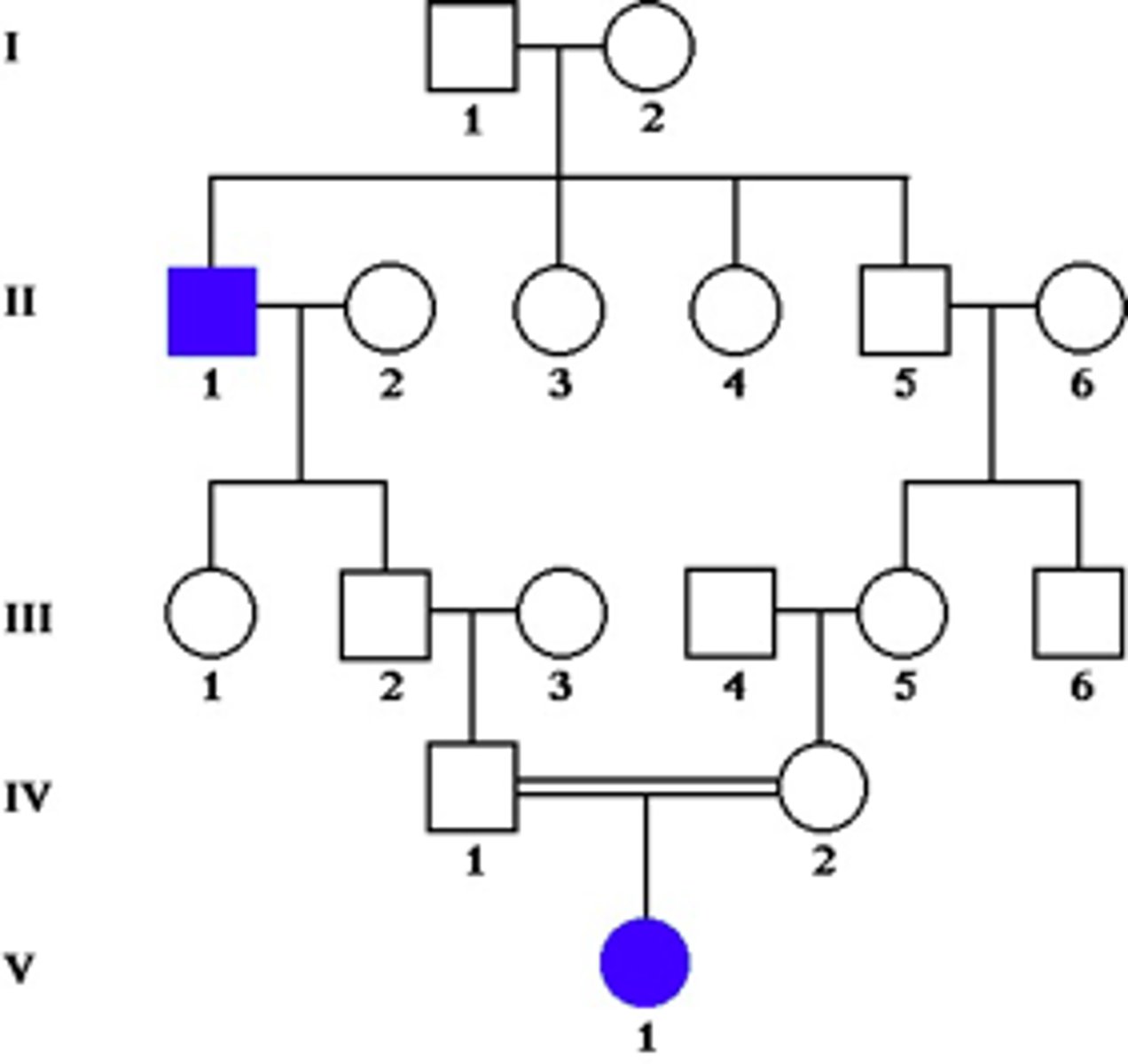
autosomal recessive inheritance
Ellis-van Creveld syndrome has what pattern of inheritance?
