Tegay - Urea Cycle Disorders
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
Urea Cycle
2 major functions
Removal of nitrogenous waste via incorporation of Ammonia into Urea
Synthesis of amino acids
Arginine, ornithine, citrulline
Primarily occurs in liver in heptocytes
All autosomal recessive except OTC
OTC deficiency is X-linked recessive
Ammonia
Product of metabolism of proteins / amino acids
Adult <35 mmol / L
Neonates <100 mmol / L
Hyperammonemia
Neuronal excitation = cell death and cerebral edema
Through increasing extracellular glutamate and overactivation of NMDA receptors
Seizures, coma, death
Brain atrophy, cognitive impairment
Urea Cycle Disorder Symptoms
Early
48 hours
Decreased feeding / vomitting
Lethargy
Tachypnea (Rapid breathing)
Seizure activity
Followed by
Encephalopathy / Coma
Respiratory Failure
Cerebral Edema and Death
Late
Variable onset and severity
Headache, vomitting, ataxia and incoordination
Psychiatric / Behavioral changes
Delirium, psychosis, autism, ADD / ADHD, manic
Cognitive Impairment
DD / MR, Early dementia
Often forecased by
Feve, illness, trauma, fasting, post-partum, protein load
Still at risk for Hyperammonemic Encephalopathy
Even if previously asymptomatic, can be fatal
Etiology of Hyperammonemia
Liver diseases
Non-genetic
Infection, toxin, trauma, ischemia
Genetic other than UCD
Tyrosinemia Type I
Organic Acidemias
Mitochondrial Disorders
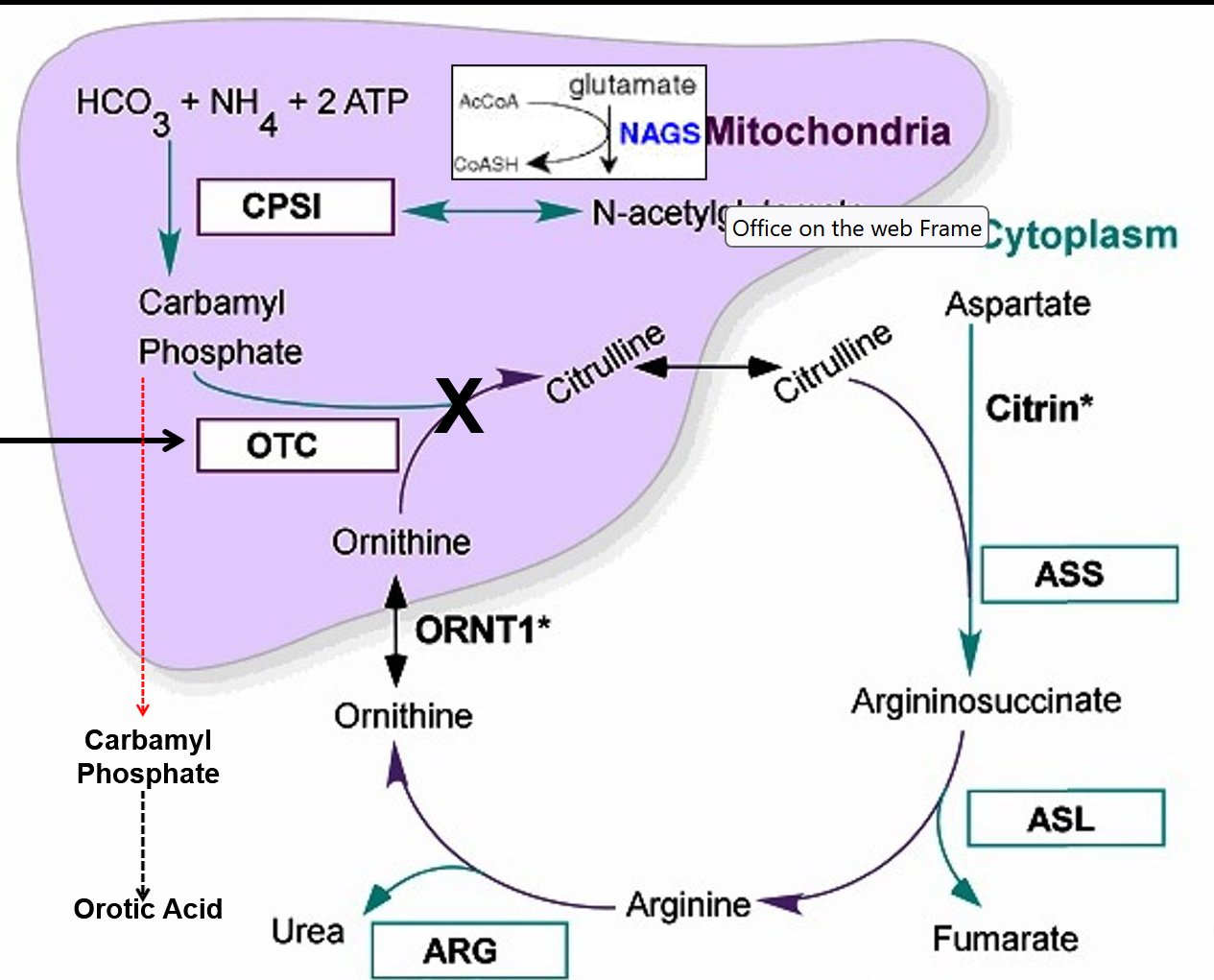
Ornithine Transcarbamylase (OTC) Deficiency
Most COMMON UCD
X-linked Recessive
Ornithine Transcarbamylase (OTC) gene mutation
3 - 4% germline mutation
Symptoms
High Orotic Acid and Ammonia, low Citrulline / ASS / ARG
Classic
Asymptomatic at birth
2 - 3 days old
Poor feeding, vomiting, lethargy, hyperventilation, seizure
1-week-old
Lethal Hyperammonemic Encephalopathy
Cerebral edema, hypothermia, coma, respiratory failure, death
Mild
Episodic Hyperammonemic Symptoms
Mild to severe / life-threatening
Chronic symptoms
Protein avoidance, headaches, neuropsychiatric difficulty
Diagnosed via low Citrulline, not on some newborn screenings
Ammonia level tests
Blood gas/ metabolic profile / lactic acid level tests to exclude metabolic acidosis and high anion gap
Plasma amino acid profile and urine organic acids
Typically glutamine / alanine high and citrulline / ASA / arginine low
Increased orotic acid on uOA and or elevated after an allopurinol load
Confirmed via Enzyme activity analysis which requires liver biopsy
Not useful for preimplantation / prenatal
OTC gene sequencing with 60% - 90% detection rate
Treatment
Variable outcomes if treated, neuralcognitive development depends on initial hyperammonemic encephalopathy duration
ID / ADHD, executive deficits, brain atrophy
Acute treatment
Hemodialysis
Protein cessation
IV glucose and lipids to prevent catabolism and IV arginine
IV ammonia scavengers (eg. Na + Benzoate and Na + Phenylbutyrate)
Chronic treatment
Protein restriction and essential amino acid metabolic formula
Oral citrulline (or arginine) and ammonia scavengers
Na benzoate, Na phenylbuterate (Ravicti)
Avoid Valproic acid, fasting, fever, steroids, protein load
Liver transplant

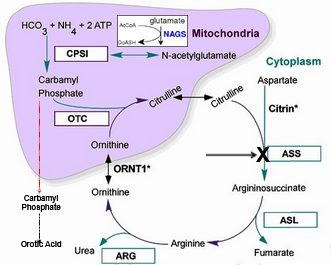
Citrullinemia (ASS1) Deficiency
Autosomal recessive
Arginosuccinic Acid Synthetase 1 (ASS1) gene
Symptoms
High citrulline, ammonia, orotic acid
Low levels argininosuccinate and arginine
Classic
Asymptomatic at birth
4 - 7 days
Progressive Hypermammonemic Encephalopathy
Poor feeding, vomiting, lethargy, hyperventiliation, seizures
1 - 2 weeks
Lethal hyperammonemic Encephalopathy
Cerebral edema, hypothermia, coma, respiratory failure, death
Late-onset
Episodic Hyperammonemic Symptoms
Mild - severe / life-threatening
Chronic Symptoms
Protein avoidance, recurrent headaches, neuropsychiatric difficulty
Diagnosed via high citrulline
Ammonia level test
Blood gas/ metabolic profile / lactic acid level tests to exclude other acidosis and other IEM
Plasma amino acid profile and urine organic acids where citrulline/glutamine/alanine very high, ASA/arginine, ornithine low
Increased orotic acid on uOA
ASS1 Enzyme activity in fibroblasts, liver, CVS or amniocytes, useful for prenatal / preimplanation genetics
ASS1 genotyping with deletion / duplication analysis has 96% detection
Treatment
Variable outcomes if treated, neuralcognitive development depends on initial hyperammonemic encephalopathy severity
ID / ADHD, executive deficits, brain atrophy
Acute treatment
Hemodialysis / hemofiltration
Protein cessation
IV glucose and lipids to prevent catabolism and IV arginine
IV ammonia scavengers (eg. Na + Benzoate and Na + Phenylbutyrate)
Chronic treatment
Protein restriction and essential amino acid metabolic formula
Oral arginine NOT citrulline and ammonia scavengers
Na benzoate, Na phenylbuterate (Ravicti)
Avoid Valproic acid, fasting, fever, steroids, protein load
Liver transplant
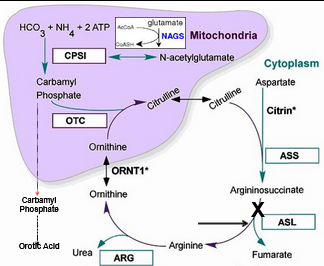
Arginosuccinate Lyase (ASL) Deficiency
Autosomal recessive
Arginosuccinate Lyase (ASL) gene
Symptoms
High Citrulline and Arginosuccinate
Low Arginine, Hyperammonemia, and mild to NO Orotic Acid
Brittle hair and hypertension
At birth asymptomatic
Classic
4 - 7 days
Progressive Hypermammonemic Encephalopathy
Poor feeding, vomiting, lethargy, hyperventiliation, seizures
1 - 2 weeks
Lethal hyperammonemic Encephalopathy
Cerebral edema, hypothermia, coma, respiratory failure, death
Late-onset
Episodic Hyperammonemic Symptoms
Mild - severe / life-threatening
Chronic Symptoms
Protein avoidance, recurrent headaches, neuropsychiatric difficulty
Diagnosed via high citrulline
Ammonia level test
Blood gas/ metabolic profile / lactic acid level tests to exclude other acidosis and other IEM
Plasma amino acid profile and urine organic acids where citrulline/ASA, glutamine, alanine high
Arginine / ornithine low
ASL Enzyme activity in fibroblasts, liver, RBC, CV, or amniocyte
Useful in prenatal / preimplanation
ASL genotyping with deletion / duplication analysis has 90% detection
Treatment
Most have some degree of neurcognitive deficiency, ADHD, seizures, eventual liver failure
Acute treatment
Hemodialysis / hemofiltration
Protein cessation
IV glucose and lipids to prevent catabolism and IV arginine
IV ammonia scavengers (eg. Na + Benzoate and Na + Phenylbutyrate)
Chronic treatment
Protein restriction and essential amino acid metabolic formula
Oral arginine NOT citrulline and ammonia scavengers
Na benzoate, Na phenylbuterate (Ravicti)
Avoid Valproic acid, fasting, fever, steroids, protein load
Liver transplant
Arginase (ARG) Deficiency
Autosomal recessive
Arginase (ARG1) gene
Symptoms
Increased arginine, mild intermittent hyperammonemia, occasional mild orotic acid elevations
Asymptomatic at birth
After 1 - 3 years
Growth slows
Motor and cognitive development slows and regression occurs
Spasticity and seizures develop
Adulthood
Severe MR, microcephaly
Short stature
Severe spasticity and joint contractures
Lack of ambulation, bowel and bladders control
Low risk of hyperammonemic encephalopathy
Diagnosed via elevated arginine
Ammonia level test
Blood gas/ metabolic profile / lactic acid level tests to exclude other acidosis and other IEM
Plasma amino acid profile and urine organic acids where arginine high, orotic acid minimally elevated or may be normal
ARG1 Enzyme activity in fetal red blood cells
Useful in prenatal / preimplanation but need umbilical blood sampling
ARG1 genotyping with deletion / duplication analysis
Treatment
Improved but still increased risk for ID, short stature, join contactures, etc
Not typically encephalopathic
Chronic treatment
Protein restriction and essential amino acid metabolic formula
Oral ammonia scavengers NO oral arginine or citrulline (eg. Na + Benzoate and Na + Phenylbutyrate)
Avoid valproic acid, fasting, fever, steroids, protein loud
Liver transplant if neuro intact but poor response to treatment
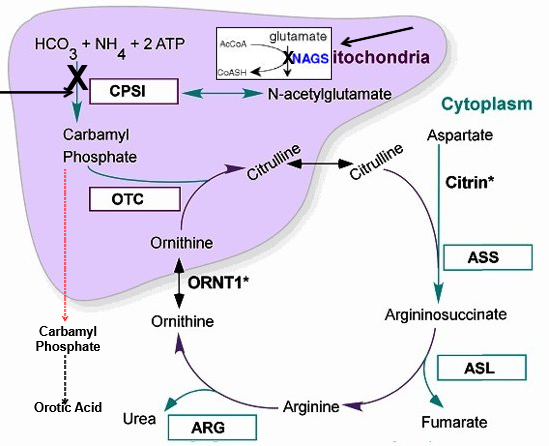
NAGS and CPS1 Deficiency
Preo-Orotic UCD, rarest
Both Autosomal Recessive
N-AcetylGlutamate Synthestase (NAGS)
Carbamoyl Phosphate Synthetase 1 (CPS1)
NAGS and CPS1 genotyping and deletion / duplication analysis
Symptoms
High ammonia, glutamine, alanine
Low citrulline, ASA, arginine
NO orotic acid
Symptoms indistingusihable from OTC/ASS1/ASL
Diagnosed via
High ammonia, glutamine, alanine
Low citrulline, ASA, arginine
NO orotic acid
Confirmed via Enzyme Activity analysis via liver biopsy
Treatment
Outcome varies, no enzyme / metabolite testing is useful
Acute treatment
Hemodialysis / hemofiltration
Protein cessation
IV glucose and lipids to prevent catabolism and IV arginine
IV ammonia scavengers (eg. Na + Benzoate and Na + Phenylbutyrate)
Chronic treatment
Protein restriction and essential amino acid metabolic formula
Oral arginine or citrulline and ammonia scavengers
Na benzoate, Na phenylbuterate (Ravicti)
Avoid Valproic acid, fasting, fever, steroids, protein load
Liver transplant
Carglumic acid for NAGS deficiency, synthetic N-acetylglutamate