BSC1011 Test 3
1/217
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
218 Terms
The three basic plant organs are the
-leaves
-stem
-roots
Plant organs are divided into two systems, which are the
-Shoot system
-Root system
Parts of a plant cell (that we need to know)
-Nucleus
-Chloroplast
-Mitochondrion
-Central Vacuole
-Plasmodesma
-Cell Wall
-Plasma Membrane
Plant cell wall structures
-Primary cell wall
-Secondary cell wall
-Middle Lamella
-Plasmodesmata
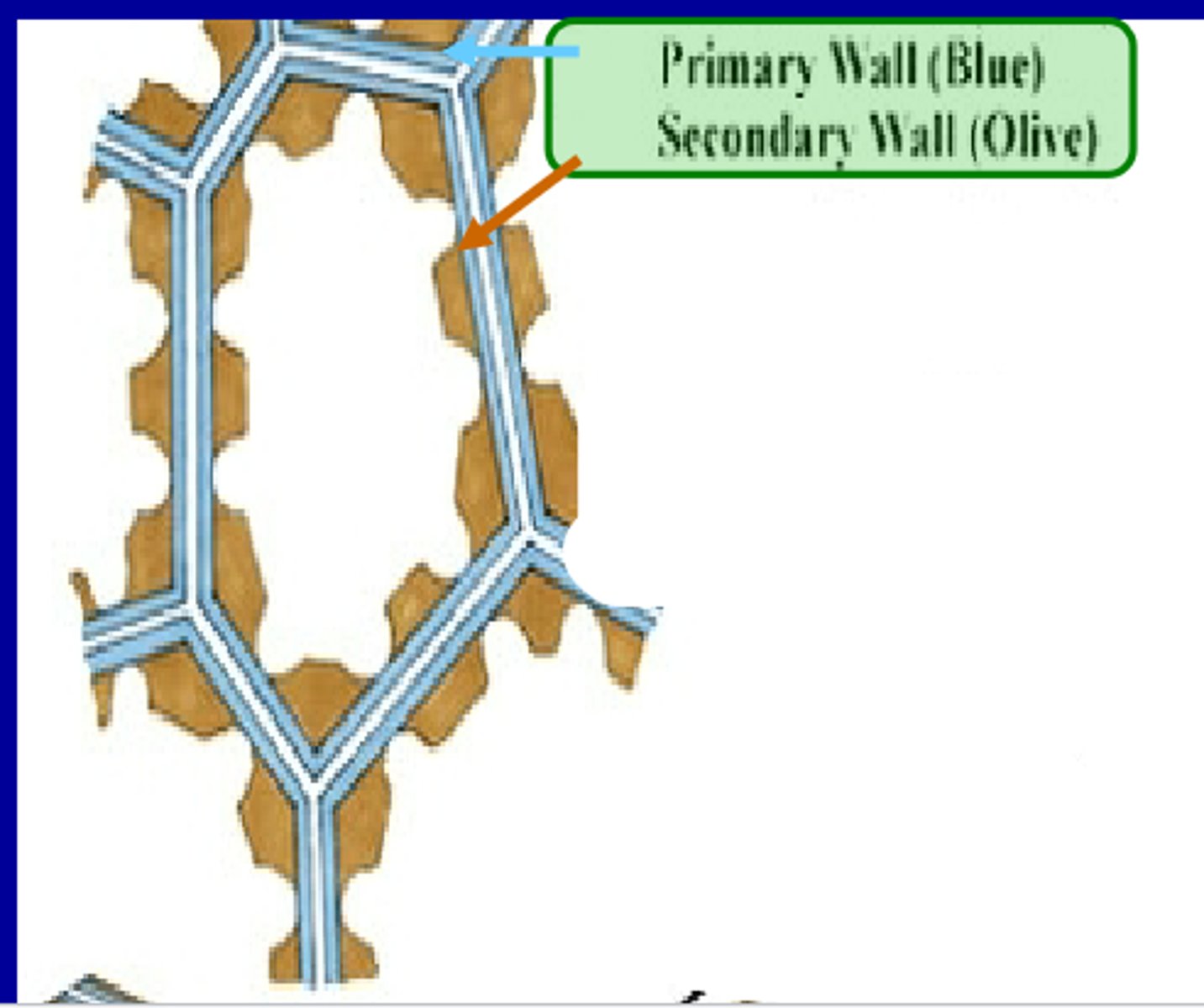
Primary Cell wall
-The first cell wall layer that every plant cell has
-made of cellulose
-contains plasmodesma in order to allow for cellular communication
What are plant cell walls made out of?
cellulose
Are primary cell walls made of living or dead cells at maturity?
Living cells
Secondary cell wall
-Deposits beneath the primary cell wall that are completely impermeable to water and gasses
-Cover the plasmodesmata
-At maturity, the cells will die (makes wood)
Are secondary cell walls made of living or dead cells at maturity?
Dead cells
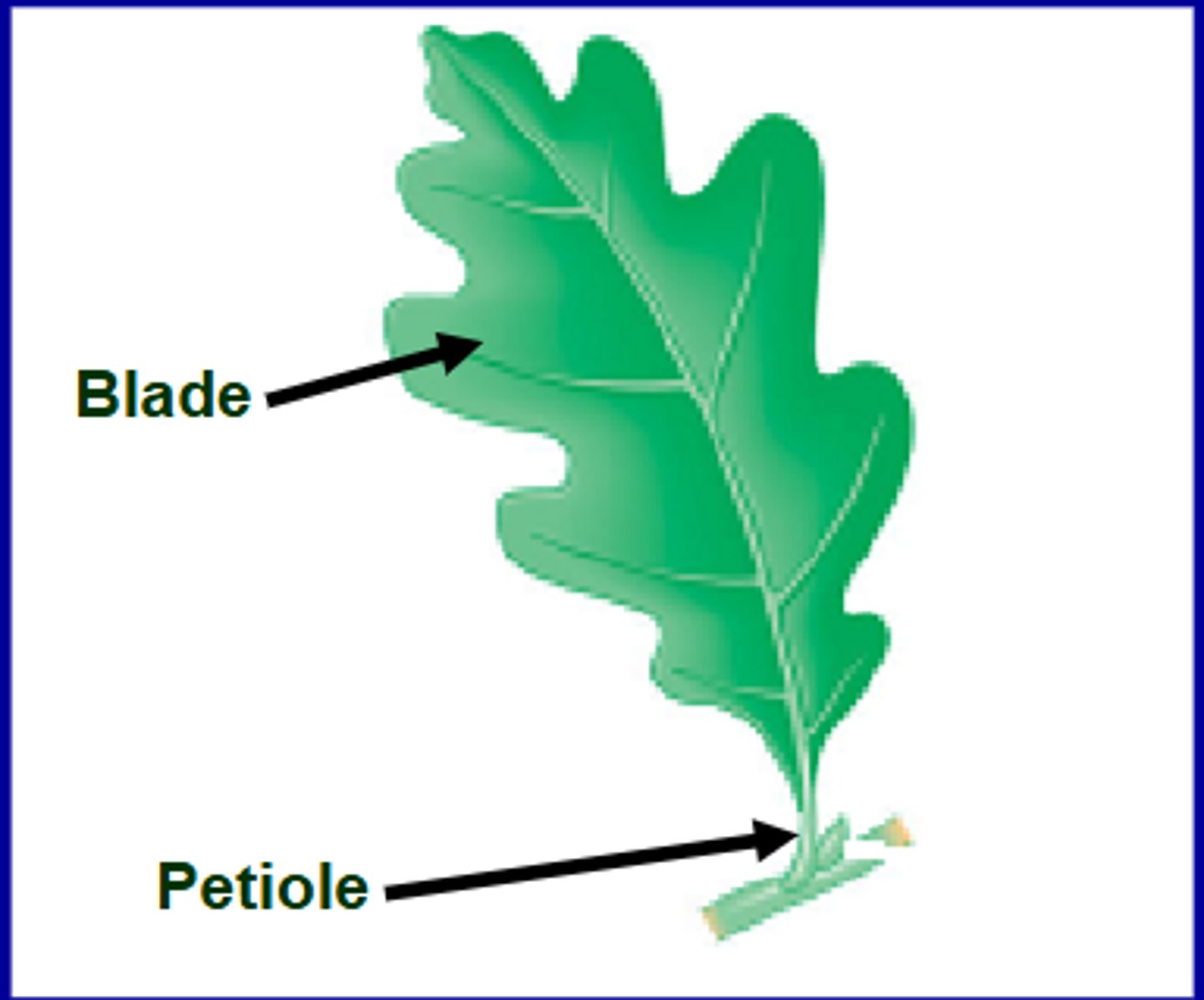
Leaf
Main photosynthetic organ of most vascular plants
Parts of the leaf
-Flattened blade
-Petiole
Leaf structures
-Cuticle
-Stomata (and guard cells)
-Leaf Hairs/Trichomes (2 types)
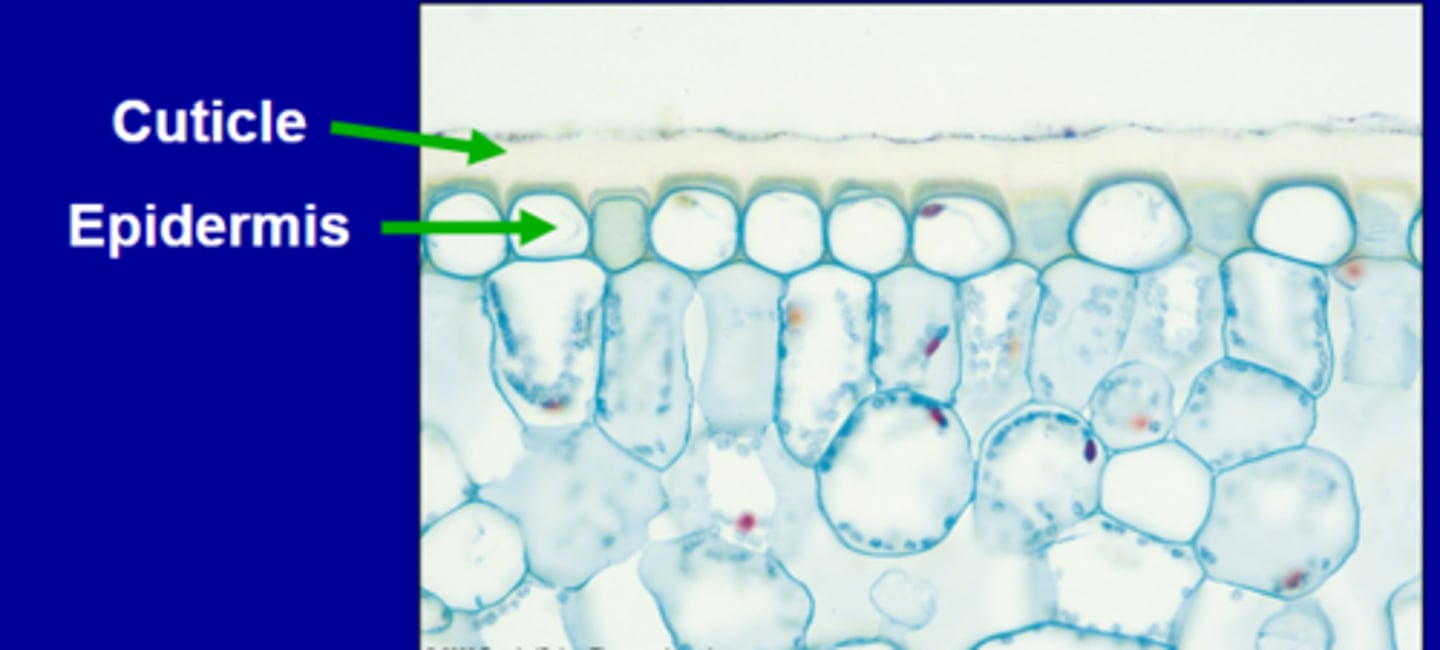
Cuticle
Layer of wax that waterproofs the leaf
Stomata
Openings formed by guard cells to allow for gas exchange
