Organisms response - Controlling heart rate
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What is the autonomic nervous system?
The part of the nervous system responsible for control of the bodily functions not consciously directed, such as breathing, the heartbeat, and digestive processes
What are the two parts of the autonomic nervous system?
Parasympathetic and sympathetic
What happens to the heart rate in the parasympathetic nervous system?
The heart rate is slow/normal
What happens to the heart rate in the sympathetic nervous system?
The heart rate accelerates/is very fast
What happens to digestion in para/sympathetic nervous system and why?
Para = digestion occurs
Symp = Inhibits anything to do with digestion so blood flow is directed to muscles
Why does the sympathetic nervous system direct all the blood to the muscles?
Because it controls our fight or flight response which usually means we need to use our muscles e.g. run away
Control of heart rate diagram.
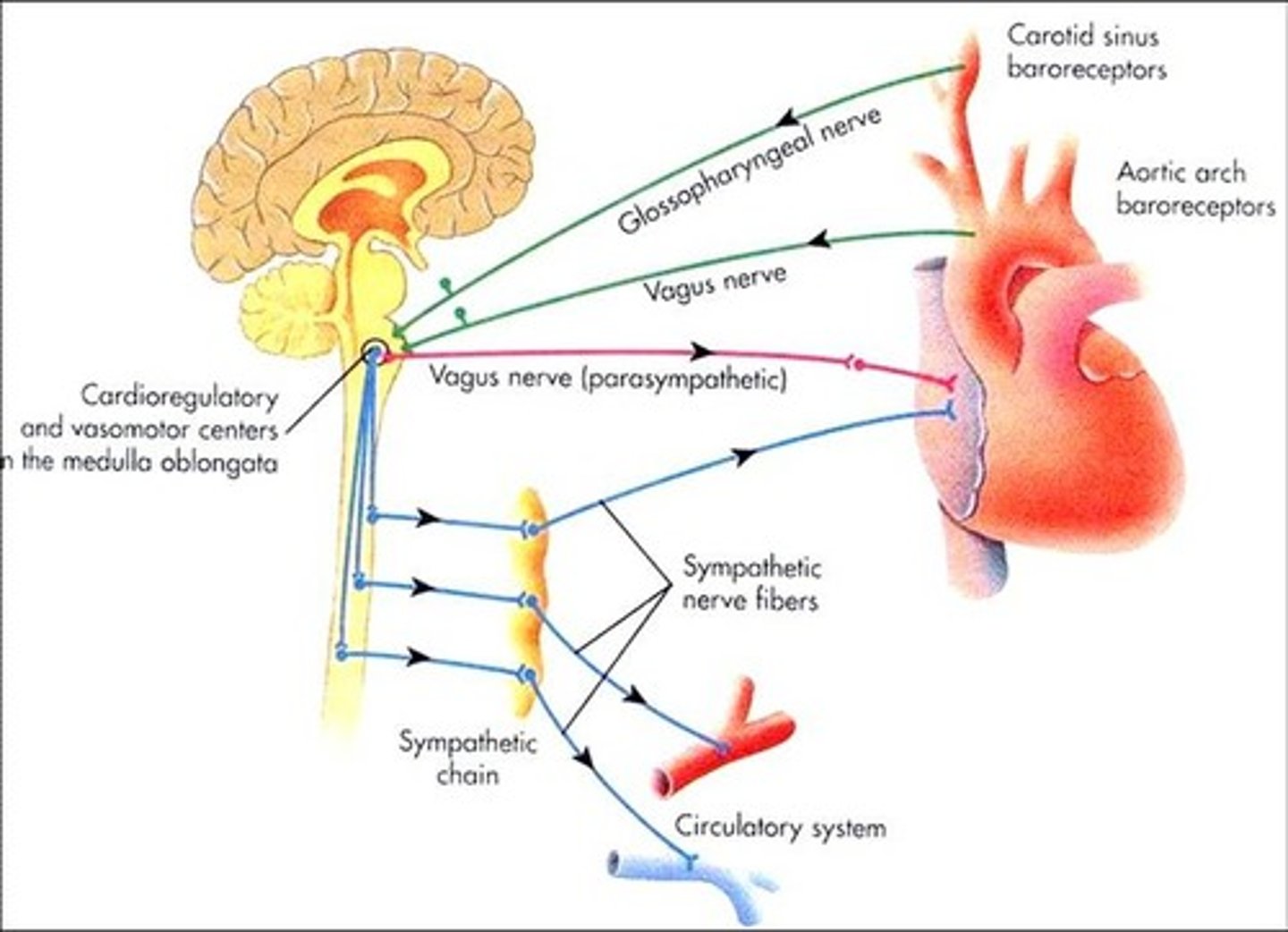
What is the medulla oblongata?
Base of the brain that controls autonomic functions such as heart rate
What are the receptors and effectors involved in controlling heart rate?
Receptors = chemoreceptors and baroreceptors
Effectors = Medulla oblongata and SAN
What are chemoreceptors?
This is a type of receptor responds to chemical stimuli, such as CO2 concentration (detects changes in pH)
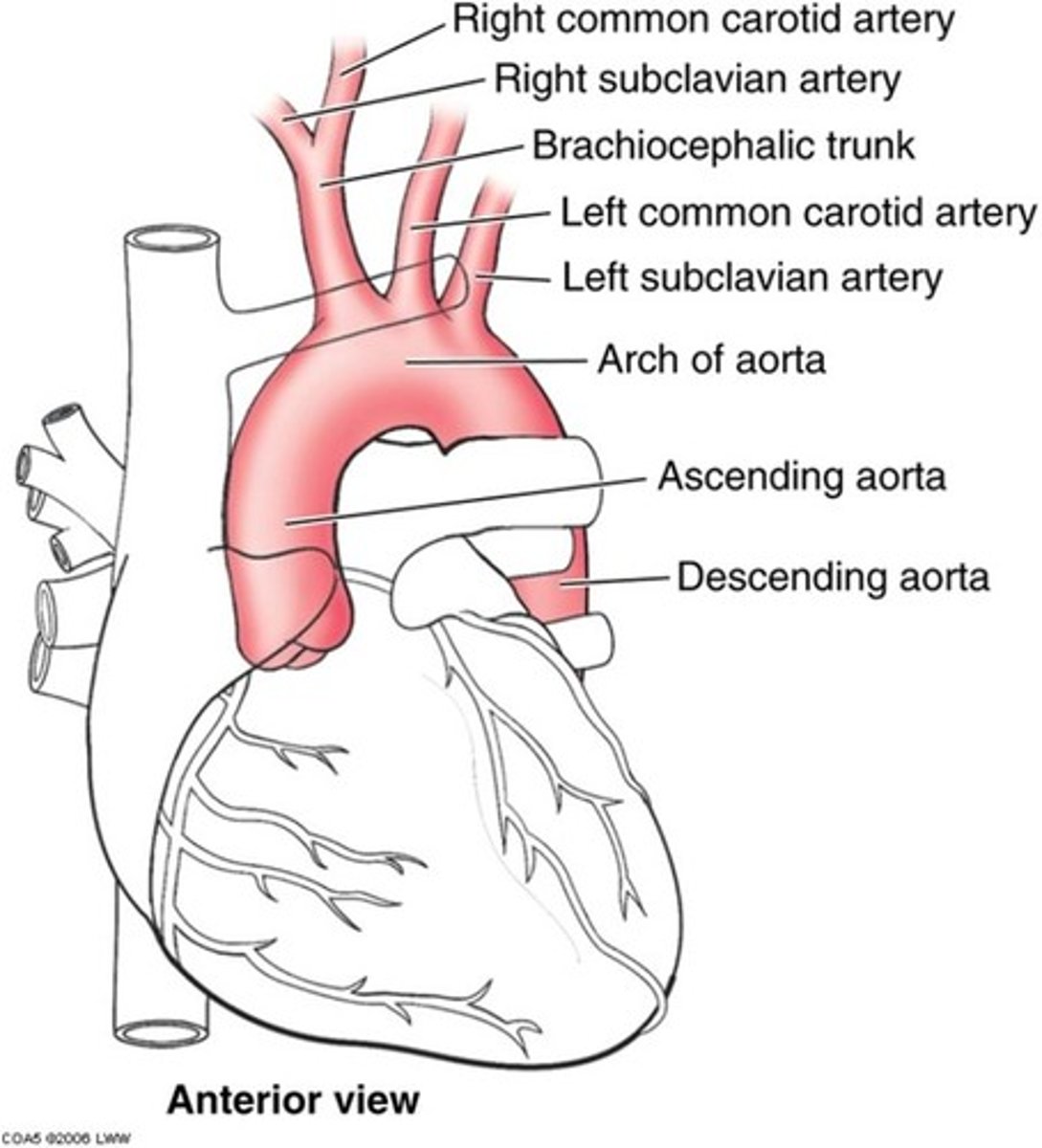
Where are chemoreceptors found?
In the wall of the carotid arteries and in the aortic arch
What is the aortic arch?
Curved portion of the aorta
What happens to the blood during exercise?
Due to increased respiration in cells, there is increased CO2 in the blood stream
What do chemoreceptors do when they detect higher levels of CO2 in the blood stream and how does this increase heart rate?
It transmits more signals to the part of the medulla oblongata that increases heart rate which then sends more signals to the SAN causing said increase in heart rate
What do chemoreceptors do when they detect lower levels of CO2 in the blood stream and how does this increase heart rate?
It transmits more signals to the part of the medulla oblongata that decreases heart rate which then sends less signals to the SAN causing said decrease in heart rate
Why does increased heart rate help when there is high CO2 conc in the blood?
More blood is pumped around the body so more is removed by exhalation in the lungs
What are baroreceptors?
Blood pressure receptors
Where are baroreceptors found?
Carotid sinus and aortic arch
What happens when baroreceptors detect higher blood pressure?
It transmits more signals to the part of the medulla oblongata that decreases heart rate which then sends less signals to the SAN causing said decrease in heart rate
What happens when baroreceptors detect lower blood pressure?
It transmits more signals to the part of the medulla oblongata which increases heart rate which then sends more signals to the SAN causing said increase in heart rate
What are the steps that dictate the effects of exercise on cardiac output?
1. Increased muscular/metabolic activity
2. More CO2 produced due to cells respiring
3. Blood pH is lowered
4. Chemoreceptors detect this change and increase frequency of signals to the rate increasing part of the medulla oblongata
5. This part increases the frequency of signals to the SAN
6. Heart rate increases
7. Increased blood flow decreases conc of CO2
8. CO2 levels return to normal
What factors not to do with blood pressure or pH can affect heart rate?
- Hormones
- Posture
- Age
- Gender
What is a hormone that has a very significant impact on heart rate?
Adrenaline
What does adrenaline stimulate?
Glycogenolysis and the breakdown of fats and proteins to glucose
What is glycogenolysis?
The breakdown of glycogen to glucose
In what order does the body break down its supplies to provide energy?
1. Glycogen
2. Fats
3. Proteins
What does adrenaline do to blood flow in different parts of the body?
Decreases blood flow to organs such as the gut and kidneys as these are not needed for physical activity. Increases blood flow to the muscles and lungs for activity.
(Parasympathetic becomes sympathetic response)
How long does the effect of adrenaline last and why?
Only a few minutes because it is rapidly metabolised
How can posture impact heart rate?
Heart rate is lower when lying down and higher when sitting/standing up
How can gender impact heart rate?
Females generally have higher heart rates than males
How can age impact heart rate?
The older you get, the slower your heart rate
What is an extraneous variable to do with the impact of age on heart rate?
Though heart rate decreases, we could expect it to increase due to increased body weights and potential decreased fitness as we get older