BOT 14 LAB - EXERCISE 3 EVOLUTION OF VASCULAR TISSUES: FERNS AND ALLIES
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
1. recognize representatives of the cryptogams;
2. compare their spore-bearing structures;
3. distinguish different types of steles;
4. differentiate a megaphyll from a microphyll;
Provide the learning objectives.
xylem and phloem
One remarkable adaptation of plants to life on land is the evolution of vascular tissues, the ______________ and the ______________.
vascular plants; tracheophytes
Most of the land plants have vascular tissues and are known as _____________________ or ___________________.
stele; stele
Vascular tissues form the _____________ collective term for the central cylinder with other tissues inner to the cortex. The ______________ consists of the primary vascular system of the plant axis (stem) and its associated ground tissues.
stelar theory
Stele formation is best explained by the _______________, proposed by Van Tieghem and Douliot in 1886.
cryptogams
Essentially, the spore-bearing vascular plants (_______________) the ferns and fern allies.
Psilophyta, Lycophyta, and Sphenophyta; lower vascular plants; microphylls; homosporous
stele; uni-veined; sporophyte; gametophyte
The cryptogams, specifically divisions _____1______, _______1_______, and ______1______, are often considered the __________2___________ representing the earliest forms of tracheophytes due to the following features:
1) a simple but well differentiated __________;
2) ______________ lateral appendages called ______3______;
3) an erect, conspicuous, free-living ______________________;
4) an inconspicuous, subterranean, tuberous, but free-living ______________________;
5) mostly one type of spores within the sporangium (________5________).
Pterophyta
Ferns belong to the division ________________ other cryptogams, they are spore-bearing and mostly homosporous.
Ferns; exosporic
______________?
Their gametophytes are conspicuous although reduced, independent of the sporophyte, and can germinate outside of the spores (____________).
megaphylls
Unlike the rest of the spore-bearing plants, ferns have a more complex stele organization and possess photosynthetic leaves with a more intricate vascular system called _______________.
leaf traces; leaf gaps; higher vascular
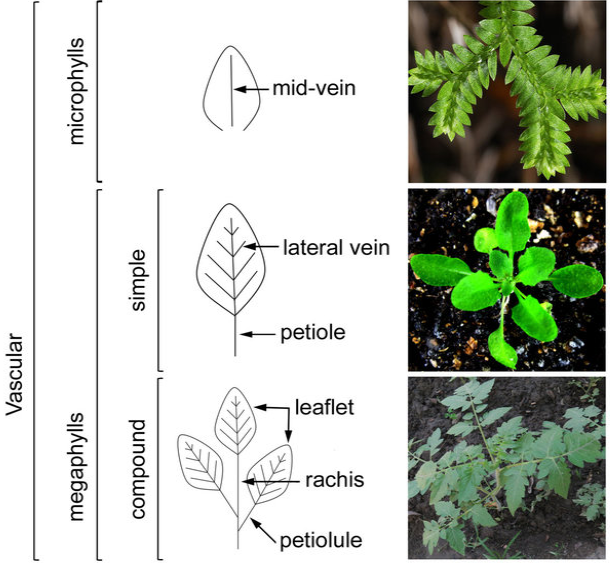
Megaphylls are associated with ________________ and _________________ on the stem. These features have included them among the ________________ plants along with the gymnosperms and angiosperms.
Ferns
They also play as pioneers in ecological succession.
Division Psilophyta: Whiskferns or Forkferns
They are the least complex of all vascular plants primarily because they lack both roots and leaves.
enation
Division Psilophyta: Whiskferns or Forkferns
Attached to the upright stem are epidermal outgrowths called ________________.
rhizome; rhizoids
Division Psilophyta: Whiskferns or Forkferns
The plant has an underground stem, the ________, with ____________ for anchorage and water absorption.
synangium; sporangia; homosporous
In some branches, along the axils of the enations, are the yellow-colored __________, made up of three fused ___________. Each sporangium contains just one type of spores, thus, described as ___________.
Lycopodiopsida; Selaginellopsida; Isoetopsida
2. Division Lycophyta: Clubmosses, Spikeferns, and Quillworts
There are around 1,200 living species divided into three main classes: _____________ represented by Lycopodium; _____________ where Selaginella belongs; and _____________ represented by Isoetes.
Most species are tropical to subtropical commonly found in moist forests, either as ground dwellers or epiphytes.
Lycopodium: Clubmosses
Selaginella: Spikeferns
Isoetes: Quillworts
Lycopodium: _____________
Selaginella: _____________
Isoetes: _____________
heterophylly
Selaginella: Spikeferns
Examine the live specimen of Selaginella sp. Unlike Lycopodium, it has two types of microphylls: the large lateral ones and smaller middle rows.
This condition is known as ____________ or anisophylly.
rootstock
Obtain an herbarium specimen of I. philippinensis and observe it carefully. Its leaves are elongated and narrow with spoon-like bases arising from a corm-like base called the __________.
eusporangiate; leptosporangiate
Ferns maybe classified as either _______________ or _______________.
eusporangium; leptosporangium
A _____________ originates from a series of superficial parent cells or initials. Each develops a wall two or more cell layers thick (although at maturity, the inner wall layers may crush) and a high number of spores.
On the other hand, a _____________ originates from a single cell initial which first produces a stalk and then a capsule. Each gives rise to a relatively small number of spores.