Leaf Hairs/Trichomes function
Defense against herbivores or as a weapon
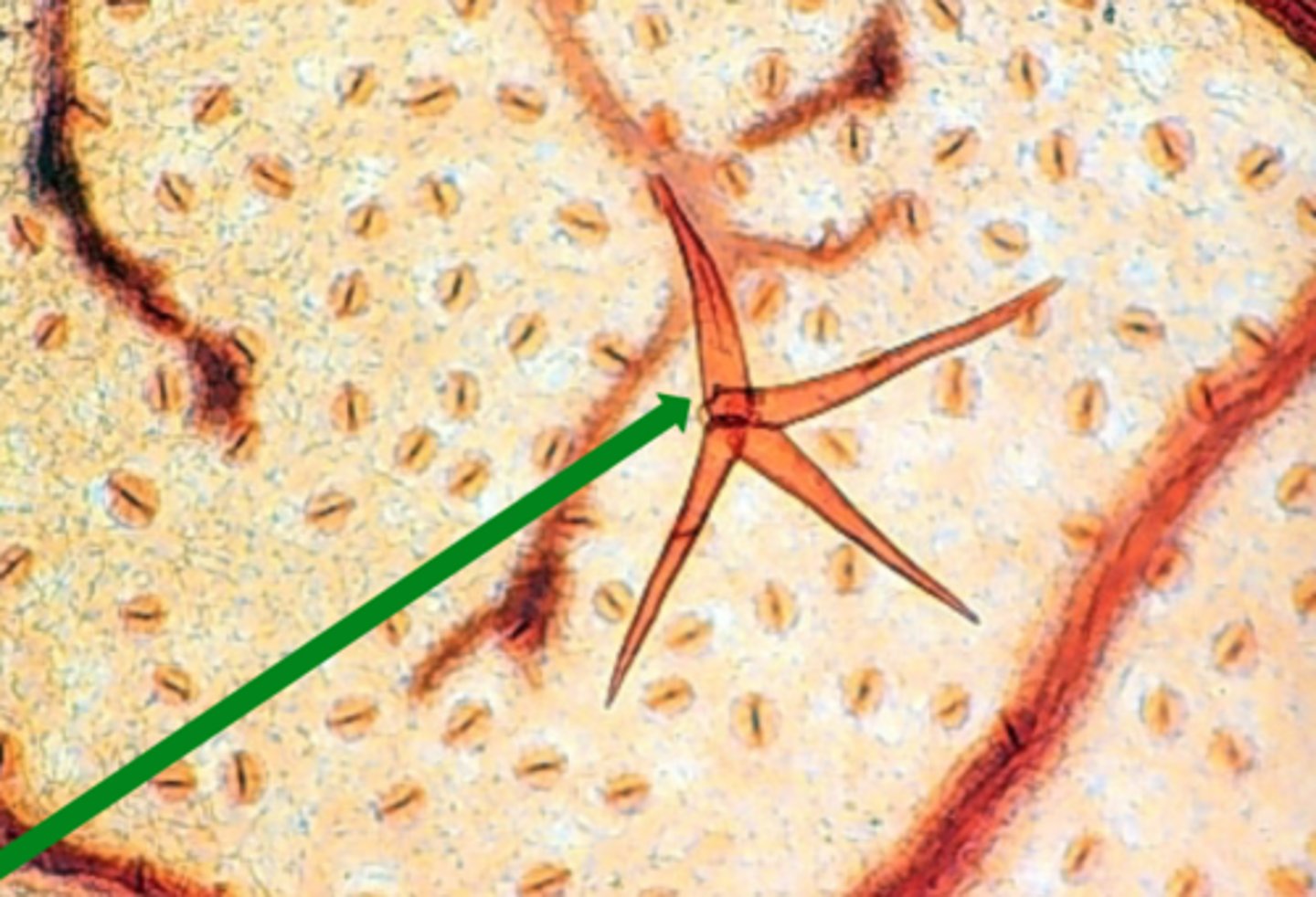
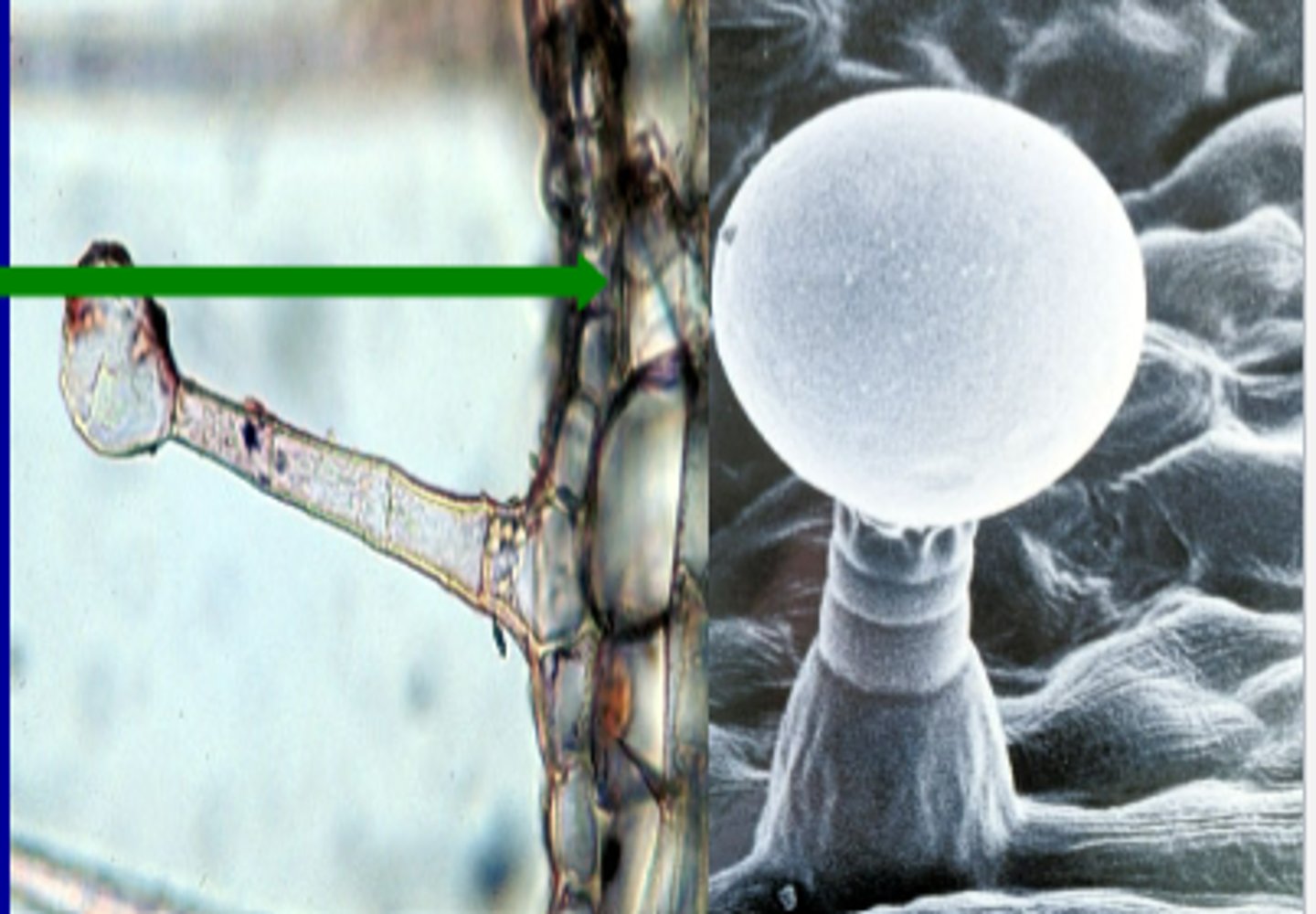
Types of leaf hairs/trichomes
-Simple
-Glandular
Simple leaf hairs/trichomes
Glandular leaf hairs/trichomes
Petiole
The stalk of a leaf, which joins the leaf to a node of the stem.
Types of leaves
-Simple
-Compound
Simple Leaves
Leaves that have one continuous blade
Types of compound leaves
-Pinnate
-Bipinnate
Pinnate Compound Leaves
A leaf whos blade is broken down into leaflets
Bipinnate Compound Leaves
A leaf whos blade is broken down into leaflets and the leaflets are broken down into even more leaflets
What are types of modified leaves?
-Tendrils
-Spines
-Storage
-Bracts
-Reproductive
-Flowers
Stem
-An organ that positions and supports the leaves
-May become modified and perform other functions as well
Stem anatomy
-An axillary or lateral bud
-An apical or terminal bud
Axillary (lateral) bud
-A structure that has the potential to form a lateral shoot, or branch
-Located where the leaf meets the stem
Apical (terminal) bud
-Located near the shoot tip and causes the elongation of a young shoot
-Allows the plant to grow up
-Apical buds inhibit the growth of lateral buds. If the apical bud is removed, the lateral buds will grow.
Apical Dominance
Apical buds inhibit the growth of lateral buds. If the apical bud is removed, the lateral buds will grow.
