PT 536 Life and Death of Neurons
1/139
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
140 Terms
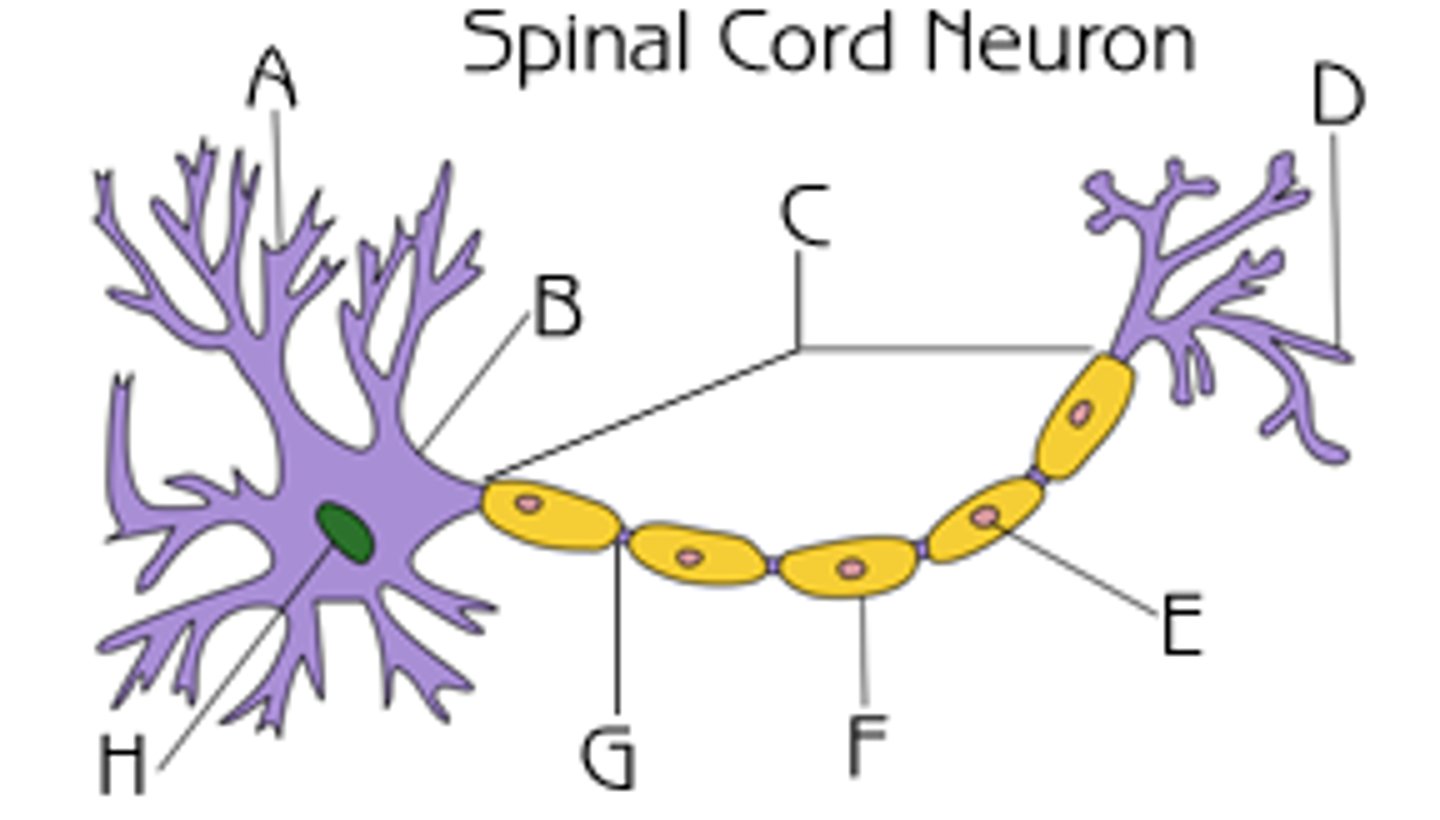
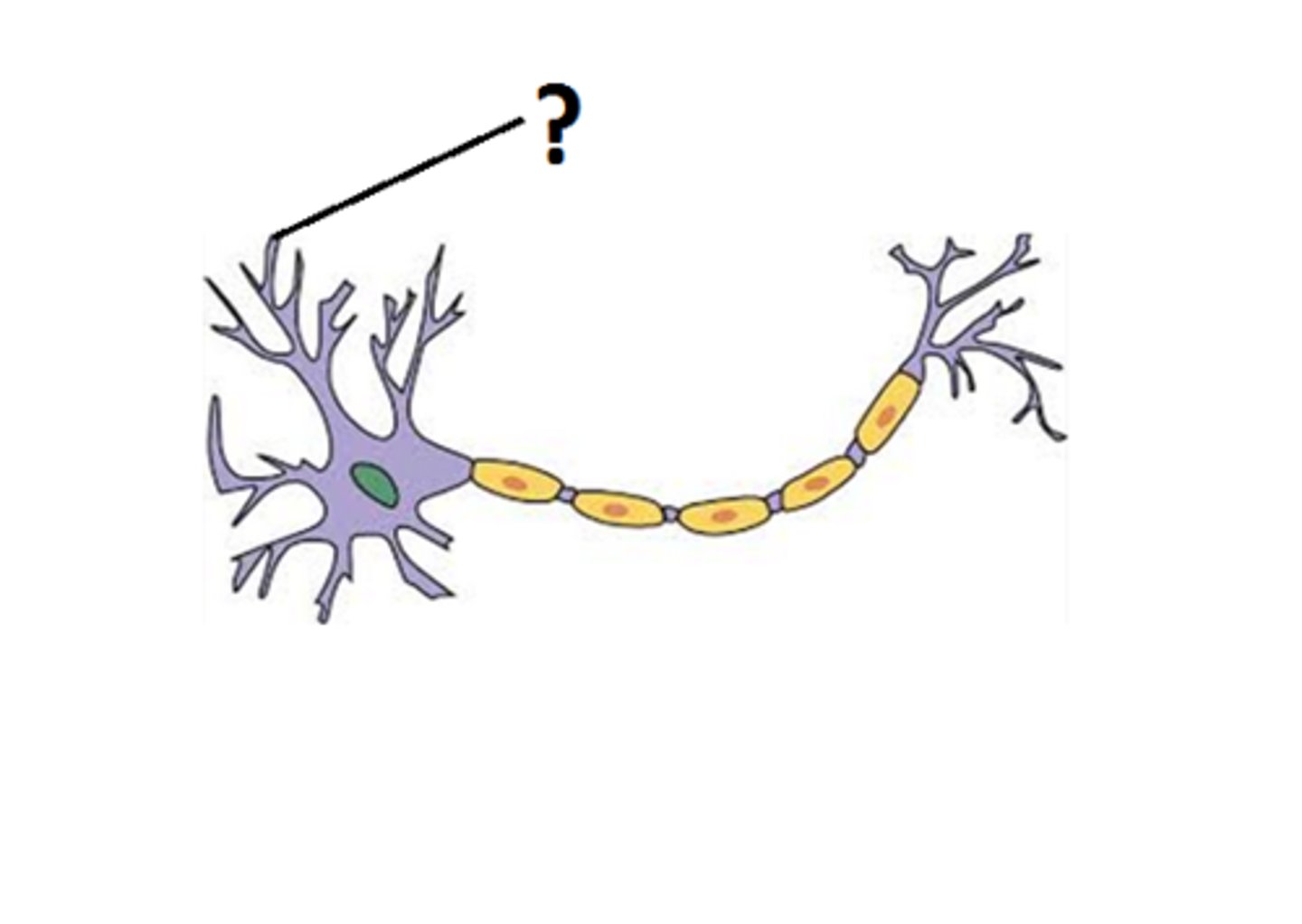
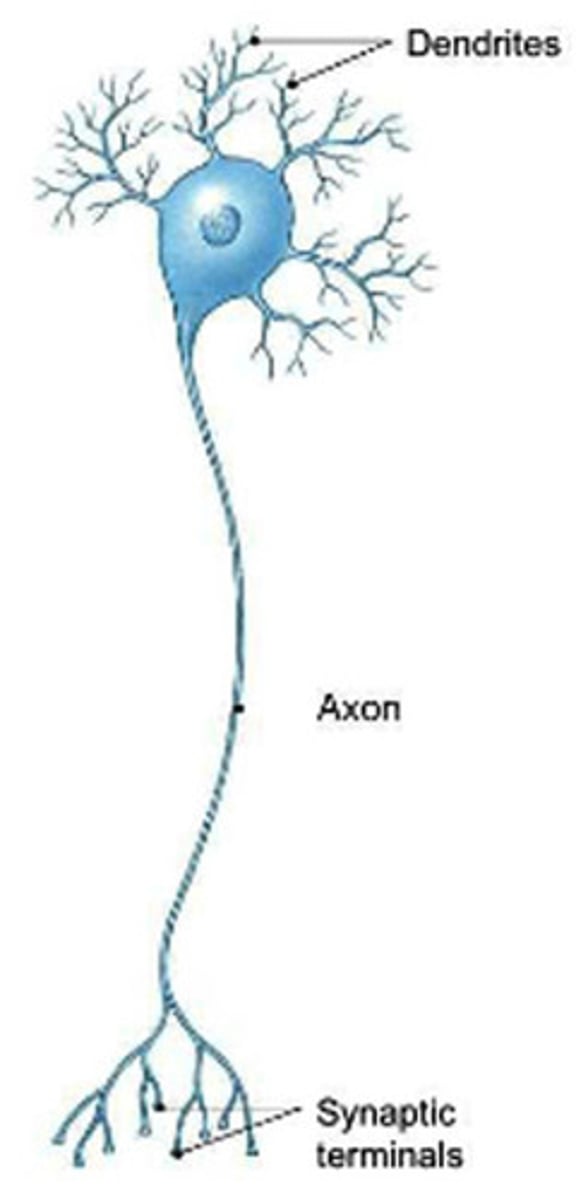
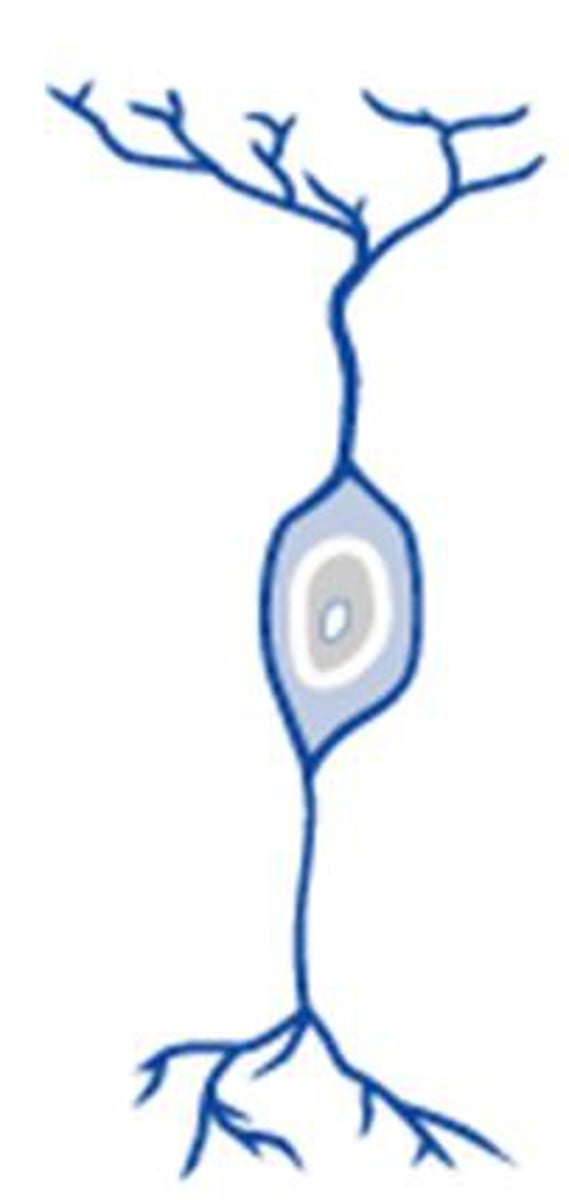
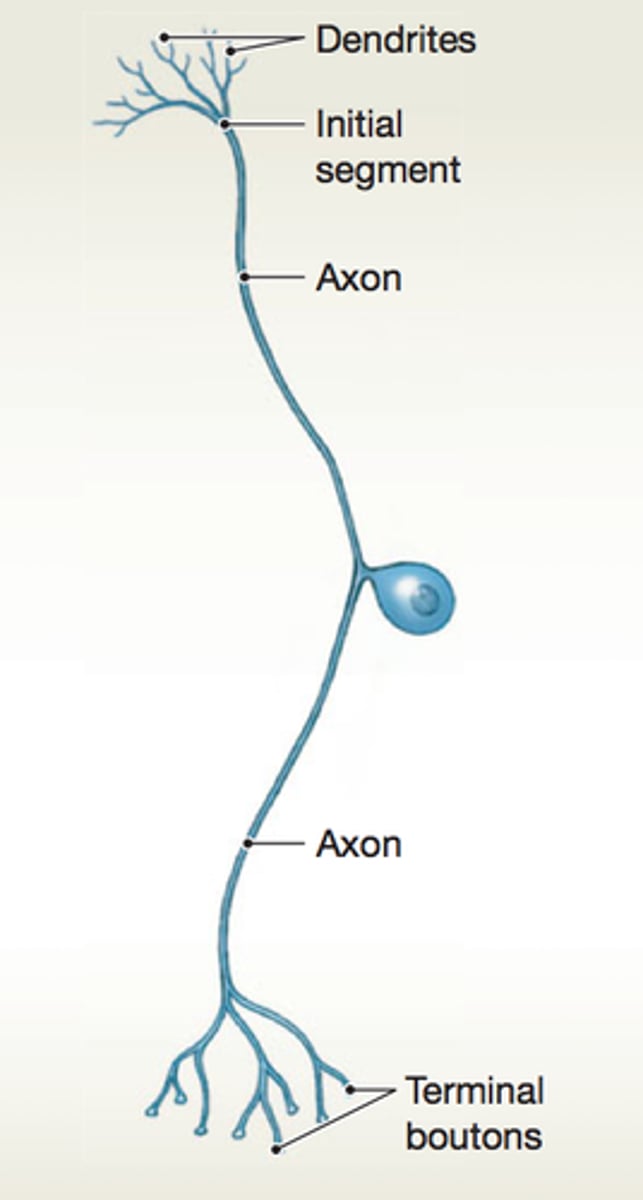
soma, dendrites, axon
What are the basic components of a neuron?
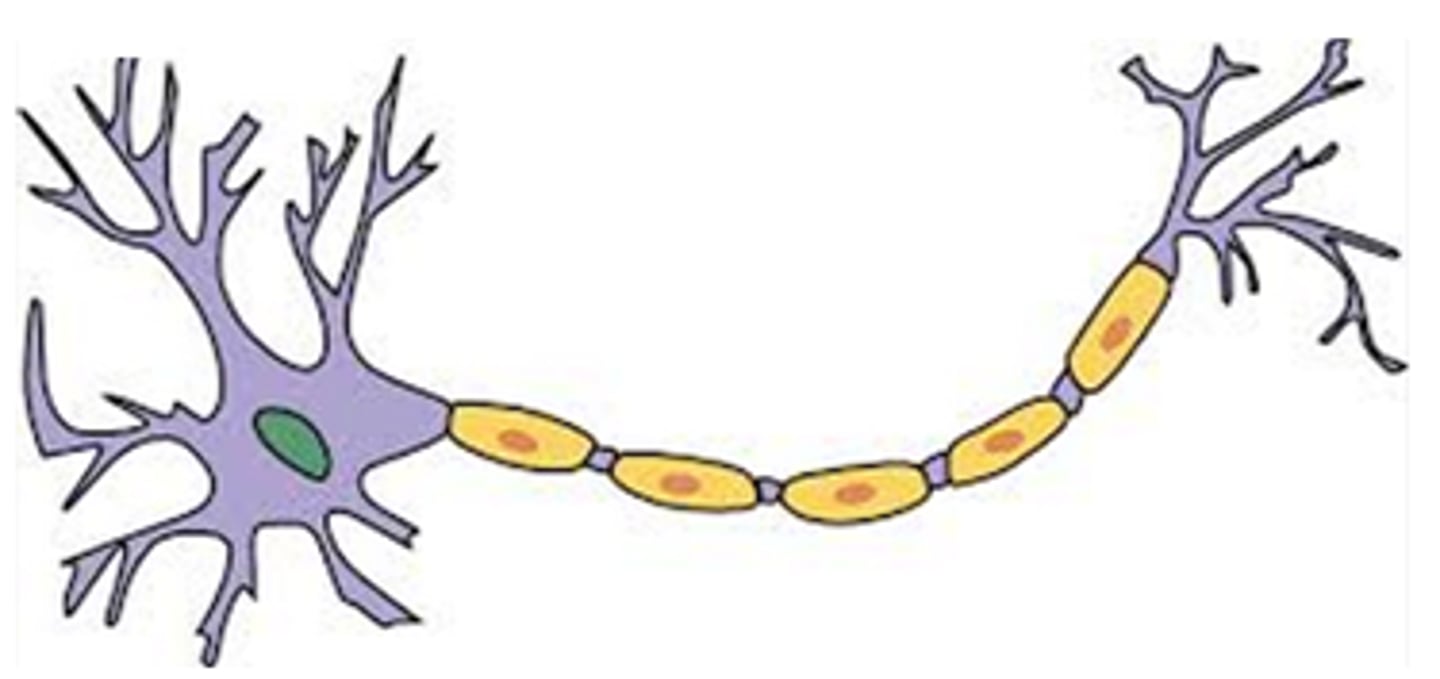
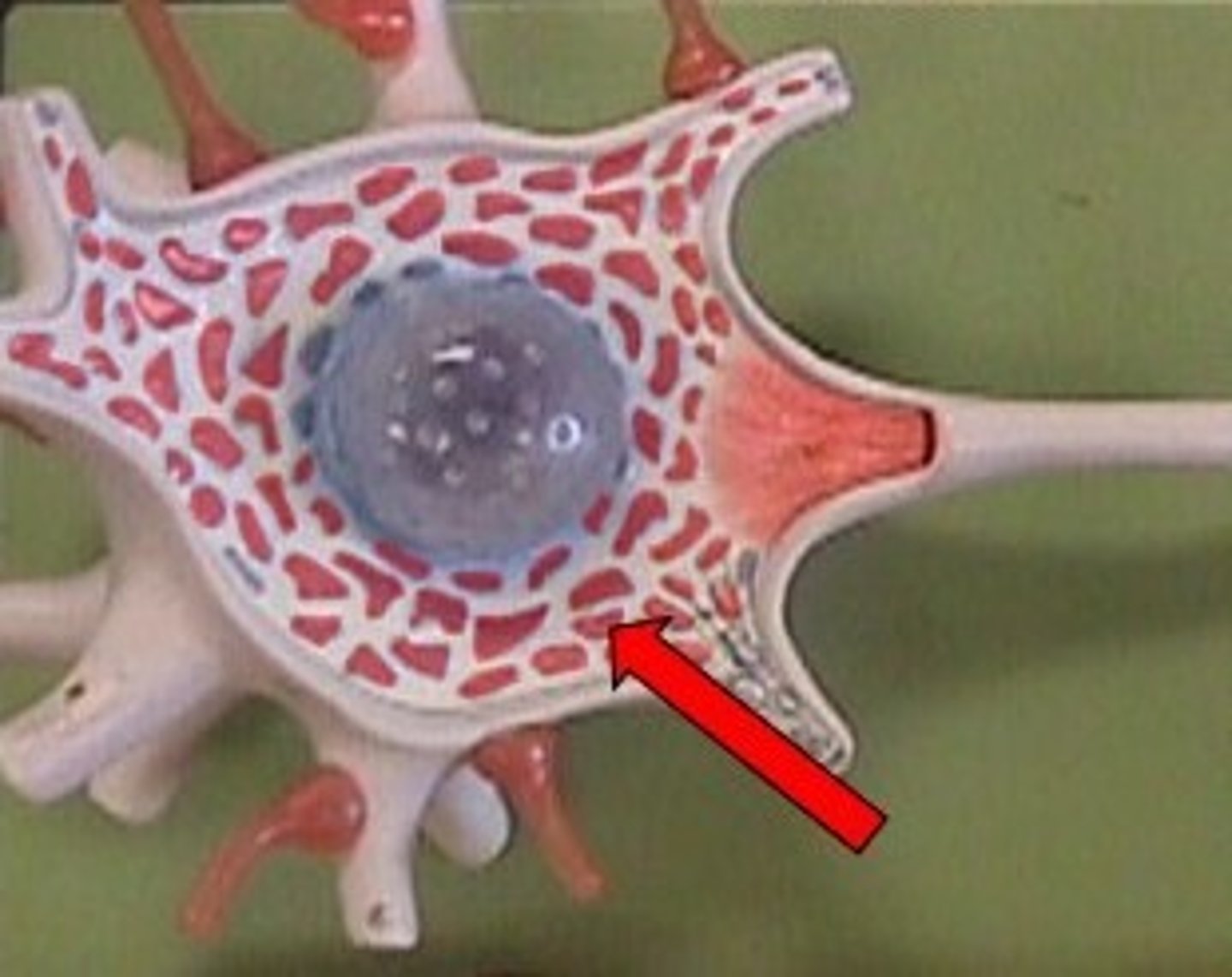
cell body
site of protein synthesis and synapatic integration
nucleus
substance on the cell body when helps make proteins via RNA transcription
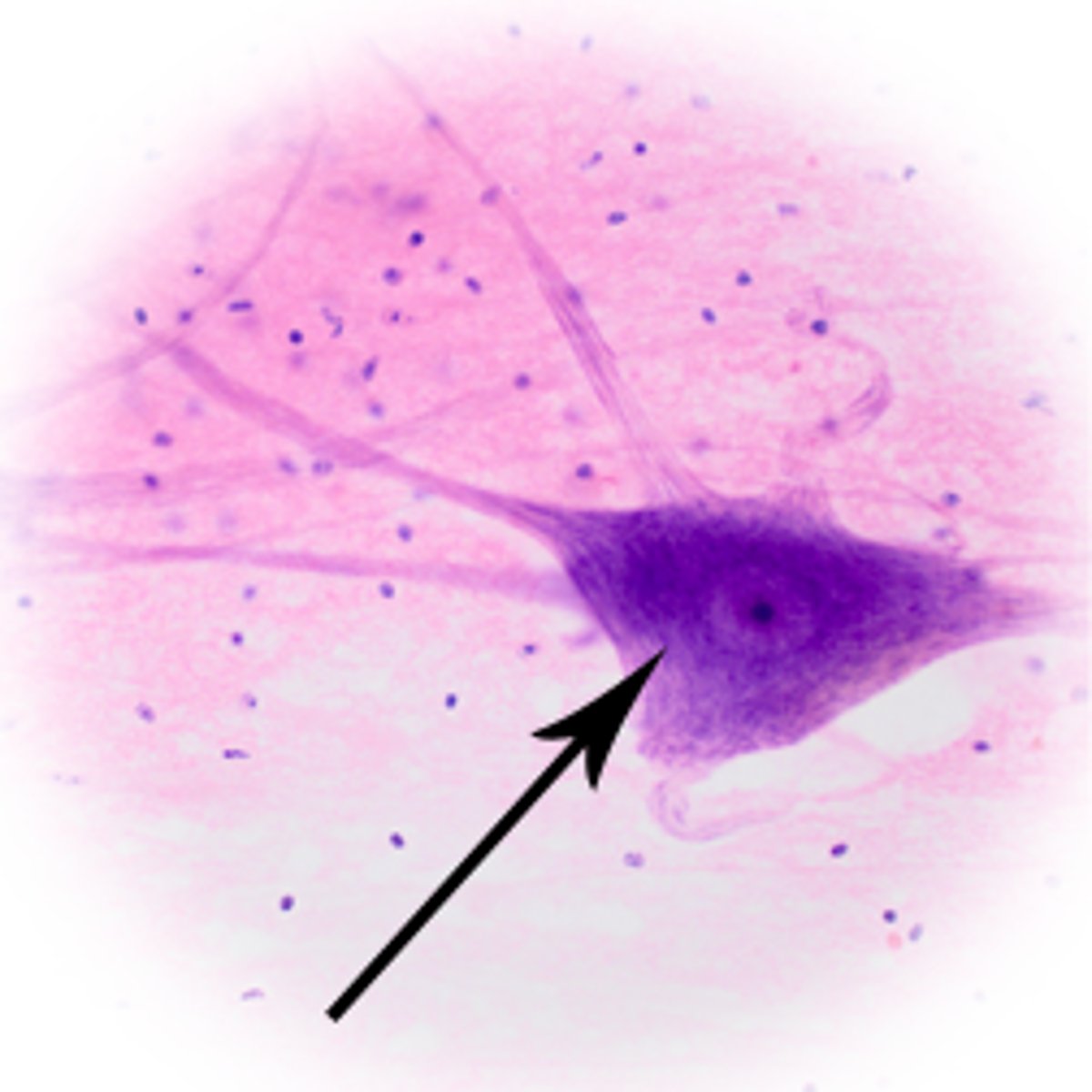
nissl substance
substance on the cell body when helps make proteins via translation
