Case Studies-3: Wound & Stool
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
A 35y.o male was seen by a physician for a purulent abscess on his right toe. The physician evaluated and determined the abscess may be deep in the toe. She aspirated the material and transported it to the lab in a sterile container.
In the lab, this specimen should be inoculated on what media?
BAP, CHOC, CNA, MAC, THIO, Set a Gram Stain
BAP, CNA, THIO, no gram stain.
BAP, MAC, Gram Stain
Reject the specimen because it is not on a swab
BAP, CHOC, CNA, MAC, THIO, Set a Gram Stain
Correct, an abscess can have mixed flora including anaerobes, so all media will be set. A gram stain will help evaluate the culture results.
A superficial wound specimen is submitted for culture.
Gram Stain Result: Mod squamous epithelial cells, NO PMN's, Few GPC, Few small GPB.
Culture Result: Moderate Growth Diptheroids, Moderate Growth alpha-hemolytic streptococci; Moderate Growth coagulase negative staphylococci
The NEXT step is to:
Report as Moderate Growth Normal Skin Flora
Ask for a repeat specimen
Perform a complete identification of the alpha-hemolytic streptococci
Perform ID/MIC on the Staph spp.
Report as Moderate Growth Normal Skin Flora
Gram stain result with squamous epithelial cells and no WBC's indicates this is a non-infectious state. The organisms grown are normal skin flora.
Use the following description for the next 3 questions:
A pustule drainage specimen for the right leg of a professional football player is submitted for culture.
Gram Stain: Many PMN's, Many Gram Positive Cocci in Clusters
Is this a quality specimen and why?
No, the lack of squamous epithelial cells indicates skin contamination.
No, the presence of many PMN's indicates skin contamination
Correct!
Yes, the presence of many PMN's indicates an infectious process
Unable to determine until the culture grows.
Yes, the presence of many PMN's indicates an infectious process
A pustule drainage specimen for the right leg of a professional football player is submitted for culture.
Gram Stain: Many PMN's, Many Gram Positive Cocci in Clusters
After overnight incubation, the BAP and CHOC agar plate grow 4+ white colonies that are beta-hemolytic; MAC = NG.
Gram Stain = Gram Positive Cocci
Catalase = POS
What is the possible genus of this organism?
Streptococcus
Staphylococcus
Neisseria
Corynebacterium
Staphylococcus
A pustule drainage specimen for the right leg of a professional football player is submitted for culture.
Gram Stain: Many PMN's, Many Gram Positive Cocci in Clusters
What would be the most appropriate test for additional identification of the isolate?
Coagulase
Indole
Oxidase
TSI
Coagulase
Coagulase is used to distinguish S. aureus, which is a potential pathogen in wound cultures, from Coag Neg Staph, which is normal skin flora.
Staph latex reagents can also be used.
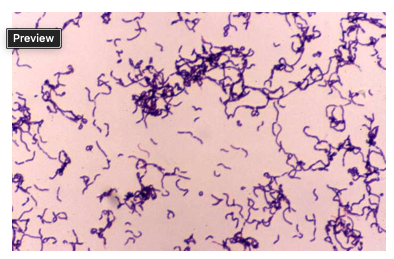
A 65 y.o retired woman assists her son in his veterinary office. On a Monday morning, the office receives a call about an injured pig at a local farm. They travel to the farm and find that the pig has an infected, swollen leg. They clean the leg and remove a splinter.
On Friday, the woman notices a small cut on her finger that is swollen and tender. She ignores it, but then a day later the cut has become larger and presents as a spreading cellulitis like lesion on her hands and fingers. She also has a low grade fever and the hand is painful. She goes to an urgent care for evaluation. The lesion is drained and an aspirate specimen is sent to the lab for culture.
The gram stain of the aspirate demonstrates Gram Positive Bacilli (image above).
The organism barely grew on a blood agar plate and showed alpha hemolysis. The colonies are small, smooth, and translucent. Catalase = NEG
What organism is the most likely isolate from this culture?
Bacillus cereus
Lactobacillus
Pasturella multocida
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae causes erysipeloid which is a soft tissue infection seen as an occupational infection of those working with animals.
A patient who recently attended a barbecue that served hamburgers, hot dogs, and several types of deli salads, is experiencing severe abdominal pain and watery diarrhea, with little or no fever. A stool sample is collected and sent to the laboratory for culture. The culture revealed the following growth patterns on primary media:
Media | Growth |
Sheep Blood Agar | 4+ large gray nonhemolytic colonies. 3 morphotypes present with one swarming |
MacConkey | 4+ clear colonies; 3+ pink colonies; 3+ mucoid pink colonies |
Hektoen | 4+ clear colonies w/ black centers; 3+ orange colonies; 3+ mucoid orange colonies |
MacConkey w/Sorbitol | 4+ clear colonies; 3+ pink colonies |
Campy | No Growth |
Based on the growth pattern observed on MacConkey agar, what additional testing should be performed and why?
Biochemicals on the pink colonies to rule in or out Salmonella or Shigella
Biochemicals on the mucoid pink colonies to rule in our out Salmonella or Shigella
Biochemicals on the clear colonies to rule in our out Salmonella or Shigella
Biochemicals on the swarming ornanism
Biochemicals on the clear colonies to rule in our out Salmonella or Shigella
Salmonella and Shigella are colorless (NLF) on MacConkey agar
A patient who recently attended a barbecue that served hamburgers, hot dogs, and several types of deli salads, is experiencing severe abdominal pain and watery diarrhea, with little or no fever. A stool sample is collected and sent to the laboratory for culture. The culture revealed the following growth patterns on primary media:
Media | Growth |
Sheep Blood Agar | 4+ large gray nonhemolytic colonies. 3 morphotypes present with one swarming |
MacConkey | 4+ clear colonies; 3+ pink colonies; 3+ mucoid pink colonies |
Hektoen | 4+ clear colonies w/ black centers; 3+ orange colonies; 3+ mucoid orange colonies |
MacConkey w/Sorbitol | 4+ clear colonies; 3+ pink colonies |
Campy | No Growth |
Based on the growth patter observed on Hektoen agar, what additional testing should be performed and why?
Biochemicals on the clear colonies with black centers to rule in our out Salmonella
Biochemicals on the clear colonies with black centers to rule in our out Shigella
Biochemicals on the orange colonies to rule in or out Salmonella or Shigella
No further testing needed from HE agar
Biochemicals on the clear colonies with black centers to rule in our out Salmonella
Salmonella can produce H2S which is demonstrated by black centers on HE agar
A patient who recently attended a barbecue that served hamburgers, hot dogs, and several types of deli salads, is experiencing severe abdominal pain and watery diarrhea, with little or no fever. A stool sample is collected and sent to the laboratory for culture. The culture revealed the following growth patterns on primary media:
Media | Growth |
Sheep Blood Agar | 4+ large gray nonhemolytic colonies. 3 morphotypes present with one swarming |
MacConkey | 4+ clear colonies; 3+ pink colonies; 3+ mucoid pink colonies |
Hektoen | 4+ clear colonies w/ black centers; 3+ orange colonies; 3+ mucoid orange colonies |
MacConkey w/Sorbitol | 4+ clear colonies; 3+ pink colonies |
Campy | No Growth |
Further testing of the suspicious isolates from MacConkey and Hektoen agar revealed:
MacConkey isolate
TSI = K/A, H2S positive, Gas
Urea = Negative
HE isolate
TSI = K/A H2S positive, Gas
Urea = Negative
Based on the results of the TSI and Urease, is further testing needed on the isolates and if so, what additional testing would be most appropriate?
NO, the negative urease rules out Salmonella and Shigella
NO, the TSI results rule out Salmonella and Shigella
YES, perform a complete biochemical ID panel and serological typing for Shigella somatic antigens
YES, perform a complete biochemical ID panel, and serological typing for Salmonella somatic antigens
YES, perform a complete biochemical ID panel, and serological typing for Salmonella somatic antigens
The TSI slant is suspicious for Salmonella, so further work up is warranted.
A patient who recently attended a barbecue that served hamburgers, hot dogs, and several types of deli salads, is experiencing severe abdominal pain and watery diarrhea, with little or no fever. A stool sample is collected and sent to the laboratory for culture. The culture revealed the following growth patterns on primary media:
Media | Growth |
Sheep Blood Agar | 4+ large gray nonhemolytic colonies. 3 morphotypes present with one swarming |
MacConkey | 4+ clear colonies; 3+ pink colonies; 3+ mucoid pink colonies |
Hektoen | 4+ clear colonies w/ black centers; 3+ orange colonies; 3+ mucoid orange colonies |
MacConkey w/Sorbitol | 4+ clear colonies; 3+ pink colonies |
Campy | No Growth |
Based on the growth patter observed on MacConkey with Sorbitol agar, what additional testing should be performed and why?
Latex agglutination of O157 antigen on the pink colonies to rule out E. coli O157
Latex agglutination for O157 antigen on the clear colonies to rule in or out E.coli O157
Shigella antiserra A-D on the pink colonies to rule in or out Shigella
Salmonella polyvalent antisera on the clear colonies to rule in or out Salmonella
Latex agglutination for O157 antigen on the clear colonies to rule in or out E.coli O157
E.coli O157 colonies are colorless on Mac Sorb agar