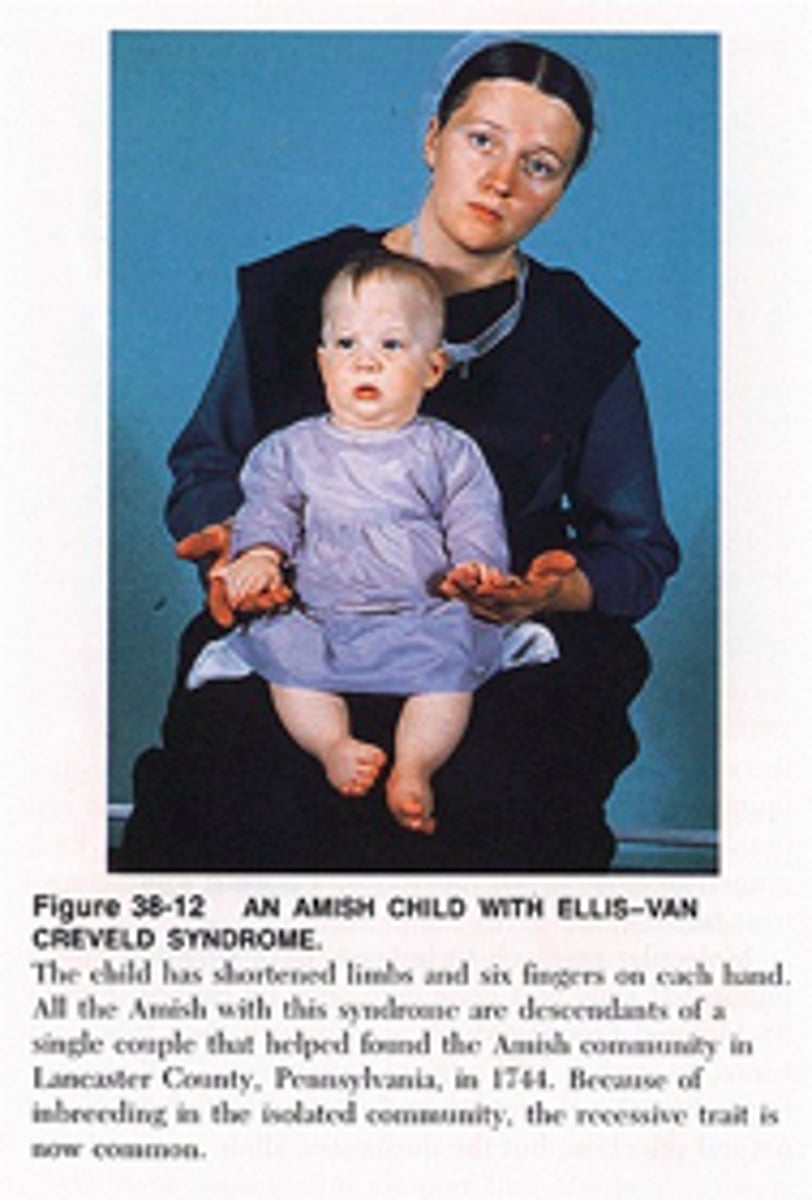
autosomal recessive inheritance
Identify the pattern of inheritance:
•Two mutated gene copies are necessary for expression of trait
•Usually only one generation is affected
•Parents are most often not affected
•Family history may be negative
•Males and females are equally likely to be affected
•Consanguinity may be present
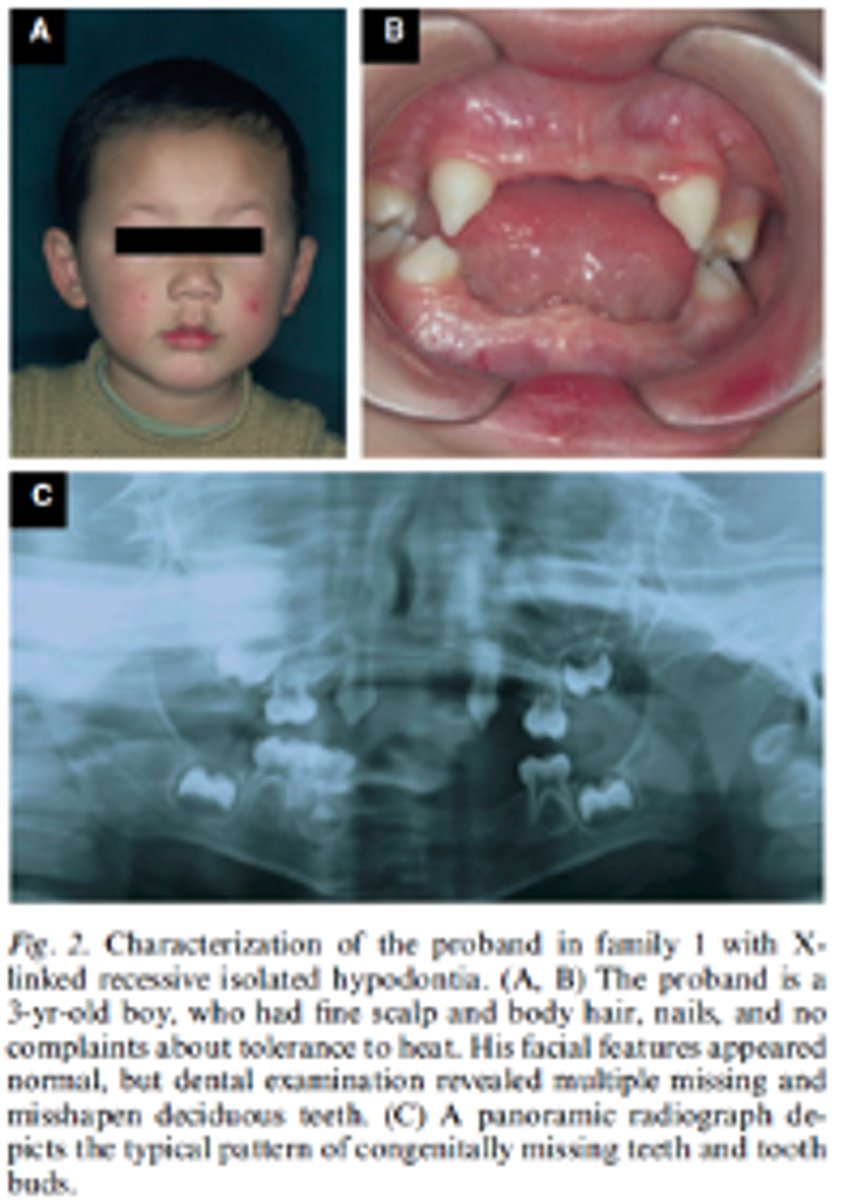
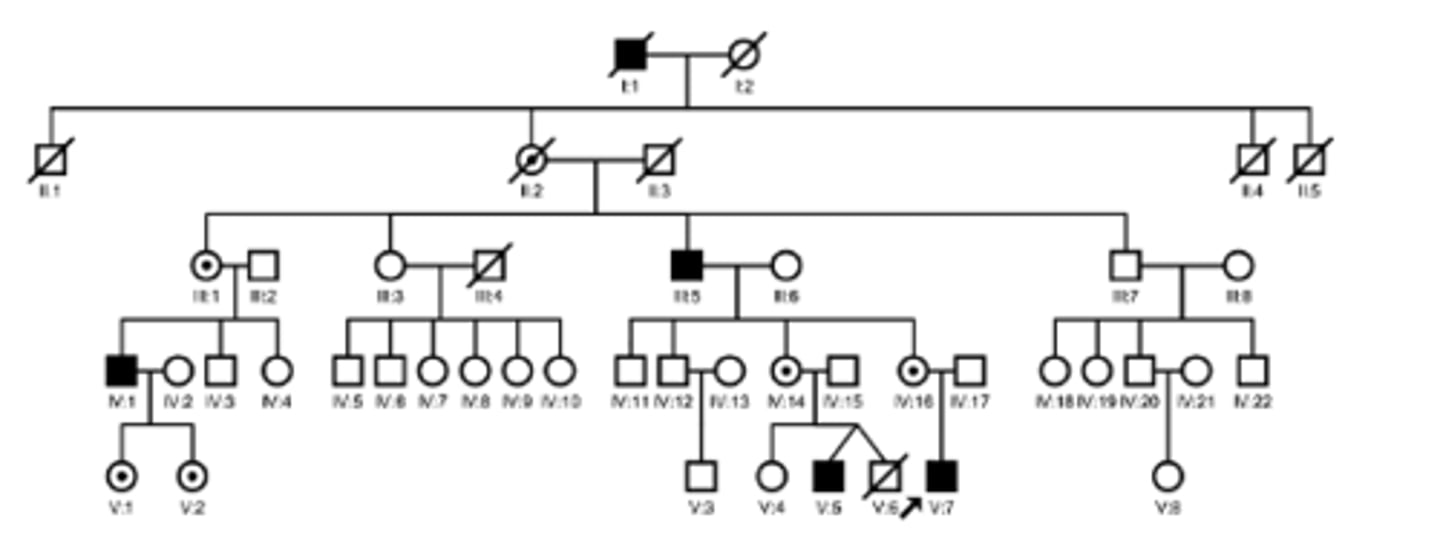
X-linked recessive inheritance
Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia and hypodontia has what pattern of inheritance?
X-linked recessive inheritance
Identify the pattern of inheritance:
Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia and hypodontia
caused by EDA gene mutations
•Symptoms:
reduced ability to sweat (hypohidrosis);
sparse scalp and body hair;
Missing teeth (hypodontia)
1/4 affected male ( 1/4 carrier female)
in X-linked recessive inheritance, if the mother is a carrier and the father is unaffected, what is the probability that they will have an affected child?
X-linked dominant inheritance
Amelogenesis Imperfecta has what pattern of inheritance?
