Gross Anatomy: Lecture 1
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
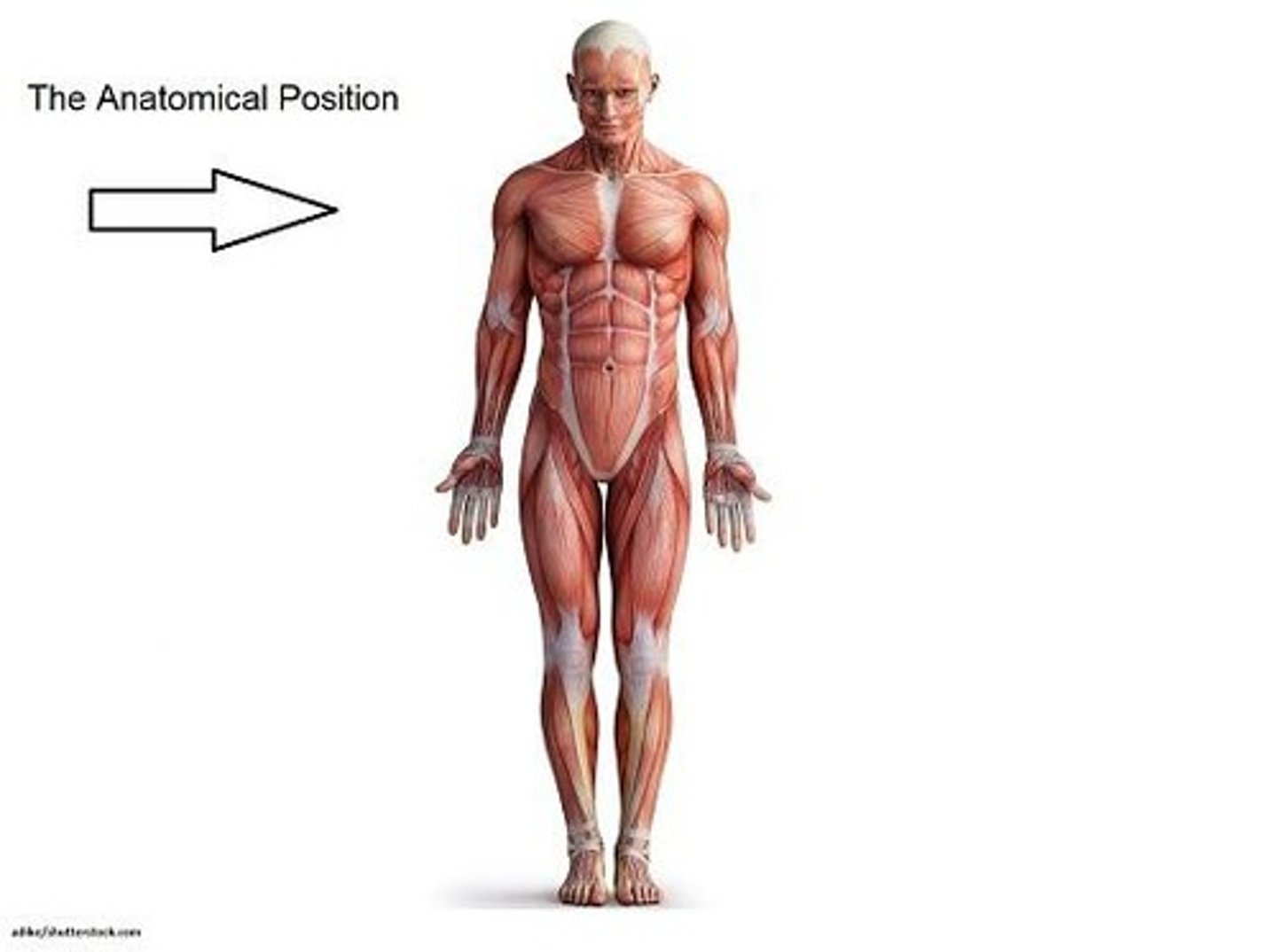
Anatomical position description
Standing upright, feet slightly apart, arms at sides, palms forward, head and eyes facing forward.
Frontal (Coronal) Plane
divides the body into anterior and posterior sections.
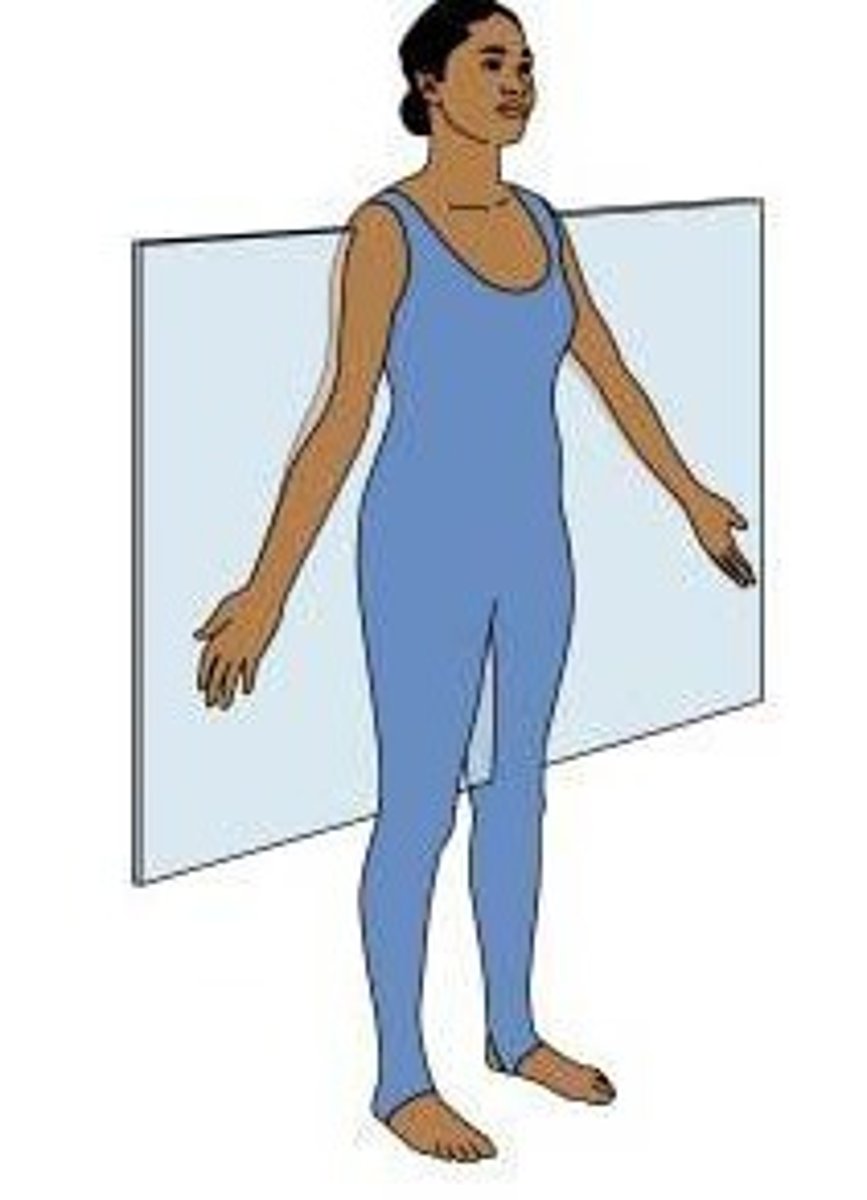
Medial plane
central sagittal plane that divides the body into equal left and right halves
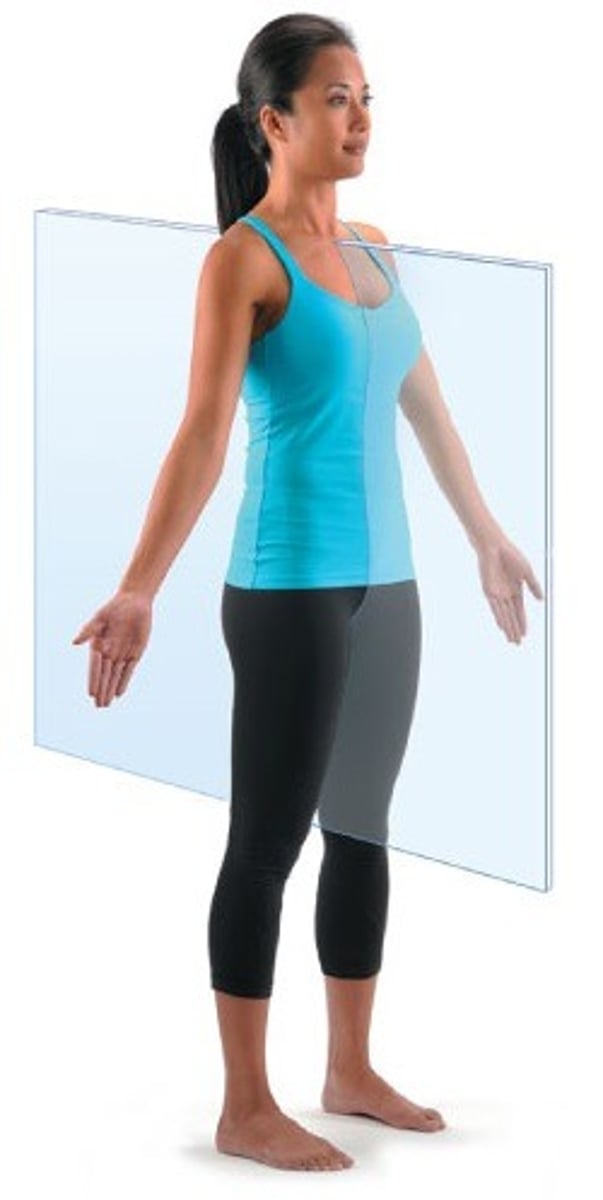

Sagittal plane
vertical division of the body into right and left portions (not necessarily equal unless midsagittal)
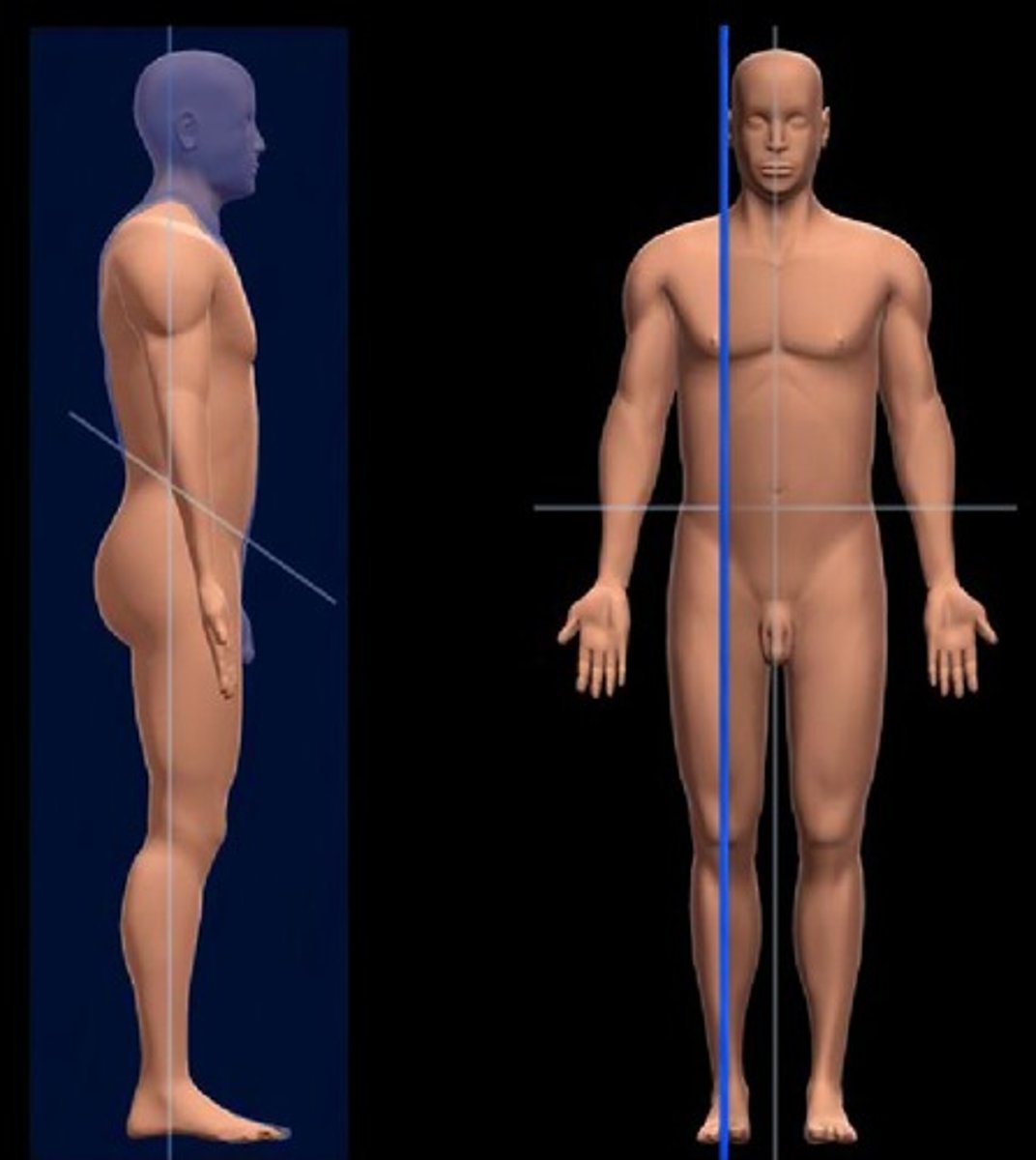
