excretion 5.1.2
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What is excretion
the removal/processing of waste from the body
What happens in deamination
what happens in transamination
Amino group (NH2) is removed from each amino acid with a H+
These combine to form NH3 (ammonia)
The part left of the amino acid is called a keto acid which can be converted into glycogen, fat and storage, be converted into glucose
an amino group is removed from an amino acid converting it into ammonia
What happens in the ornithine cycle
Ammonia is combined with carbon dioxide to form urea, which the kidneys remove from the body
What is detoxification and outline it’s role in the liver
breakdown of substances that are not needed or that are toxic
Once consumed alcohol or ethanol it’s absorbed in the stomach and transported in the blood until it reaches hepatocytes
In hepatocytes the enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase converts ethanol into ethanal which is converted into molecules for respiration
Continuous alcohol detoxification can cause liver problems
Where is the liver found
Below the diaphragm in abdomen
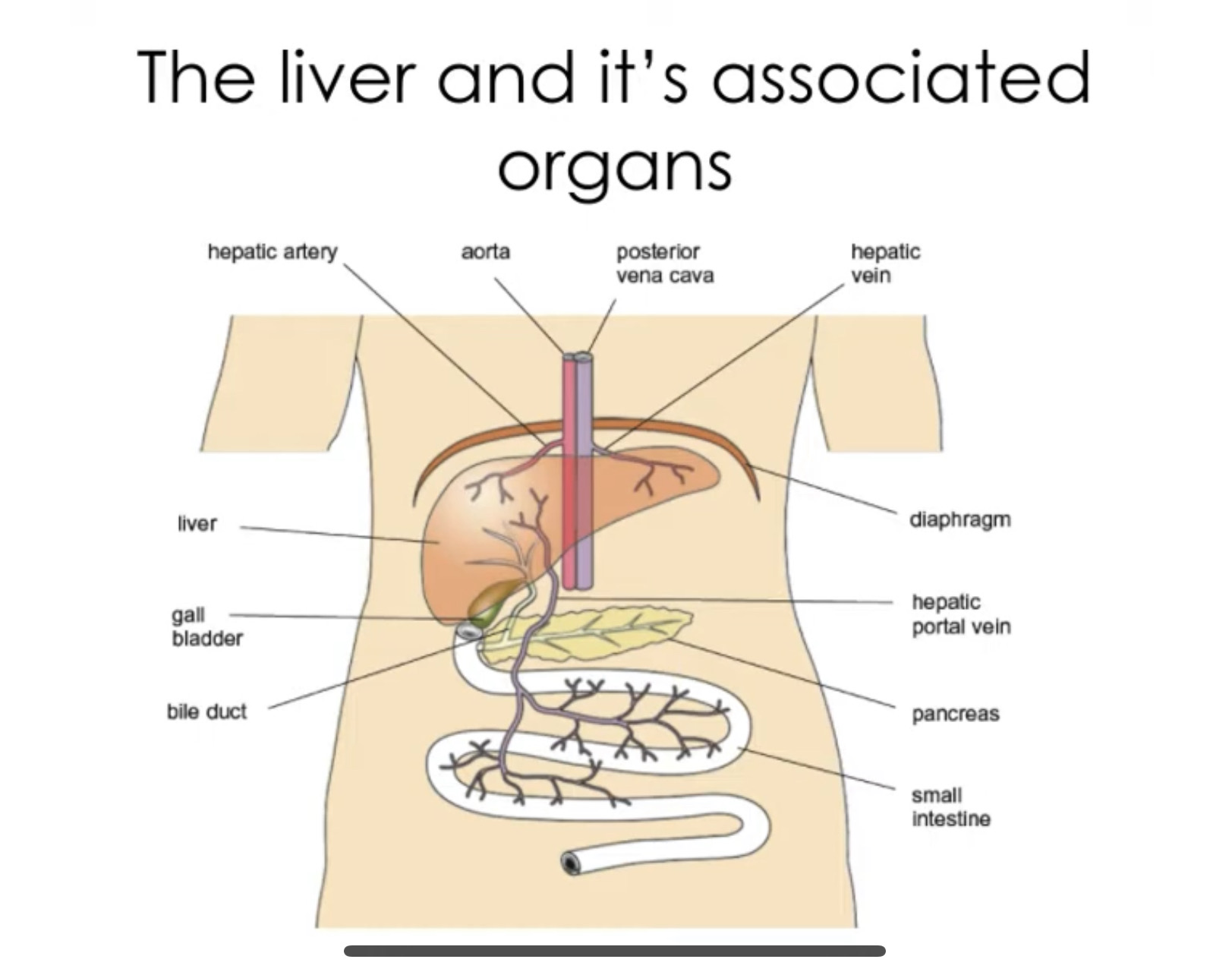
External liver structure
Oxygenated blood from heart is carried to liver by hepatic artery
The liver receives blood from digestive system via hepatic portal vein
Deoxygenated blood exits hepatic vein and flows back to the heart.