Stem Anatomy
-An axillary (lateral) bud
-An apical (terminal) bud
-Internode
-Node
Node
Where the leaf meets the stem
Internode
The space between nodes of a stem
Modified Shoots
-Runner
-Rhizomes
-Tubers
-Bulb
-Corm
Roots
-An organ that anchors the vascular plant
-Absorbs minerals and water
-Often stores organic nutrients
-May become photosynthetic as in orchids
-Absorption mainly occurs at the root tip
Where does water/nutrient absorption mainly occur in roots?
Near the root tip, where vast numbers of tiny root hairs increase the surface area of the roots
Modified Roots
-Prop roots
-Storage
-Strangling
-Buttress
-Pneumatophores
Dicot roots
"Tap Roots"
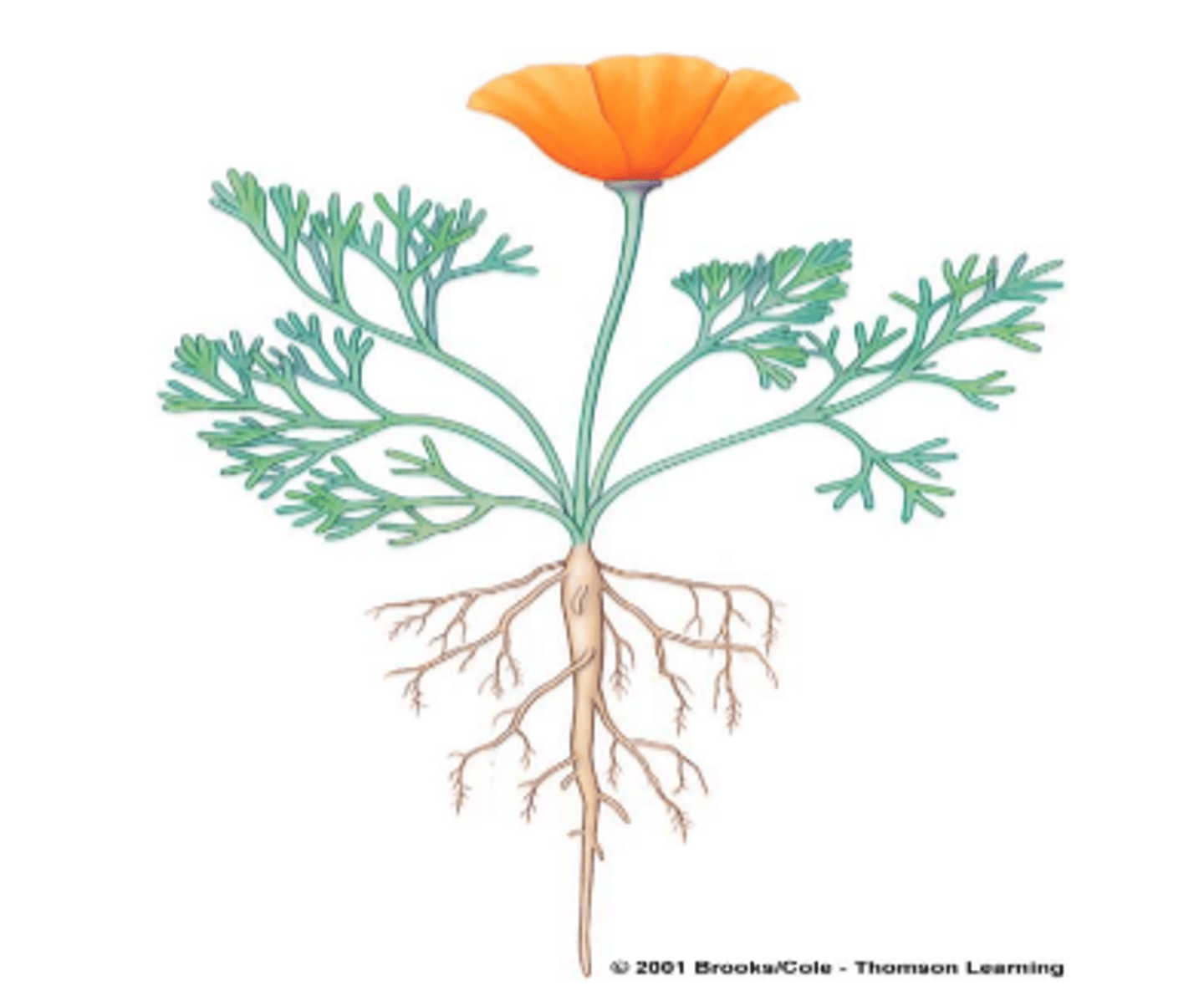
Monocot roots
"Fibrous Roots"

What are the three tissues of each plant organ?
-Dermal
-Vascular
-Ground
Dermal tissue system
-Consists of the: epidermis (in primary growth), and the cuticle.
Vascular tissue system
-Carries out long distance transport of materials between roots and shoots
-Consists of the xylem and phloem
What are the two tissue types in the vascular tissue system?
-Xylem
-Phloem
Xylem
-Part of the vascular tissue system
-Unidirectional (UPWARDS)
-Conveys water and dissolved minerals upward from the roots into the shoots
-Made up of dead cells (secondary cell walls)
-Consists of tracheids and vessel elements
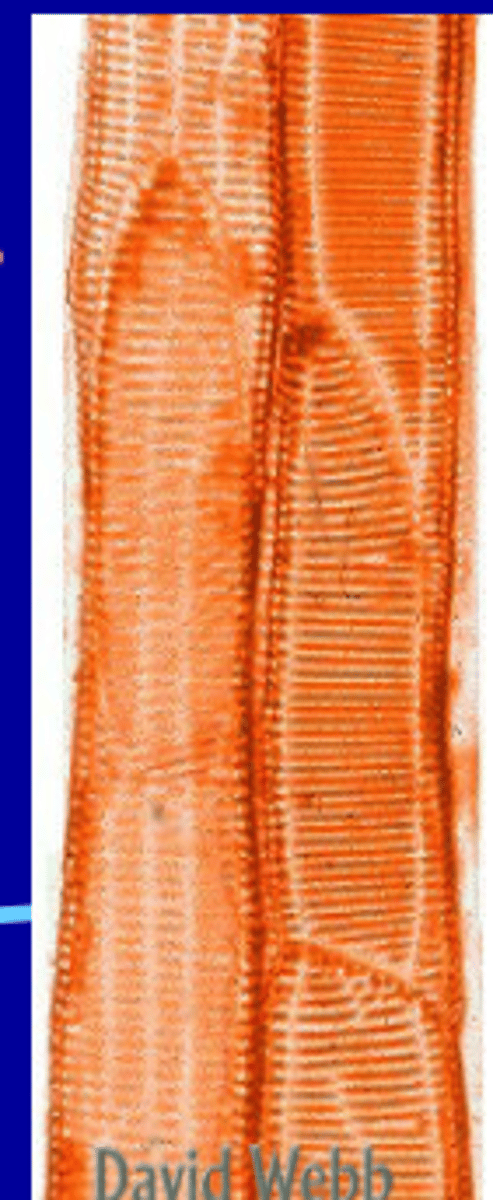
Tracheids
In the xylem, long, pointy cells that have perforations (pits) so water can seep out into neighboring cells. Contain lignin in their cell walls and are dead at maturity.
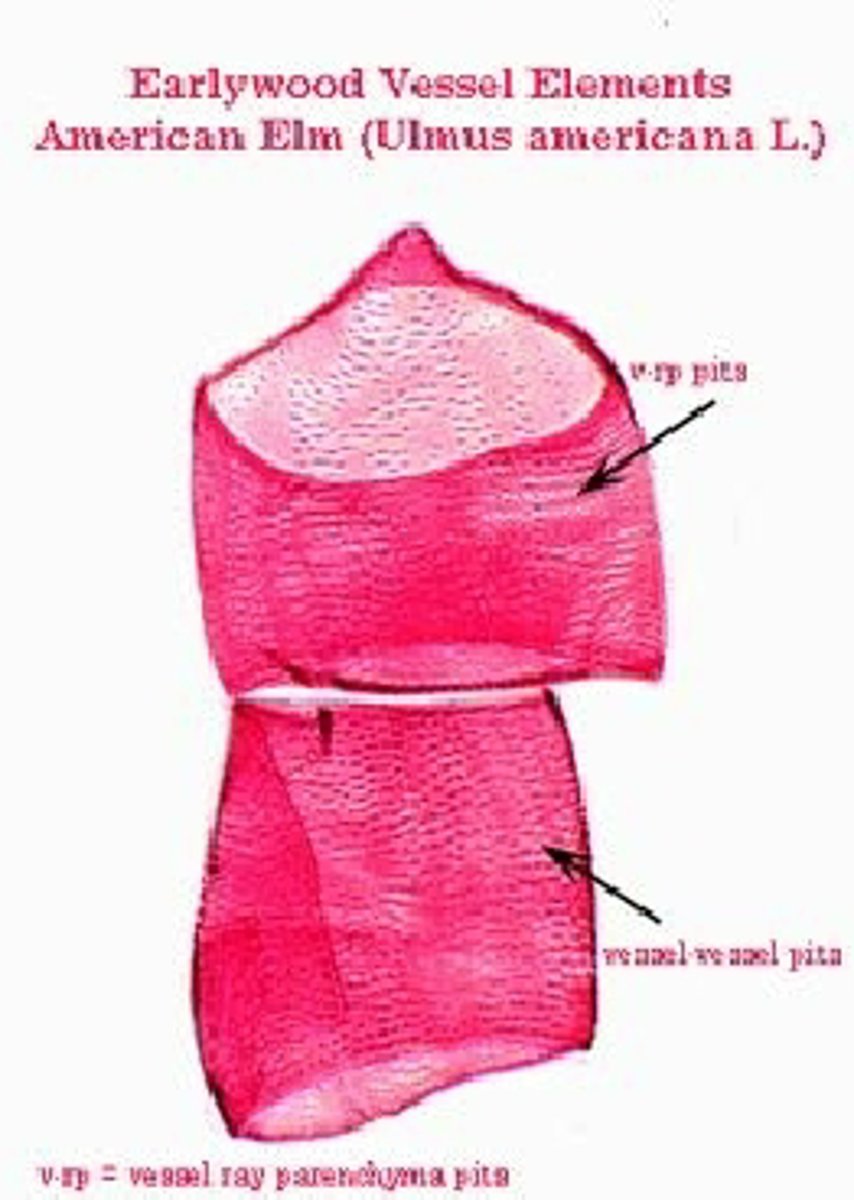
Vessel elements
In the xylem, shorter and wider cells with partially perforated walls. Contain lignin in their cell walls and are dead at maturity.