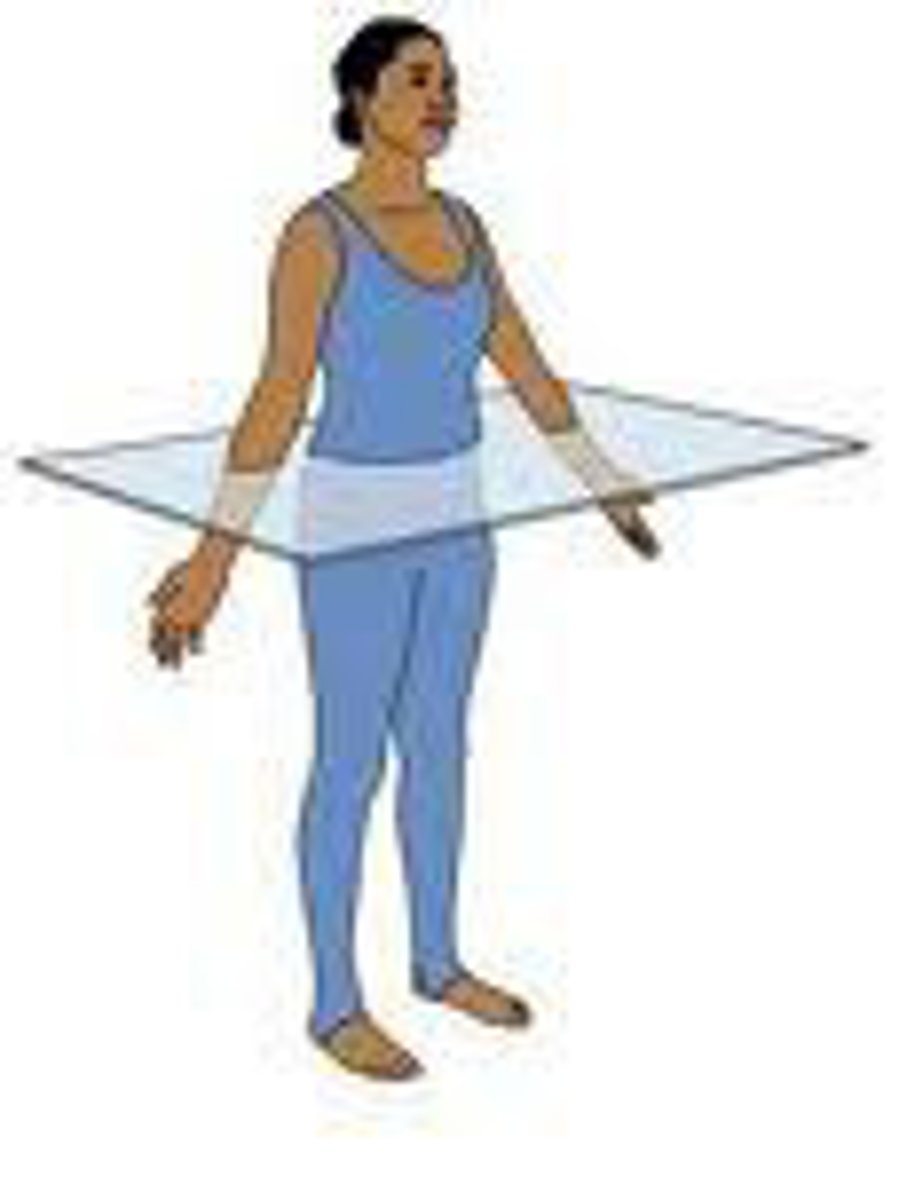
Transverse plane
horizontal division of the body into top and bottom sections (superior/inferior)
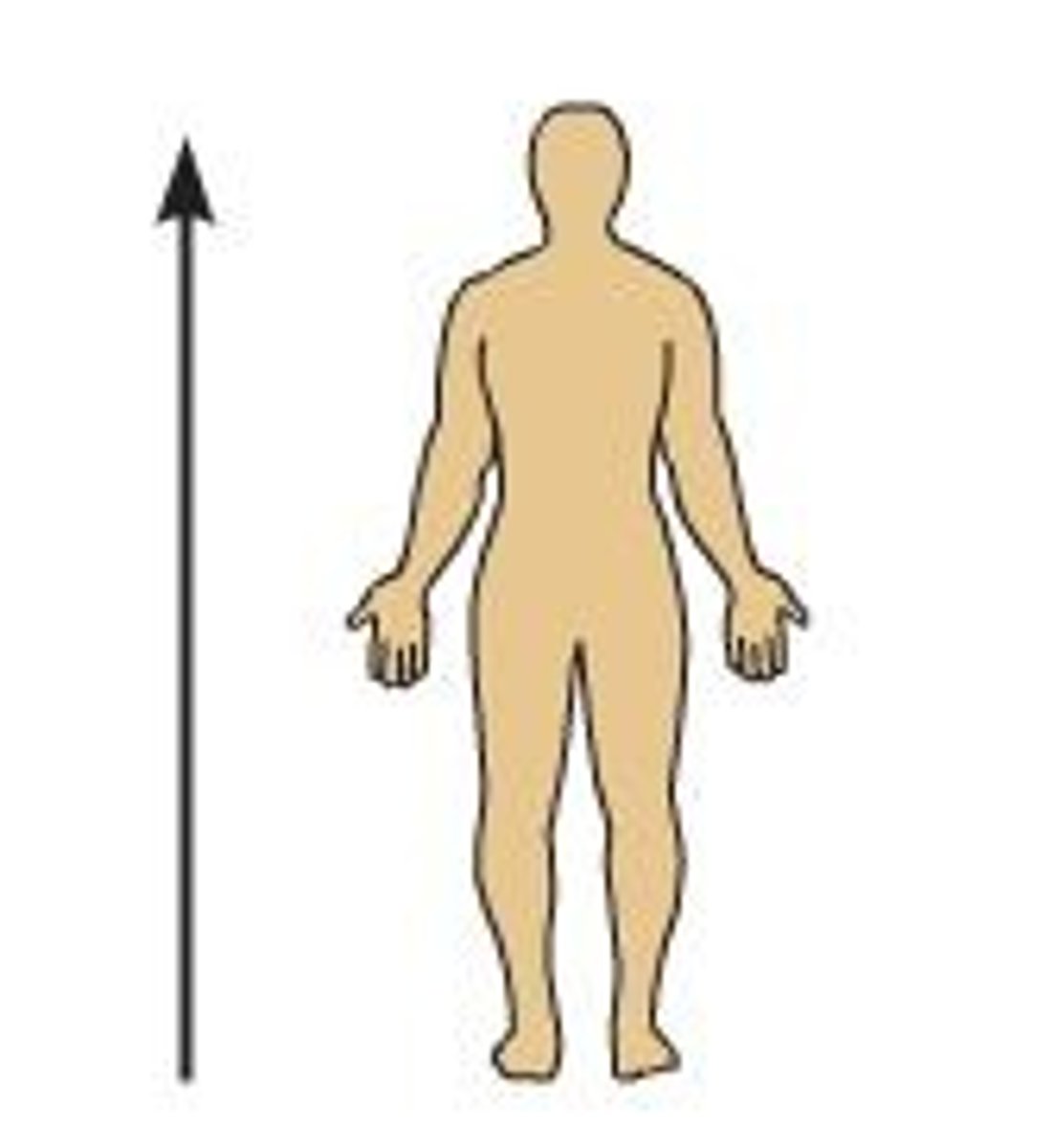
Superior
Higher on the body, nearer to the head
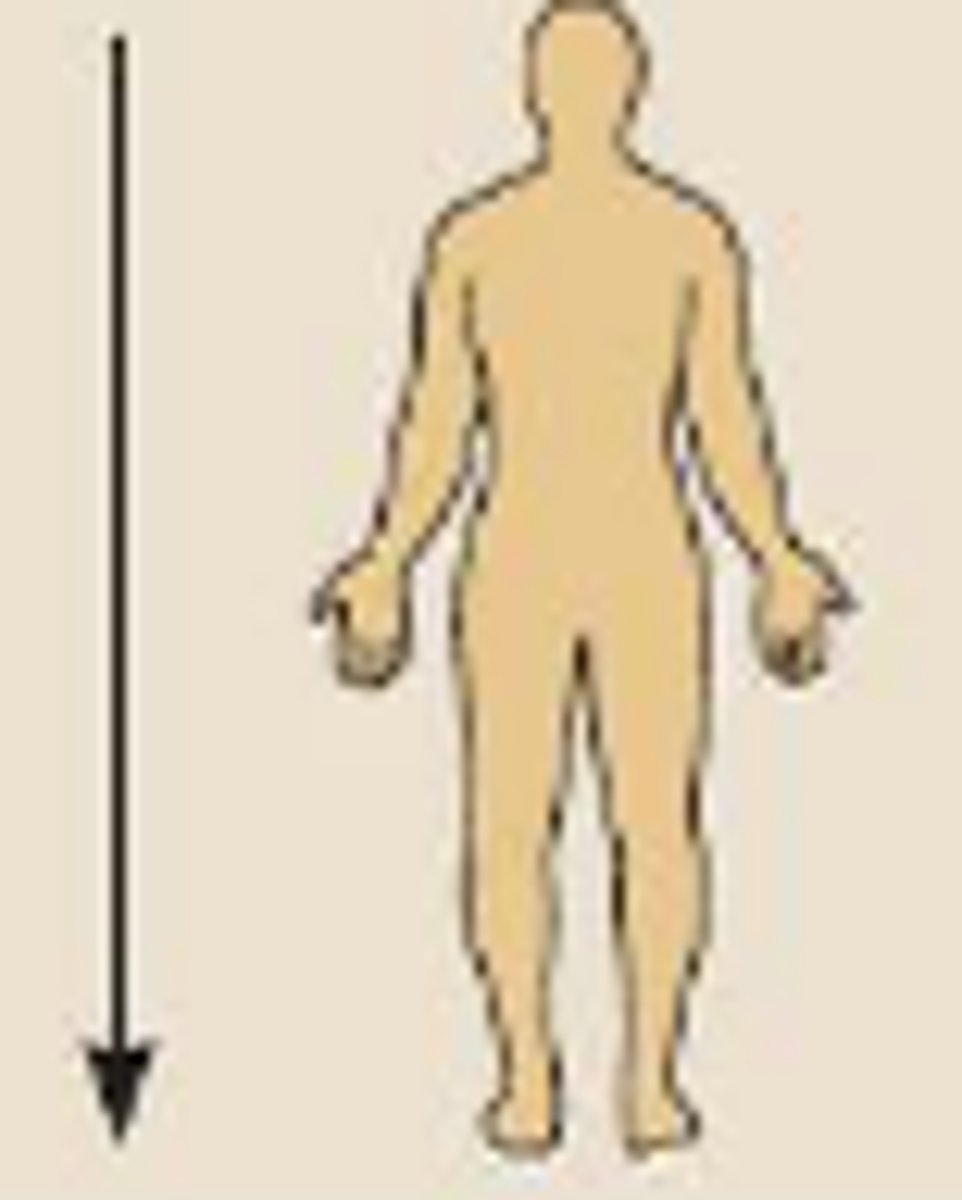
Inferior
Lower on the body, farther from the head
Anterior (ventral)
front of the body
Posterior (dorsal)
back of the body
Medial
nearer to median plane
Lateral
farther from median plane (side)
Proximal
nearer to trunk and/or point of origin
Distal
furthest from trunk and/or point of origin
Superficial
nearer to surface
Intermediate