synaptic integration
summation of all electrical currents within a neuron, typically arising from the dendrites
dendrites
capable of limited protein synthesis and mainly serve as the site of synaptic input
neurotransmitter receptors
surface proteins on dendrites that serve as the binding sites for chemical signals
ionotropic receptor, metabotropic receptor
after a neurotransmitter (NT) binds, the NT receptors can function as either what two things?
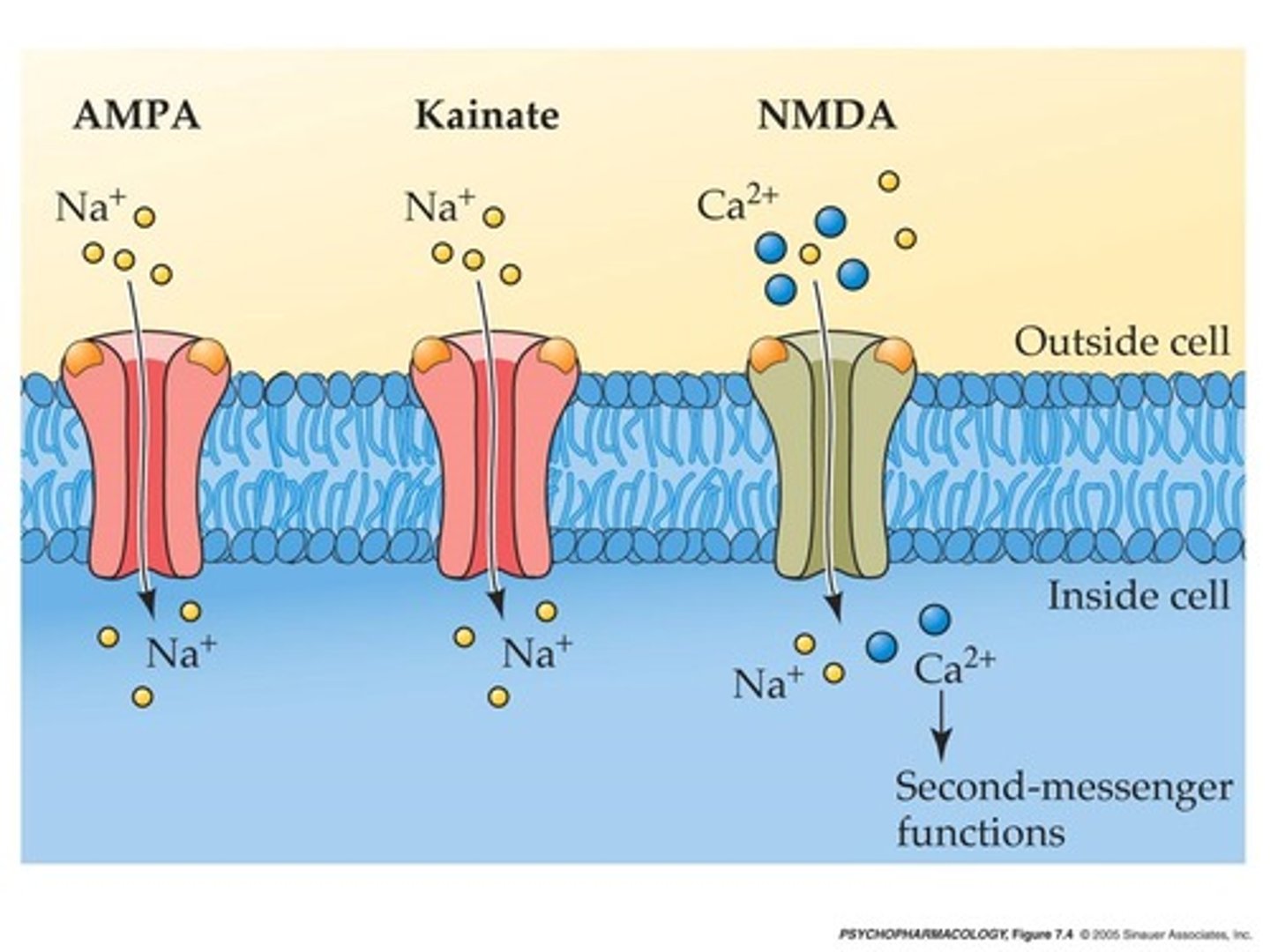
Ionotropic receptors
ion channels that open after the neurotransmitter binds. Small ions (Na+, K+, Ca2+, or Cl-) then move across the membrane to create electrical currents
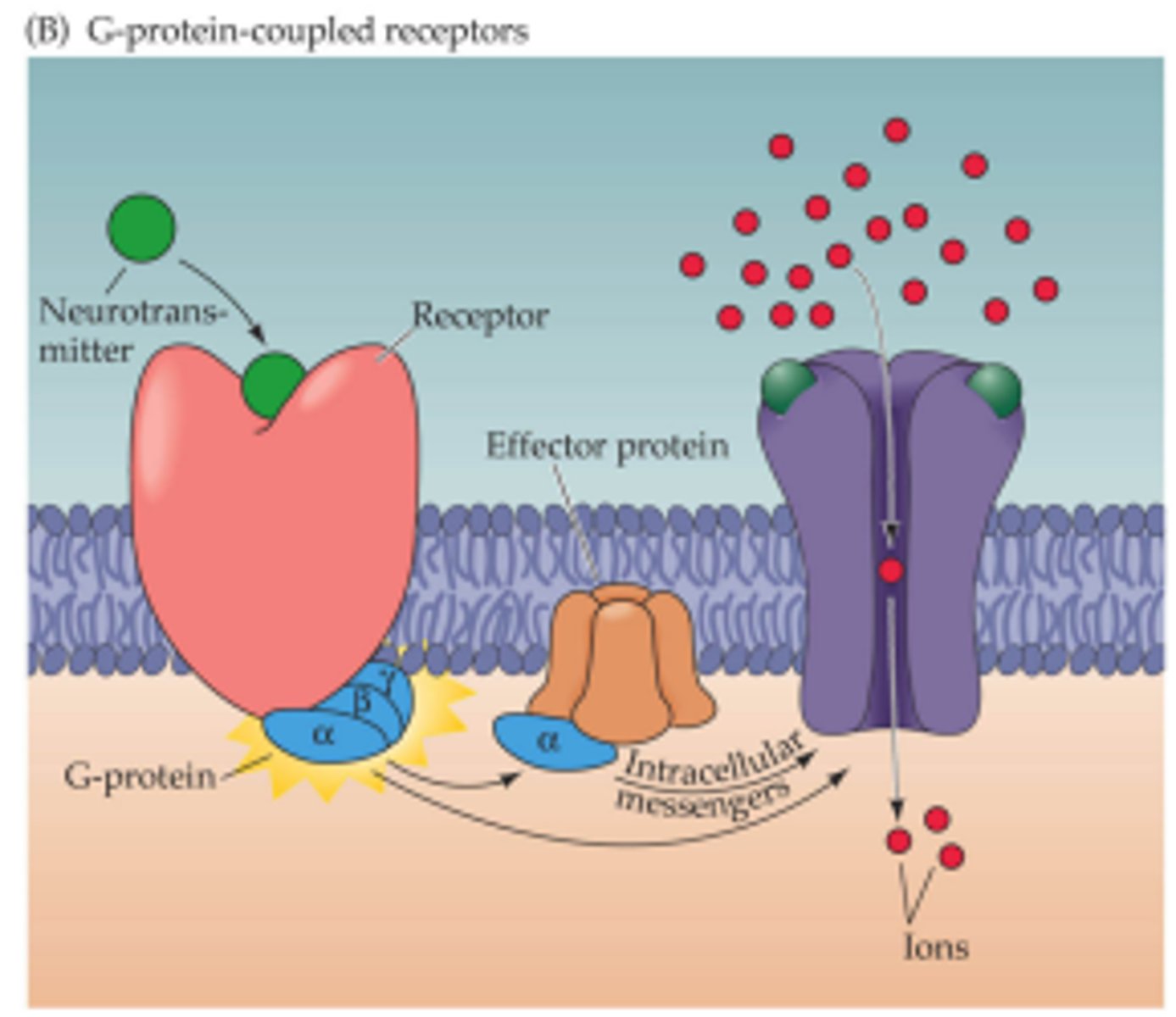
metabotropic receptors
