CHEM 101-017 Chapter 4: Reactions in Aqueous Solution
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Define solution.
Any homogenous mixture that is physically and chemically the same throughout the whole system/reaction.
How many components does a solution have?
Two
What are the components of a solution?
The solvent and solute.
Define the characteristics of a solvent.
They’re present in large amounts; the solvent is usually water in the case of aqueous solutions.
Define the characteristics of a solute.
It’s the substance that is dissolved in the solvent and usually present in small amounts.
What formula is used to the find the molarity or concentration of a substance?
Moles of solute/Liter of solution
What formula is used to dilute concentrated solutions and what does each variable mean?
M1 x V1 = M2 x V2
M1 = initial molarity
V1 = initial volume
M2 = final molarity
V2 = final volume
Give me three types of chemical reactions that we’ll focus on this chapter.
1.) Precipitation Reactions
2.) Acid-Base Neutralization Reactions
3.) Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Reactions
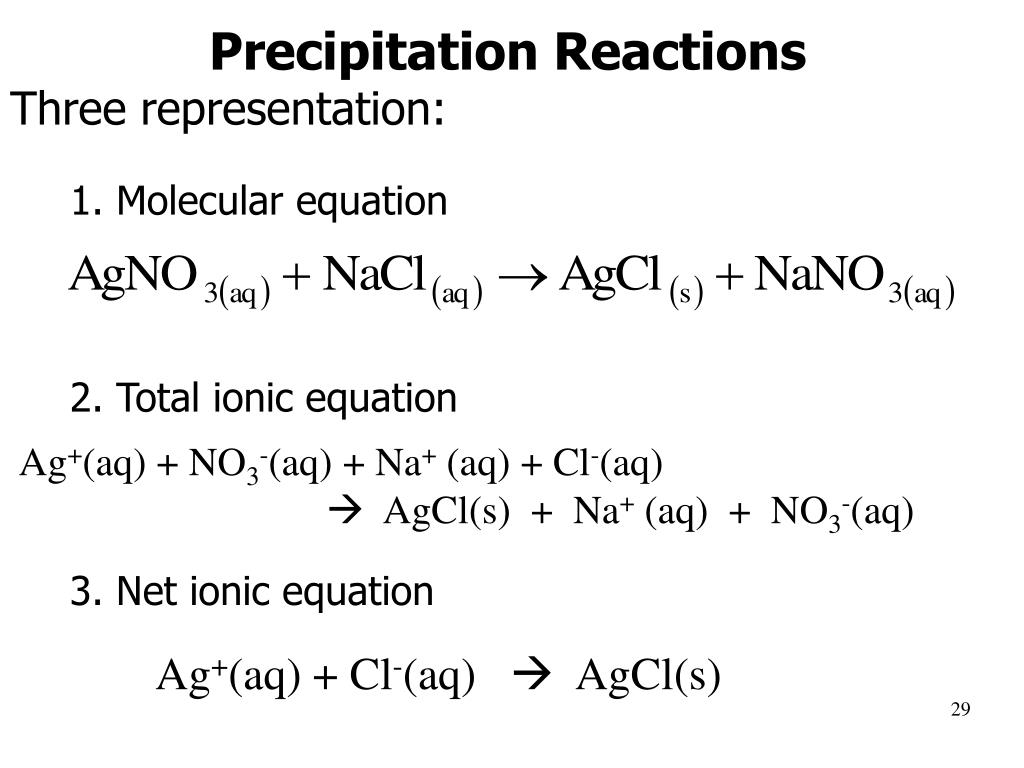
Define precipitation reactions.
Process in which soluble reactants yield an insoluble solid product that falls out of the reaction.
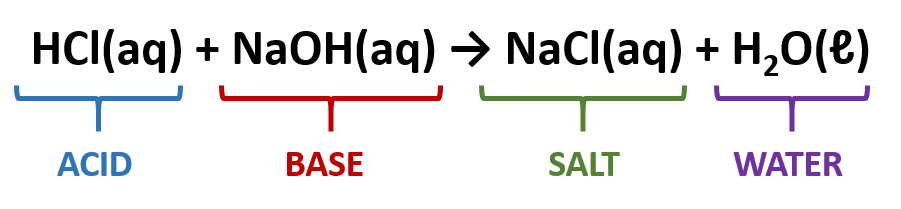
Define acid-base neutralization reactions.
Process in which an acid reacts with a base to yield water and an ionic compound (salt).
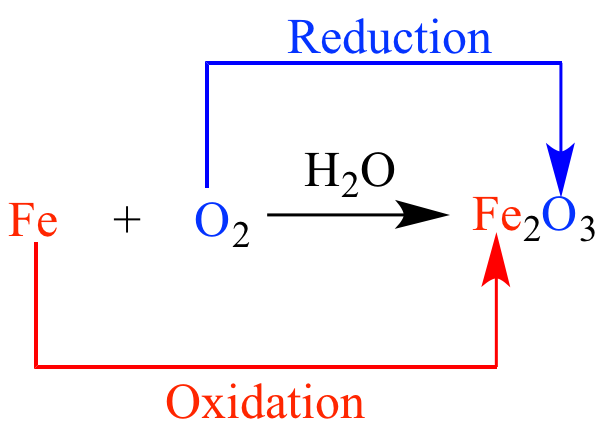
Define oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions.
Process in which one or more electrons are transferred between reactants AND includes oxygen on the reactant side of the balanced equation.
Ionic solids and some polar compounds, such as ____ acids and ____ bases, tend to have the _____ solubility and form ions when dissolved in water.
1.) strong
2.) strong
3.) highest
What is an electrolyte?
Defined as any aqueous solution that conducts electricity in water and substances that dissolve in water produce conducting solutions of ions.
What is a nonelectrolyte?
Substances which do not produce ions in aqueous solutions.
What are some characteristics of weak electrolytes?
They consist of weak acids and weak bases. They partially dissolve in water, resulting in low conductivity.
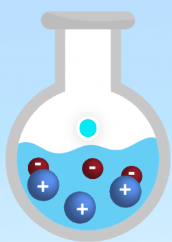
Is this an example of a strong electrolyte, weak electrolyte, or nonelectrolyte?
Weak electrolyte.
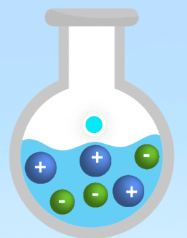
Is this an example of a strong electrolyte, weak electrolyte, or nonelectrolyte?
Strong electrolyte.
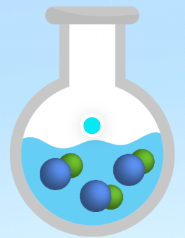
Is this an example of a strong electrolyte, weak electrolyte, or nonelectrolyte?
Nonelectrolyte.
What are characteristics of strong electrolytes?
They consist of strong acids and strong bases. They completely dissolve in water, resulting in high conductivity.
What are examples of acid halides and are they characterized as a strong or weak acid? Are they examples of weak or strong electrolytes?
HF (hydrofluoric acid) - weak acid
HCl (hydrochloric acid) - strong acid
HBr (hydrobromic acid) - strong acid
HI (hydroiodic acid) - strong acid
All of these substances are strong electrolytes, except for HF.
What are examples of Acid oxy halides and are they characterized as a strong or weak acid? Are they examples of weak or strong electrolytes?
HOF (hypofluorous acid) - weak acid
HOCl (hypochlorous acid) - weak acid
HOBr (hypobromous acid) - weak acid
HOI (hypoiodous acid) - weak acid
All of these substances are weak electrolytes.
What are examples of oxyacids and are they characterized as a strong or weak acid? Are they examples of weak or strong electrolytes?
HNO3 (nitric acid) - strong acid
H2SO4 (sulfuric acid) - strong acid
HClO4 (perchloric acid) - strong acid
HIO4 (periodic acid) - strong acid
H2CO3 (carbonic acid) - weak acid
H3PO4 (phosphoric acid) - weak acid
HNO2 (nitrous acid) - weak acid
HCN (hydrocyanic acid) - weak acid
HNO3, H2SO4, HClO4, and HIO4 are strong electrolytes. H2CO3, H3PO4, HNO2, and HCN are weak electrolytes.
What are two types of organic acids, are they strong or weak acids/bases, and do they have strong or weak electrolytes?
HCOOH (fermic acid) - weak acid
CH3COOH (acetic acid or vinegar) - weak acid
These substances are weak electrolytes.
What are four examples of non-electrolytes that are soluble in water?
C2H6O (ethanol)
C2H6O2 (ethylene glycol)
C6H12O6 (glucose)
C12H22O11 (sucrose)
What types of compounds are characterized as a strong electrolyte/strong base?
Group 1 A and Group 2 A elements paired to an OH- ion.
What are examples of strong electrolytes, particularly strong bases?
NaOH (sodium hydroxide)
KOH (potassium hydroxide)
Ba(OH)2 (barium hydroxide)
Ca(OH)2 (calcium hydroxide)
And many more
Any element paired to a _____ atom is a weak base!!!!
nitrogen
Strong electrolytes are soluble ____ solids, ____ acids, and ____ bases.
1.) Ionic
2.) Strong
3.) Strong
Is ammonia (NH3) a weak electrolyte and is it a weak acid or base?
NH3 is a weak electrolyte and a weak base.
Waters, soluble alcohols, sugars, and any polar covalent compounds that is not an acid or base are either strong electrolytes, weak electrolytes, or nonelectrolytes?
Nonelectrolyte
Are group one elements (Li+, Na+, K+, Rb+, Cs+) and NH4+ soluble?
Yes, they’re soluble with no exception.
Are NO3-, ClO4-, and C2H3O2- soluble or insoluble in water?
These ions are soluble in water without any exceptions.
Are the halides (F-, Cl-, Br-, I-) soluble? What are its exceptions?
Yes, these ions are soluble except for Ag+, Hg2 +2, and Pb+2.
Is SO4-2 soluble? What are its exceptions?
Yes, sulfate is soluble except for Sr+2, Ba+2, Hg2 +2, and Pb+2.
Is CO3 -2 soluble? What are its exceptions?
No, carbonate is insoluble except for group one elements, ammonium, Ca+2, Ba+2, and Sr+2.
Is S-2 soluble? What are its exceptions?
No, sulfide is insoluble except for group one elements, ammonium, Ca+2, Ba+2, and Sr+2.
Is OH- soluble? What are its exceptions?
No, hydroxide is insoluble except for group one elements, ammonium, Ca+2, Ba+2, and Sr+2.
Is PO4-3 soluble? What are its exceptions?
No, phosphate is insoluble except for group one elements and ammonium.