X-linked dominant inheritance
Identify the pattern of inheritance:
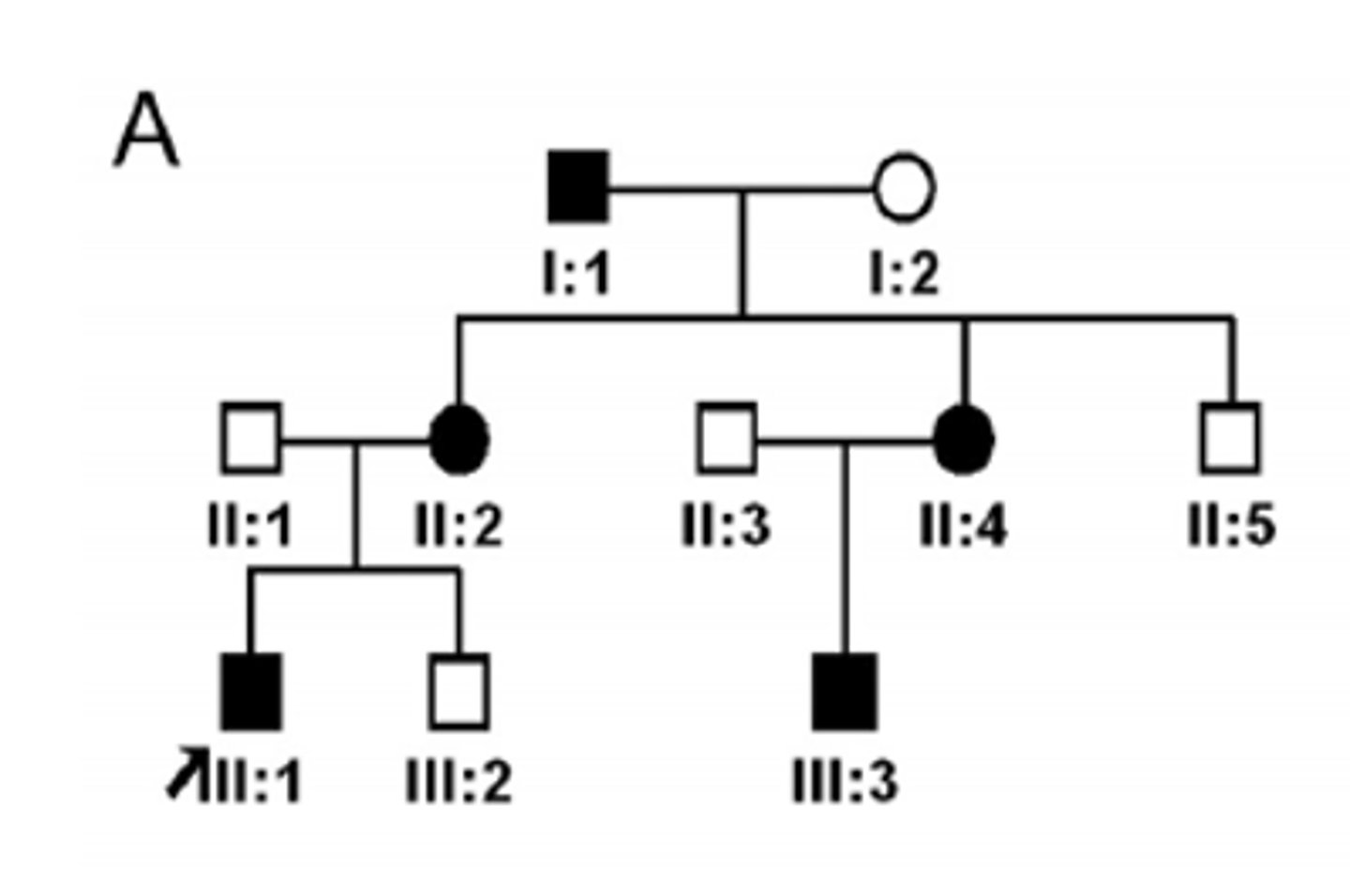
X-linked dominant inheritance
Identify the pattern of inheritance:
•All daughters of an affected male are affected