Phloem
-Part of the vascular tissue system
-Multidirectional
-Transports organic nutrients from where they are made to where they are needed
-Made up of living cells
-Consist of sieve-tube members and companion cells
Sieve-Tube members
In the phloem, wide, living cells which contain sieve plates at their ends, have a cytoplasm but NO NUCLEUS OR ORGANELLES (it is able to live through the companion cells)
Companion cells
In the phloem, living cells that maintain the metabolism of the sieve-tube member cells
Ground tissue system
-Includes various cells specialized for functions such as storage, photosynthesis, and support
-Contains 3 types of cells: Parenchyma, Collenchyma, Sclerenchyma
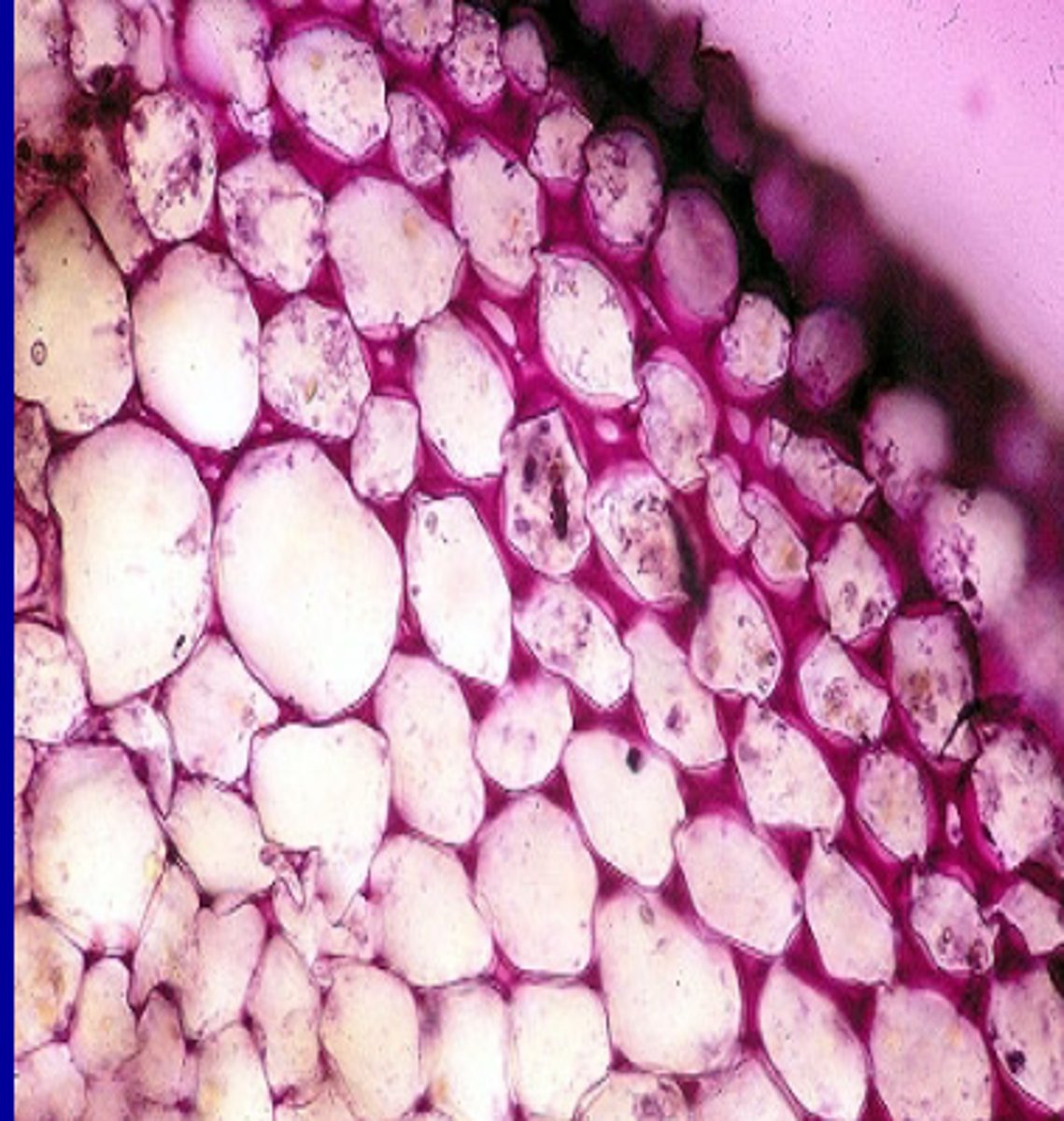
Parenchyma
-Part of the ground tissue system
-Also associated with vascular tissues
-Live at maturity
-Flexible primary cell wall
-Metabolically active
-Non specialized and can divide to become other cells
-Function is photosynthesis and storage
Collenchyma
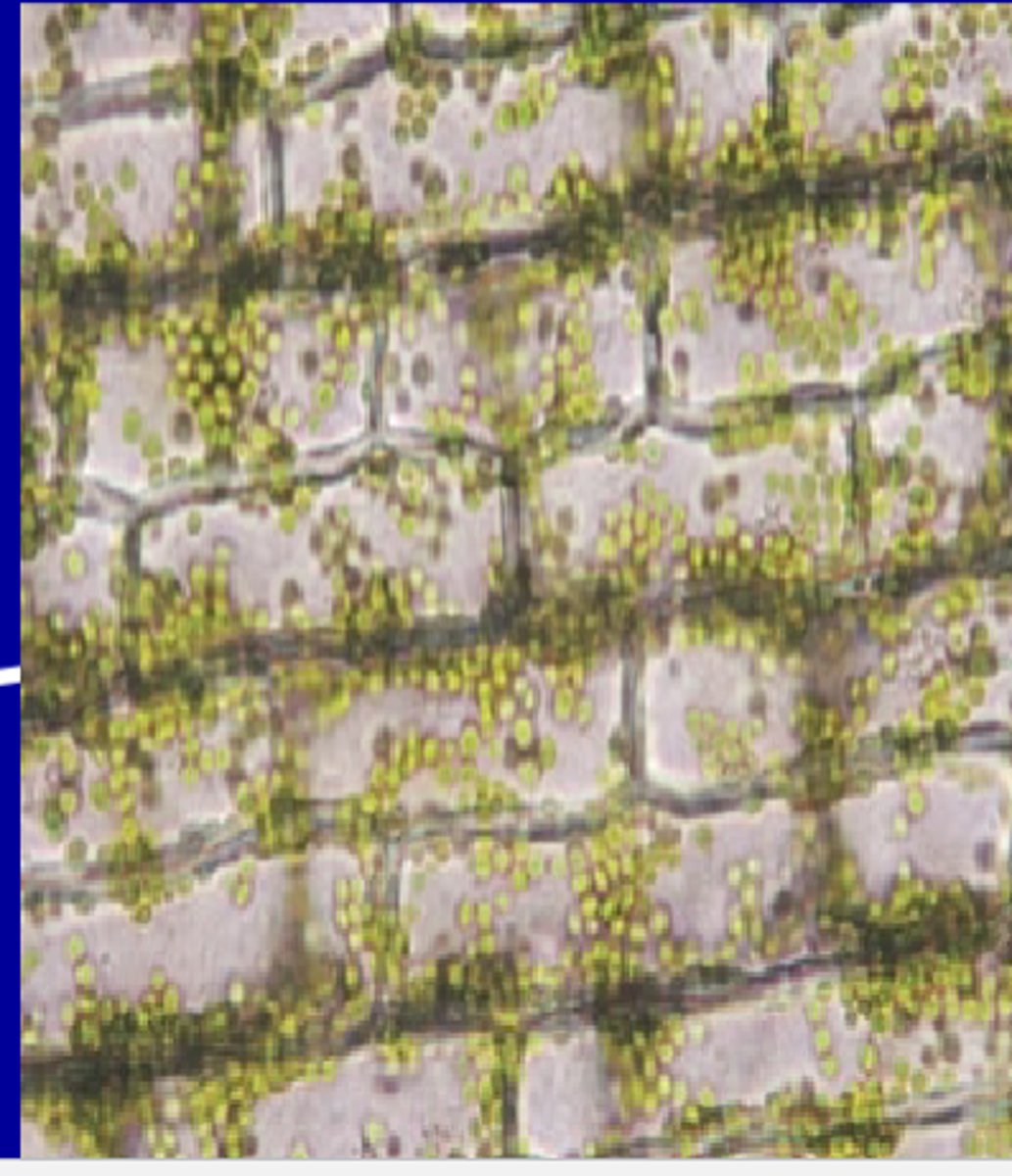
-Part of the ground tissue system
-Also associated with phloem
-Live at maturity
-Unevenly thickened primary cell wall
-Common in the ground tissues of stems and petioles
-Function is flexible support which allows for plant growth
Sclerenchyma
-Part of the ground tissue system
-Dead at maturity
-Thickened cell wall containing lignin
-Common in ground and vascular tissues
-Have two cell types (sclerids and fibers)
-Function is support
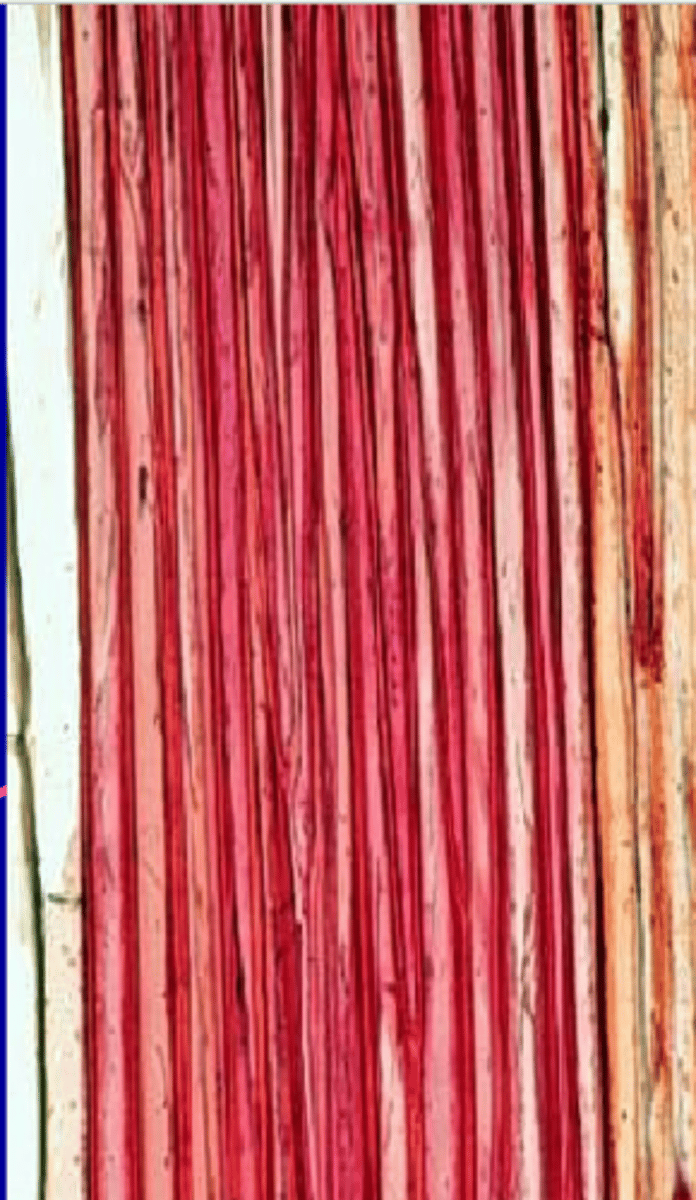

What are the two cell types in sclerenchyma?