Liver is directly connected to what
Gall bladder
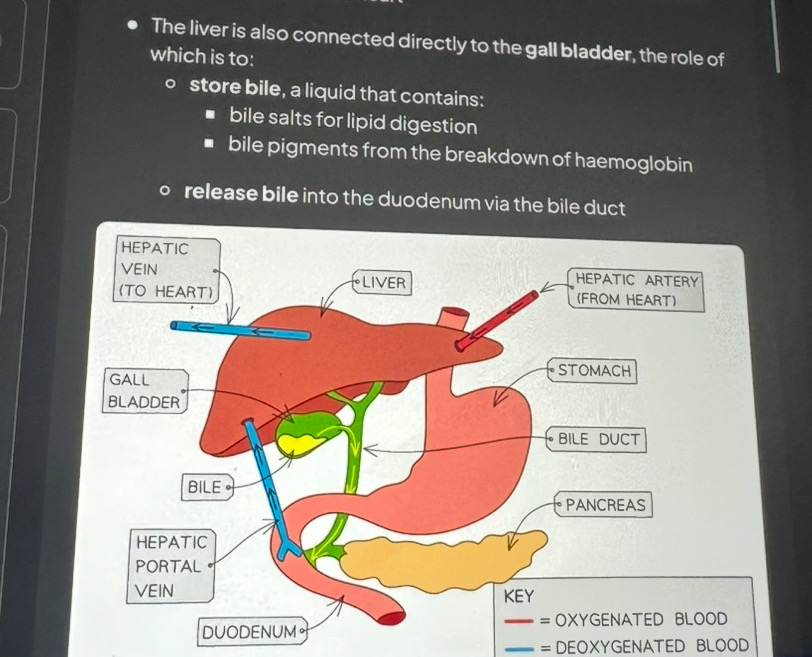
Liver internal structure
Made up of hepatocytes
Liver cells are arranged into structures called lobules
Contain wide capillaries called sinusoids - they connect hepatic artery and hepatic portal vein
How do you tell the difference between hepatic portal vein and hepatic artery
The lumen of the hepatic portal vein is thicker
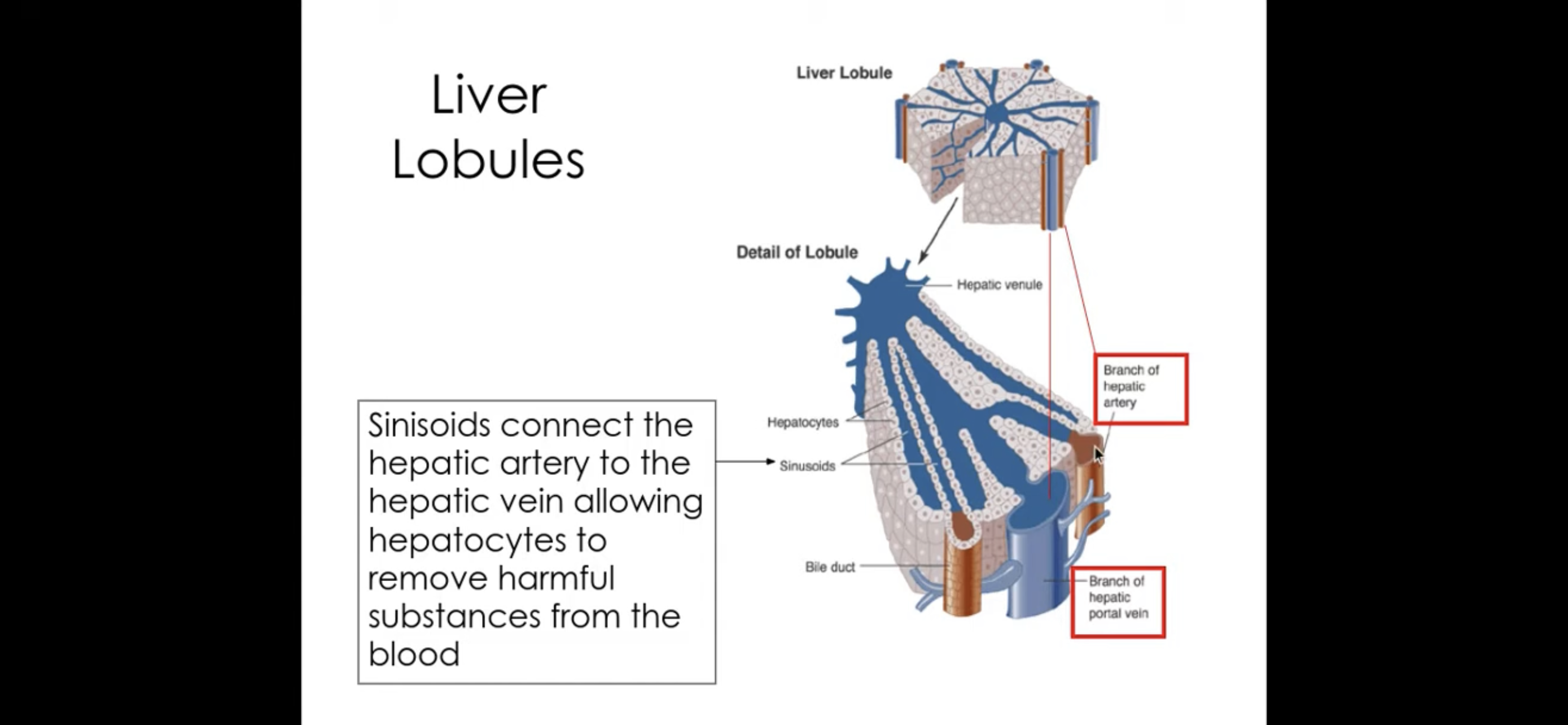
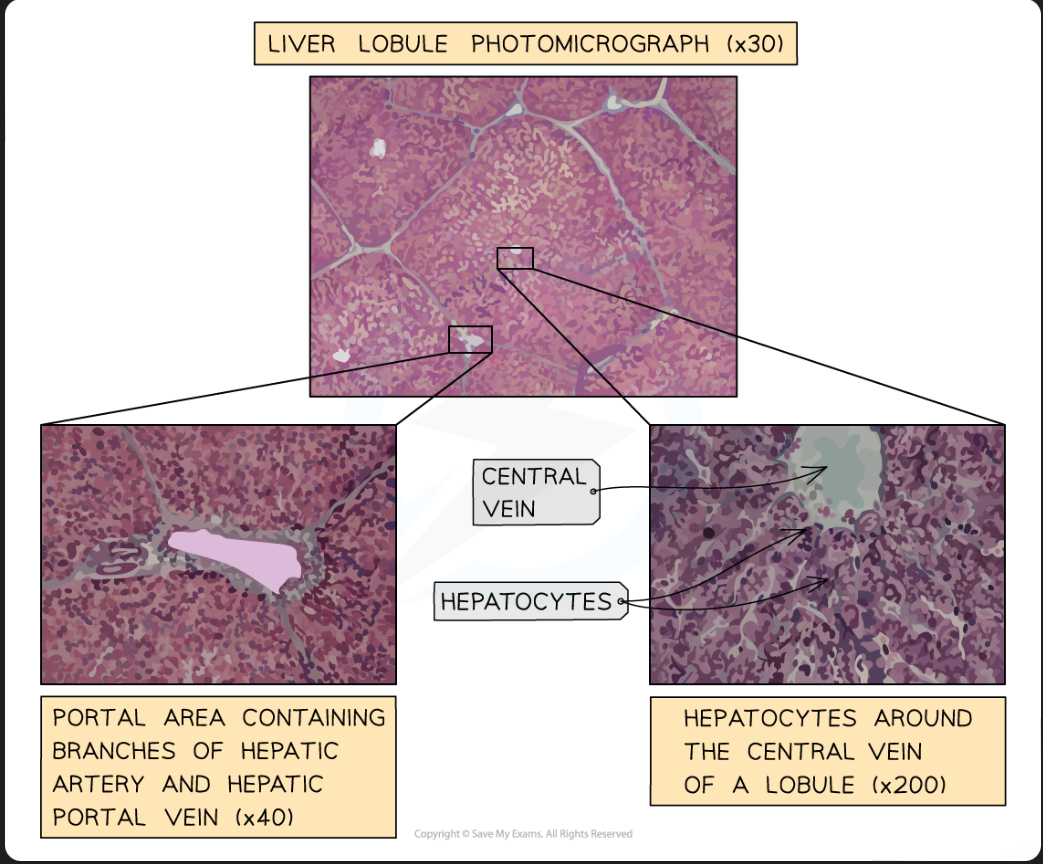
Histology of liver/ liver underneath a microscope
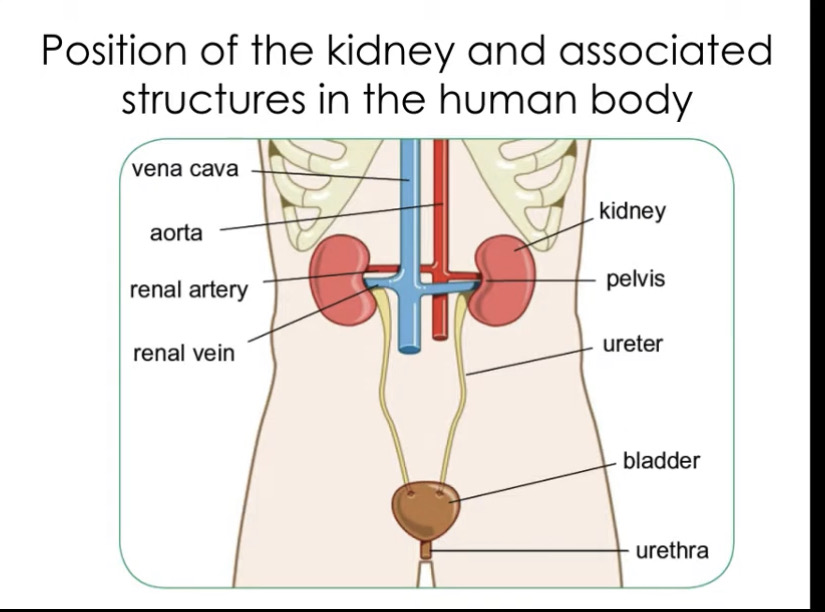
Where are the kidneys found
Under rib cage at back of body
Renal artery - carries oxygenated blood to kidneys
Renal vein - carries deoxygenated blood away from kidneys
Ureter - carries urine from kidney to bladder
Bladder - holds urine
Urethra - releases urine
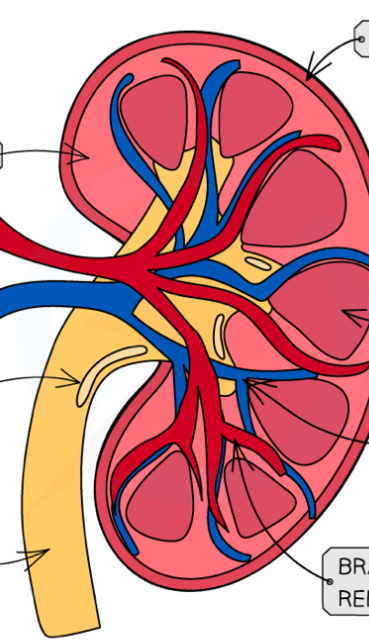
Cross section of kidney
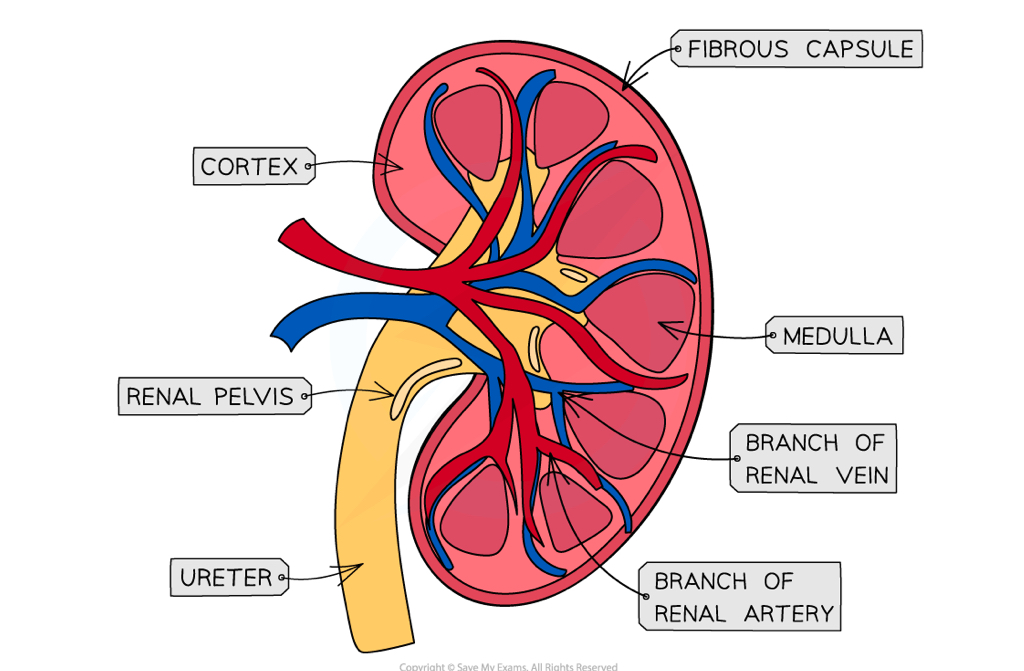
In kidney there are tiny tubes called what
Nephrons
Nephrons are responsible for formation of what
Formation of tissue fluid
Components nephron is made up of
Glomerulus
• Bowman’s capsule
• Proximal tube
• Loop of Henle
• Distal tube
• Collecting duc
Structure of nephron
In the bowman’s capsule there is the glomerulus
Glomerulus has afferent arteriole ( carries blood from renal artery) and efferent arteriole (carries to renal vein)
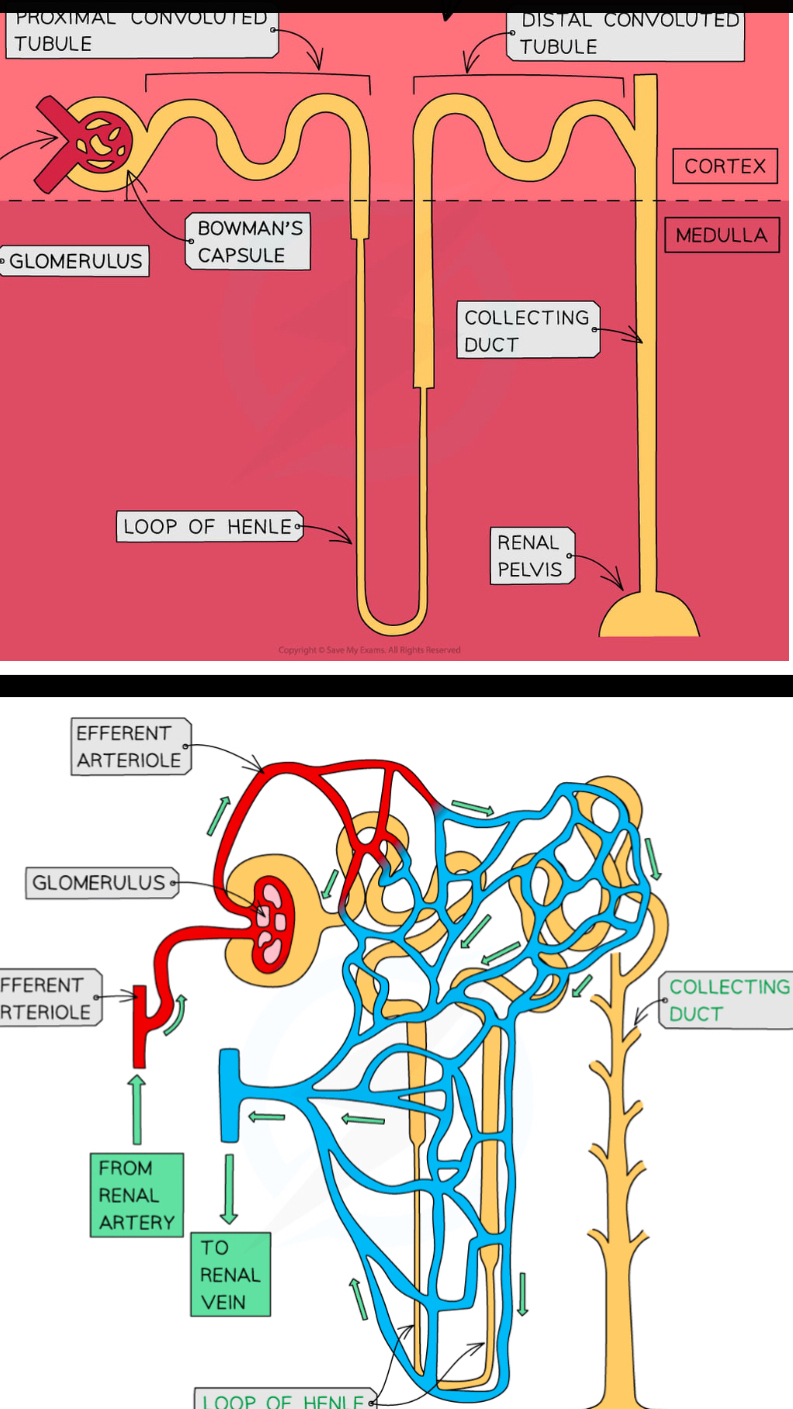
adaptations of glomerulus
gaps between epithelial cells allow molecules to leave blood
large diameter of afferent arteriole than efferent arteriole causes an increase in blood pressure
Magnification of cortex
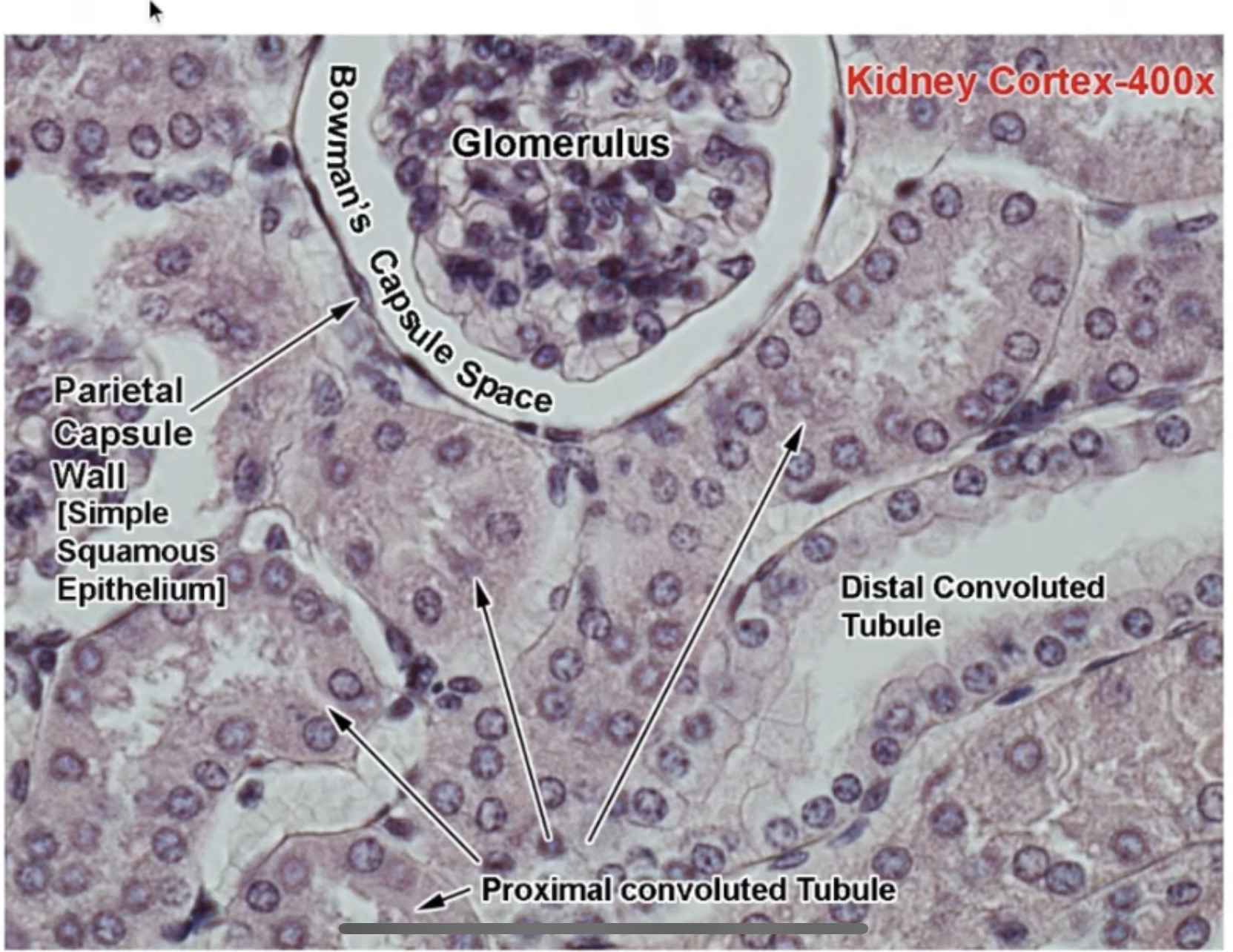
Urine formation occurs in 2 stages which are
Ultrafiltration and selective re absorption
What happens in ultrafiltration
