X-ray Detectors
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
what is an analogue detector and give examples
produces a continuous electrical signal
examples:
screen film
image intensifier
what is a digital detector and give examples
converts incoming x-ray energy directly into numerical data, allowing instant image processing and storage
Examples:
computed radiography , use a CR plate
integrated digital systems : direct conversion using a-se Amorphous Selenium , indirect conversion , x-rays converted to light then to electrical signal , uses charge coupled device or a-si amorphous silicon
what are phosphors
substances that emit light when exposed to radiant energy
what are xray phosphors
covert x-ray photons into visible light
what are scintillators
solids that emit light when exposed to ionizing radiation
what 2 step system do x-ray detectors usually have
phosphor layer
light detection device
what are fluorescent phosphors
emit light very quickly after simulation by x-rays
what are phosphorescent phosphors
emit light after a delay
which materials are ideal as phosphors
materials with a higher Z , photoelectric effect dominates, best conversion of x-rays to light photons
the x-eays must first interact with phosphors atoms mainly through which 2 effects?
Photoelectric effect
Compton scattering
what is a valence band
where electrons normally are, bound to the atom
what id s conduction band
where electrons can move freely, conduct electricity or generate light when dropping back
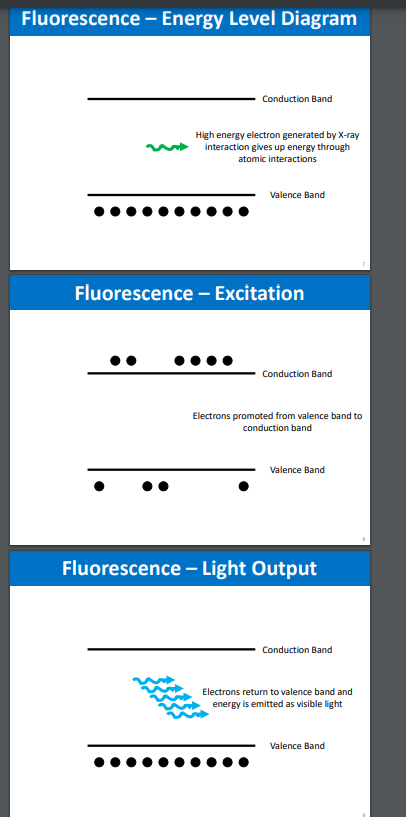
explain a fluorescene energy level diagram
high energy electron generated by x0ray interaction gives up energy through atomic interaction
electrons promoted from valence band to conduction band
electrons return to valence band and energy is emitted as visible light
explain phosphorescence energy level diagram
high energy electron generated by x-ray interaction give up energy through atomic interaction
electrons excited from valence to conduction band
some electrons return immedistly to the valence band and fluorescnece takes place
some electrons fill energy traps
after a delay some electrons in the energy traps return to valence band and light is produced

what is photo-simulated luminescence
when irridation with IR laser light causes electrons in energy traps to return to valence band and light is emitted
what is bright white light used for
to remove any residual charge and the phosphor is returned to its ground state
what are the two types of common phosphors and give what they are used for
turbid phosphor goddlinium oxysulphide, used for screen/film
structured phosphor caesium iodide, used for integrated digital systems
what is a screen/film
a film coated in silver halide crystals suspended in gelation , suspended in an emulsion. This is being phased out
how does a film work
light from the phosphor screen hits the silver halide crystals
some silver ions are reduced to metallic silver→ image invisible
chemical treatment reduces exposed silver halide ions to metallic silver → forms visible black image
unexposed silver halide ions are removed
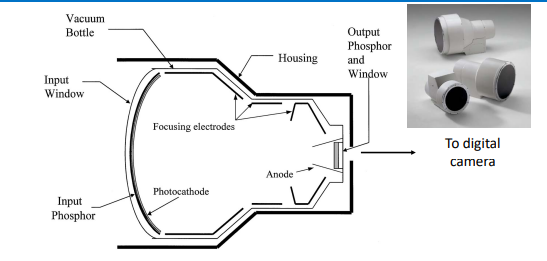
what is an image intensifier
a device used in fluoroscopy to convert x-rays into bright visible images in real time , also being phased out
how does an image intensifier work
x-rays exit a patient and hit a phoshor layer
emitted light hits a photocathode, coverts photons to electrons
electrons are accelerated and focused by an e.f which increases brightness
electrons hit output phosphor+window which convert back into light
what is computed radiography
a digital x-ray imaging system that uses phosphor plates instead of traditional film
how does computed radiography work, what is it only for and what are some properties
image is stored in the phosphor plate as a latent image and then read by a laser scanner to produce a digital image.