•Male to male transmission is not observed
•Much less common than X-linked recessive disorders
Mitochondrial inheritance
Identify the pattern of inheritance:
- Both males and females can be affected, but only females can transmit the disease to their offspring, all children affected, but man will never pass it to children
Mitochondrial inheritance
Identify the pattern of inheritance:
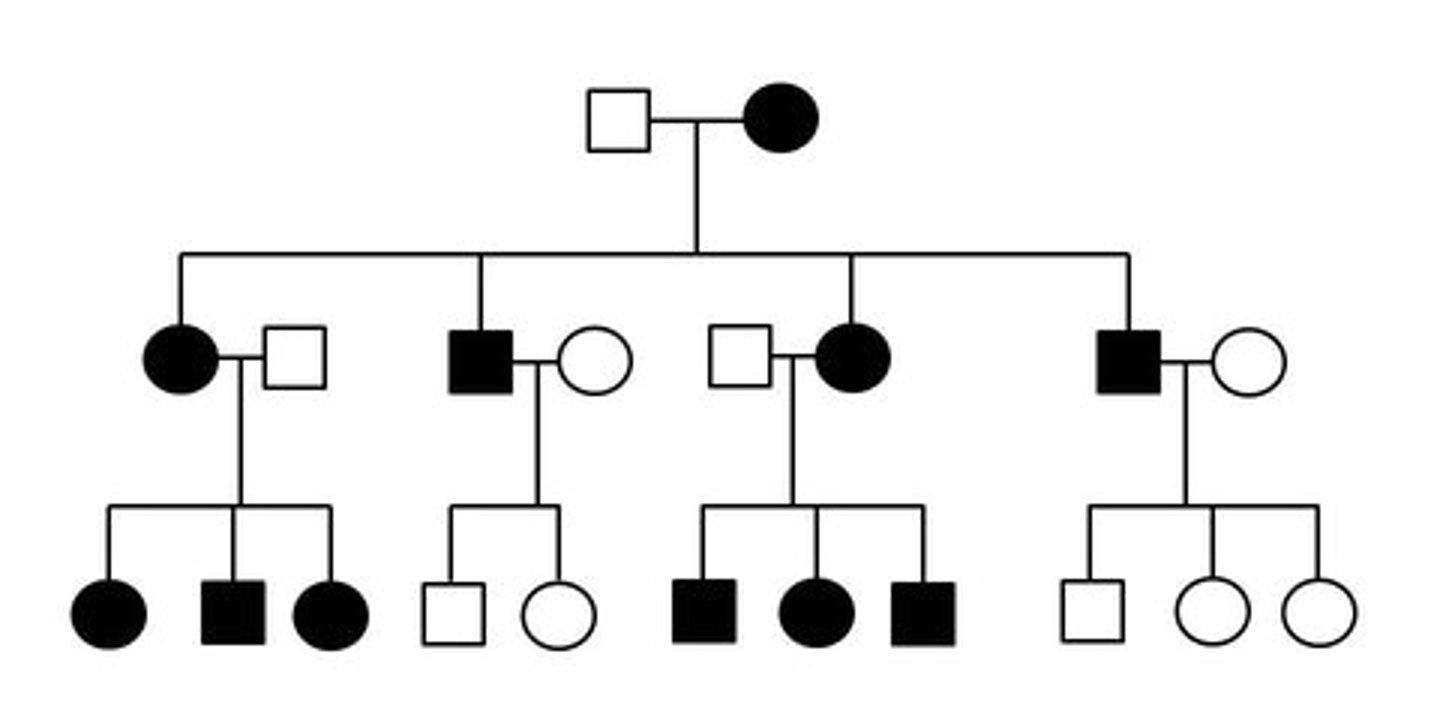
autosomal dominant inheritance