The arteriole entering the glomerulus (afferent arteriole) has a wider diameter than the efferent arteriole (leaving glomerulus). Afferent has a higher blood pressure because the lumen of afferent arteriole is wider. (There is also a high hydrostatic pressure in glomerulus)
This high blood pressure causes smaller molecules being carried in the blood to be forced out of capillaries of glomerulus into bowman’s capsule and form glomerular filtrate
The substances that pass out of capillaries and form glomerular filtrate are: amino acids, water, glucose, urea
Blood cells and large proteins remain in the blood as they are too large to pass out of holes in endothelial cells
What substances are absorbed in selective reabsorption
Glucose
Amino acids
Water
Most of selective reabsorption takes place where
Proximal convoluted tubule
How does selective reabsorption work
Sodium ions Na+ are actively transported from proximal convoluted tubule into surrounding tissue by active transport. This creates an electrical chemical gradient causing chloride ions to move in by diffusion.
Sugars and amino acids are transported into surrounding tissue by a co transporter protein
Sodium potassium pump actively transport sodium ions out epithelial cells into blood
This lowers concentration of sodium ions in epithelial cells causing sodium ions to diffuse down concentration gradient into epithelial cells
These sodium ions move via co transporter protein into membrane, as they move the proteins transport another solute at the Same time eg: glucose or amino acid
Once inside epithelial cells these solutes diffuse down their concentration gradients into the blood
Describe reabsorption for water and salts for ascending limb
Sodium and chloride ions are active,y transported out of ascending limb of loop of henle into medulla region lowering its water potential
The ascending limb of loop of henle is impermeable to water, so water is unable to leave loop by osmosis