-Sclerids (variable shape)
-Fibers (long and tapered)
Tissue organization of leaves
-Epidermal barrier
-Ground tissue
-Vascular tissue
Epidermal barrier in leaves
-Is interrupted by stomata, which allow carbon dioxide exchange between the surrounding air and the photosynthetic cells within a leaf
Ground tissue in leaves
-Is sandwiched between the upper and lower epidermis of the leaf
Vascular tissue in leaves
-Is continuous with the vascular tissue of the stem
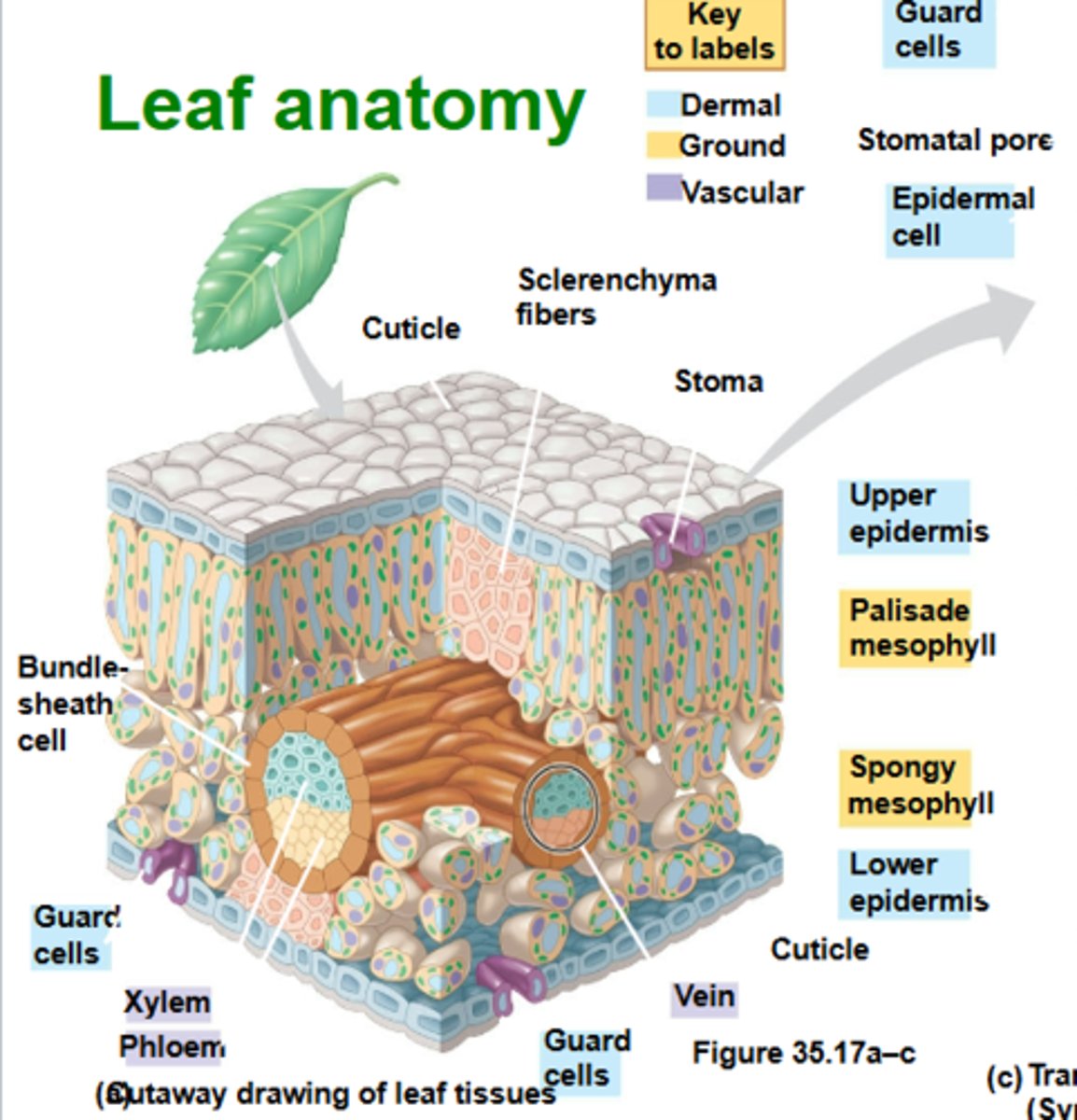
Leaf anatomy (in depth)
-Cuticle
-Sclerenchyma fibers
-Guard cells
-Stoma
-Upper epidermis
-Palisade mesophyll
-Bundle sheath cell
-Vein
-Xylem
-Phloem
-Spongy mesophyll
-Lower epidermis
How many layers of parenchyma cells do monocots have in their leaves
One
How many layers of parenchyma cells do dicots have in their leaves
Two (pallisade and spongy parenchyma)
Meristems
-In plants, structures that contain embryonic tissues that continuously generate cells for new organs
What are the embryonic tissues in plants
-Protoderm (gives rise to the dermal tissue
-Ground tissue
-Vascular cambium (gives rise to the vascular tissue)
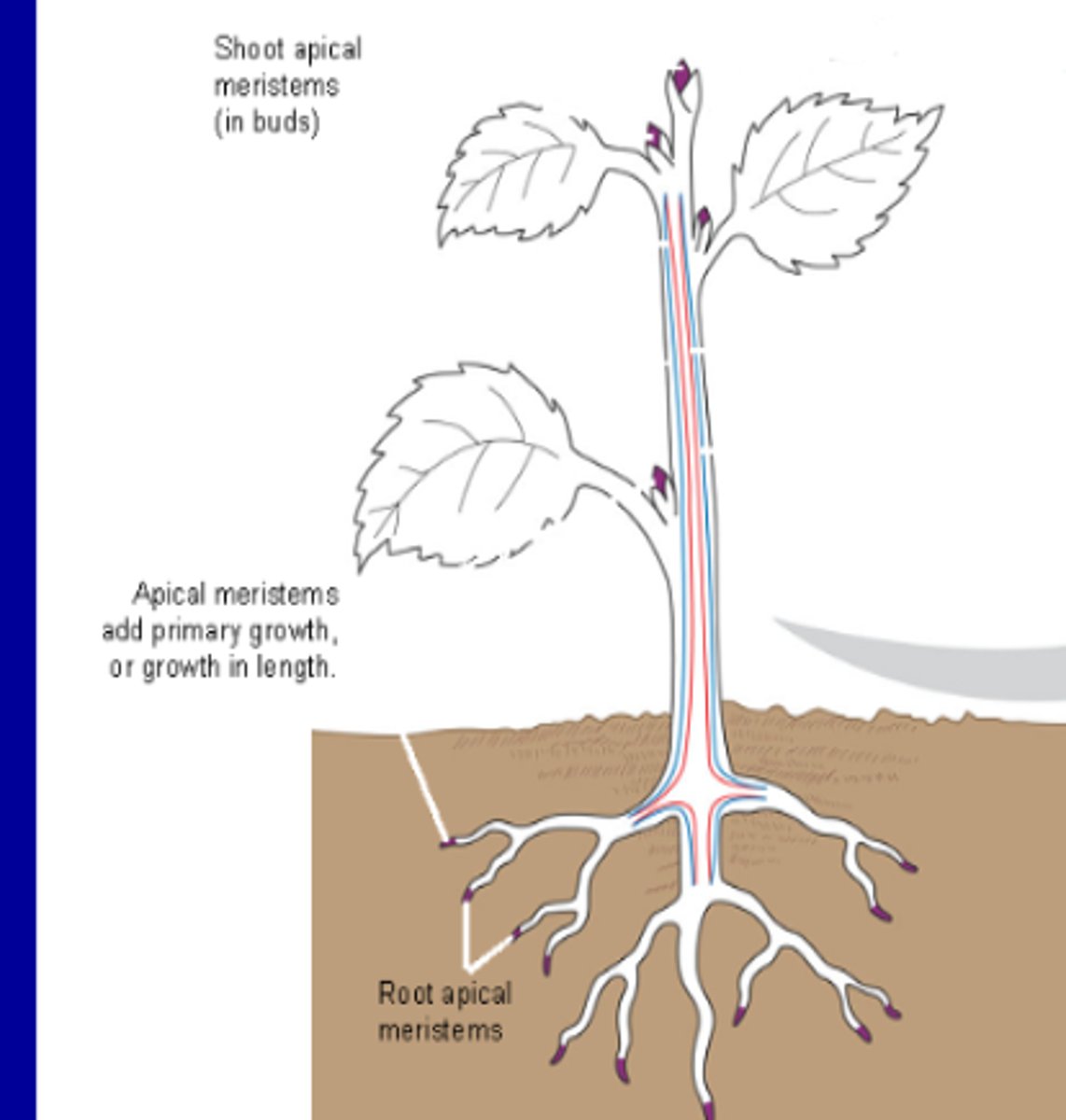
Apical Meristems
-Located at the tips of roots and shoots
-Elongate shoots and roots through primary growth
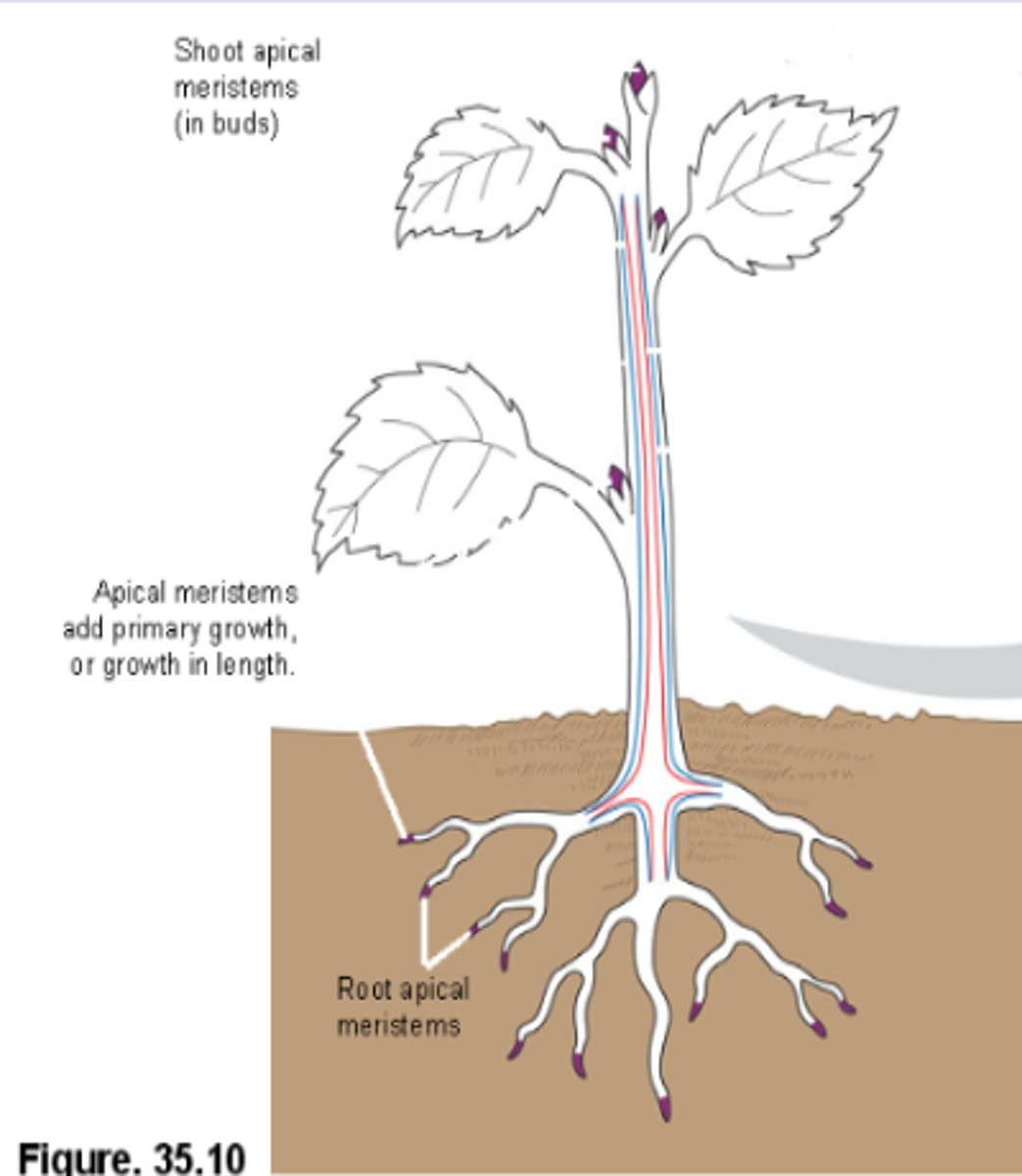
Primary Growth
-Growth in length of apical meristems in roots and shoots
-All plants have this
-Herbs only have this growth and flexible green stems
-There are annuals and biannuals
Apical shoot meristems
-A dome shaped mass of dividing cells at the tip of the terminal bud
-Gives rise to a repetition of internodes and leaf-bearing nodes
Stem Structure in Primary Growth of DICOTS
-Epidermis (one layer of cells, rarely more)
-Cortex (support tissues, contain all ground tissue cell types)
-Vascular Bundles (containing xylem, phloem, procambium)
-Pith (containing parenchyma cells)
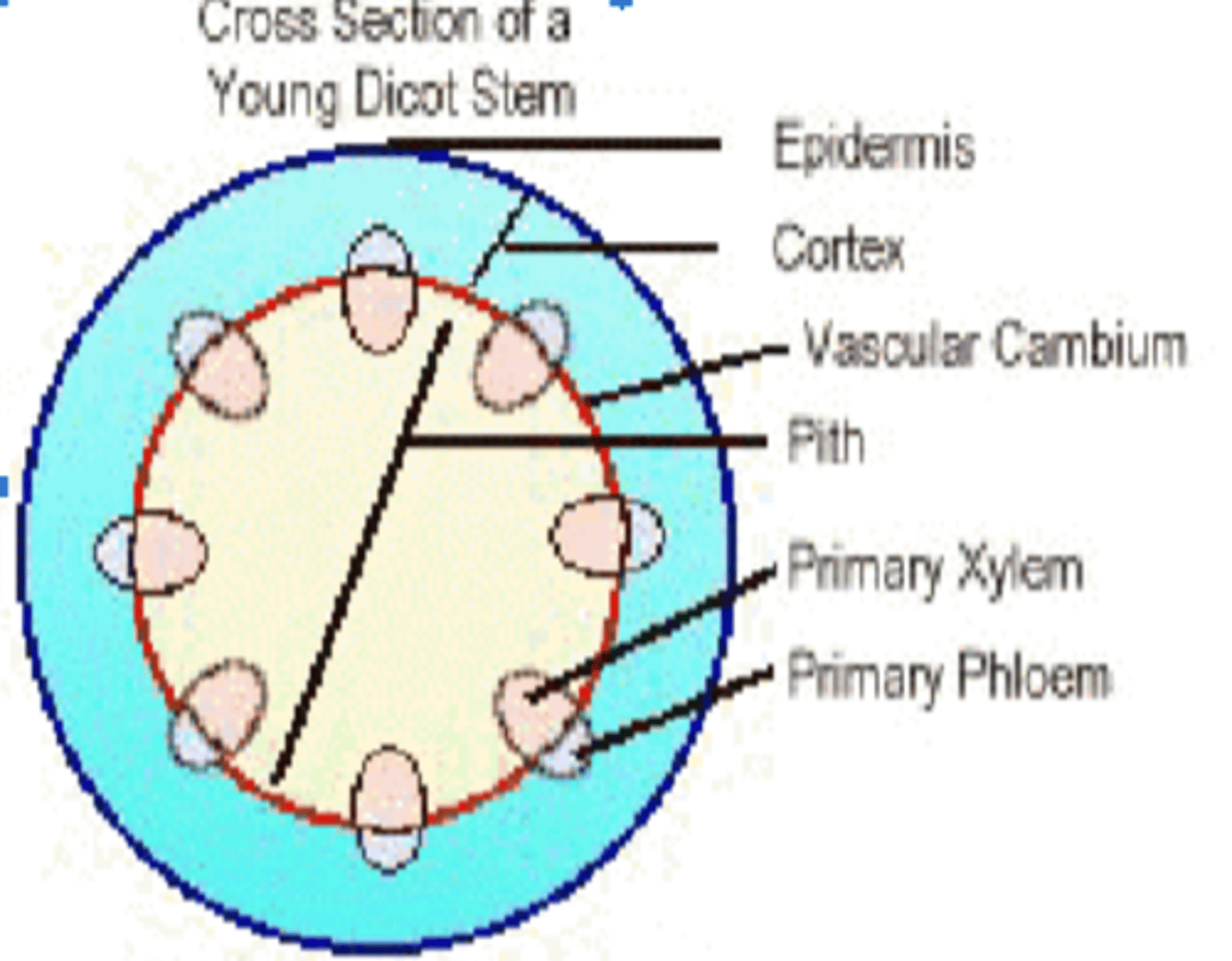
Stem Anatomy in Primary Growth of DICOTS
-Epidermis
-Cortex
-Vascular Cambium (in a ring)
-Primary phloem (on the OUTSIDE of the vascular cambium)
-Primary xylem (on the INSIDE of the vascular cambium)
-Pith
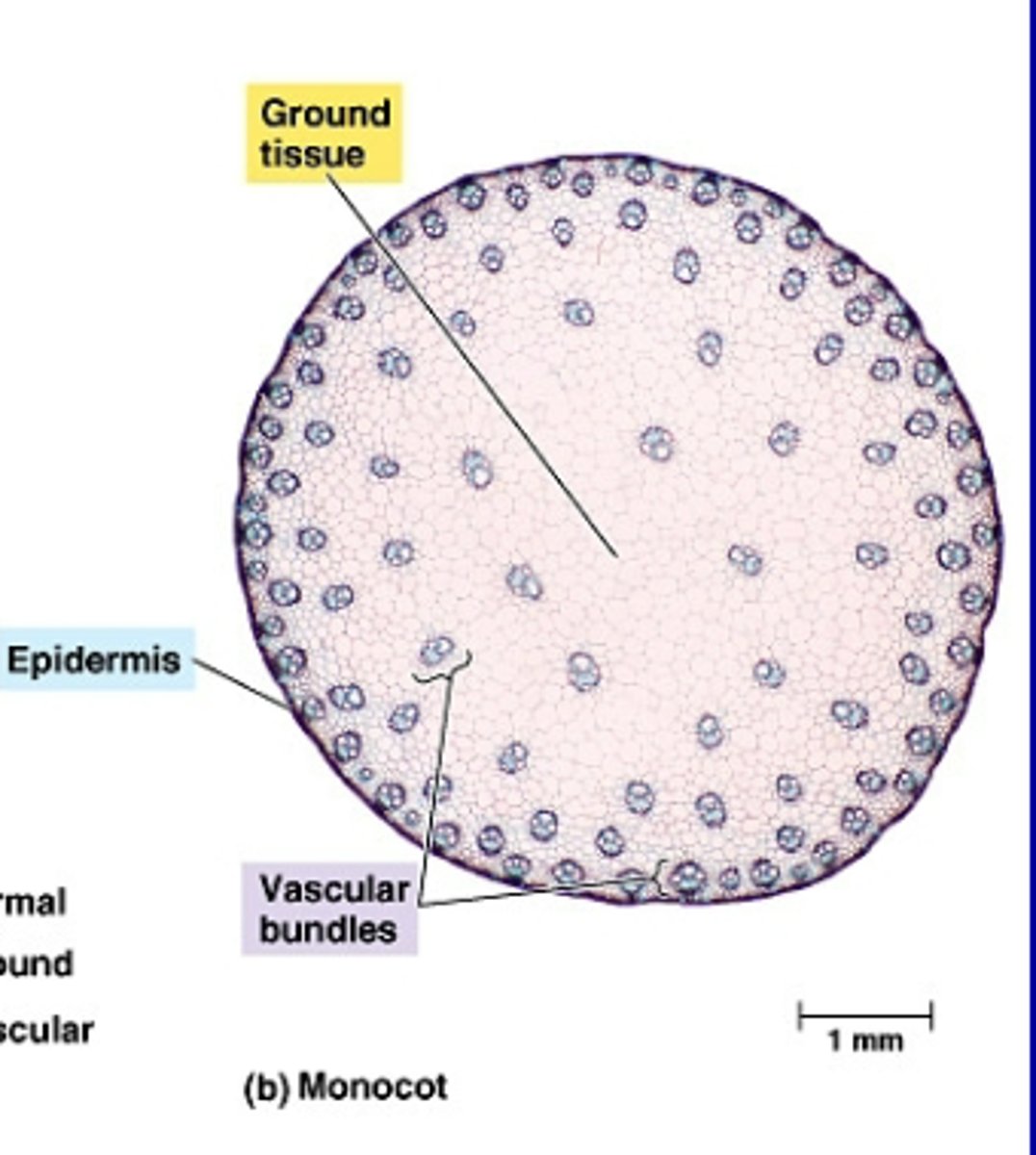
Stem Structure in Primary Growth of MONOCOTS
-The vascular bundles are scattered throughout the ground tissue, rather than forming a ring
-Closed vascular bundle
-No vascular cambium
-No secondary growth
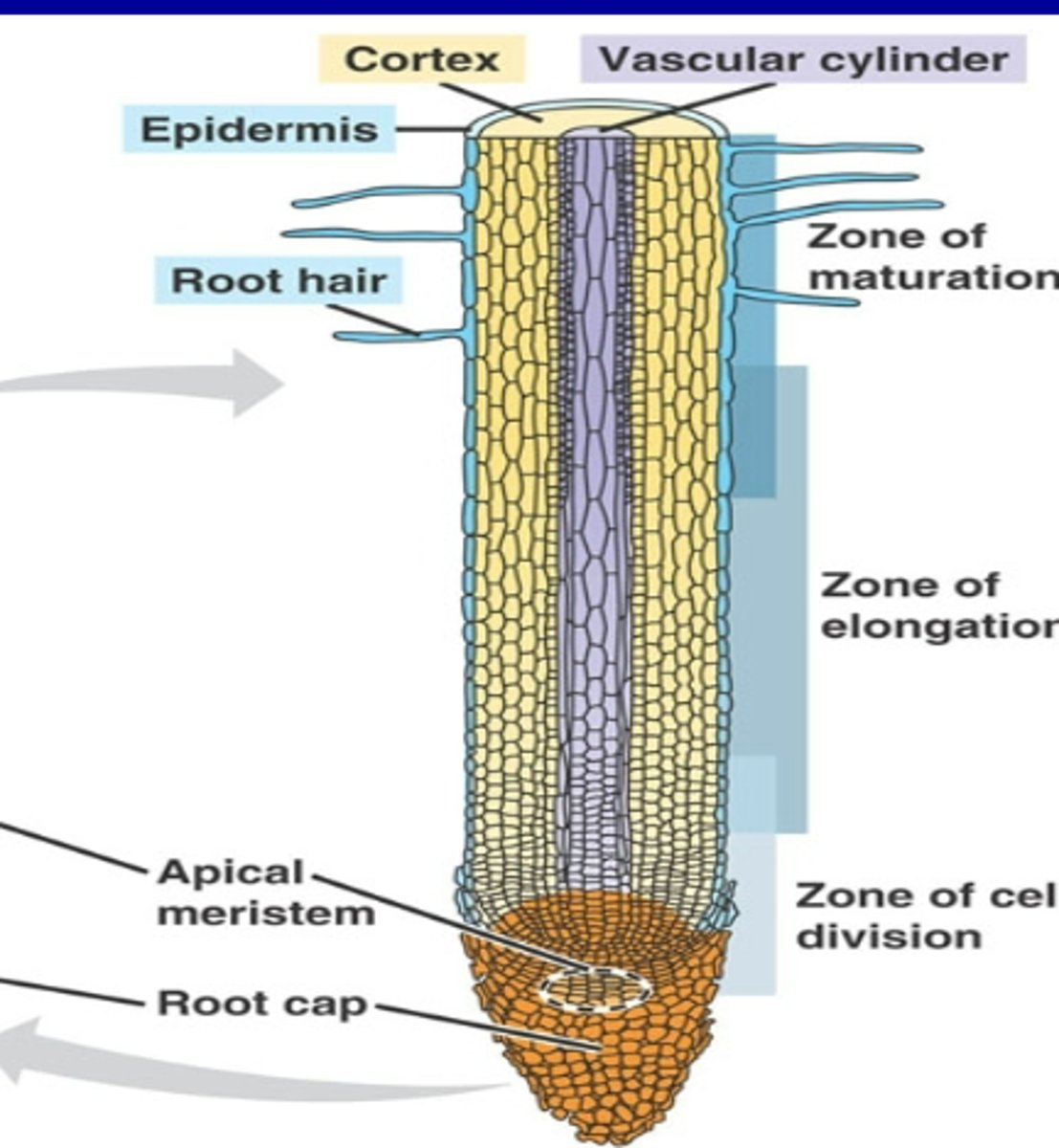
Primary Growth of Roots
-The root tip is covered by a root cap, which protects the delicate apical meristem as the root pushes through soil during primary growth
Root Anatomy in Primary Growth
-Root Hairs
-Epidermis
-Cortex
-Vascular cylinder
-Zone of maturation (highest of the three zones)
-Zone of elongation (middle of the three zones)
-Zone of cell division (lowest of the three zones)
-Root cap
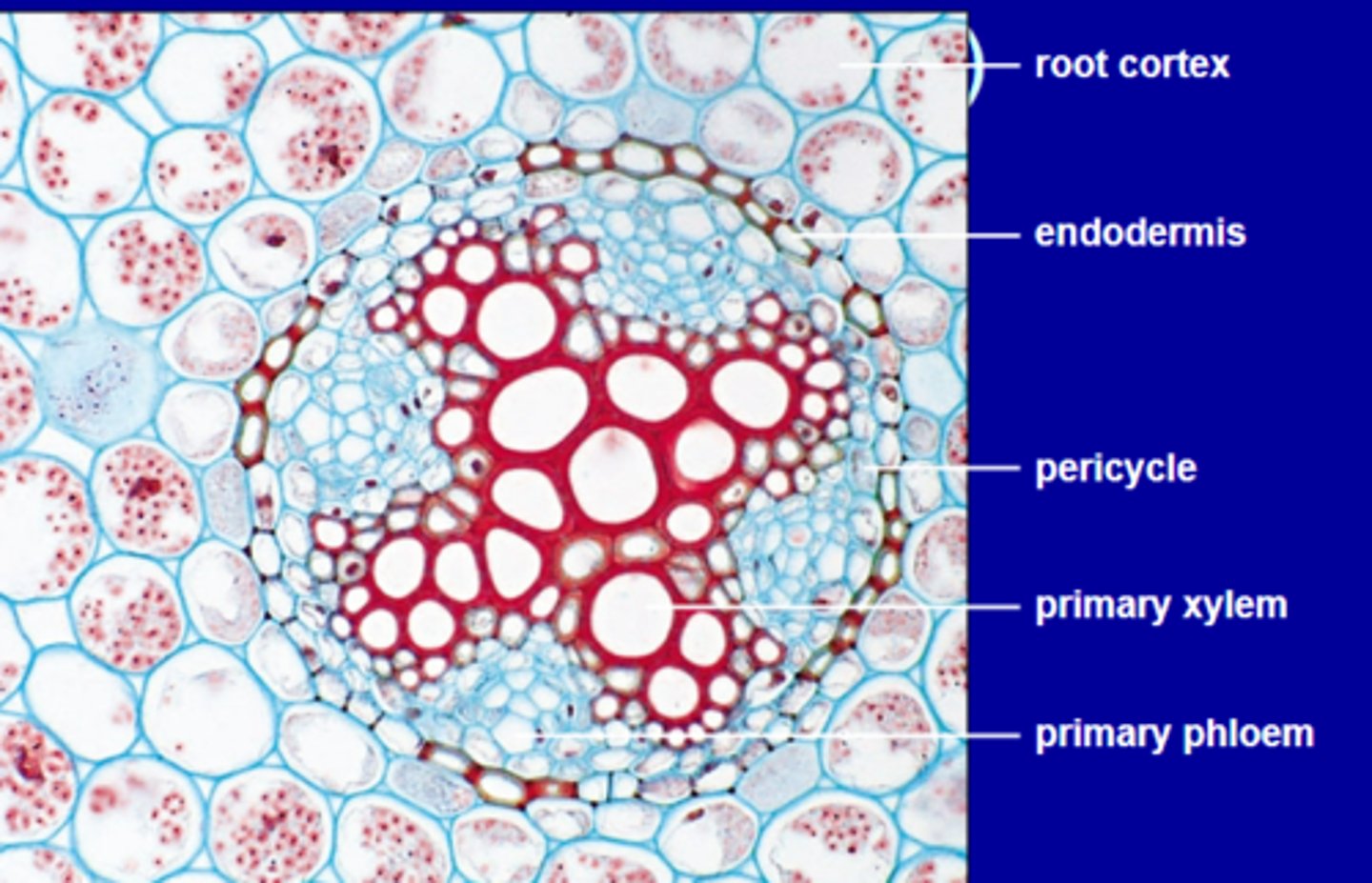
Primary Tissue Organization of roots in Primary Growth of DICOTS
-Root cortex
-Endodermis
-Pericycle (lateral roots arise within here)
-Primary xylem
-Primary phloem
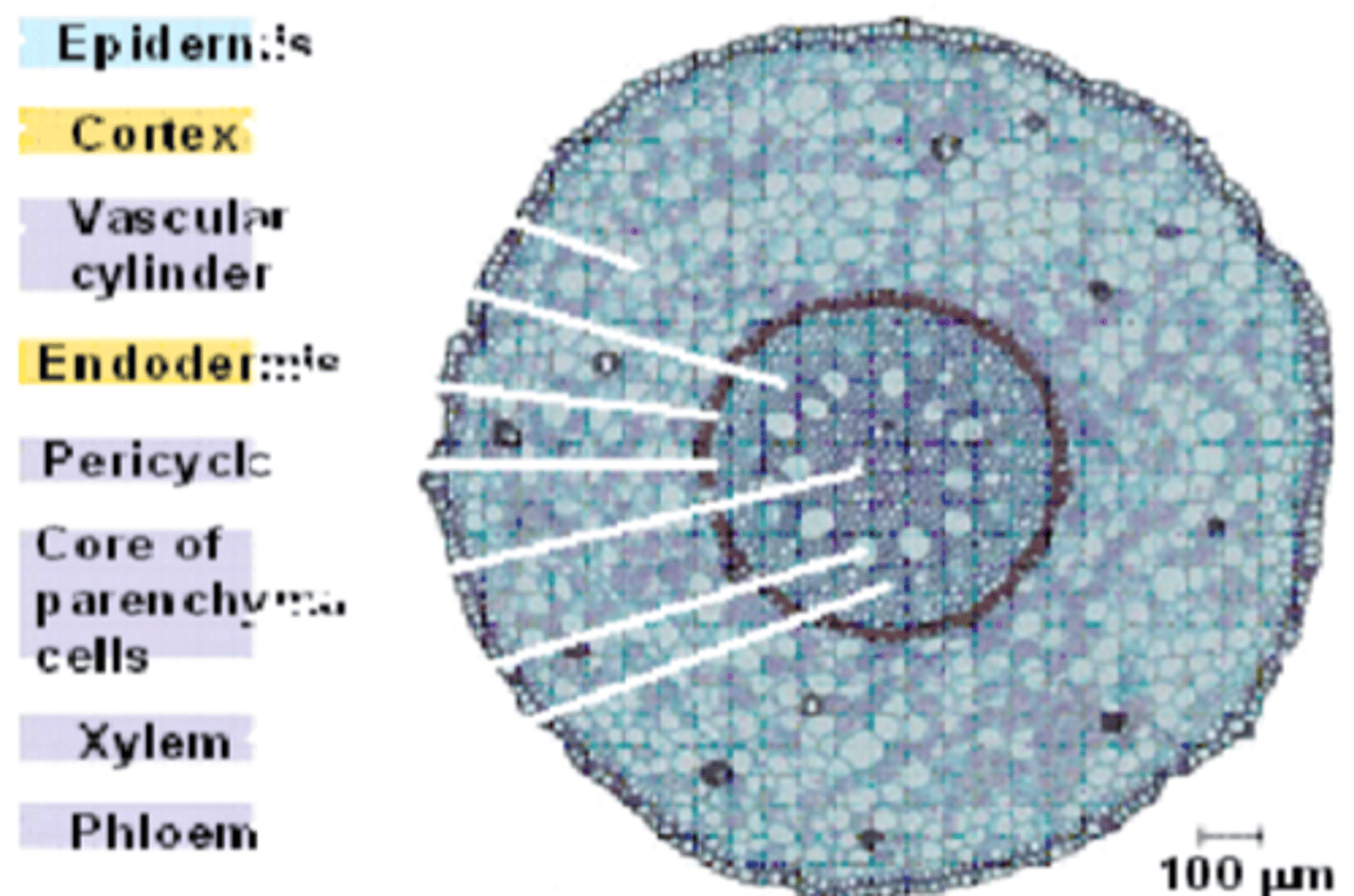
Primary Tissue Organization of roots in Primary Growth of MONOCOTS
-Epidermis
-Cortex
-Vascular cylinder
-Endodermis
-Pericycle
-Core of Parenchyma Cells
-Xylem
-Phloem
Root Structure in Primary Growth
-Epidermis with root hairs
-Cortex
-Endodermis with Casparian strips
-Stele (vascular tissue)
-Movement of water and nutrients (apoplastic pathway or symplastic pathway)
Apoplastic route
-Water sneaks between the cells between the cell walls until it hits the endodermis
-Goes through the endodermal cell and into the xylem
-Faster than symplastic pathway
-No options for filtration
Symplastic route
-Water and whatever is dissolved in it goes through the cytoplasm of every single cell until it hits the endodermis and then goes into the cytoplasm of the endodermis
-Slower than apoplastic
-Offers several avenues for filtration
Secondary Growth
-Adds girth to stems and roots in woody plants (mainly dicots)
-Occurs in stems and roots of woody plants but rarely in leaves
-The secondary plant body consist of the tissues produced by the vascular cambium and cork cambium
Lateral Meristems
Consists of the vascular cambium (red) and cork cambium (blue) in secondary growth
Vascular Cambium in Secondary Growth
-Cylinder of meristematic cells one cell thick
-Develops from the original vascular cambium within the vascular bundles and some parenchyma cells in the cortex
-Mostly stems and roots of dicots
-Produces xylem inward and phloem outward
Cork Cambium in Secondary Growth
-Cylinder of meristematic cells on cell thick
-Mostly stems and roots of dicots
-Develops from parenchyma cells in the cortex
-Forms cork to the outside
-Cork cells contain lignin and suberin in their cell walls and are dead at maturity.
-Lenticels are cuts through the cork layer which allow gases into the deeper layers of plant tissues
Anatomy of a tree trunk
-Bark (Periderm (cork, cork cambium), Living Phloem)
-Vascular cambium
-Sapwood (conducting secondary xylem)
-Heartwood (nonconducting secondary xylem)
Girdling plants
removal of bark in girdle around the trunk of a tree.