only for radiography
reusable and digital
what is an integrated digital system CCD
indirect digital x-ray detectors that use phosphor to convert x-rays to light which is then captured by a CCD camera, converts light to a digital signal and then its digitised
what happens in CCD, what is it used for
CSI scintillator converts x-ray to light
lens or fibre optics transmit light to ccd panel
ccd commonly used in cameras turns light into a electrical signal that is then digitised
used for radiography and fluoroscopy
replaced by flat panels
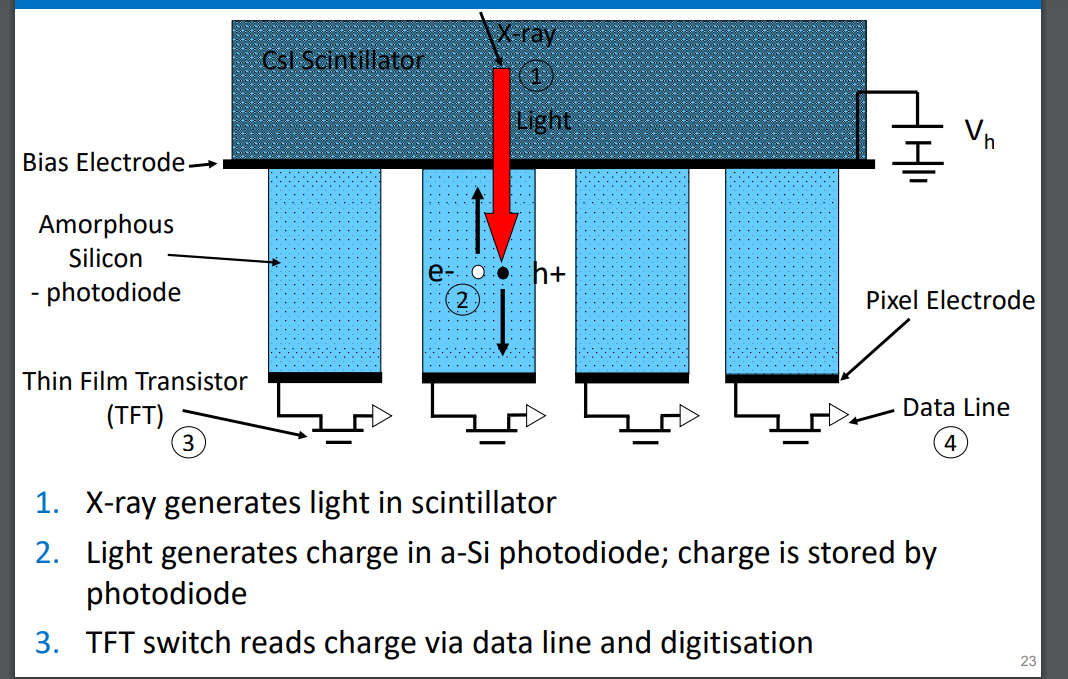
how does an indirect flat panel detector work
Csi scintillator converts x-rays to light , this makes it indirect
a-si (Amorphous silicon) detects light and produces electric charge proportional to light intensity and stores it. (acts as a photodiode)
each photodiode is paired with an TFT switch (thin film transistors)
TFT activated row by row , transferring stored charge to electronics which is then digitised
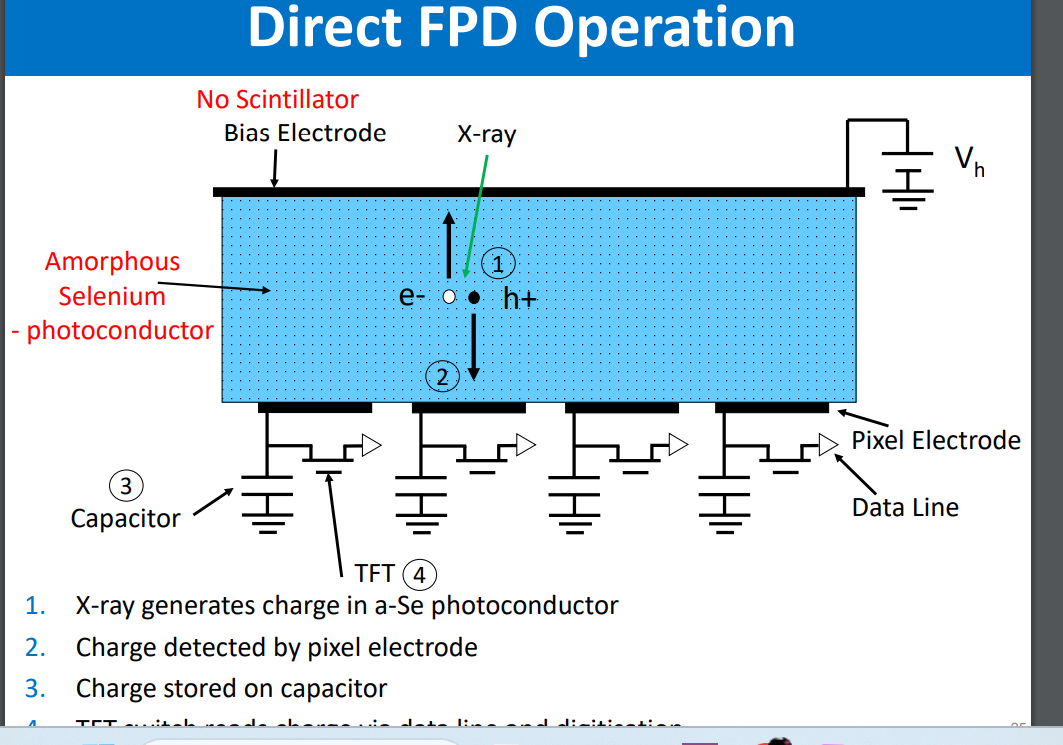
how does an indirect flat panel detector work and whats it used for
no Csi scintillator
a-se used instead
added capacitors
mainly for low energy applications i.e mamography
x-ray generates charge in a-se photoconductor
charge detected by pixel electrode
charge stored by capacitor
TFT switch reads charge via data line and its digitised
what is FPD array operation
a large matrix of tiny detector elements, converts x-ray to electrical signals which are then digitised to form a digital x-ray image
how does FPD array operation work
a row of TFT’s is turned on electronically
stored charge in those pixels flows out into electronics and digitised
the row is turned off, next row is activated
entire matrix is read out row by row

what are some FPD properties
used for radio and fluoroscopy
high spatial resolution
high temporal resolution
excellent image quality
what is spatial resolution
How much detail you can see.
what is temporal resolution
How well the system freezes motion / how fast it can image.
ability of an imaging system to accurately capture motion over time.
what is FPD pixel binning , give advantages and disadvantages
combining signals from neighboring pixels to form a superpixel
allows faster frame rate (fewer superpixels need to be read)
increases signal to noise ratio ( summing charges reduces effect of electronic noise)
lower spatial resolution (fine details blurred)
what is meant by signal to noise ratio
How clear the image is compared to the amount of graininess or random noise.
Higher SNR → clearer, smoother, more diagnostic image
Lower SNR → grainy, noisy, poor-quality image