The water potential of ascending limb increases and rises to cortex due to removal of solutes and retention of water
Describe reabsorption for water and salts for descending limb
The descending limb is permeable to water so water moves out of descending limb by osmosis
The descending limb has few transport proteins in membrane so has low permeability to ions
So water potential decreases as descending limb moves down to medulla due to loss of water and retention of ions
what is countercurrent system
what is multiplier system
the movement of filtrate in opposite direction through ascending and descending limb in loop of henle
the multiplication of osmotic balance and amount of water that is reabsorbed
What is osmoregulation
Control of water potential in the blood
What happens in osmoregulation
Osmoreceptors (found in hypothalamus) detect a decrease in water potential of the blood
Nerve impulses go along sensory neurone to posterior pituitary gland
This gland releases ADH
ADH enters the blood and travels through the body
ADH causes kidneys to reabsorb more water
This reduces loss of water in urine
What is the effect of ADH on the kidneys
Water is reabsorbed by osmosis, this occurs as filtrates pass through structures called collecting ducts
ADH causes membranes of collecting duct to become more permeable to water
It does this by increasing aquaporins (water permeable channels) in the membrane
This occurs in the following way: collecting ducts contain vesicles (membrane is aqauporins) , ADH molecules bind to receptor proteins causing phosphorylation of aquaporin molecules, causing vesicles to fuse with membrane, this increases permeability
Filtrate in collecting duct loses more water so is more concentrated
So urine becomes more concentrated
If ADH levels are low what happens to urine
Membrane is less permeable and urine is more dilute