Identify the pattern of inheritance:
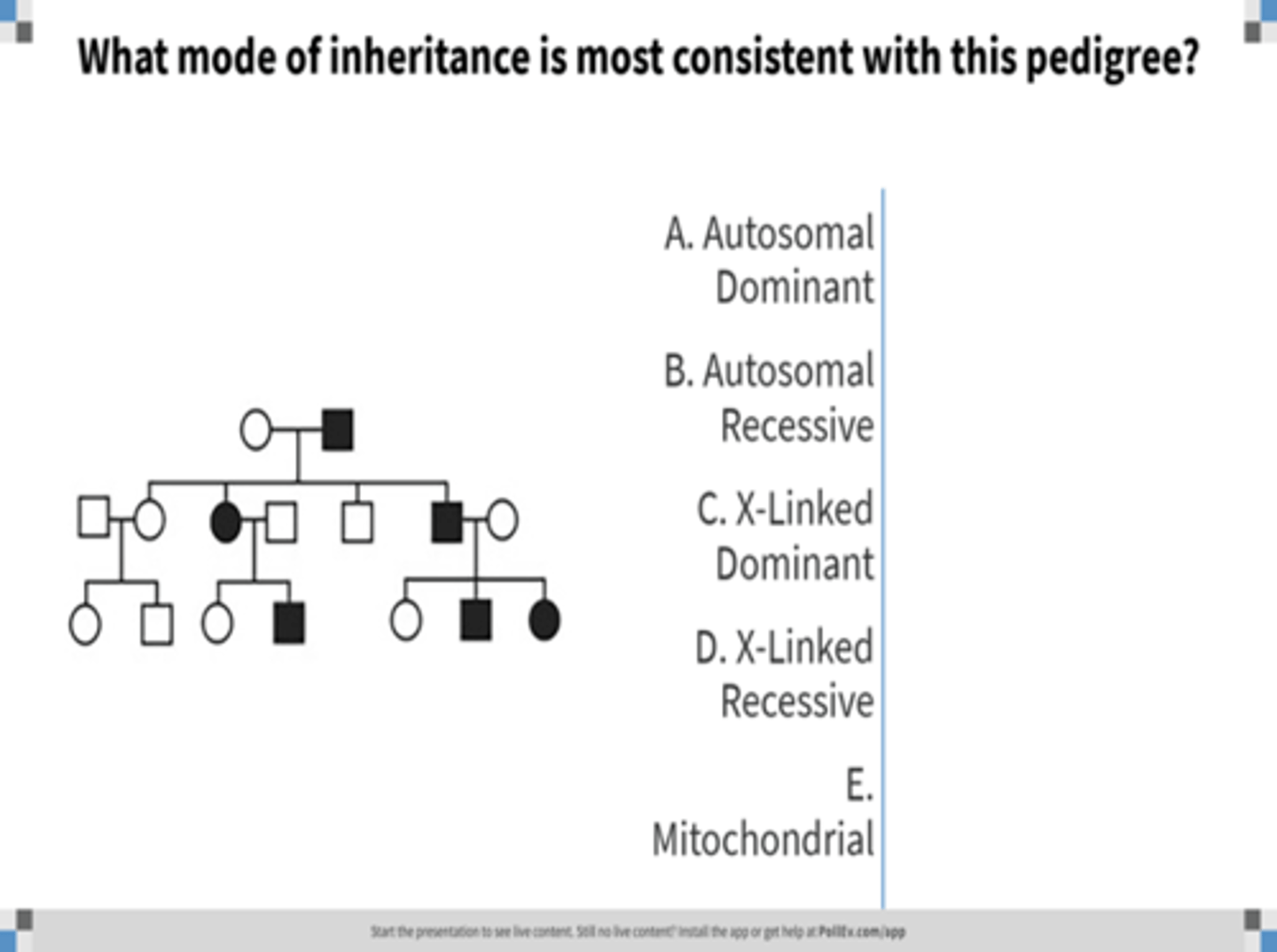
autosomal recessive inheritance
Identify the pattern of inheritance:
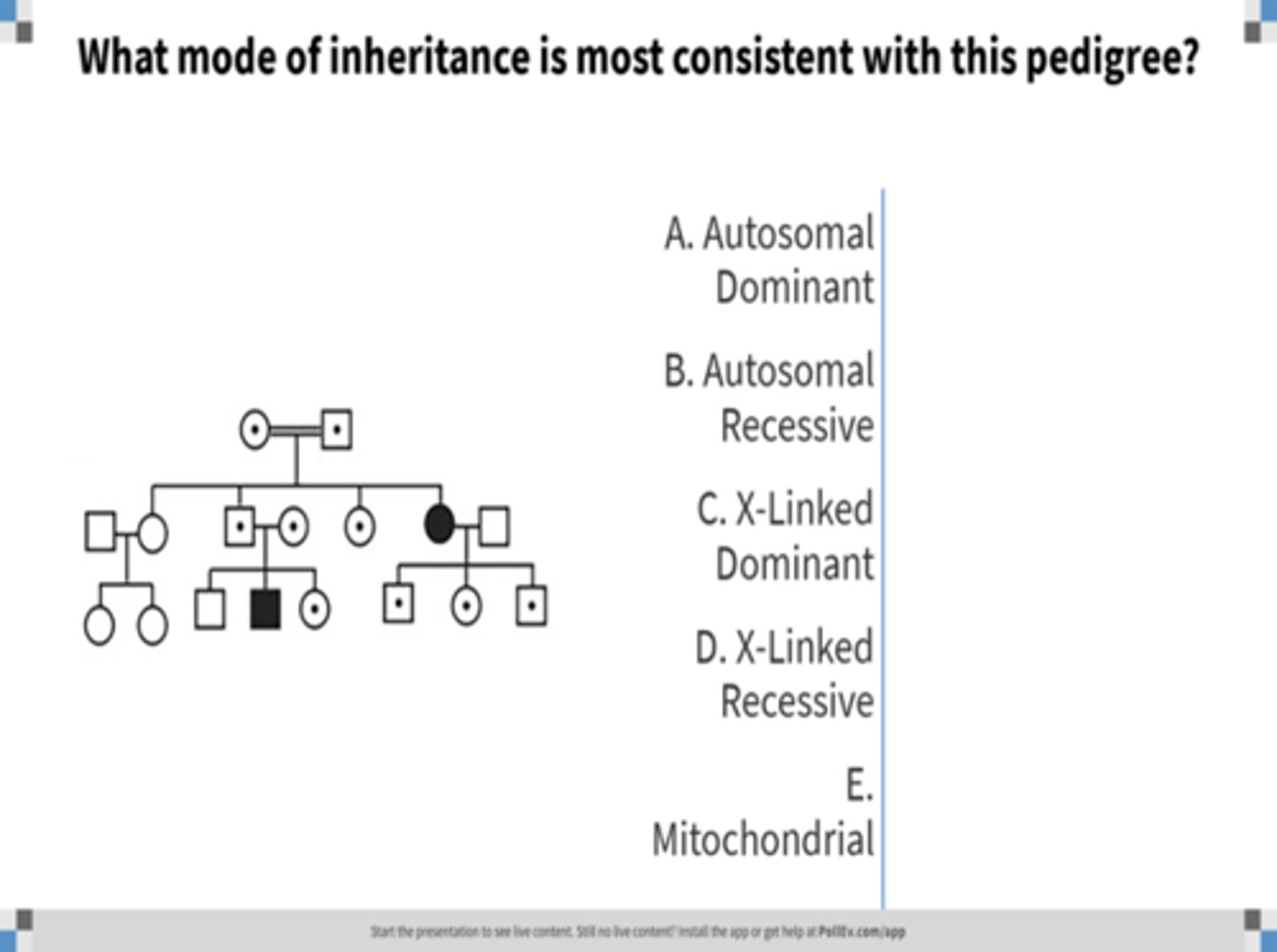
X-linked dominant inheritance
Identify the pattern of inheritance:
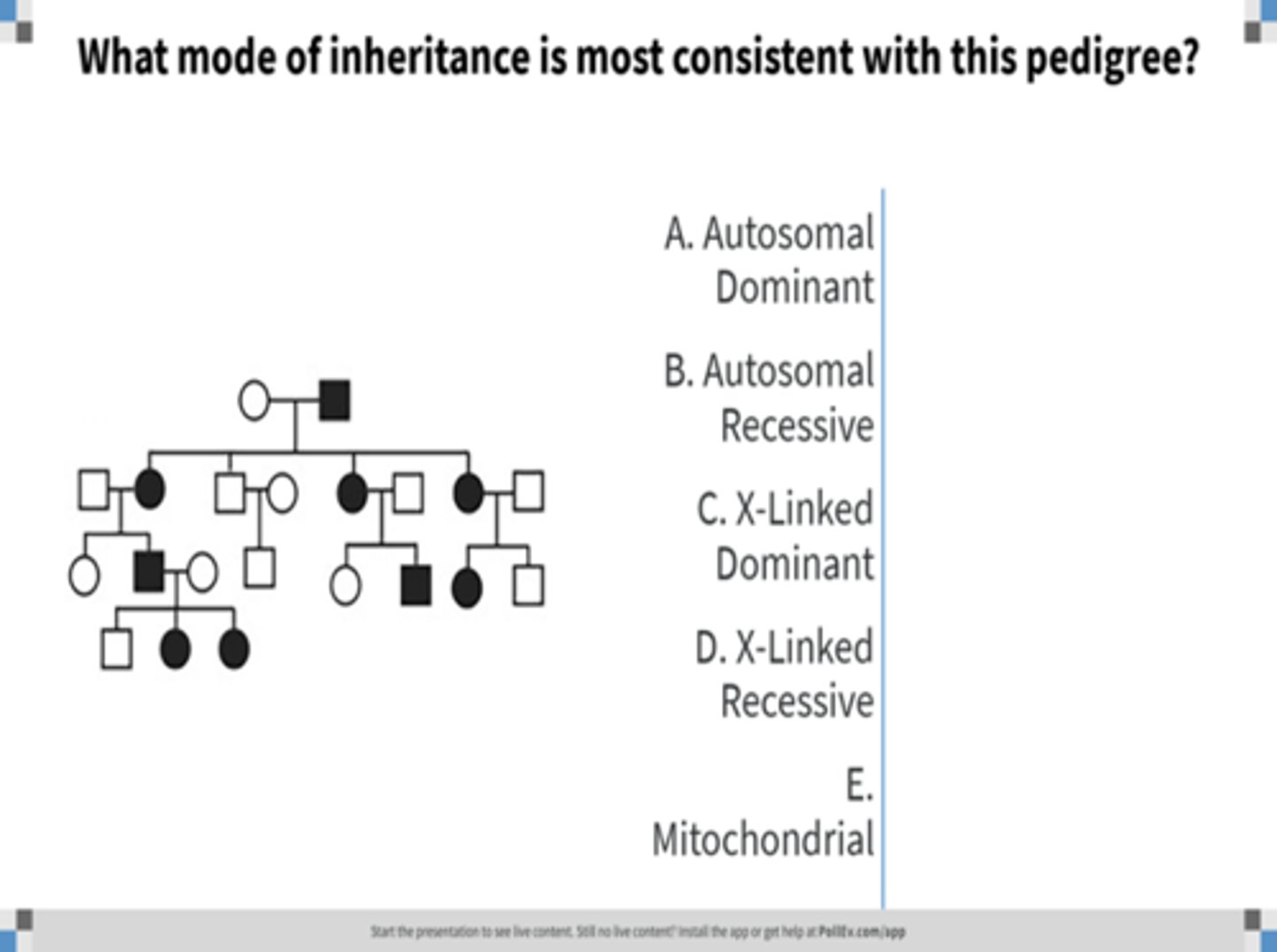
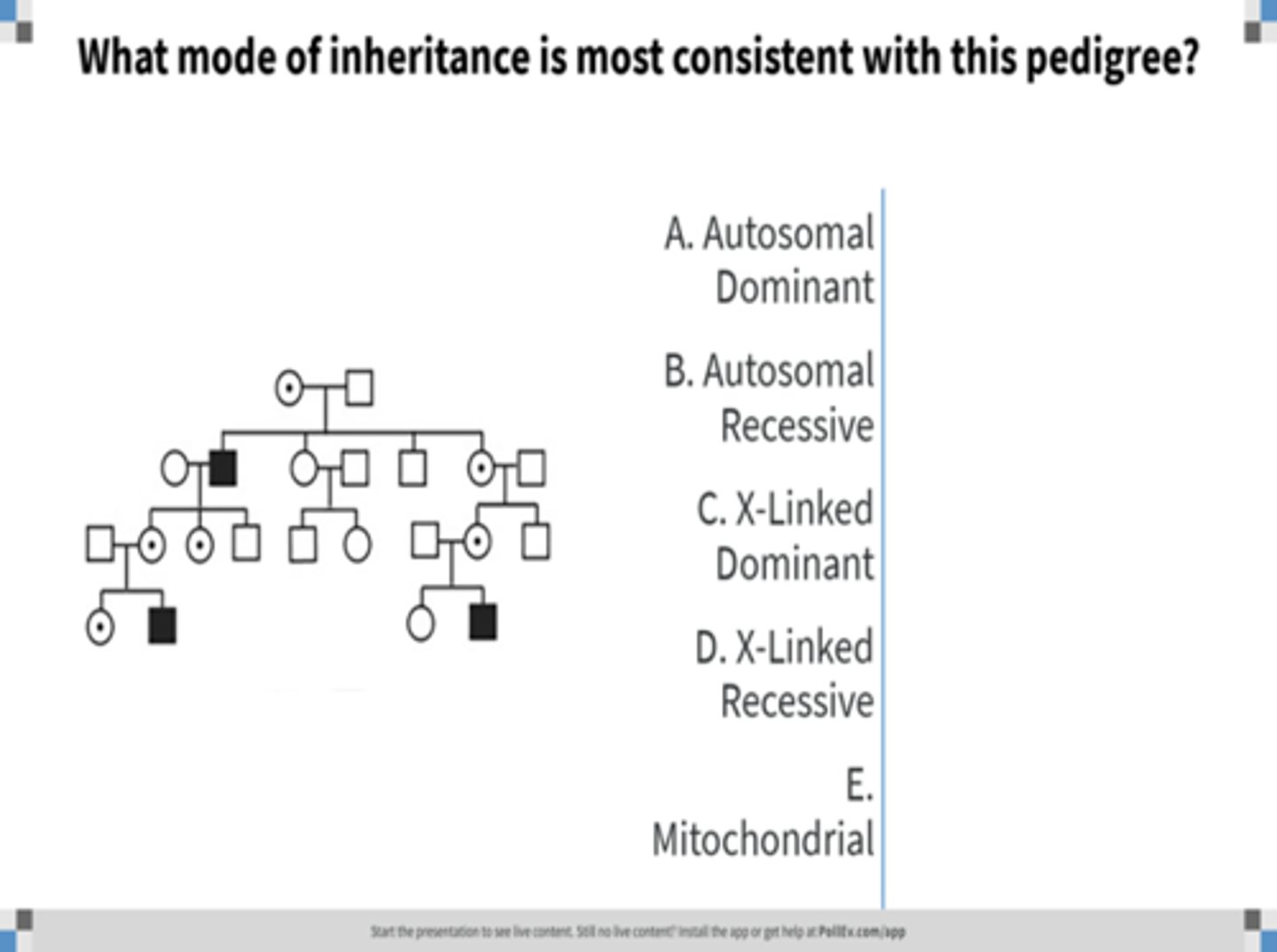
X-linked recessive inheritance
Identify the pattern of inheritance:
Mitochondrial inheritance
Identify the pattern of inheritance: