Background of Quantum Mechanics
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
In quantum mechanics, microscopic is ___ as macroscopic
Not the same
The failures of classical mechanics
Blackbody radiation
Photoelectric effect
Line spectra - spectroscopic transitions
Newton’s laws applied to the _
Motion of macroscopic objects
Maxwell’s _ applied to _
Electromagentic theory
Electricity, magnetism, and waves
Energy and other variables, change in a _ manner
Continuous
Physics was thought to be complete
19th Century
revealed the failure of classical mechanics in such systems
further probe of small body systems (atoms, electrons)
A principle that states the total energy radiated per unit surface area of a black body is proportional to the fourth power of its temperature.
Stefan-Boltzmann Law
Stefan Boltzmann Law
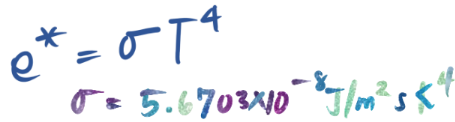
A law that describes the relationship between the temperature of a black body and the wavelength at which it emits radiation most strongly, stating that the wavelength is inversely proportional to the temperature.
Wien’s Law
Wien’s Law
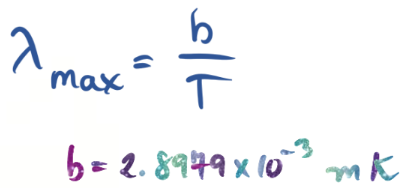
a perfect emitter
Blackbody
oscillations in the blackbody emit _
radiation
average energy of each oscillator
kT
in a blackbody, all incident radiation is _
absorbed
in a blackbody, the emitted radiation is a function of _
radiator’s temperature
classical mechanics predicts an __ intensity of emitted radiation as wavelength __
increasing; decreases
rayleigh-jeans law fails at
short wavelengths
rayleigh-jeans law

a prediction that an ideal black body would emit an infinite amount of energy in the ultraviolet range
uv catastrophe
introduced quantization of energy
max planck
the energy of electromagnetic oscillations have discrete values
quantization of energy
discrete energy eqn
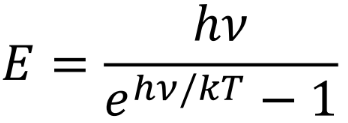
planck equation
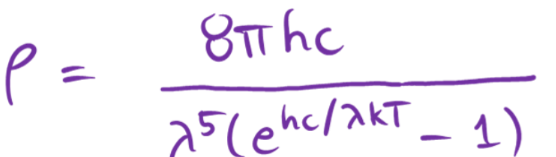
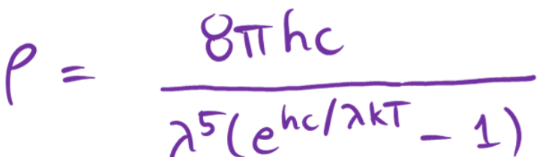
wavelength description in
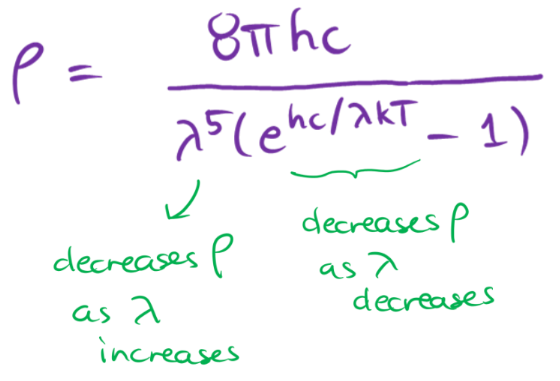
planck constant
h = 6.626 × 10^-34 Js
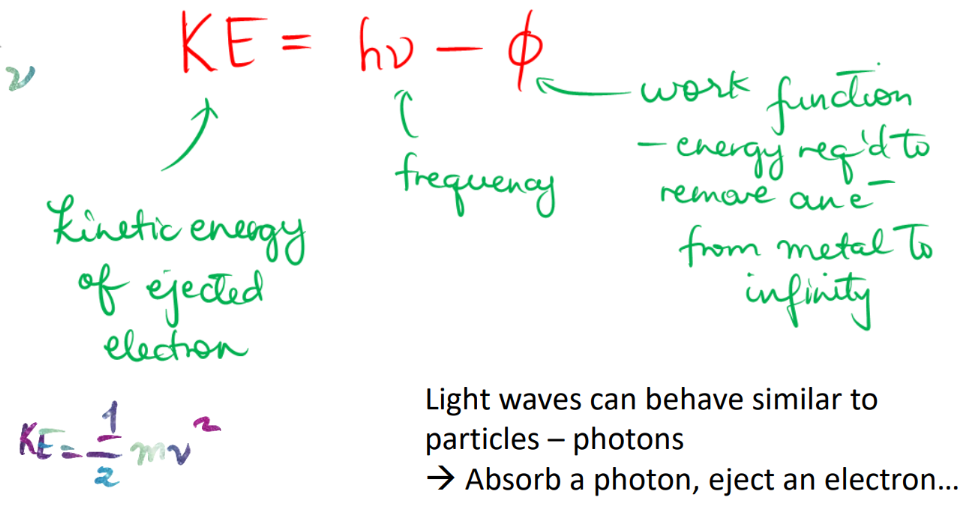
photoelectric effect
particle behavior of light (wave)
KE of e- is _ to frequency
proportional
KE of e- is _ of intensity
independent
no of e- ejected is _ of frequency
independent
no of e- ejected is _ of intensity
proportional
foundation of quantum mechanics
einstein’s theory of photoelectric effect
photoelectric effect (formula)
1ev = 1.602 × 10^-19 J
line spectra series
1 - lyman
2 - balmer (vis)
3 - paschen (infrared)
4 - brackett
5 - pfund
6 - humphreys
rydberg equation
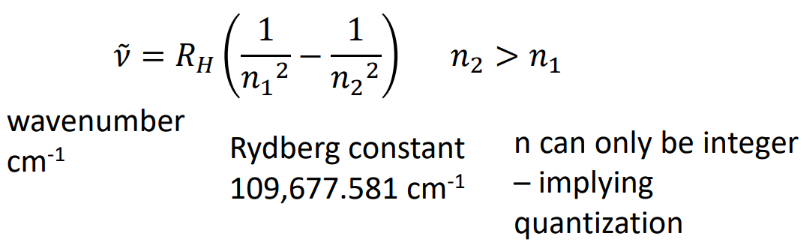
Bohr frequency relation
\Delta E = hv
emission of light as photons