Chapter 9 Stochastic Effects and Late Tissue Reactions of Radiation in Organ Systems
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
radiobiology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Epidemiology

“science that deals with the incidence, distribution, and control of disease in a population.” (Travis, 1989)
Studies consist of observations and statistical analysis of data, such as the incidence of disease within groups of people.
Studies include the risk of radiation-induced cancer.

what does it mean when something has a A stochastic effect?
A stochastic effect is a radiation effect where the probability of occurrence increases with dose, but the severity of the effect does not depend on the dose. Examples include cancer and genetic mutations
How do we model the relationships between dose to a population and adverse effects caused by ionizing radiation?
These relationships are modeled using radiation dose–response curves, which graphically demonstrate the relationship between radiation dose and the observed biological effects.
What are the four basic types of dose-response curves?
The four basic types of dose–response curves are:
Linear nonthreshold (LNT)
Linear threshold
Nonlinear threshold
Sigmoid (S-shaped) nonlinear threshold
out of the four basic types of dose-response curves which one is utilized for the ALARA model?
The Linear Nonthreshold (LNT) model is used for the ALARA (As Low As Reasonably Achievable) model.
Studies on populations exposed to high doses of ionizing radiation support the hypothesis that radiation causes cancer. Name two of the groups mentioned in the chapter.
Atomic bomb survivors of Hiroshima and Nagasaki
Chernobyl nuclear disaster victims
(radiologists or radiologic technologists studied in historical epidemiologic research)
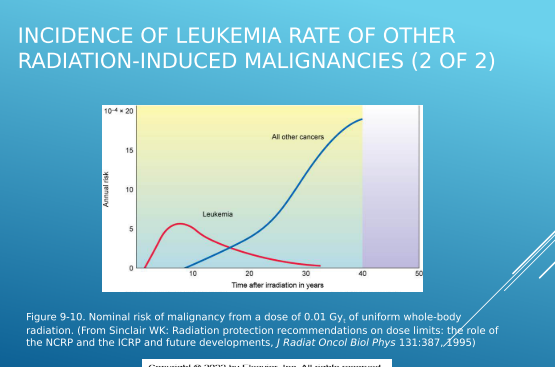
What does “extrapolation from high dose-response data” mean, and why is it controversial?
It means predicting cancer risk at low doses of radiation by using data collected from high-dose exposures.
It is controversial because the risk at low doses is not directly measurable, and may be overestimated or underestimated depending on the model used.
Children in Poland and other Eastern European countries were issued (WHAT?) to mitigate the risk of thyroid cancer following the Chernobyl disaster.
1.Children in Poland and other Eastern European countries were issued Potassium iodide pills to mitigate the risk of thyroid cancer following the Chernobyl disaster.
what women have lower cancer rates?
In general, Japanese women have a lower incidence of breast cancer than U.S. and Canadian women.

WHAT PRECENT of the exposure to the people of Nagasaki by the denotation of a plutonium bomb was in the form of gamma radiation?
90 % of the exposure to the people of Nagasaki by the denotation of a plutonium bomb was in the form of gamma radiation.
Explain the difference between a genetic effect and a teratogenic effect
Genetic effects occur when radiation damages DNA in sperm or ova, potentially causing heritable mutations passed on to future generations.
Teratogenic effects (also called embryologic effects) occur when the embryo or fetus is exposed to radiation in utero, causing birth defects, but not inherited in future generations.
Radiation-induced damage at the cellular level may lead to measurable somatic and hereditary damage in the living organism as a whole later in life. These outcomes are called late effects and are the long-term results of radiation exposure.
WHAT ARE SOME Examples of measurable late biologic damage?

Examples of measurable late biologic damage
Cataracts
Leukemia
Genetic mutations

WHY ARE Epidemiologic studies of significant value to radiobiologists?

Epidemiologic studies are of significant value to radiobiologists who use the information from these studies to formulate dose–response estimates to predict the risk of cancer in human populations exposed to low doses of ionizing radiation.

Carcinogenesis is also known as?

tumorigenesis

Carcinogenesis definition
The formation of cancer / Also known as tumorigenesis

what is the most significant late stochastic effect ?
Cancer is the most significant late stochastic effects caused by exposure to ionizing radiation.
This effect is a random occurrence that does not seem to have a threshold and for which the severity of the disease is not dose-related.

how is Radiation Dose–Response Relationship demonstrated graphically ?