Between a superficial and deep structure. - ex. biceps muscle is intermediate between the skin and humerus
Deep
farther from the surface. - ex. the humerus is deep to the arm muscles
Palmar
anterior hand (palm)
Plantar
interior of foot (sole)
Flexion
decreasing the angle between body parts, causing a joint to bend
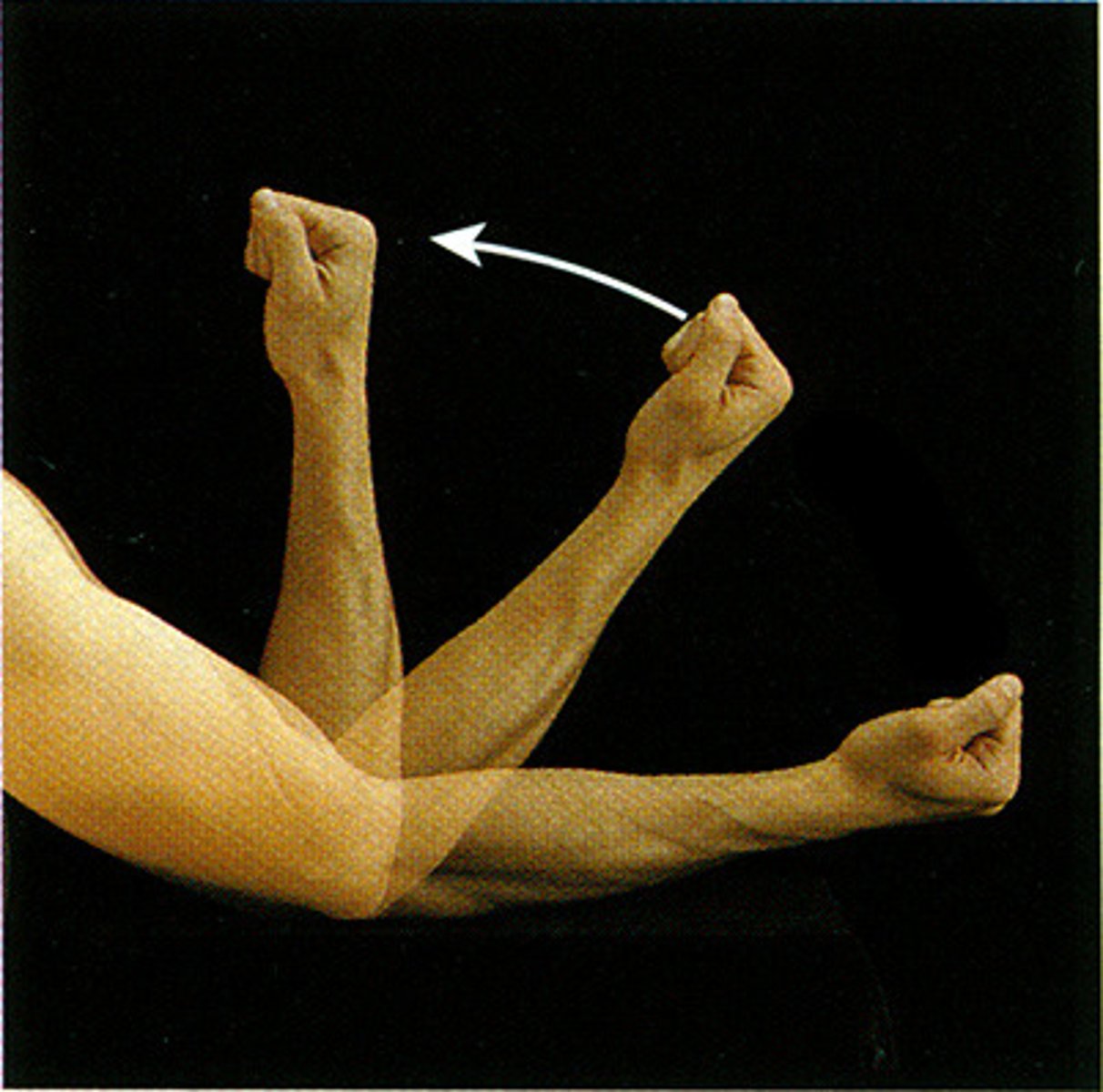
Extension
increasing the angle between body parts, causing a joint to straighten or return to anatomical position
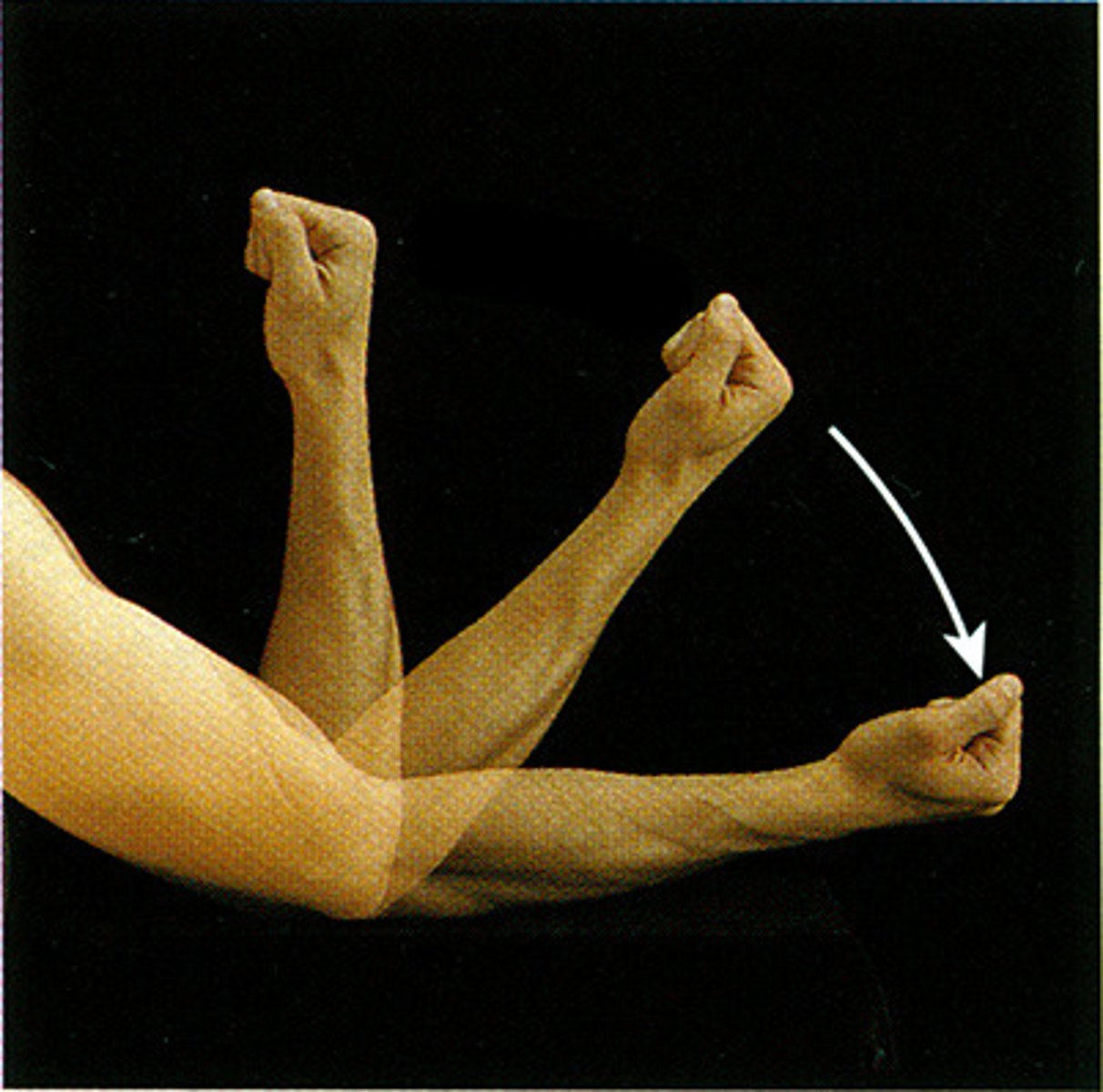
Abduction
moving away from the median plane of the body
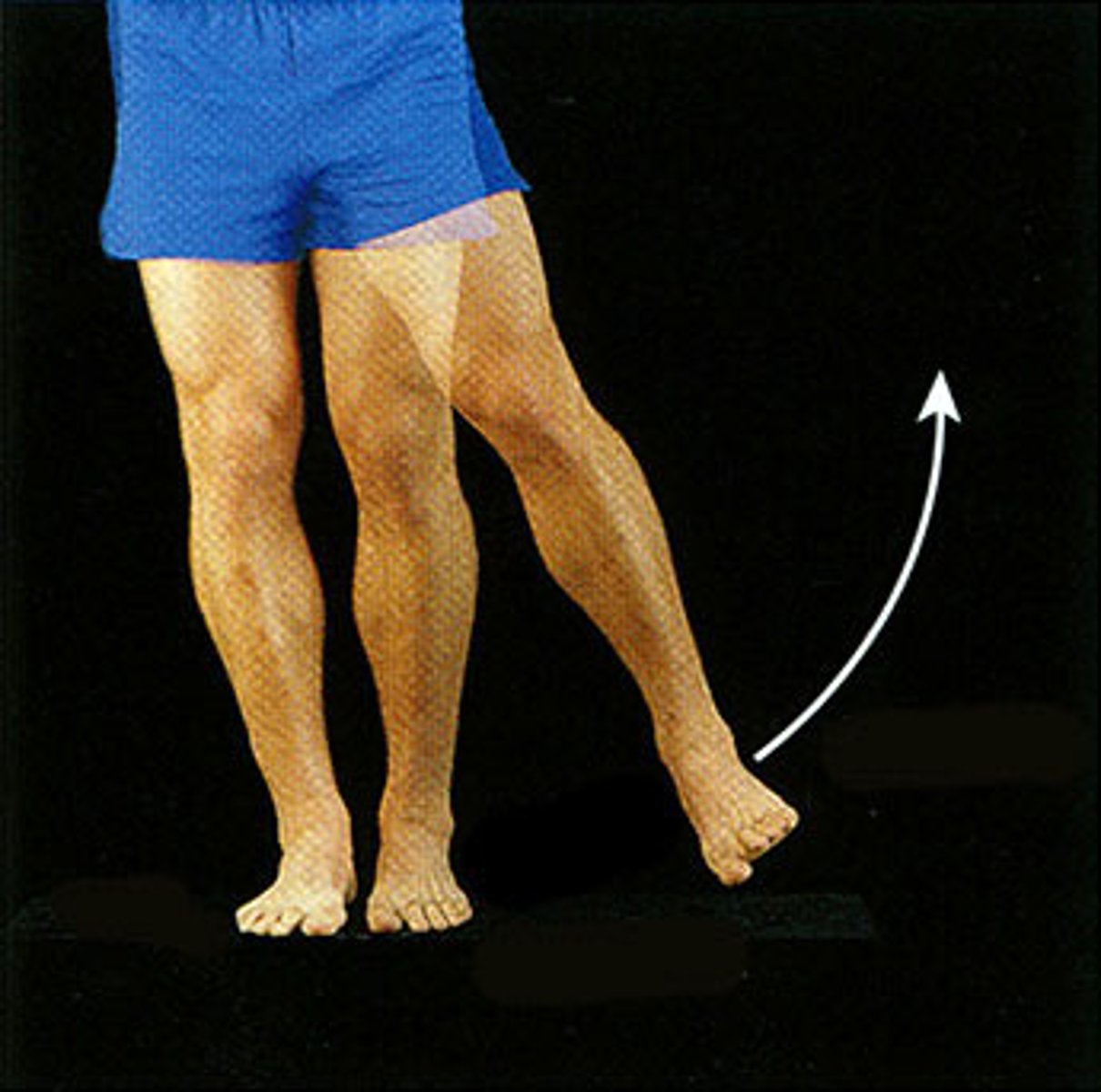
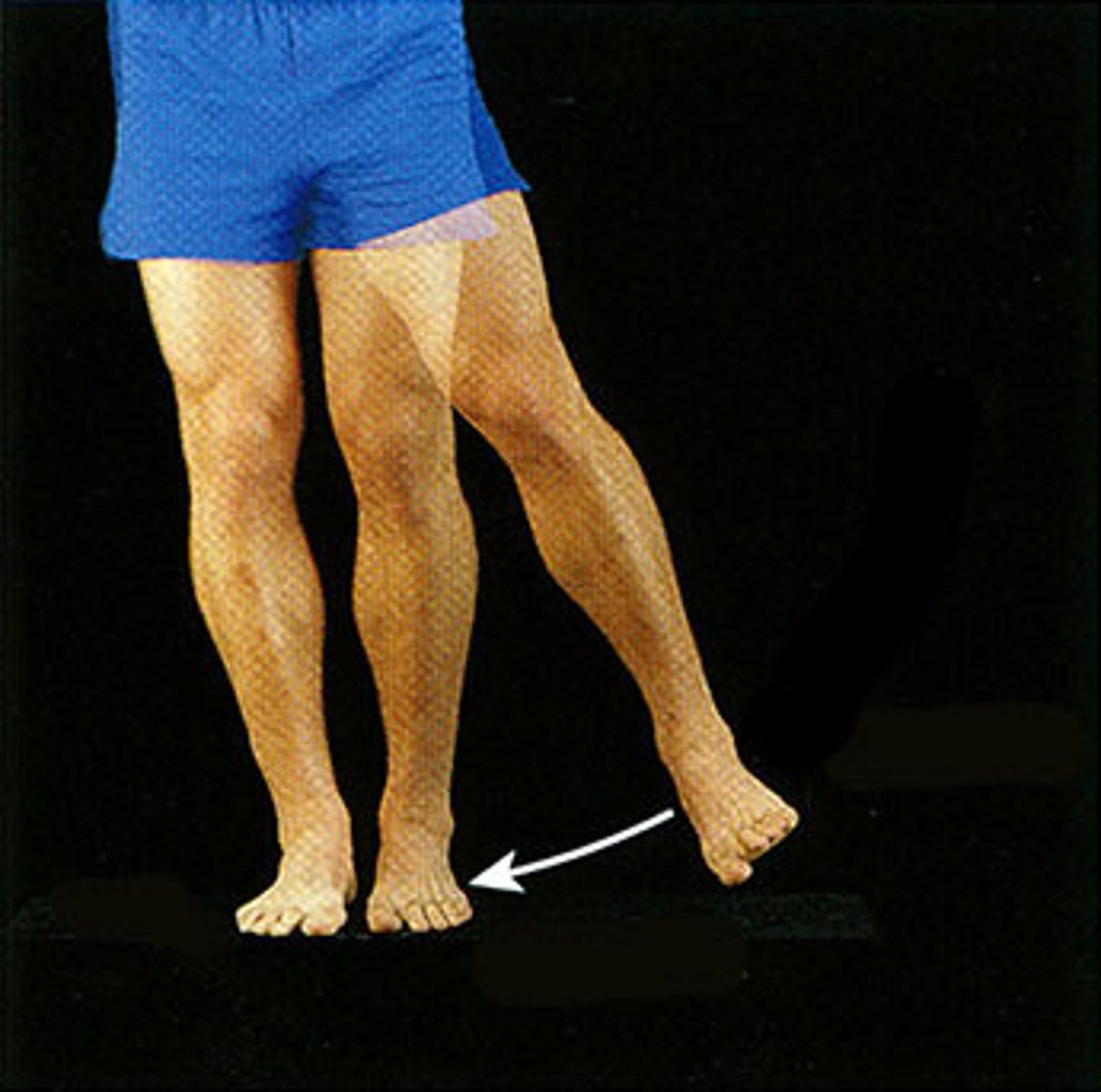
Adduction
moving toward the median plane of the body
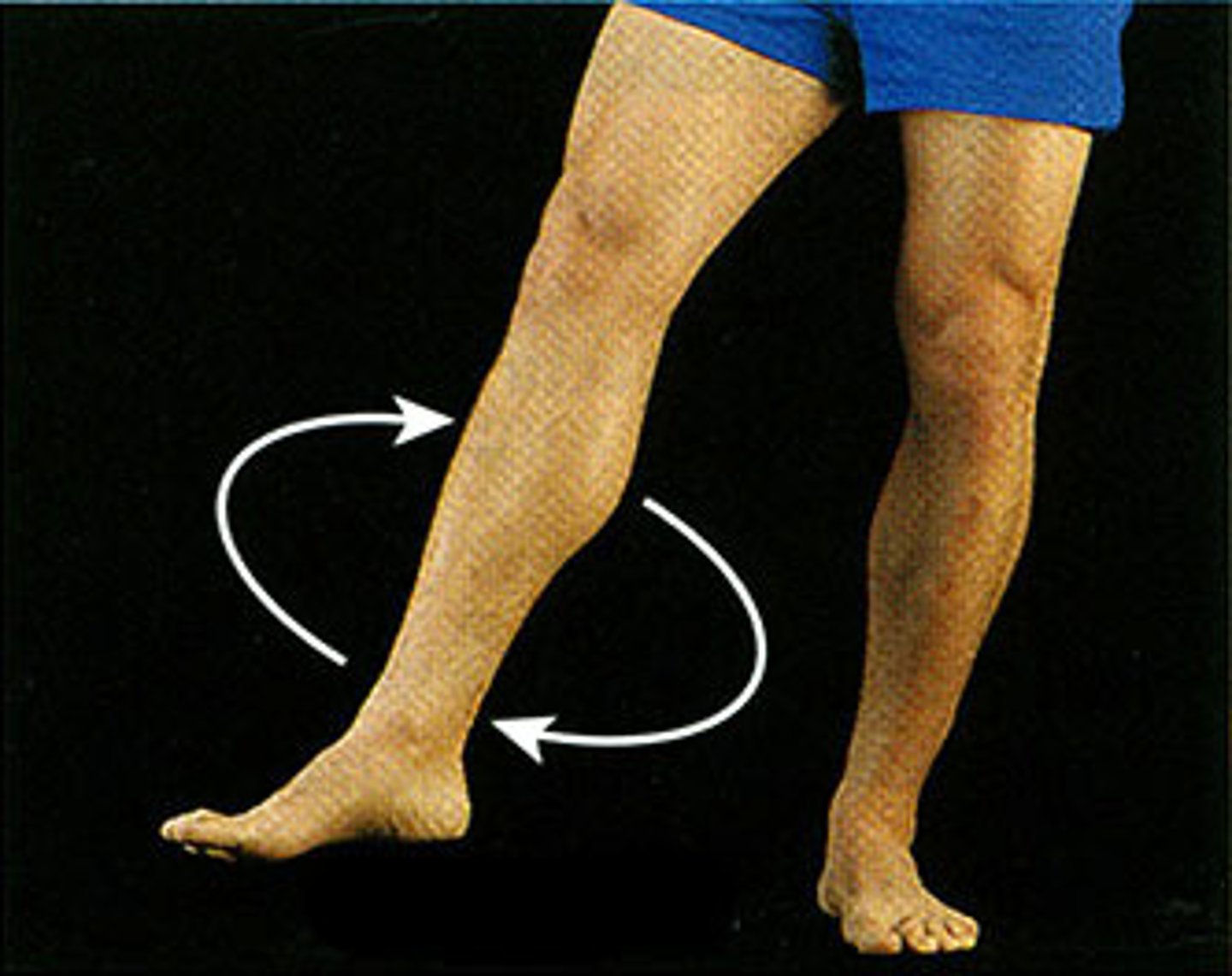
Circumduction
circular movement of (typically a limb)
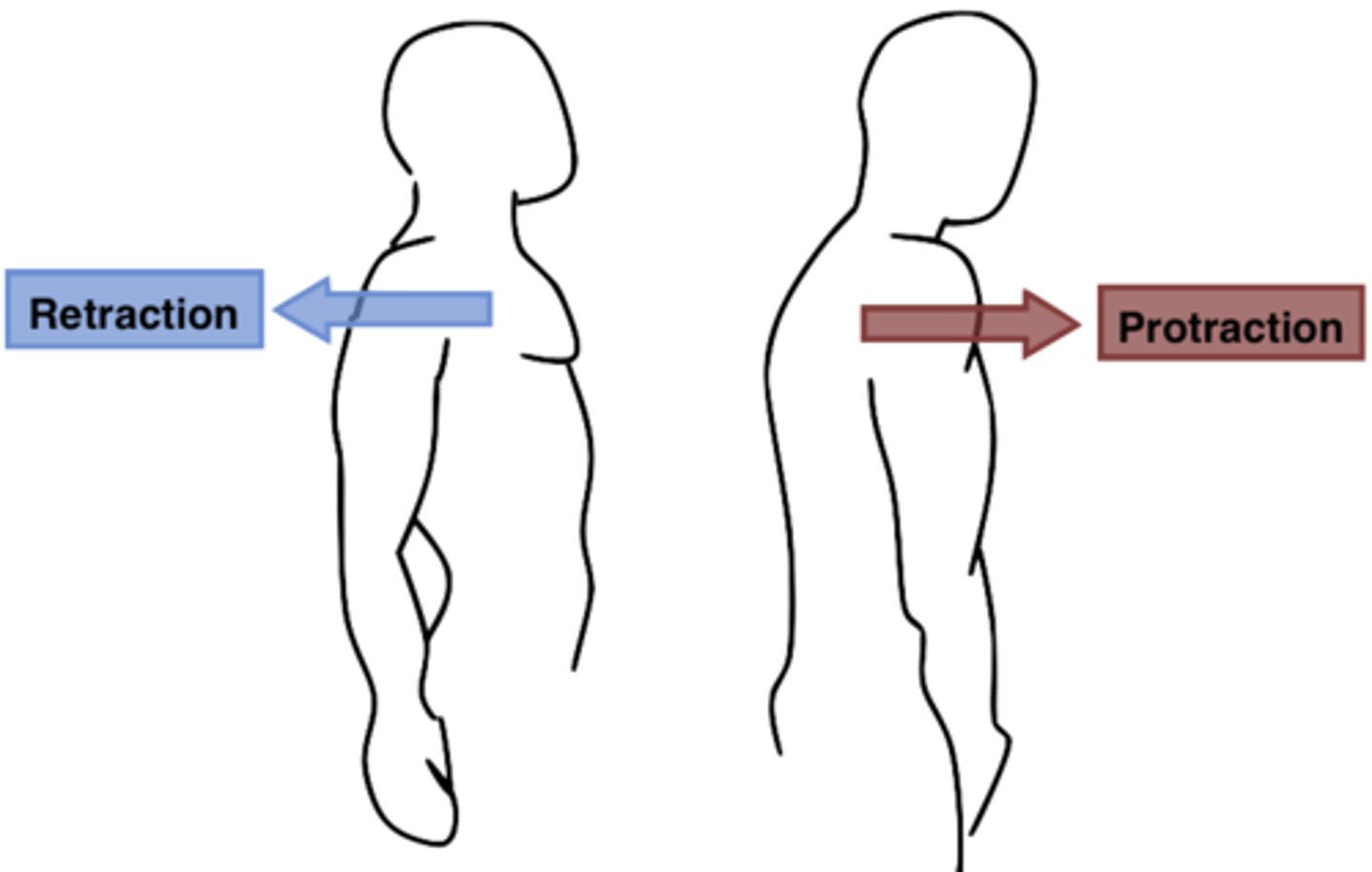
Protraction
moving of body part anteriorly ex. Moving the shoulder anteriorly
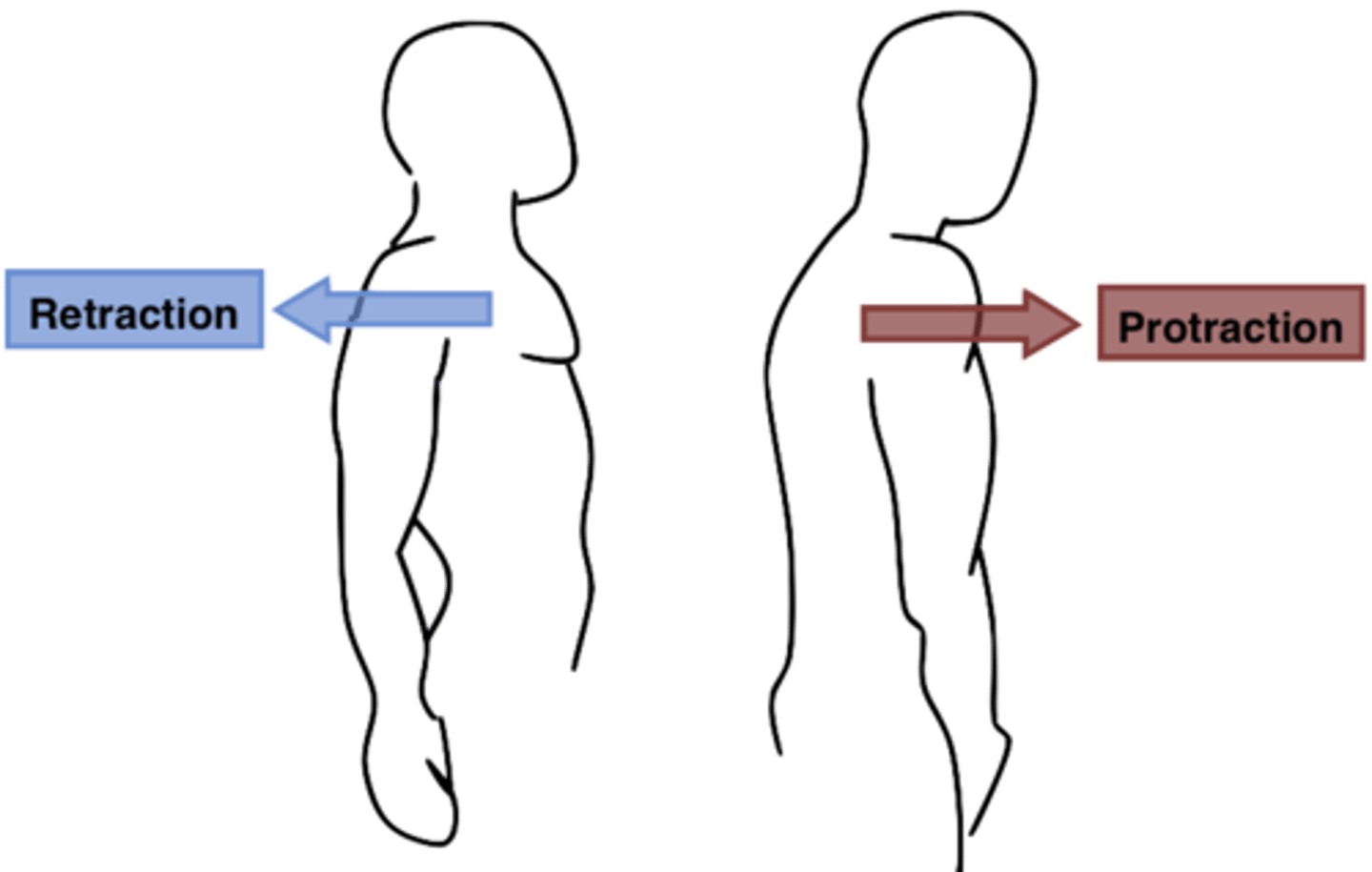
Retraction
moving of body part posteriorly ex. Moving the shoulder posteriorly
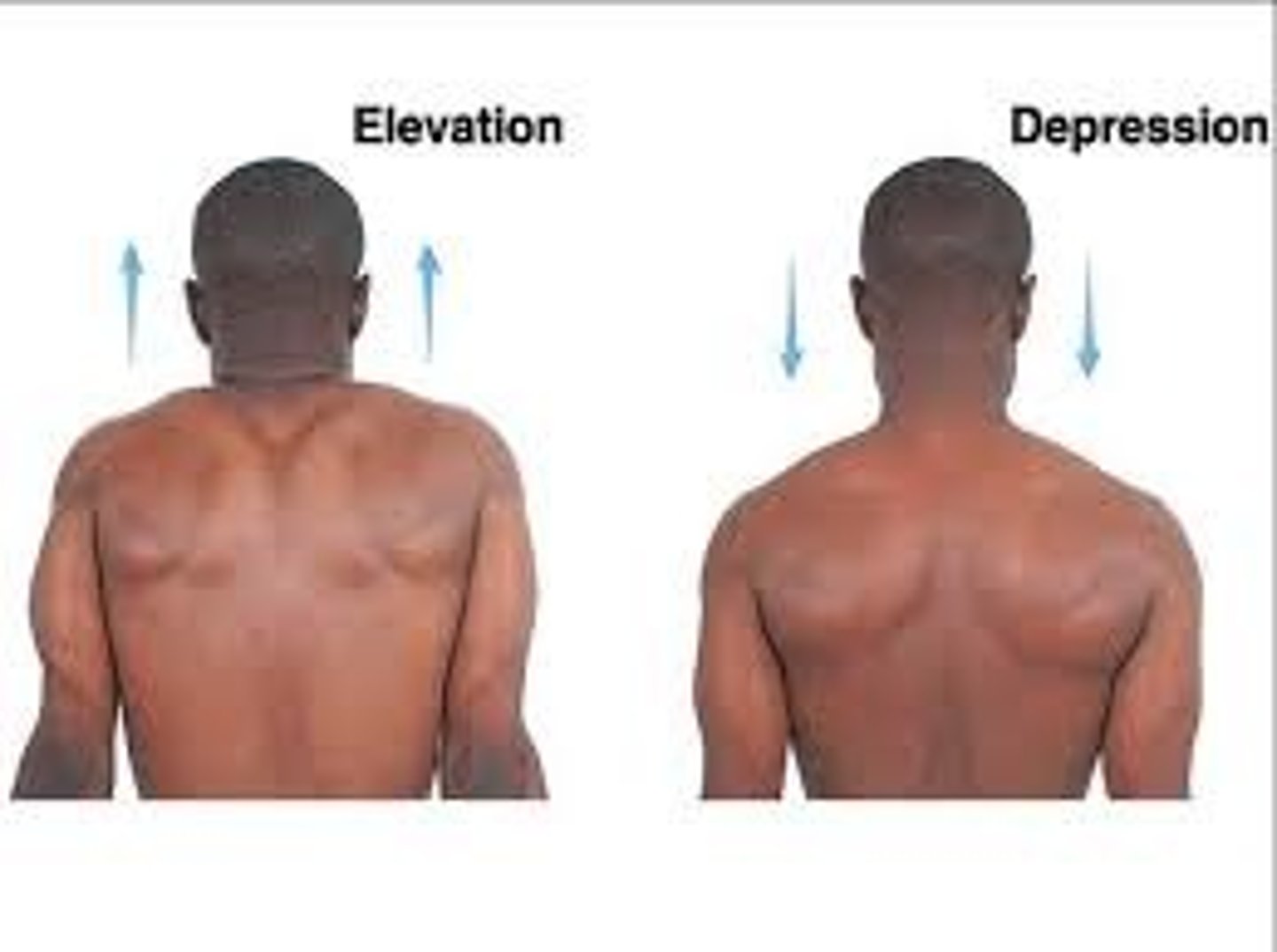
Elevation
moving a body part straight up ex. Moving the shoulders toward the head (shoulder shrug)
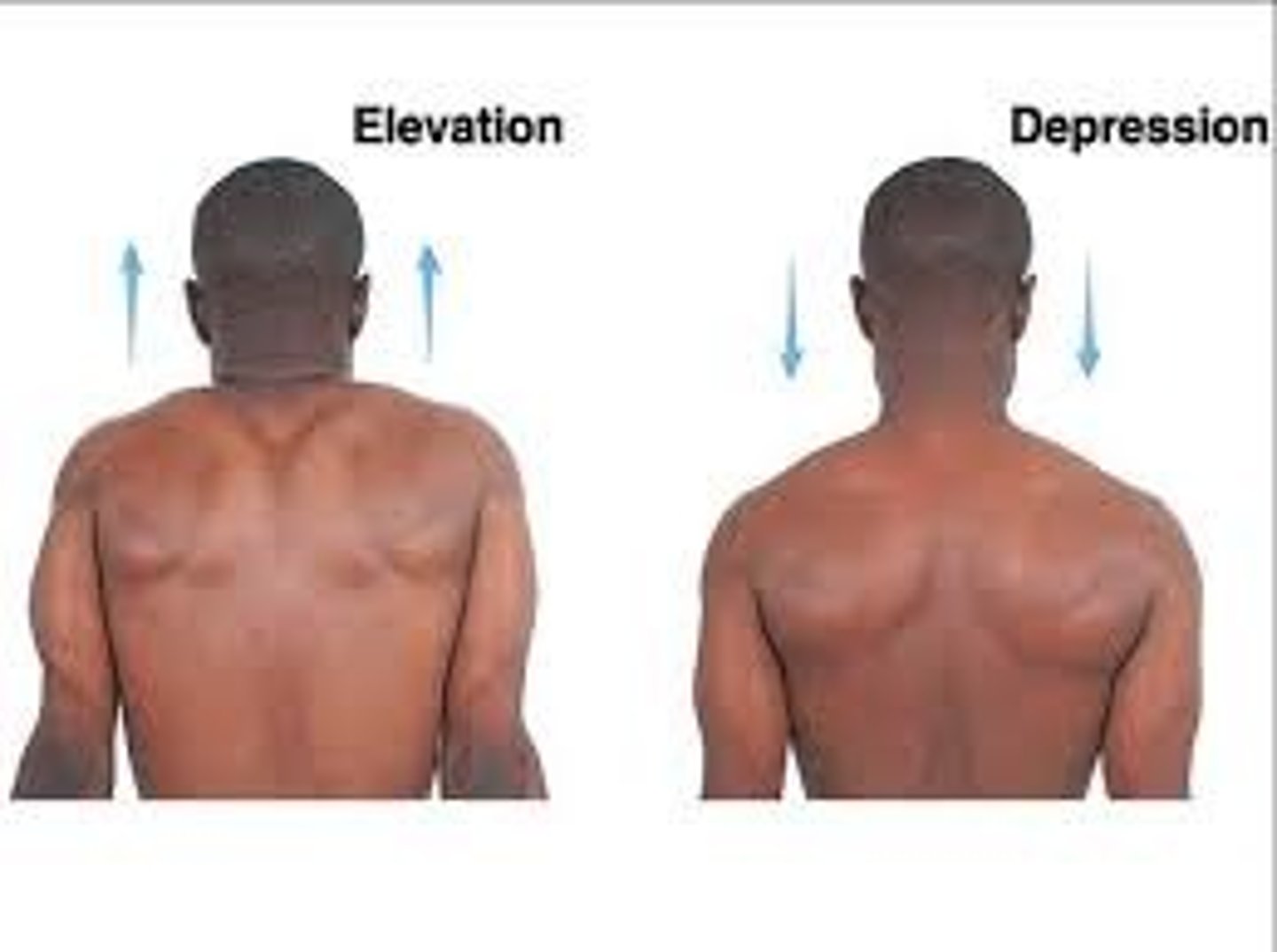
Depression
moving a body part down ex. Moving the shoulders down from head/back to normal position
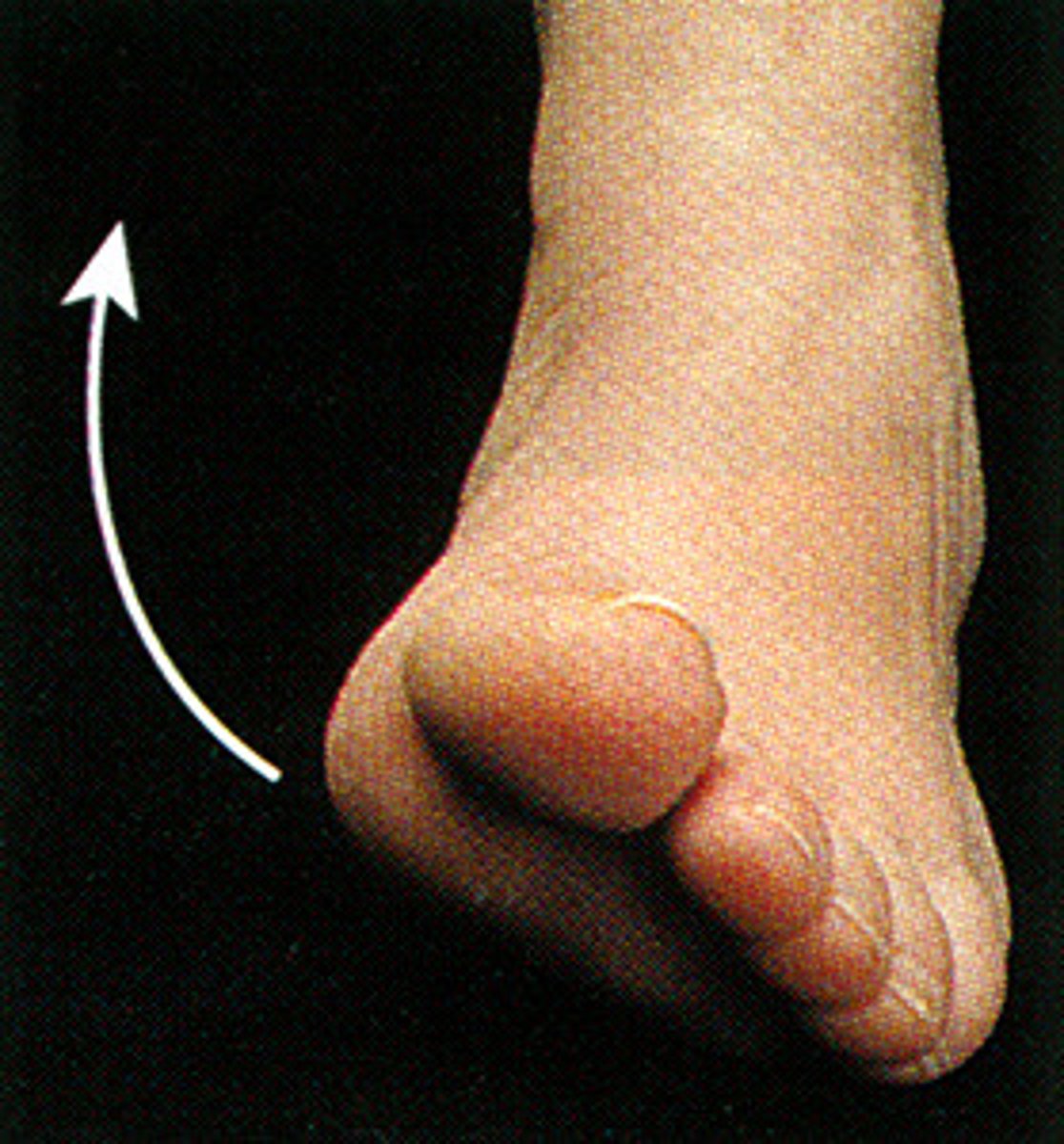
Eversion
turning body part away from midline ex. turns the sole of the foot outward away from the midline
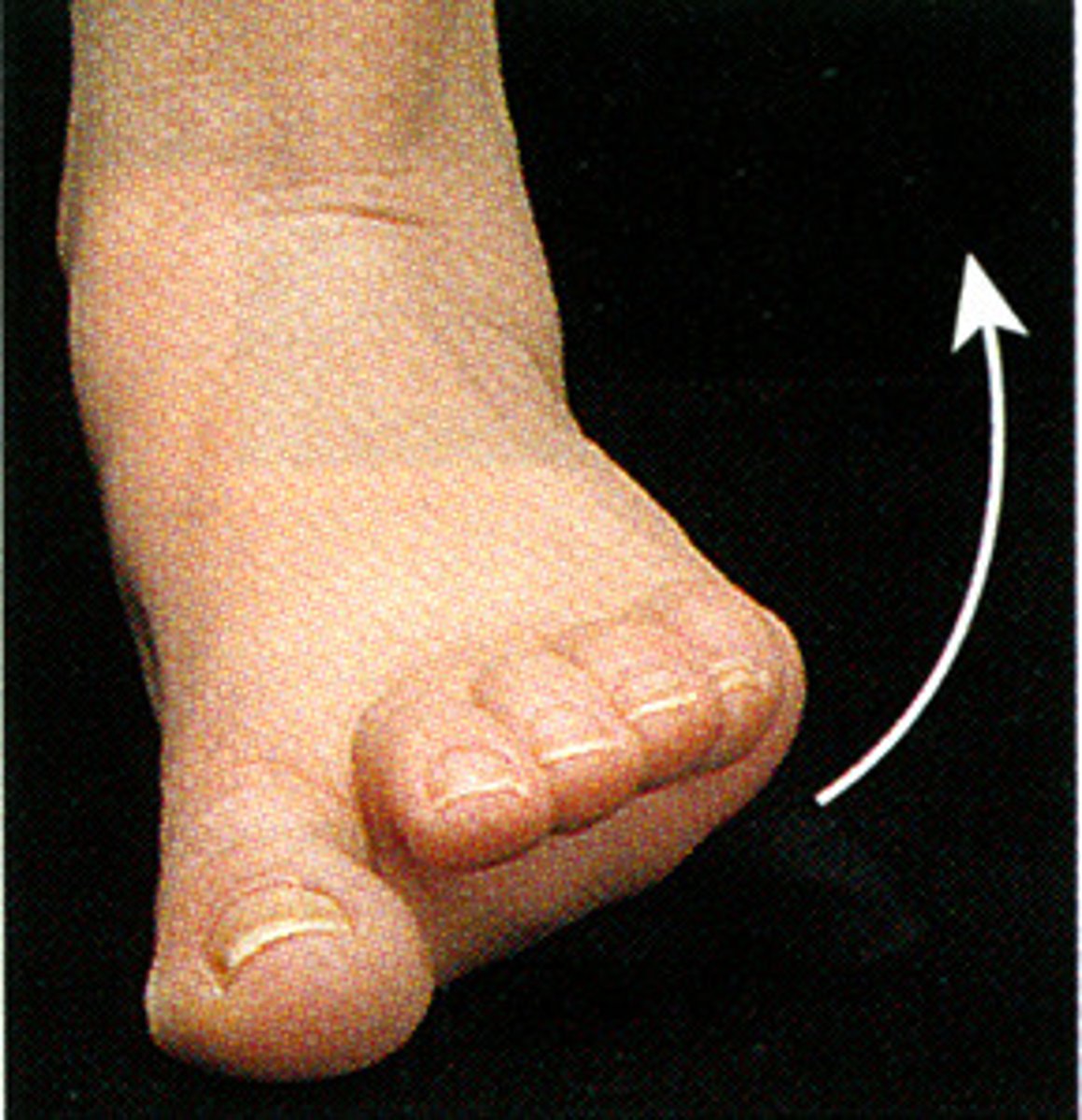
Inversion
turning body part toward midline ex. turns the sole of the foot inward toward the midline
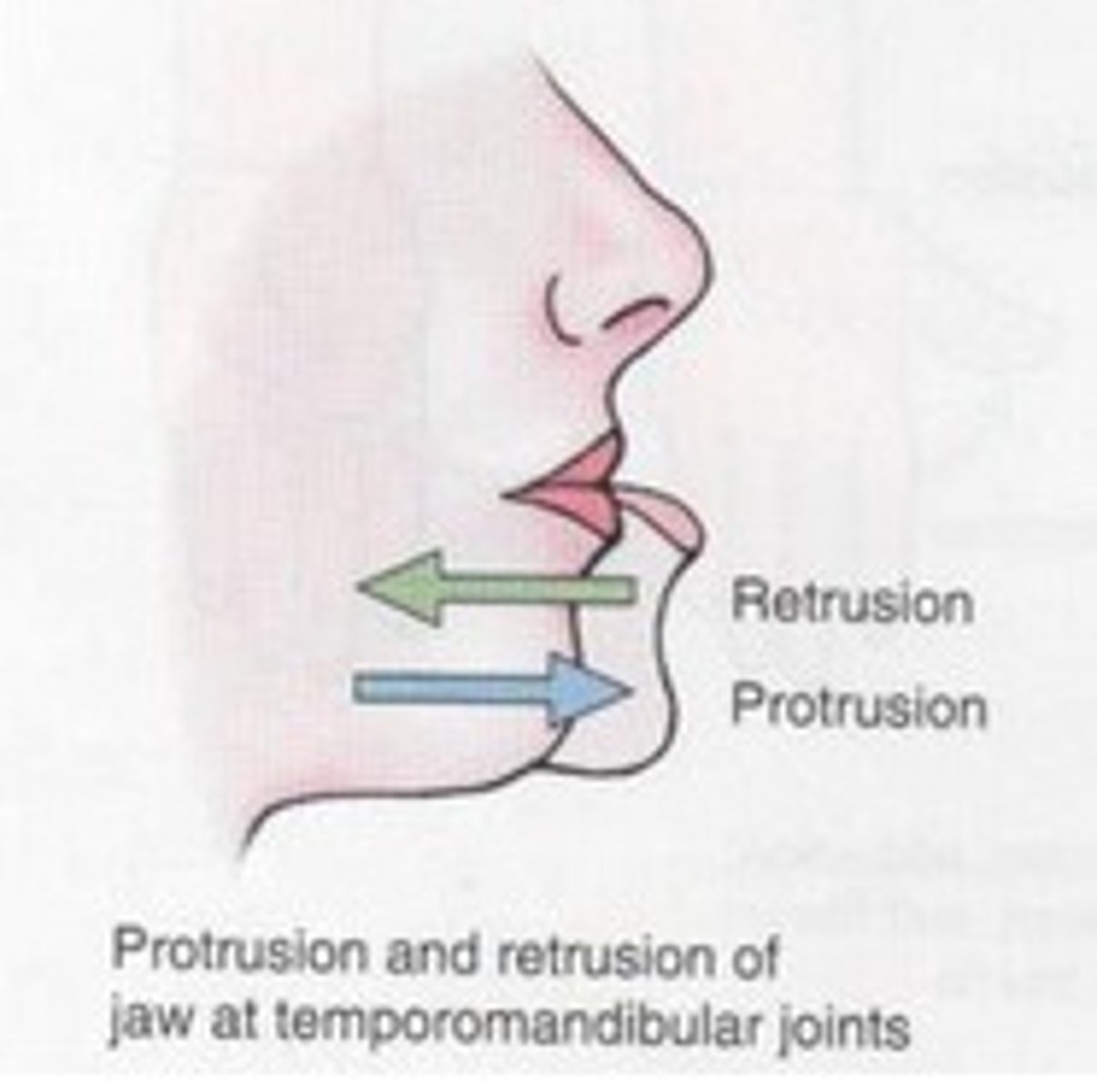
Retrusion
moving a part of the body posteriorly (as in retracting the mandible)
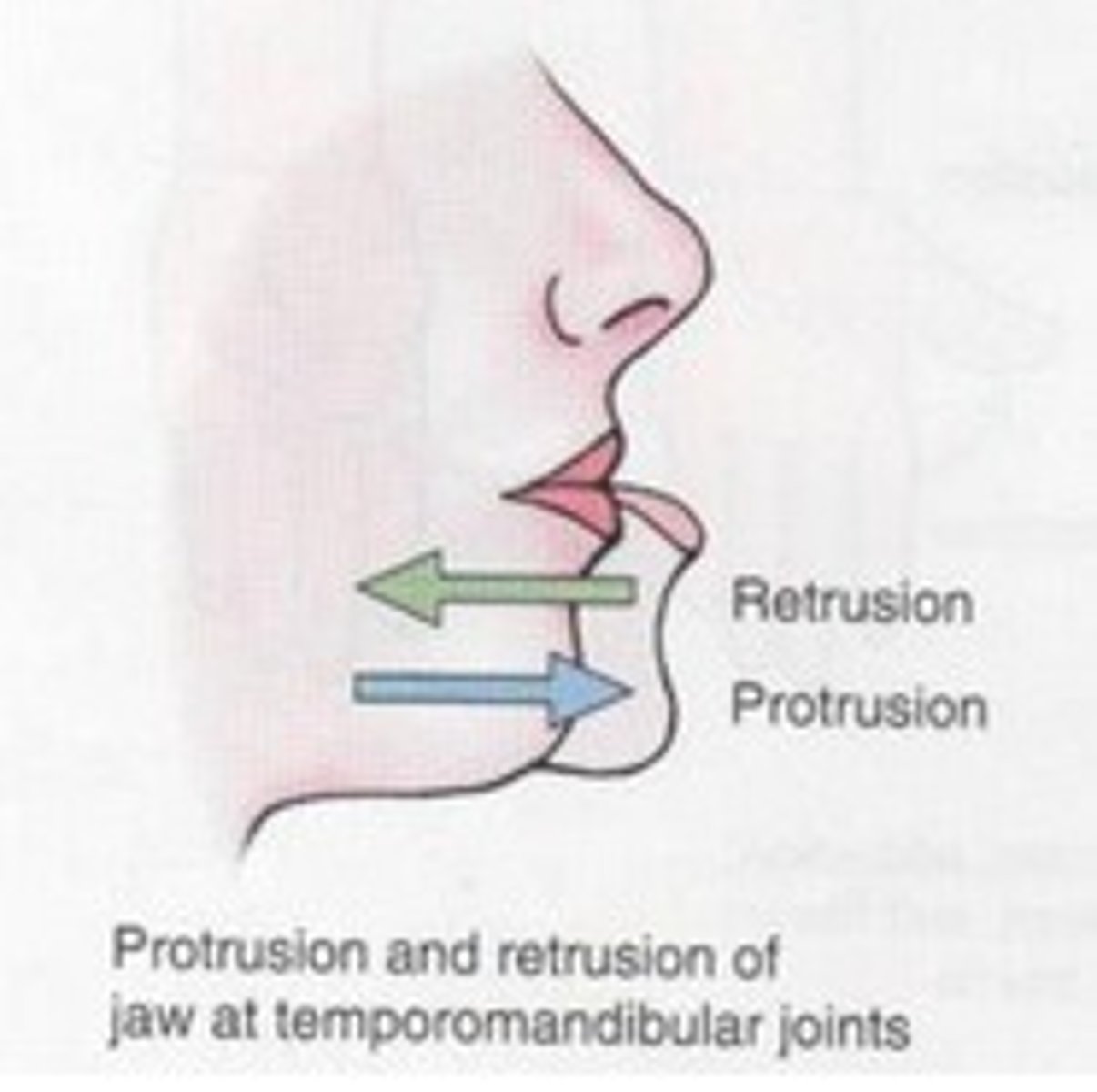
Protrusion
Moving a part of the body anteriorly (as in sticking the mandible out)
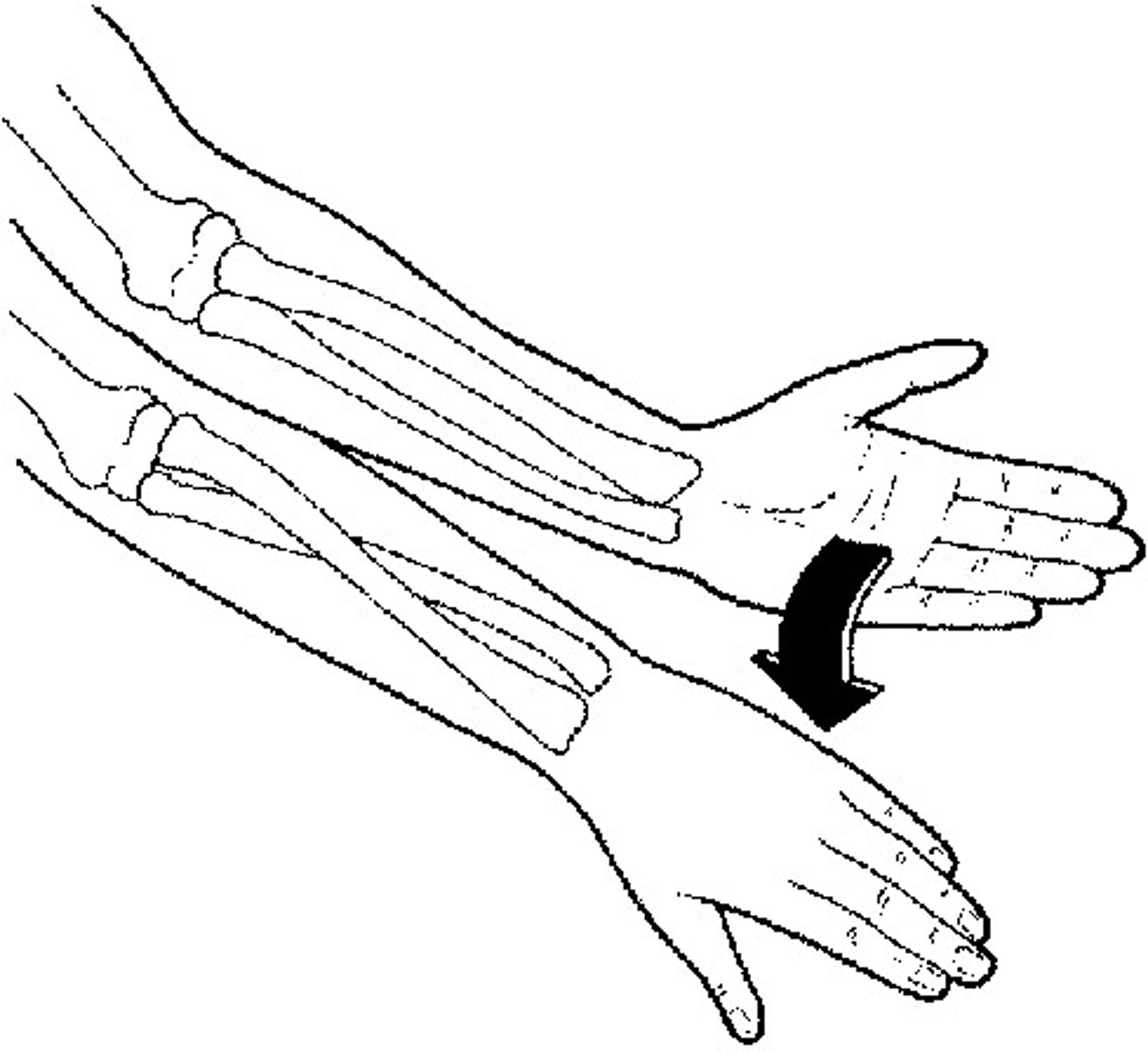
Supination
movement that turns the palm up
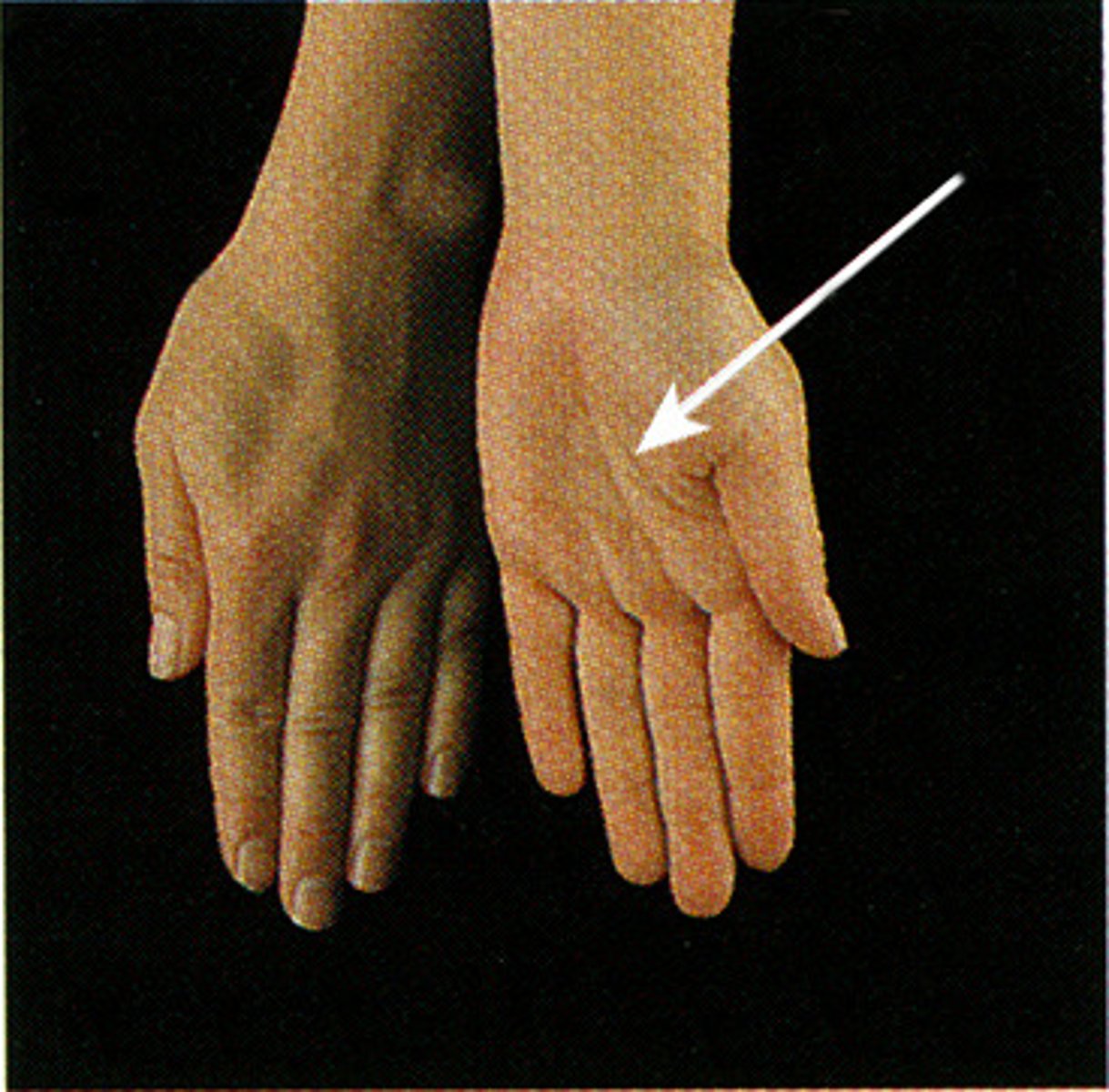
Pronation
turning the palm downward
The three general types of joints
fibrous, cartilaginous, synovial
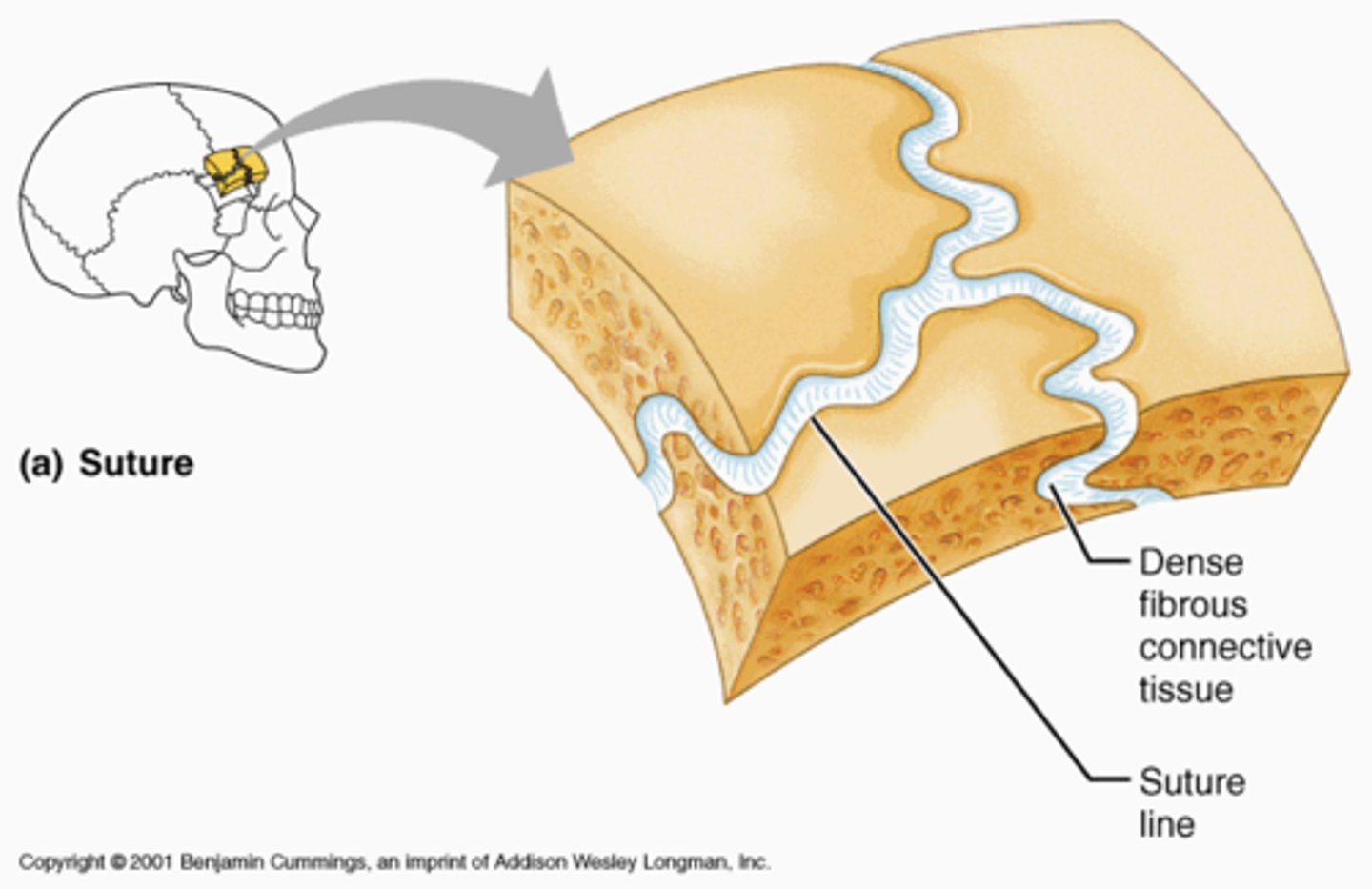
Fibrous joint
suture, dental alveolar, syndesmosis
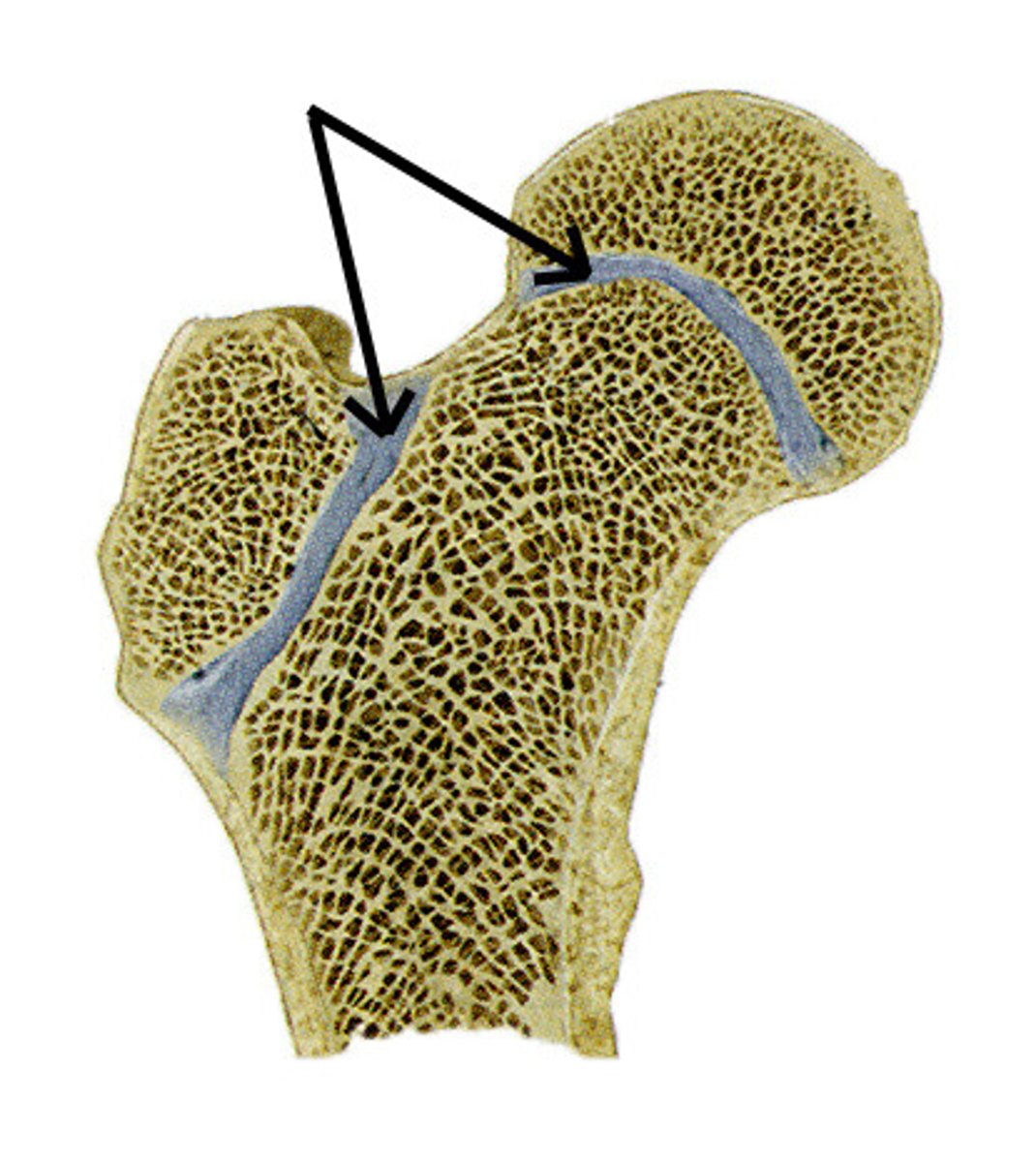
Cartilaginous joint
epiphysial line, IVD (intervertebral disc), - pain fibers
Synovial joint
Joint capsule, synovial fluid, articular cartilage; DJD (degenerative joint disease), RA (rheumatoid arthritis), Gout
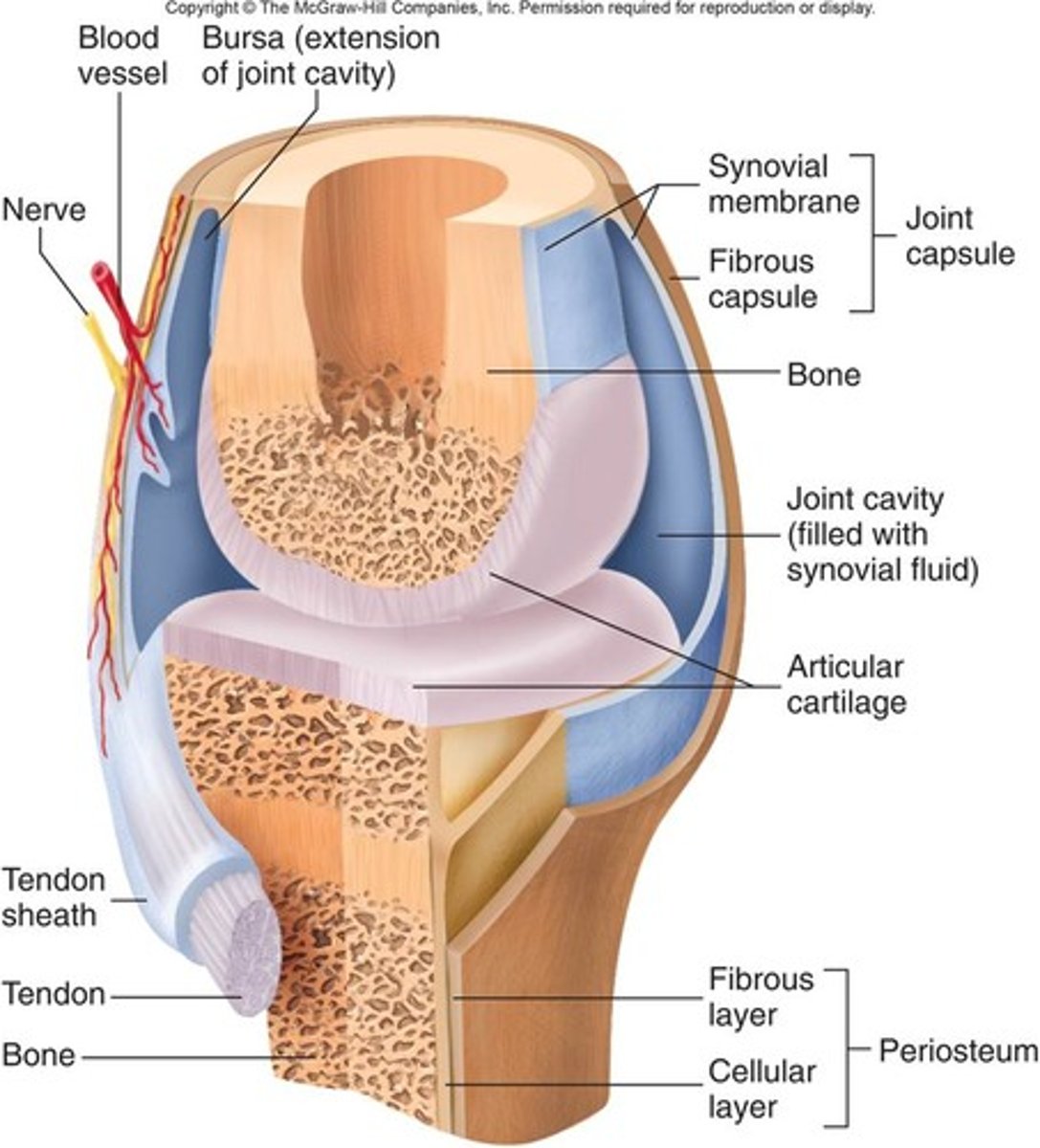
Hilton law
nerves supplying the joint also supply the muscles moving the joint and the overlying skin
3 Muscle types
Skeletal, cardiac, smooth
Skeletal muscle
striated, muscle fiber, nucleus, satellite cell
Cardiac muscle
Striated, intercalated discs, nucleus, muscle fibers
Smooth muscle
smooth muscle fiber, nucleus, non striated or striped ex. vessel walls and hollow organs
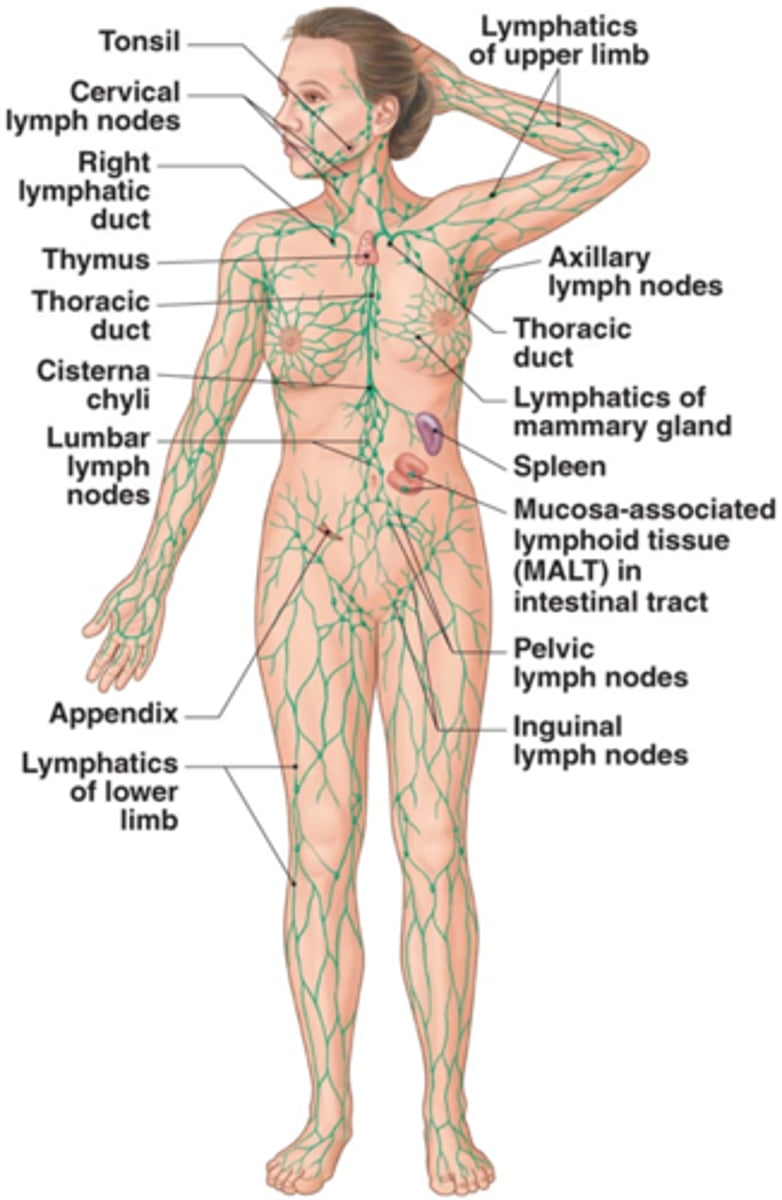
Lymphatic system diagram
interstitial fluid balance, filter system, digestive function (bile), immune function
Neuron
structural and functional units of the nervous system specialized for rapid communication
Neurogial cells
5 times more as abundant as neurons and are non-neuronal, non-excitable cells that form a major component (scaffolding) of the nervous system. Neuroglia support, insulate, and nourish neurons.
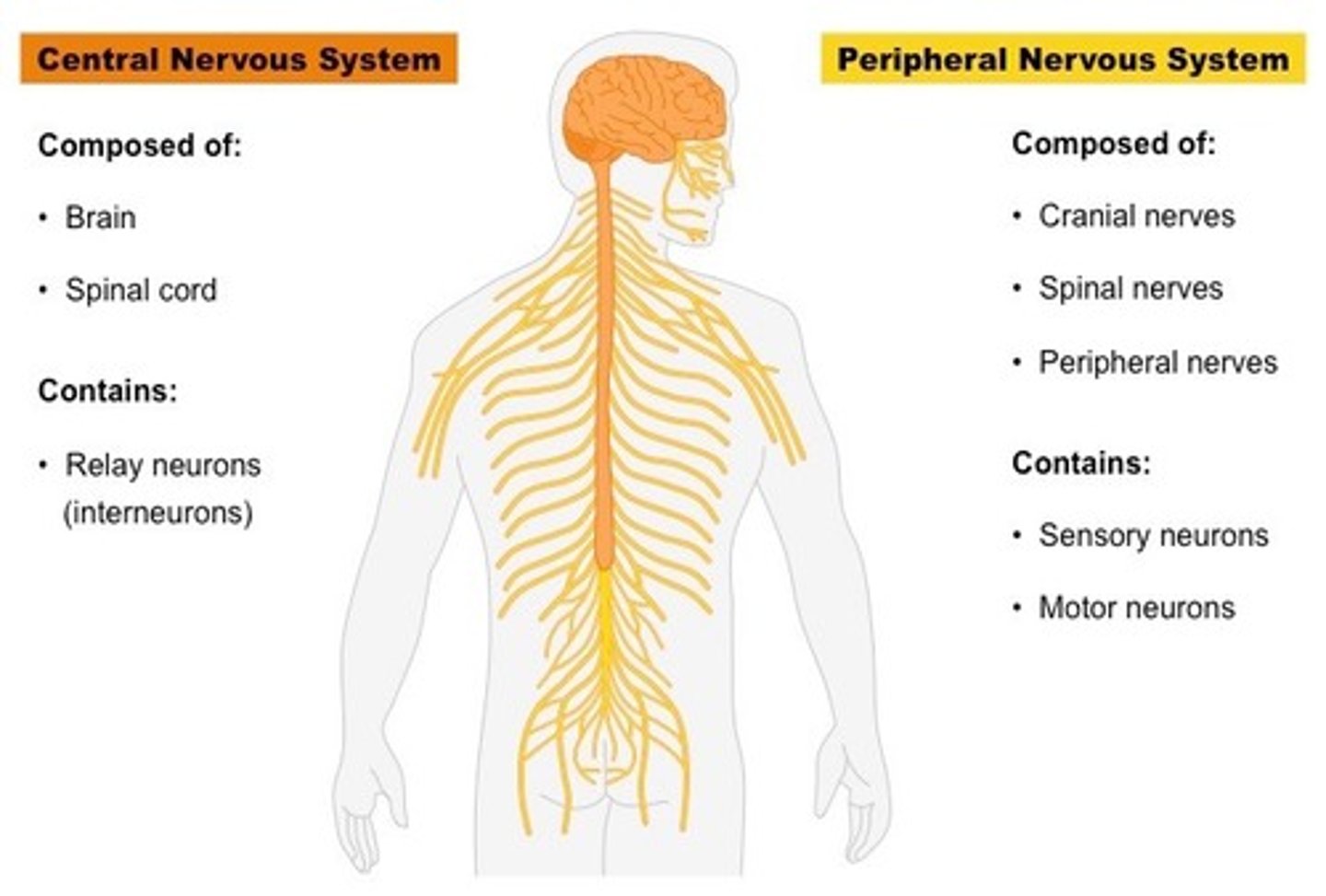
Central nervous system vs. Peripheral nervous system
- The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord. Main roles are to integrate and coordinate incoming and outgoing neural signals to carry out higher mental functions. ex. thinking and learning
- The PNS consists of nerve fibers and nerve cell bodies outside of the CNS that connect the CNS with peripheral structures
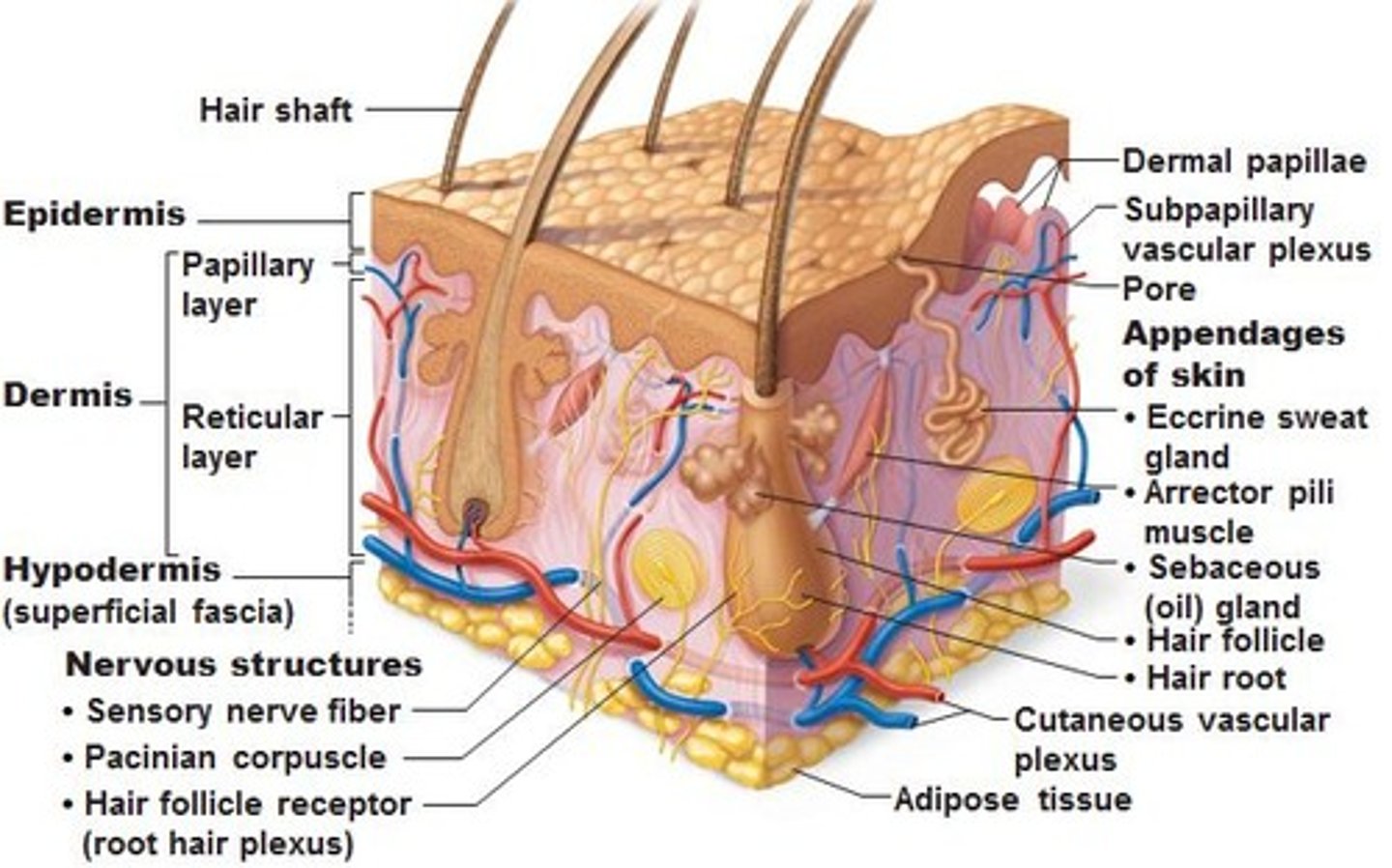
Epidermis
outermost layer of skin, stratified squamous epithelium, sheds (keratinized), avascular, afferent sensory receptors: pain, temperature, touch
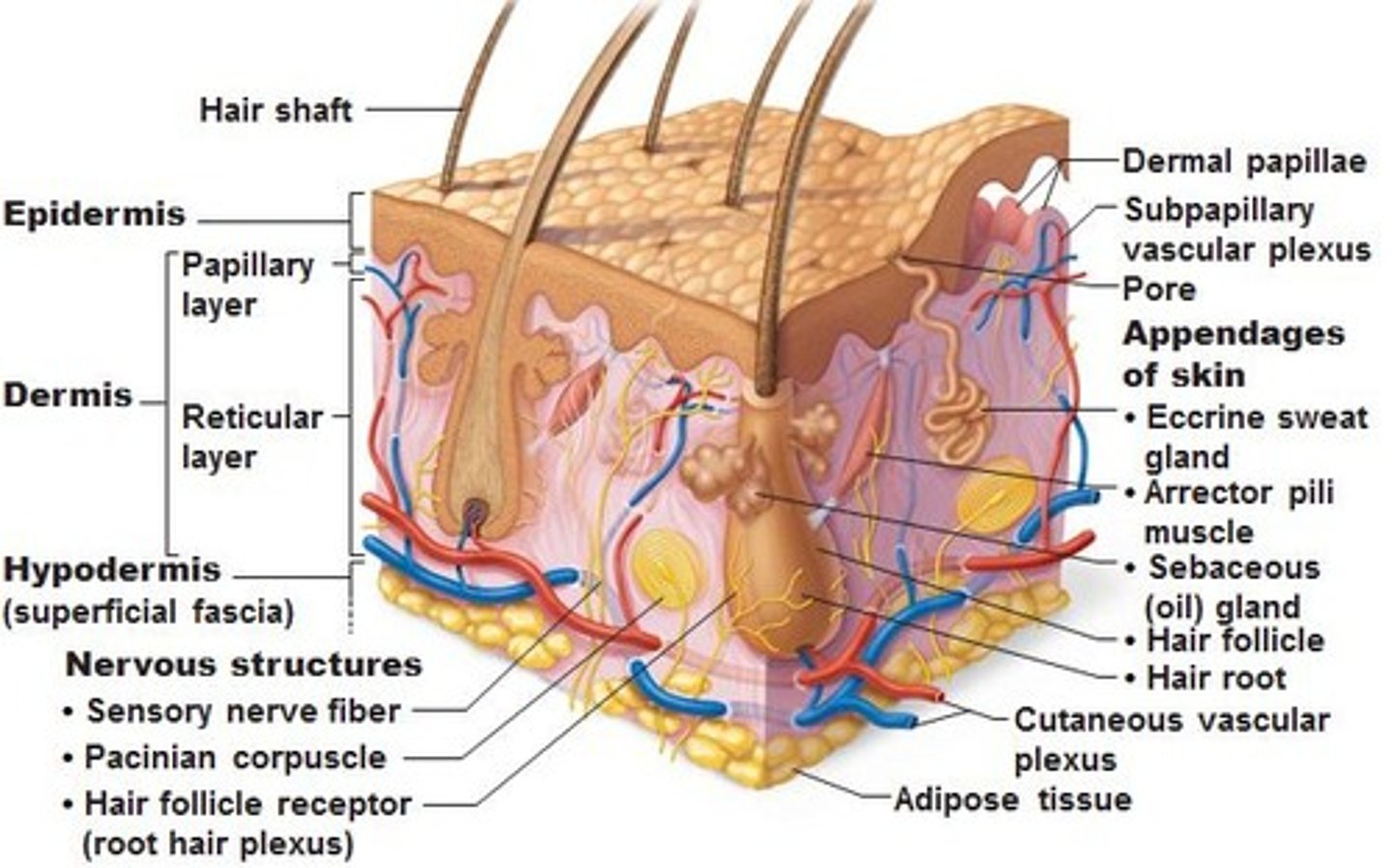
Dermis
Connective tissue, 2 layers: Papillary layer- locks onto epidermis ridges, Reticular layer- thicker, ID testing such as: PPD, allergy skin testing
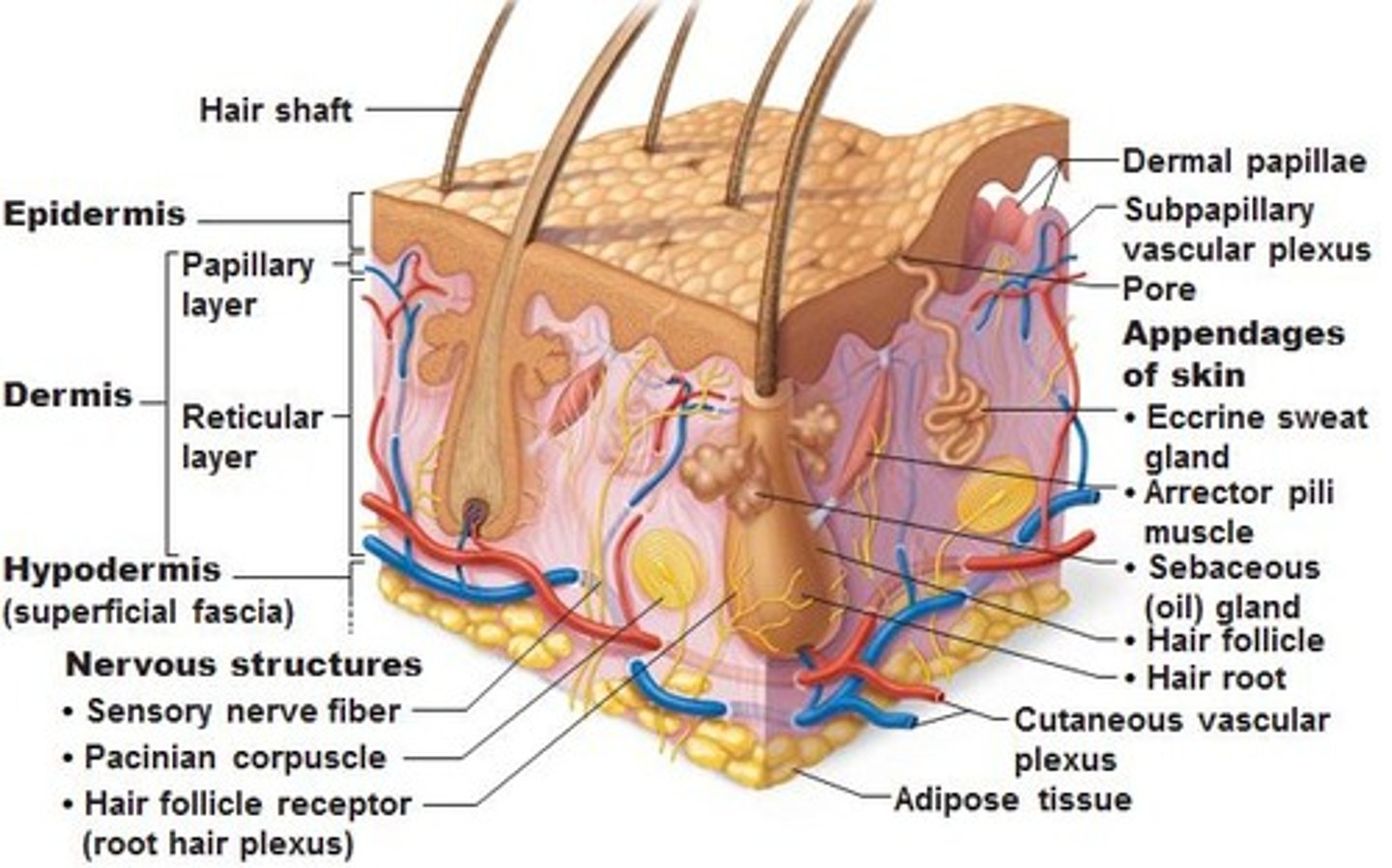
Subcutaneous layer (hypodermis/superficial fascia)
Loose connective tissue (superficial) and adipose tissue storage. Vessels, lymphatics, cutaneous nerves. Layer infiltrated for local anesthesia during minor procedures, ex. suturing or C-section