ES AMACE REVIEWER
1/103
Earn XP
Description and Tags
lets review yey
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
Hooke’s Law
stress is proportional to strain
Strength of materials
Deals with the relation between externally applied loads and internal
Continuous Beam
A type of beam with at least three or more supports.
Simple Beam
A beam that is simply supported at both ends.
Beam Deflection
The second moment of area is an important value used to calculate deflection.
vector quantities
Quantities having both magnitude and direction.
moment
Measure of the tendency of a force to make a rigid body rotate.
Concurrent Forces
A force system whose line of action passes through a common point.
Centroid
Also called the axis of zero stress.
Free Body Diagram (FBD)
A sketch of a body completely isolated from its surroundings.
Proportional Limit
The safe load a material can carry.
Triangular Load
A load whose intensity increases or decreases at a constant rate.
True
T or F:
A definite amount of matter whose parts are fixed relative to each other is a RIGID BODY
Fixed Beam
A beam restrained at both ends.
Determinate Beam
A cantilevered beam.
Principle of Transmissibility
The external effect of a force on a rigid body is the same for all points along its line of action.
Torsional Stress
Stress produced when a machine shaft is subjected to torque.
Area Moment of Inertia
Can be calculated using a rectangular coordinate system to define the area moment around the axis.
Equilibrium
The state or condition in which the resultant of all forces is zero
Modulus of Elasticity
The slope of the stress strain
Reaction Force
Force that inhibits change in the state of movement of a body.
Varignon’s Theorem
States that the moment of a resultant of two concurrent forces about a point equals the sum of the moments of its components about the same point.
Strain
Deformation caused by stress.
Newton
The SI unit of force.
Pascal
The SI unit of stress.
Yield Point
It is a point on the stress-strain diagram in which there is an appreciable elongation of the material without any corresponding increase of load.
Ultimate Strength
The highest ordinate on the stress-strain curve as maximum strength
Elastic Limit
The stress beyond which a material does not return to its original shape when unloaded.
Factor of Safety
The ratio of ultimate or yield strength to allowable strength
Centroidal Axis
An axis passing through the centroid of an area.
Concentrated Load
A load acting over a small distance, assumed to act at a point.
Newton’s 3rd Law
For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
Parallelogram Law
The resultant of two forces is the diagonal formed on the vectors of these forces.
Bearing Stress
Contact pressure between separate bodies
Cantilever Beam
A beam fixed at one end and free at the other.
Truss
A structure made of two-force members; all pin is connected at joints / each other
Overhanging Beam
A beam with one or both ends extending beyond its supports.
Shear Stress
Stress caused by forces acting parallel to the resisting area
Neutral Axis
In a beam, the layer that neither elongates nor shortens during bending.
Beams
Members in structures primarily designed to resist bending moments
Columns
Vertical structural members that resist axial compressive loads.
Statics
The study of bodies at rest or moving at constant velocity.
Dynamic Body
A body under varying motion due to unbalanced forces.
Equilibrium Equation for a Particle
A particle is in equilibrium if the resultant of all forces acting on it is zero.
System of Forces
When several forces act in a given situation.
first degree; zero degree
what kind of curve is a uniformly distributed load if plotted in a shear diagram
5N
two forces 3N and 4N are perpendicular to each other, what is the resultant of the two forces?
shear
moment of inertia is used for the stress calculations of _____?
fixed beam
a type of beam that is restrained at both ends
tangetial
what stress is a bolt double shear?
KN-m
unit of torque
length
strain is deformation divided by ___?
Zero Force member
members in the truss which cannot carry loads
stable
centroid is used to determine if the building is ___?
method of joints
a method that uses FBD of joints in the structure to determine the forces in each member
rigidity
deformation is a measure of the materials _____?
break
SOM refers to the tendency of the structure not to ___?
continuous beam
a type of the beam with at least 3 or more supports
magnitude
intensity of the force
calculate the resistance to buckling
determine the amount of deflection in a beam
determine the state of stress in a section
The second moment of area is an important value which is used to_________ It can also be called moment of inertia.
Concurrent, Coplanar
The action lines of all the forces are in the same plane and intersect a common point
center of gravity
a point within an object from which the force of gravity appears to act
lie somewhere along the line of symmetry
if an area has one line of symmetry, the centroid will ____?
moment
the measure of tendency of a force to a make rigid body rotate about a fixed axis
246000kPa
A 5cm-diameter 80cm long steel bar is restrained from moving. If its temperature is increased 100 deg. C, determine the induced compressive stress? For steel=11.7x10.6 per degree C, E =210GP
1.5N/mm
For a uniformly distributed load of 1.5 KN/m, what is the equivalent load of this N/mm
Stress is proportional to Strain
Calculate the resistance to buckling
Determine the amount of deflection in a beam
determine the state of stress ina section
65973N
What is the allowable load in kN on a 2-cm diameter, 1m long steel rod if the maximum elongation is limited only to 0.10cm. (E for steel=210x10^kPa)
Proportional limit
The straight-line portion from the origin up to the elastic limit of the stress-strain diagram is termed as the__________.
0.00686
An elevator is suspended by a 2-cm-diameter, 30-mlongsteel cable. If twenty-five people with a total weight of 15000N, how far in millimeters does the elevator drop?
unitless
unit of strain
Hooke’s Law
In linear portion, stress directly proportional to strain is given in what law?
Modulus Elasticity
The slope of the straight line portion of the stress-strain diagram is the ratio of stress to strain is called.
it is elastic
A specimen is subjected to a load when the load is removed. The strain disappears. From this information, which can be deducted about the material?
Cantilevered Beam
A beam supported on one end and the other projecting beyond the support or wall
rubber
Which of the following is a “non-hookean” material?
steel
rubber
aluminum
copper
Newton’s First Law of Motion
If the resultant force acting on a particle is zero, the particle remains at rest (if originally at rest) or will move with constant speed in a straight line (if originally in motion)
center of gravity
the point through which the whole weight of the body acts is called _____?
1 MPa
A block 100 mm×100 mm base and 10mm height. What will be the direct shear stress in the element when a tangential force of 10 kN is applied to the upper edge to a displacement of 1 mm relative to the lower face?
Hooke’s Law
States that strain produced within elastic limits is proportional to the stress producing it.
normal stress
stress which acts in a direction perpendicular to the area
shear force diagram
a diagram which shows the variations of the axial load for all sections in the span of a beam
equilibrium
a condition in which the resultants of all forces acting on the body is zero
true
True or False: Statics of rigid bodies is the study of materials, objects, or particles at rest or moving under constant velocity
a rigid body
A combination of large number of particles in which all particles remain at a fixed distance from one another before and applying a load
+96lb; +64lb
-225.90 N
If the x-and y-components of the forces on the figure shown are -105N and -200N, respectively, what is the magnitude of the resultant force? (w/diagram)
Varignon’s Theorem
States that the moment of a force about a point is equal to the sum of the moments of the force’s components about_____??
tensile
when equal and opposite forces applied to a body tend to elongate, the stress produced is ____?
yielding point
stress at which extension of a material takes place more quickly as compared to the increase in load
3.33 kN
kN/m
SI unit for bending moment
weight
gravitational force / attraction of the earth acting on a body
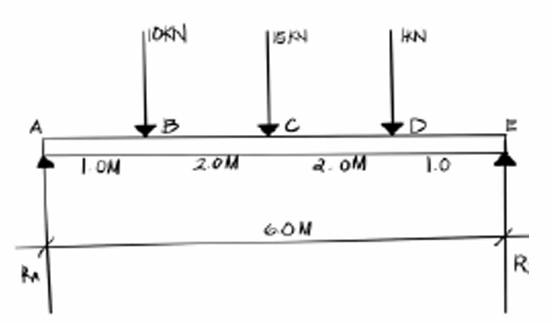
16kN
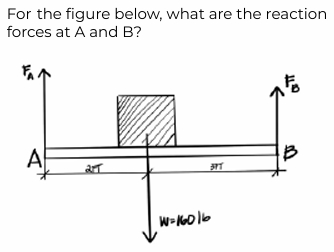
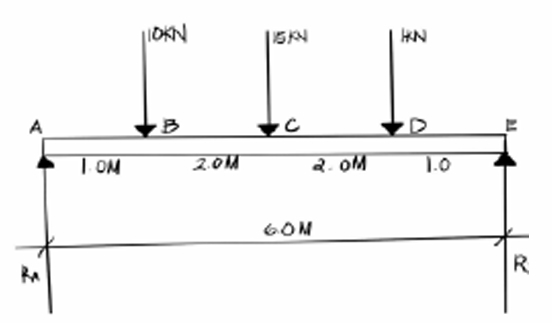
find reaction at point A or Ra
-9
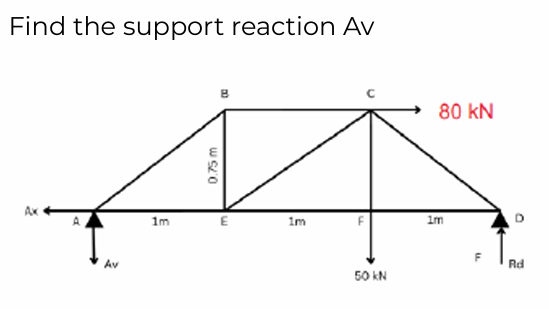
Find the computed shear at C or Vc
bending is the same at every section along its longitudinal axis
a beam is said to be uniform strength, if ____?
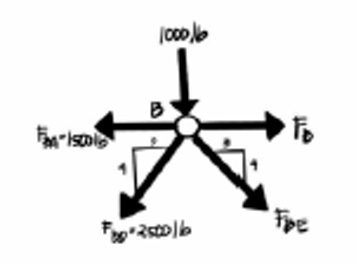
5250 lbs
in the figure below, if the system is in equilibrium, what is Fbc = ??
FBD
A _____ isolates a body from its surroundings, and one considers all the forces and only those forces, acting on the body
3
In a body loaded under plane stress conditions, how many independent stress components are present?
3
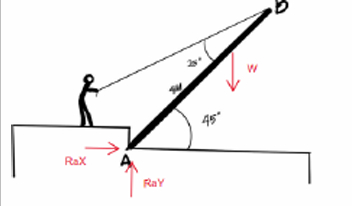
a man raises a 10kg joist, of length 4m, by pulling on a rope as shown in the picture. how many concurrent forces are acting upon the joist