coupled to other proteins and kick off an intracellular signaling cascade that creates more long-lived changes in cell function
axon
incapable of protein synthesis and is the site of synaptic output
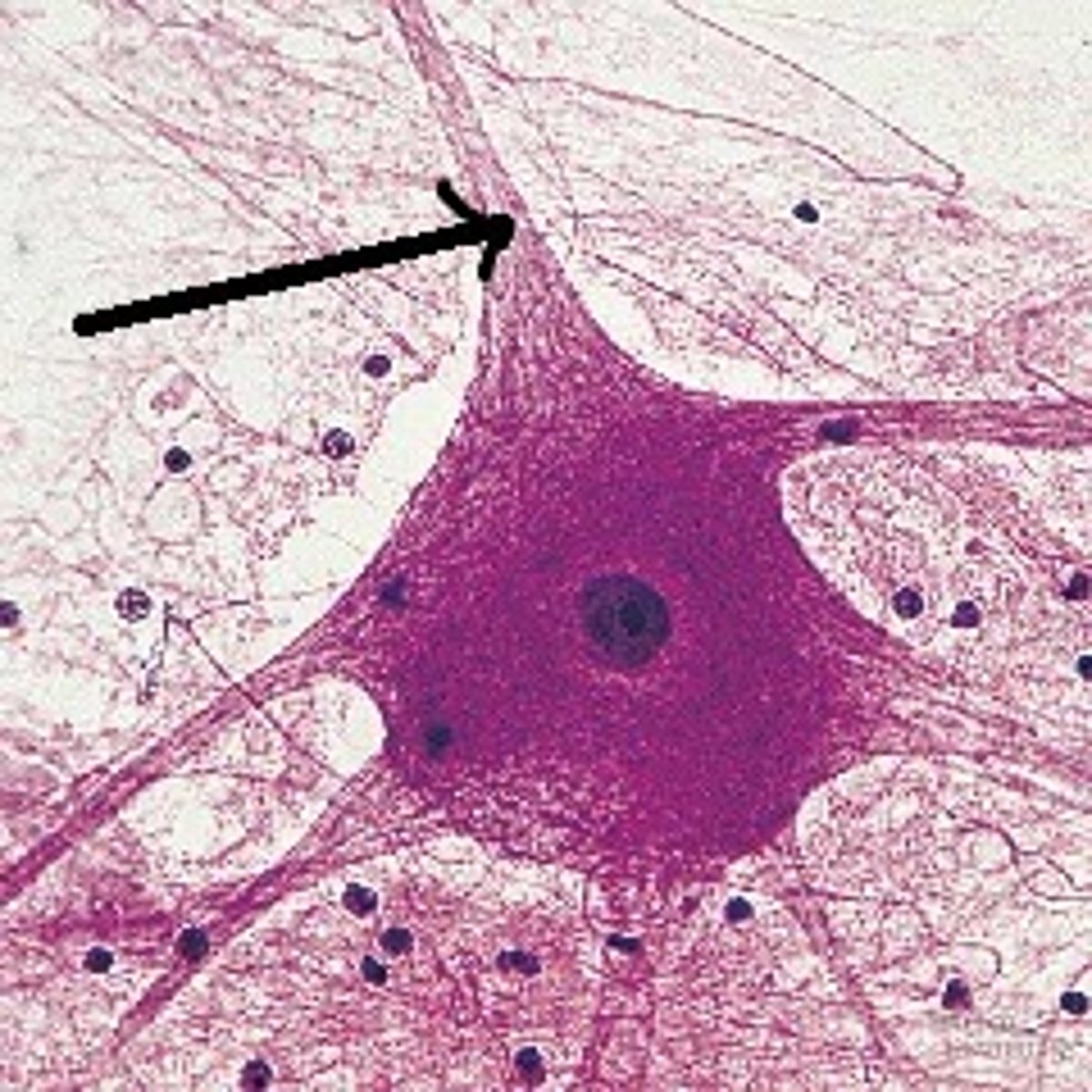
anterograde, retrograde
types of transport present in neuron axons to bring proteins where they need to go
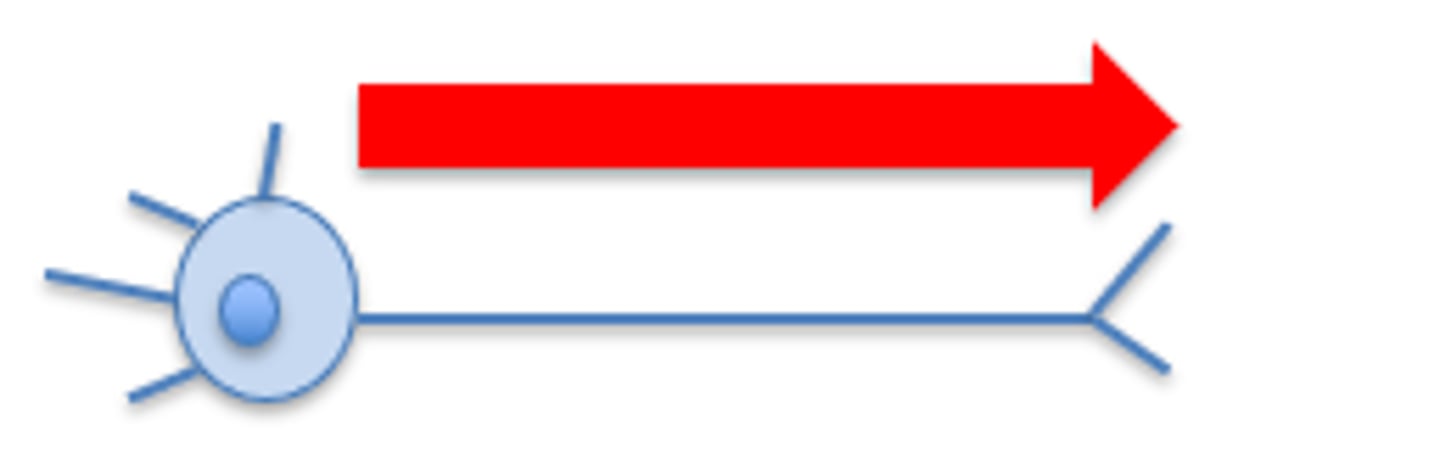
Anterograde transport
axonal transport that brings new proteins and organelles from the soma to the axon.

retrograde transport
axonal transport that brings damaged proteins, damaged organelles, and stimulated neurotrophin receptors from the axon to the soma
True
True or False? Axons branch extensively to contact multiple target cells
Action Potentials (APs)
electrical signals created by axons that travel from the cell body throughout the axon to stimulate
neurotransmitter release
multipolar neurons
Neurons that have multiple dendrites emanating from the cell body (like the neurons in the brain)
integration of multiple synaptic inputs
purpose of multipolar neurons
bipolar neuron,
Neurons that have a single dendrite and single axon
pseudounipolar neuron
Neurons that have a single process that acts as
both dendrite and axon.
sensory
Function of neurons with a single dendrite
membrane potential (Vm)
the electrical charge a cell's membrane
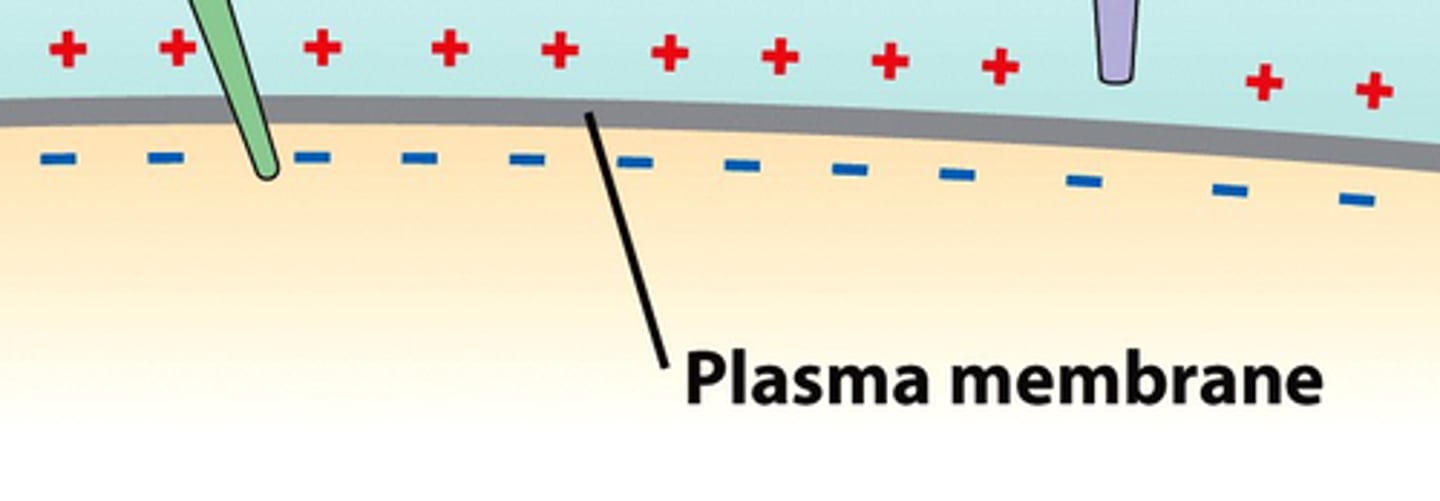
-70 mV
normal Vm of a cell
makes it more positive
How does excitatory synaptic input influence Vm?
makes it negative, prevents further positivity
How does inhibitory synaptic input influence Vm?
threshold potential
The minimum membrane potential that must be reached in order for an action potential to be generated in a neuron (A)
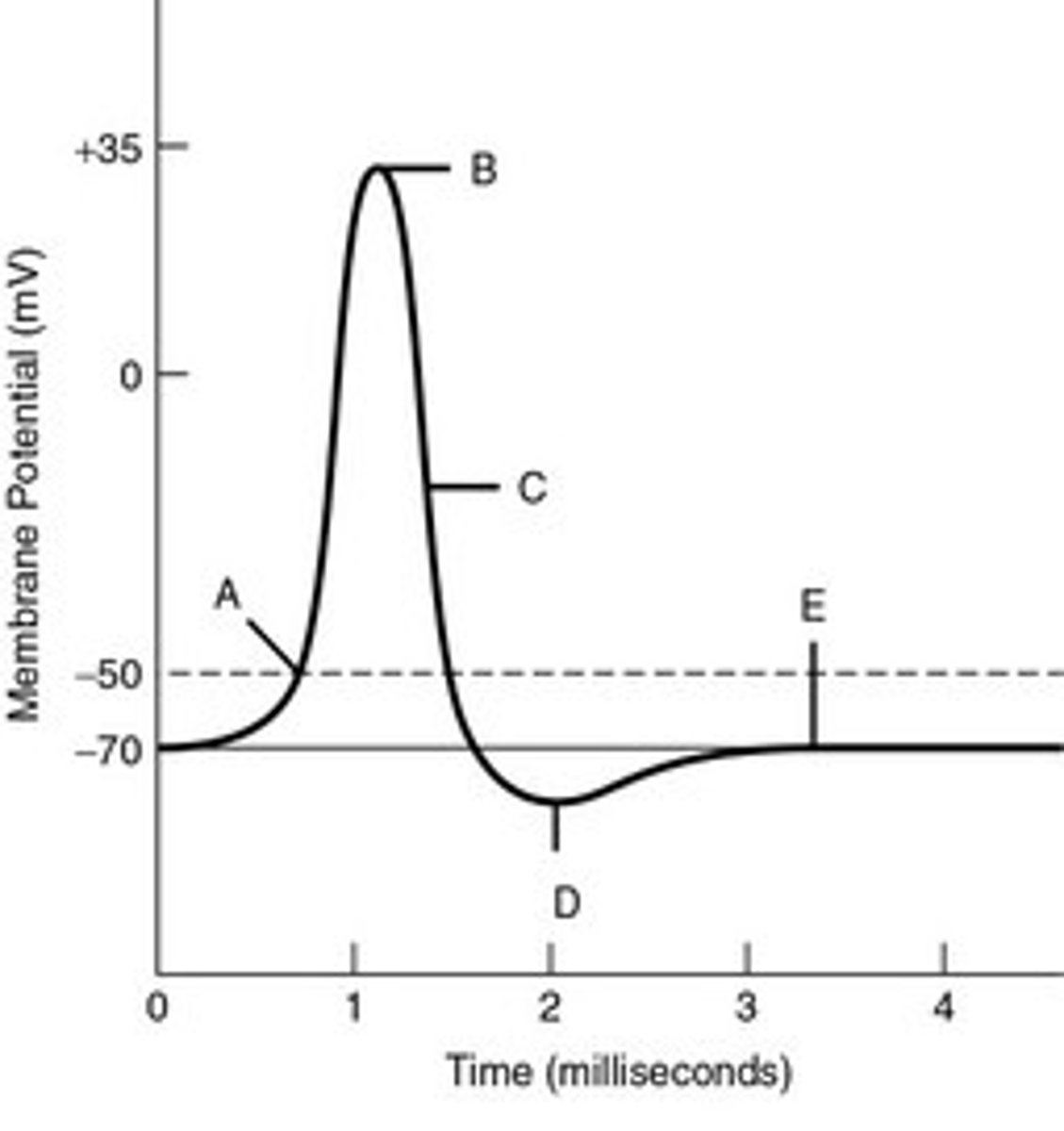
action potential
self-propagating wave of depolarization that spreads down the axon
Na+
An early influx of ______ makes Vm positive
K+
A delayed efflux of _____ brings Vm back to a negative value.
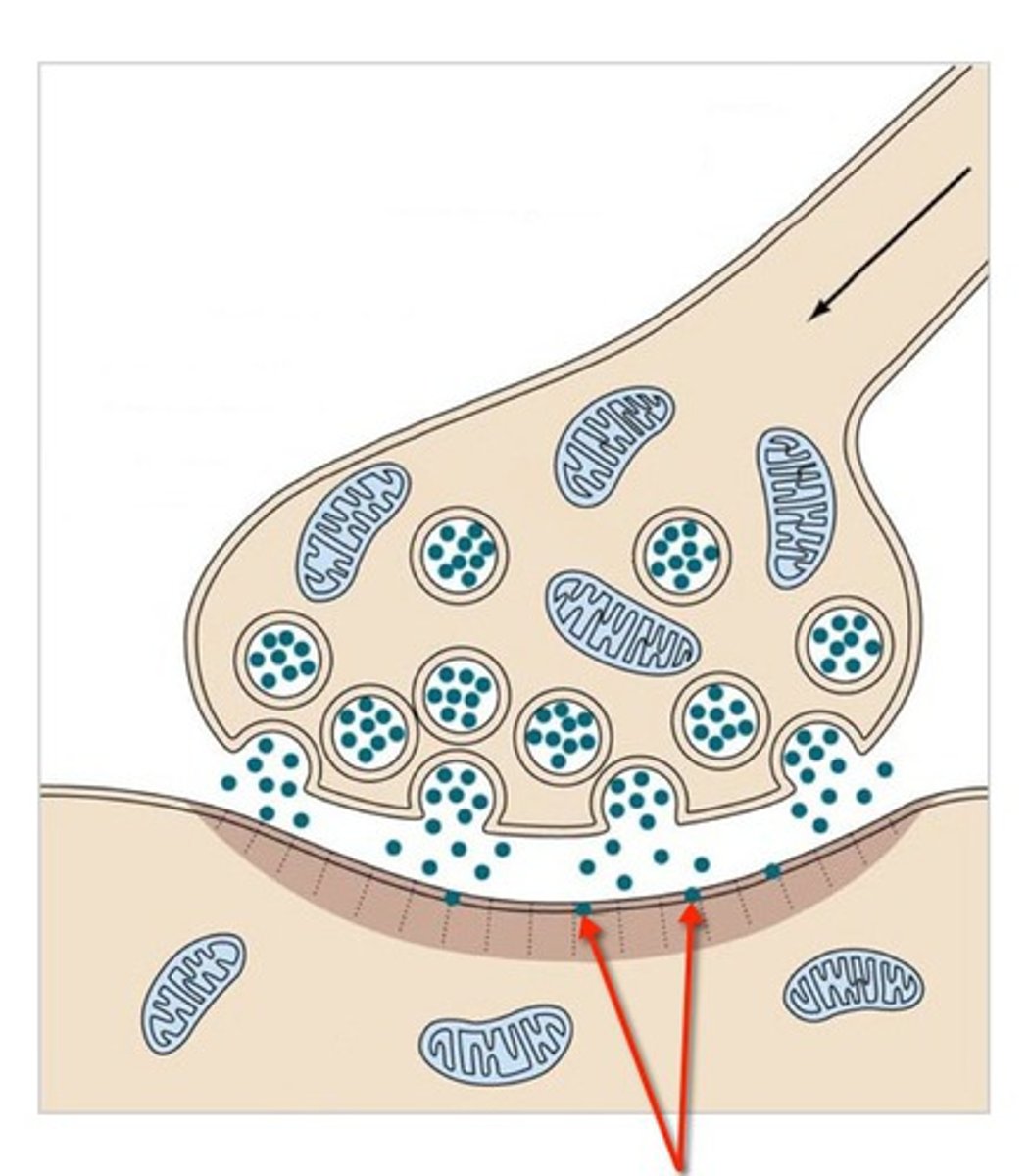
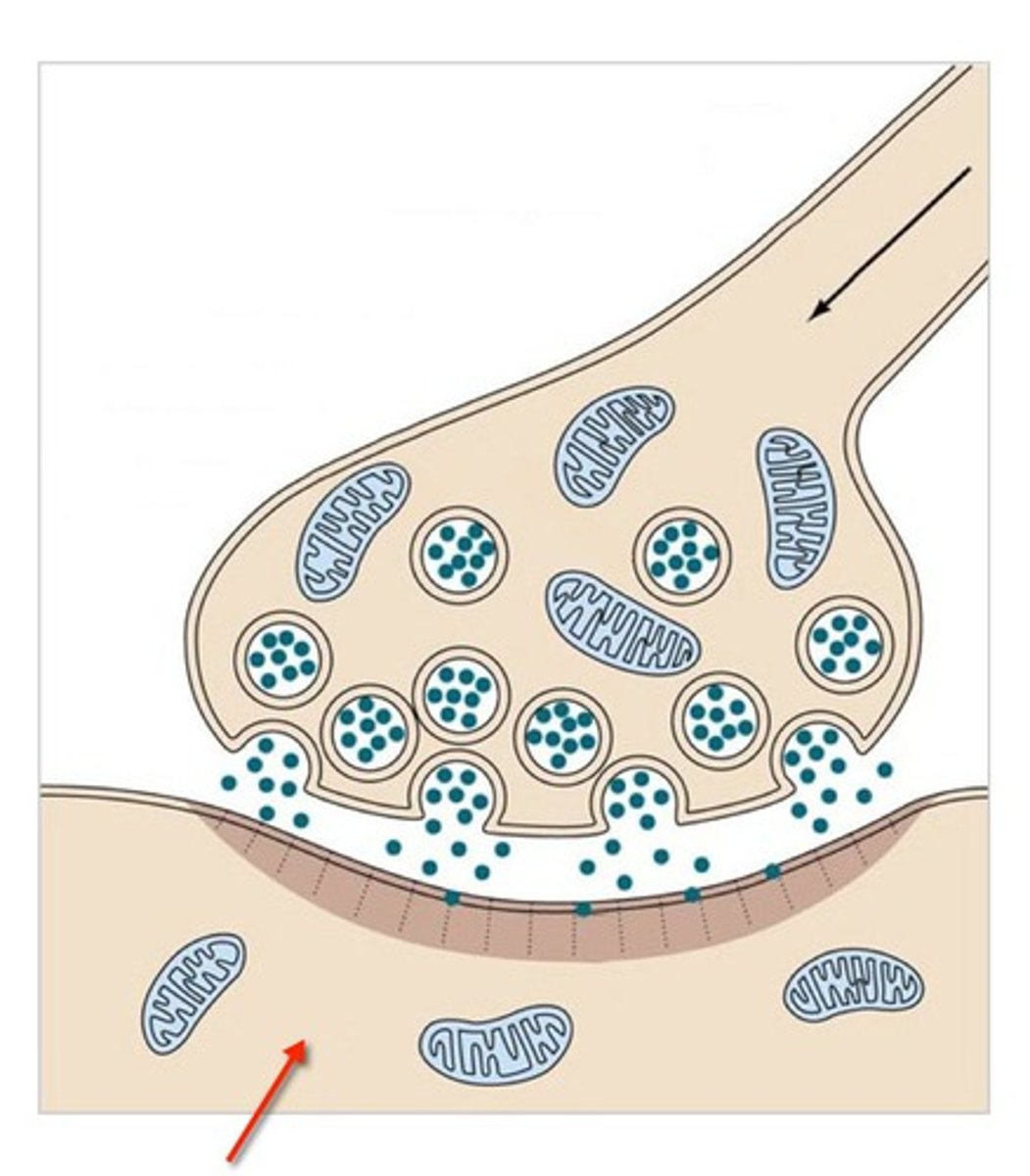
presynaptic site
A short-lived positive Vm created by an AP stimulates neurotransmitter release from what location?
synaptic vesicles
Neurotransmitters are held within the neuron in what structures?
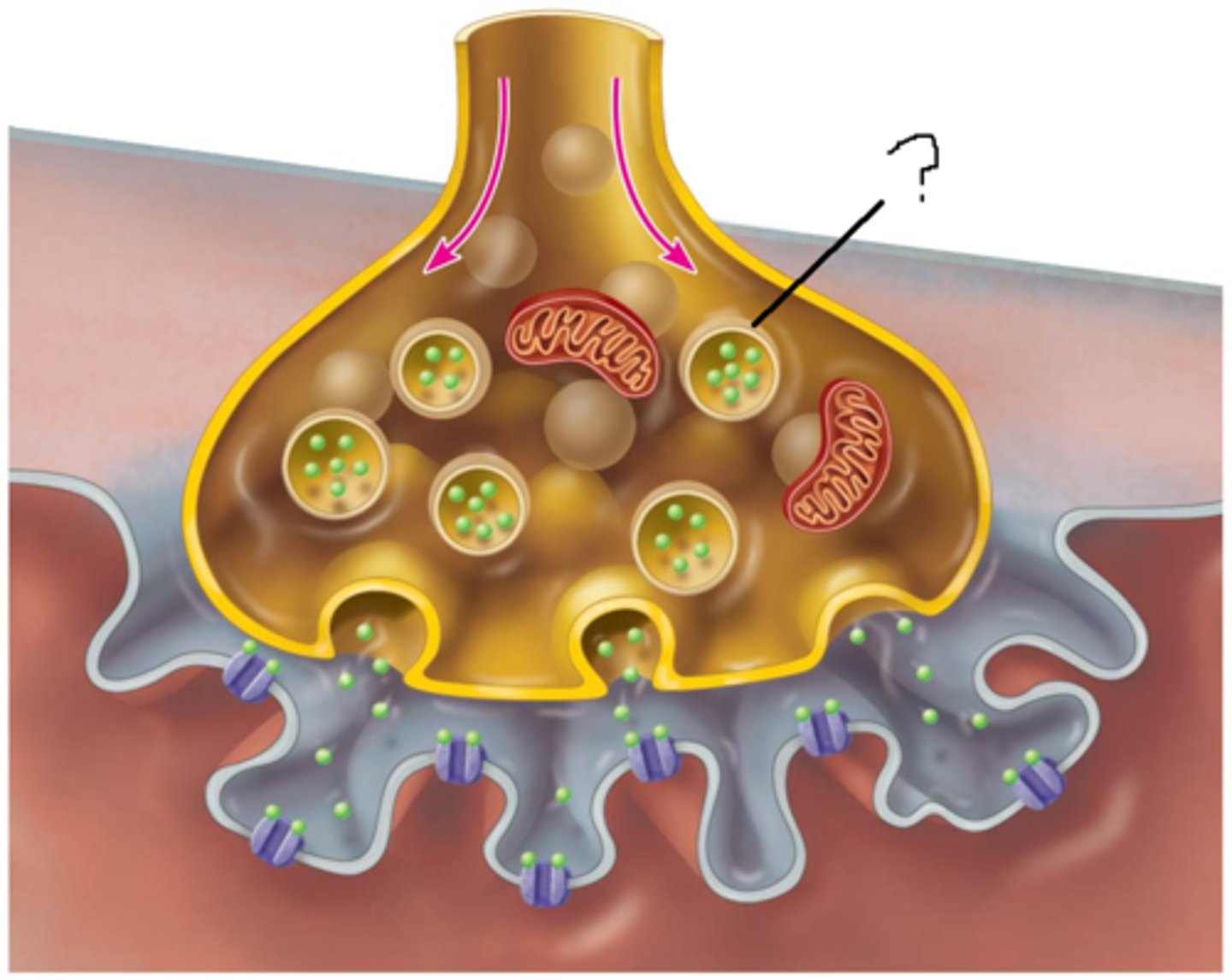
Ca2+
What ion enters into the neuron in response to a positive Vm in order to facilitate NT release from the presynaptic site?
synaptic vesicles fuse with membrane
How do NTs leave the presynaptic site?
synaptic cleft
The narrow gap that separates the presynaptic neuron from the postsynaptic cell.
postsynaptic site
The cell that is receiving the signal, contains protein receptors
glutamate, GABA
Nearly all neurons in the central nervous system release either what two NTs?
GABA
between glutamate and GABA, which one is inhibitory?
ACh, serotonin, dopamine, NE, epi
Neuromodulatory transmitters that generally create slower, more long-lived changes
in Vm
ACh, NE
Neurons in the peripheral nervous system release either what two neurons?
neuropeptides
Brain chemicals, such as enkephalins and endorphins, that regulate the activity of neurons
corticospinal tract
A simple neural pathway that illustrates the alternating pattern of electrical and chemical signaling, which is responsible for conscious movement
UMNs
motor neurons in the cerebral cortex that project their axon down the ventral horn of the spinal cord in order to control the activity of lower motor neurons (LMNs)
chemical
In the corticospinal tract, UMNs receive synaptic input from other cortical regions and the thalamus. Is this a chemical or electrical signal?
electrical
UMN dendrites receive signals and create currents generated in the dendrites and summed in the cell body, then sent down the axon. Is this electrical or chemical?
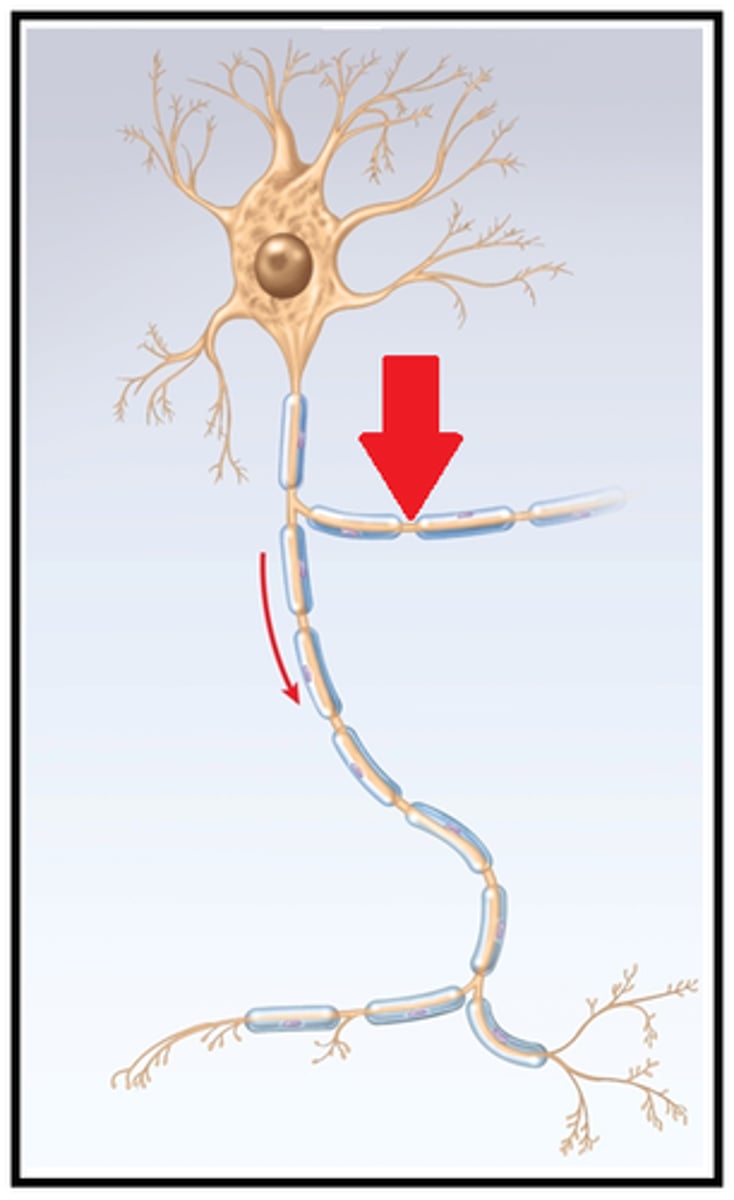
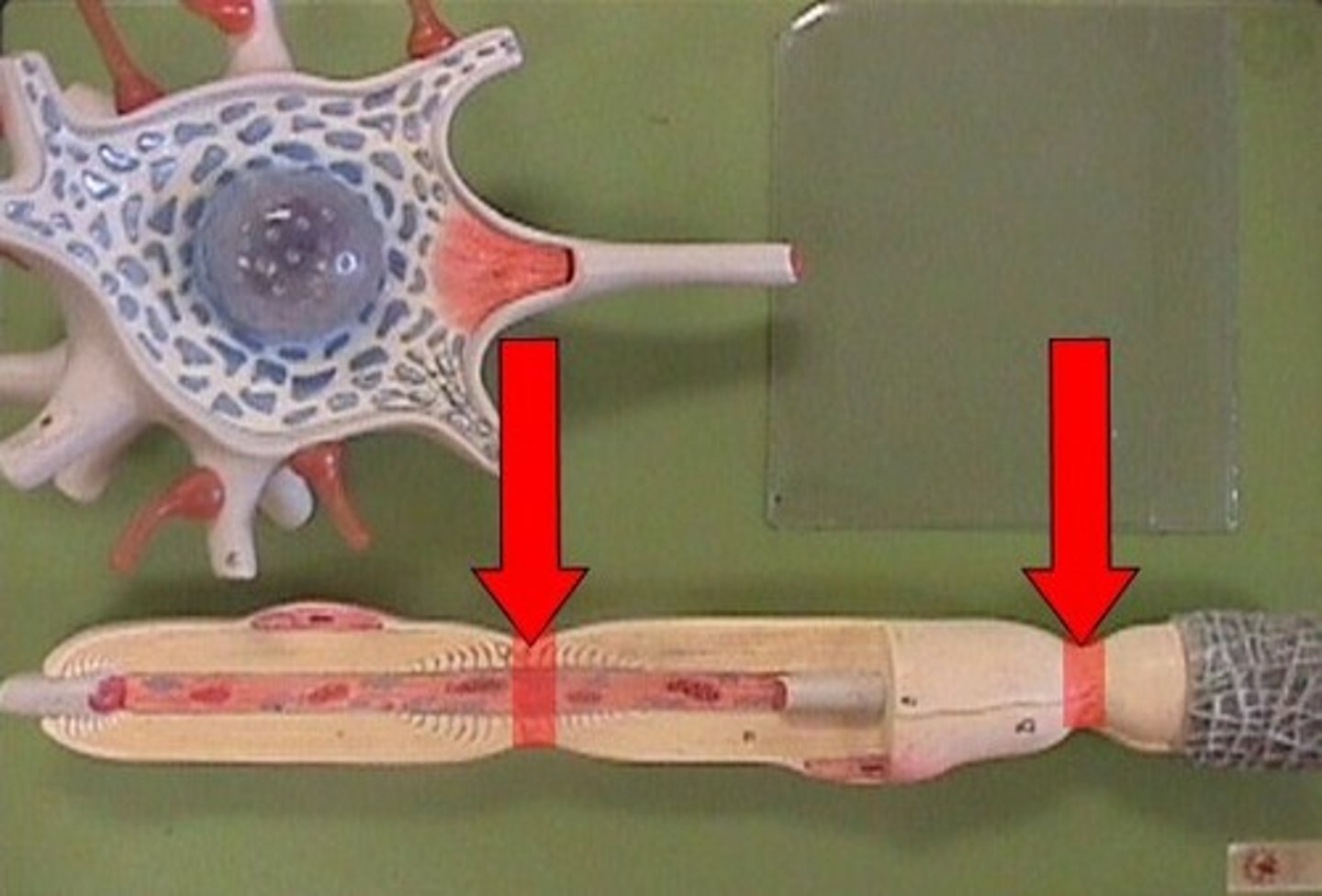
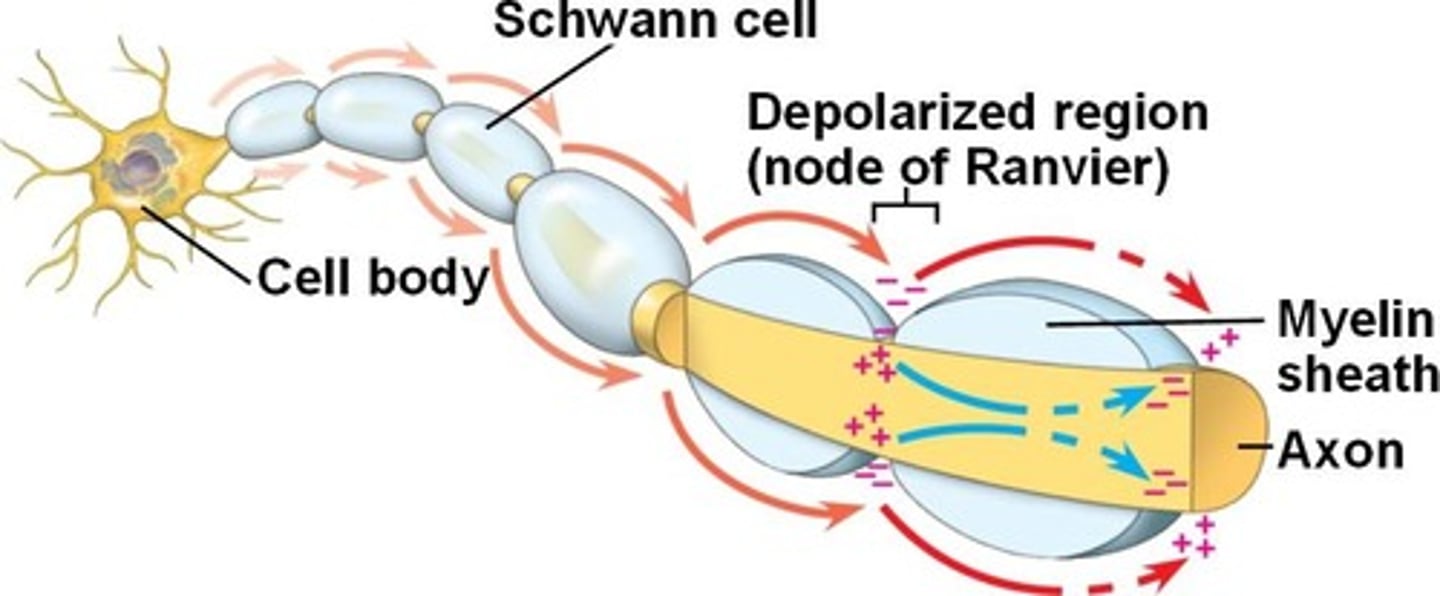
myelin
a lipid- and protein-rich that insulates axons
internodes
myelinated regions of the axon
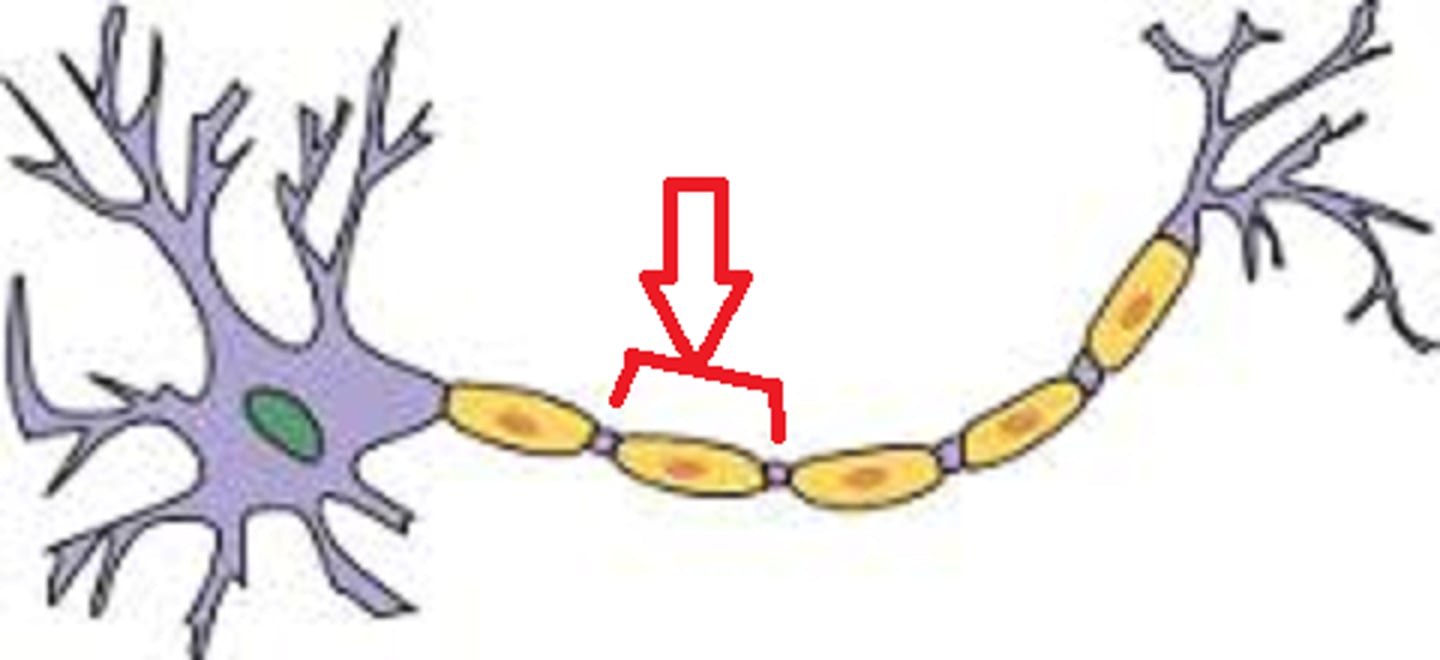
nodes
unmyelinated regions
cost, space, speed
3 advantages of myelination
saltatory conduction
Rapid transmission of a nerve impulse along an axon, resulting from the action potential jumping from one node of Ranvier to another, skipping the myelin-sheathed regions of membrane.
free radicals
Active transport requires ATP, and ATP synthesis creates ____________________, which can damage lipids, proteins, and DNA.
Oligodendrocytes
synthesizes myelin in the CNS
save space
Goal of the myelin in the CNS created by oligodendrocytes
Schwann cells
synthesizes myelin in the PNS
mechanical protection
Goal of the myelin in the PNS created by Schwann cells
Ependymal cells
produce cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and form the blood-CSF barrier.
endfoot processes
physical barrier created by astrocytes
glial limitans
collection of endfoot processes that surrounds the brain to restrict diffusion into and out of the brain.
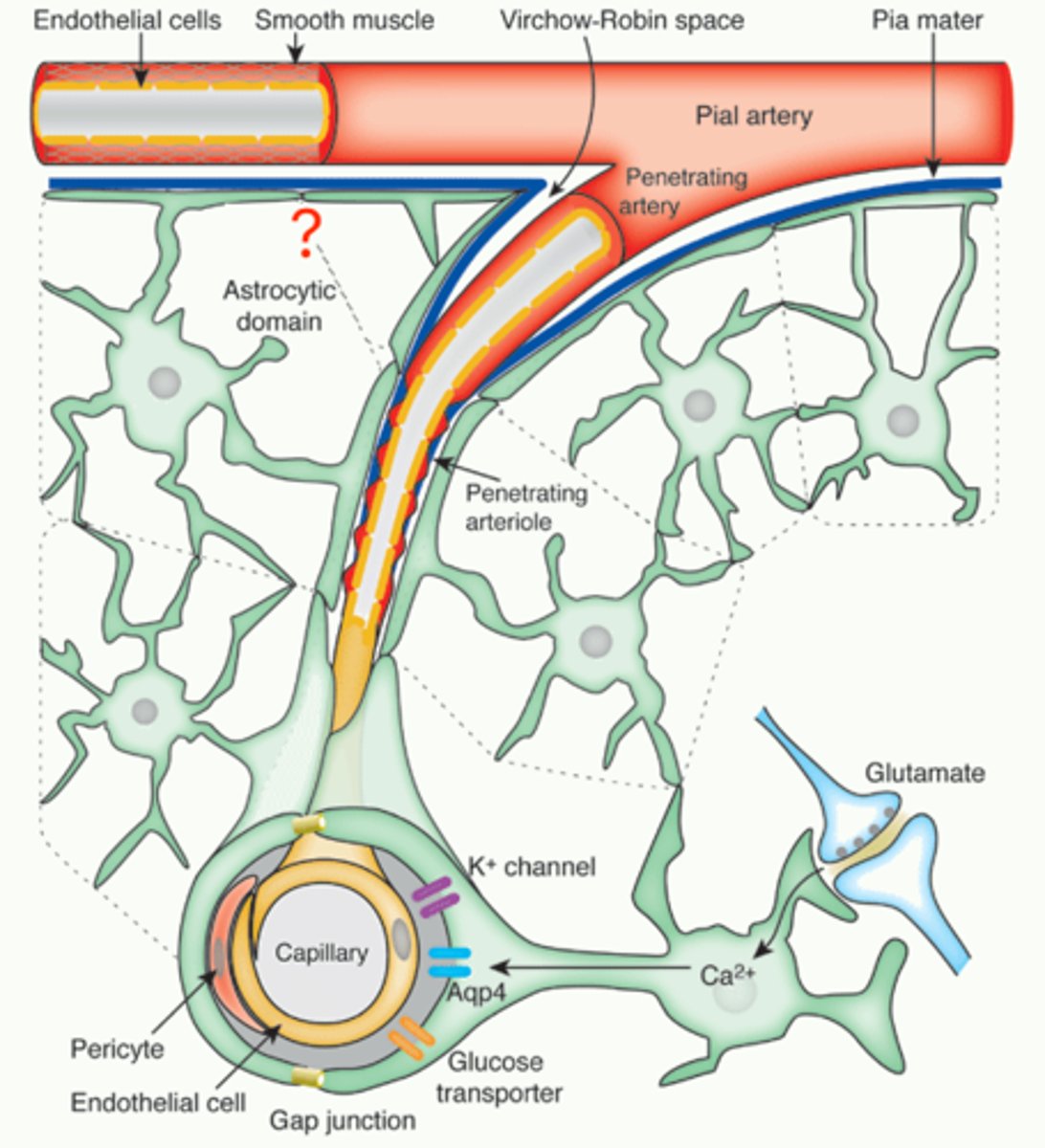
vascular epithelial cells
Endfoot processes interact with these cells to regulate blood flow
and help maintain the blood-brain barrier.
Perisynaptic processes
provide the glial component at synapses
perinodal processes
contact the nodes on axons, likely to help buffer K+ that exits the axon.3
regulate K+, recycle GABA + glutamate, shuttle metabolic substrates
3 main functions of astrocytes
microglia
macrophages that enter the nervous system throughout development
gliosis
During injury, astrocytes and microglia alter their morphology and divide in what process?
gliosis
proliferation of astrocytes/microglia in an area of neuron degeneration leading to a glial scar.
glial scar
consists of modified extracellular matrix proteins that create a rubbery, tenacious, growth-blocking membrane
amoeboid
Microglia respond to injury by withdrawing their processes to adopt what form?
reactive microglia
migrate to the site of injury and act as macrophages
Necrosis
the rupturing of the cell membrane or plasmalemma
by moving ions across plasmalemma
how are electrical currents created?
ion channels
A transmembrane protein channel that allows a specific ion to diffuse across the membrane down its concentration or electrochemical gradient.; have the fastest rate of influx.
carriers/transporters
move solutes across the membrane through a series of conformational changes. This reliance on shape changing dramatically slows the rate of ion movement, but they can move solutes against their concentration gradient
ion pumps
undergo conformational changes, are slow (up to 103 ions per second), and move solutes against their concentration gradient using ATP hydrolysis
Na+, Cl-
what ions are high in extracellular fluid?
K+
what ions are high in intracellular fluid?
passive
Opening and closing of ion channels creates an electrical current through passive or active transport of ions
pumps
How do neurons maintain an ionic imbalance?
aquaporins
water channel proteins through which water moves passively into and out of neurons
osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
traumatic injury, inflammation, hyperactivity
common causes of necrosis
osmotic necrosis/oncosis
With hyperactivity in neurons, ion currents cause the movement of water, causing these neurons to take on water and swell until the plasma
OMM
Part of the mitochondria that contains calcium channels that allow mitochondria to buffer calcium levels within the cell
IMM
Part of the mitochondria that contains the electron transport chain and ATP synthase, working together to generate ATP in aerobic respiration
Hydrogen gradient
Gradient formed by the difference in proton concentration across the mitochondrial membrane; form of potential energy that provides energy to form ATP (within the intermembrane space)
free radicals/superoxide
Produced from the mitochondria as a byproduct of ATP production
cell thinks it should die
If the ETC is impaired, what happens to the cell?
cytochrome c
soluble ETC protein, that when in the cytoplasm, may indicate the ETC is impaired
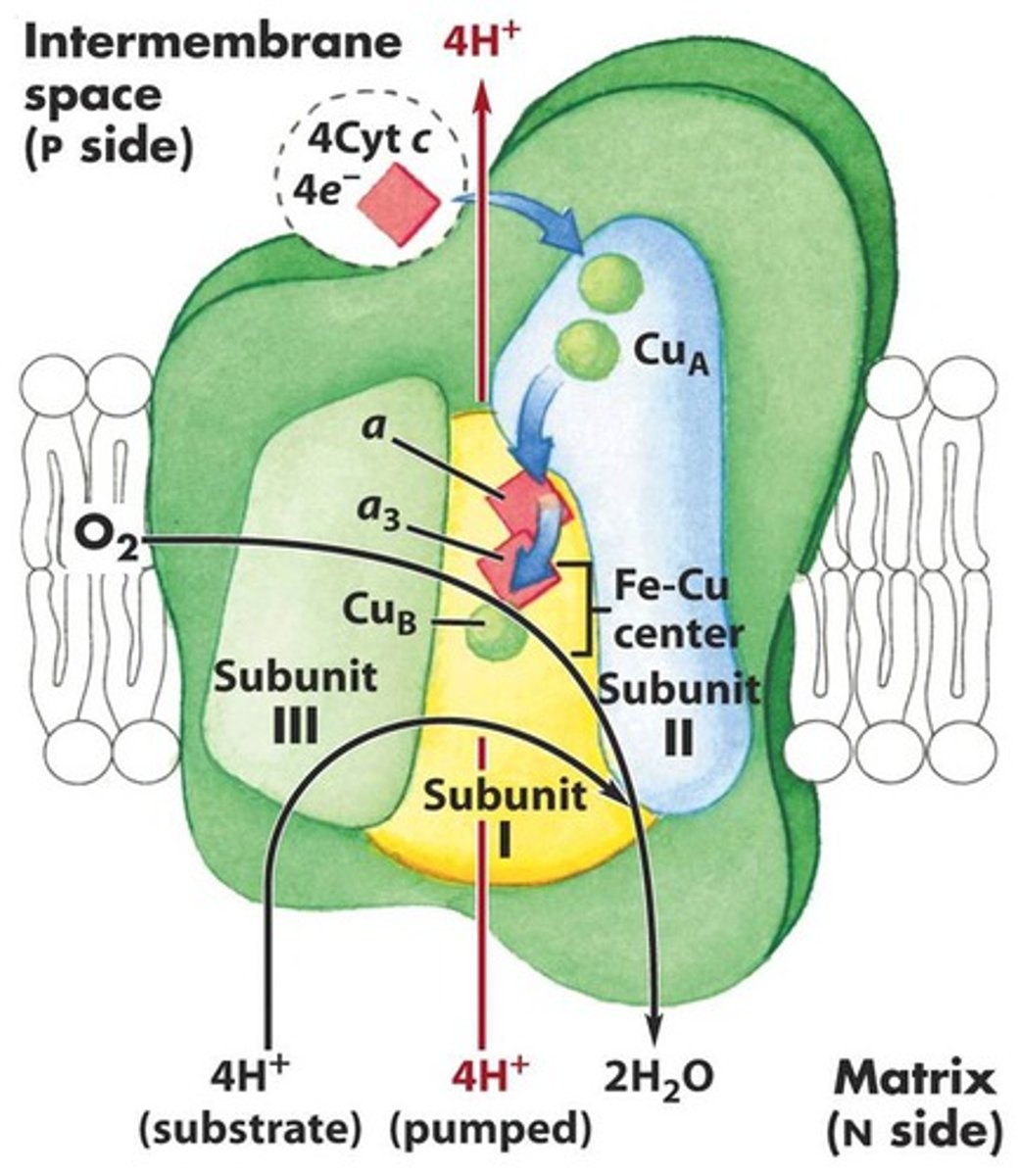
IMM
normal location of cytochrome c when mitochondria has a functioning ETC
apoptosis
what kind of cell death does cytochrome c trigger?
apoptosis
sequential, orderly cleavage of intracellular components
apoptosome
When cytochrome c enters the cytoplasm of a cell it binds with a protein called Apaf-1 to form what?
apoptosome
collection of proteins that triggers apoptosis
caspases
apoptosomes activate what kind of proteins?
caspases
collection of proteins that
cut up specific cellular components
pro-caspases
inactive caspases contained in all cells and kept inactive by a regulatory domain
cutting off regulatory domain
how are procaspases activate?
initiator caspases
first caspases to be activated, cutting up other pro-caspases to turn them on
effector caspases
turned on by initiator caspases, and cut up cellular components in order to carry out apoptosis
Bcl-2 proteins
many different proteins that regulate the permeability of the OMM within a cell
Pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins
create pores in the OMM to stimulate apoptosis
Anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins
bind to pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins and prevent them from killing the cell.