Radiation dose–response relationship is demonstrated graphically through a curve that maps the observed effects of radiation exposure in relation to the dose of radiation received.

The DR curve is either ? or ?

The DR curve is either linear (straight line) or nonlinear (curved to some degree). The observed effects of radiation exposure may be the incidence of a disease (stochastic), or it may be the severity of an effect(deterministic).


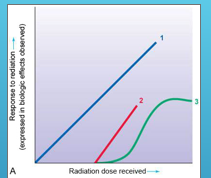
what does line 1 the blue line represent ?
1 represents a linear (straight-line) non-threshold curve of radiation dose–response relationship

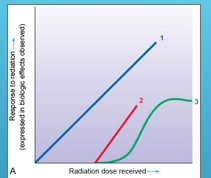
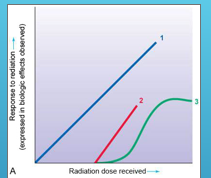
what does line 2 the red straight line represent?
2 represents a linear (straight-line) threshold curve of radiation dose–response relationship
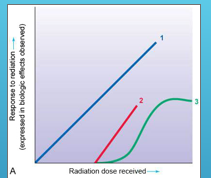
what does line 3 the green line represent ?
3 represents a nonlinear threshold curve of radiation dose–response relationship.

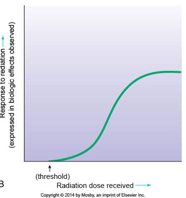
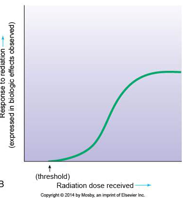
what is the Sigmoid (S-shaped, hence nonlinear) threshold curve of radiation dose?

Sigmoid (S-shaped, hence nonlinear) threshold curve of radiation dose–response relationship generally employed in radiation therapy to demonstrate high-dose cellular response.

theoretically 1 photon can cause damage true or false?
TRUE 1 PHOTON CAN CAUSE DAMAGE
With reference to ionizing radiation, threshold means?

With reference to ionizing radiation, threshold means that below a certain radiation level or dose, no biologic effects are observed. Biologic effects begin to occur only when the threshold level or dose is reached.


TRUE OR FALSE No radiation dose can be considered absolutely safe with the severity of the biologic effects increasing directly with the magnitude of the absorbed dose ?
TRUE
Non-threshold indicates?

Non-threshold indicates that a radiation absorbed dose of any magnitude has the capability of producing a biologic effect.
For the linear non-threshold curve biologic effect responses will be caused by ionizing radiation in living organisms in a directly proportional manner all the way down to dose levels approaching zero.

The BEIR III committee, in its 1980 report, focused on?
"The Effects on Populations of Exposure to Low Levels of Ionizing Radiation".Stochastic effects (e.g., cancer) and hereditary effects at low-dose levels from low-LET radiation, such as the type of energy used in diagnostic radiology, appear to follow a linear-quadratic nonthreshold curve.


BEIR IN 1990
Revised risk estimates indicated that the risk of radiation exposure was about three to four times greater that previously projected.
Currently the committee recommends the use of the linear nonthreshold curve of radiation dose–response for most types of cancer.
LNT curve implies that the biologic response to ionizing radiation is directly proportional to the dose received.
what does it mean when they say establishing radiation protection standards, the regulatory agencies have chosen to be conservative

In establishing radiation protection standards, the regulatory agencies have chosen to be conservative—that is, to use a model that may overestimate risk but is not expected to underestimate risk.

Models used by researchers for extrapolation of risk from high-dose to low-dose data

Linear
Linear-quadratic

1989 BEIR V report supported what ?
1989 BEIR V report supported the linear-quadratic model for leukemia only
For all other cancers the BEIR V Committee recommended adoption of the linear model to fit the available data.

Although studies from Hiroshima and Nagasaki confirm that high doses of ionizing radiation cause cancer, does radiation have a highly effective cancer causing agent?

no radiation is not a highly effective cancer-causing agent. (Although studies from Hiroshima and Nagasaki confirm that high doses of ionizing radiation cause cancer, radiation is not a highly effective cancer-causing agent.)

Follow-up studies of approximately 82,000 atomic bomb survivors from 1950 to 1987. Reveal an excess of only 250 cancer deaths attributed to radiation exposure; instead of the expected 4500 cancer deaths, 4750 actually occurred

about every 300 atomic bomb survivors, 1 died of a malignancy attributed to an average whole-body radiation dose of approximately 0.14 Sv