Gravitropism
Growth in the direction of gravity
Positive gravitropism is growth...
down
Shoots grow towards...
light
Transport in the xylem tissue
-Unidirectional
-Fluids move by adhesion, cohesion, evaporation, and osmosis
-Theories of movement: capillary action, root pressure, transpiration pull
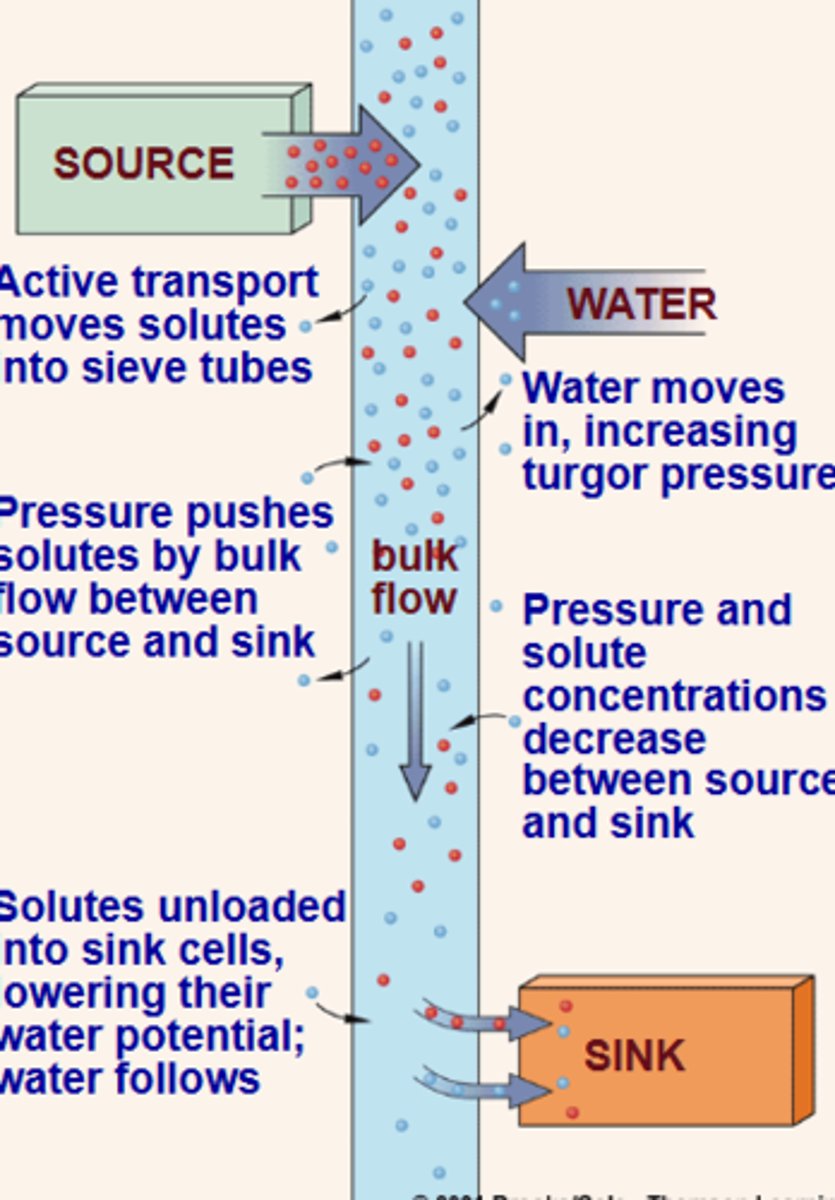
Transport in the phloem tissue
-Multidirectional
-Fluids move by mass flow
-Source (ex: old leaf) vs. Sink (ex: fruit)
Source vs. Sink
Kingdom Animalia
-Eukaryotic
-Multicellular
-Heterotrophic
-Lack cell walls
-Unique tissues (nervous and muscular)
What are the two major groups of kingdom animalia?
-Invertebrates
-Vertebrates
What are the advantages of multicellularity?
-Large size
-Mobility
-Stable internal environment
-Relatively independent from the environment
Origin of Animalia
-Colonial Choanoflagelate (protista)
-The choanoflagelate had an infolding of cells to form a digestive cavity
The phylogenetic tree of Kingdom Animalia (we must memorize!!)
Defining characteristics:
Origin:
-Ancestral choanoflagelate
Tissues:
-Parazoa
-Eumetazoa
Symmetry/Germ Layers:
-Radiata/Diploblastic
-Bilateria/Triploblastic
Body Cavity:
-Absent body cavity
-Present body cavity
Coelom?:
-Pseudocoelomates
-Coelomates
Fate of Blastopore:
-Prosotomia
Phyla:
-Placozoa (NOT LISTED ON THE PHOTO)
-Porifera
-Cnidaria
-Ctenophores
-Platyhelminthes
-Rotifera
-Nematoda
-Nemertea
-Mollusca
Types of symmetry
-Radial
-Bilateral
-Asymmetry
Radial symmetry
Multiple planes of symmetry
Bilateral symmetry
One plane of symmetry
Asymmetry
No planes of symmetry
Oral
In radial symmetry, the mouth
Aboral
In radial symmetry, the anus
Anterior
In bilateral symmetry, the front