4.1.5.4 - Monopolistic Competition
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
What is meant by a monopolistically competitive market?
A market where many small firms sell differentiated products.

Give a real-world example of a monopolistically competitive market.
Hairdressers, coffee shops, restaurants.

What are the 6 characteristics of a monopolistically competitive market?
Many sellers, differentiated products, non-price competition, no barriers to entry or exit, some price-setting power, imperfect information

In a market where there are numerous local businesses offering similar but differentiated hairdressing services with no significant barriers to entry, which market structure does this best exemplify?
Monopolistically competitive market
Why do firms in a monopolistically competitive market have some price-setting power?
Due to product differentiation.

How is monopolistic competition different from perfect competition?
Unlike perfect competition where all products are identical and firms are price takers, each firm offers unique qualities through branding, features etc, allowing them to charge a slightly higher price.

Give an analogy of imperfect competition in monopolistic competition.
For example, think of different coffee shops. Each offers its special blends, unique atmospheres, or loyalty programmes, which enables them to set prices independently. This is different from perfect competition, where all coffee beans are the same, and shops must match the market price.

How is monopolistic comeptition a form of imperfect comeptition.
Firms have some price-setting power due to product differentiation.
What is imperfect competition?
A market structure where firms have some degree of price-setting power.

What is non-price competition?
Competition among firms based on factors OTHER THAN price, such as advertising and product quality.

What are barriers to entry?
Restrictions that make it difficult for new firms to enter a market.
What is price-setting power?
The ability of a firm to influence the price of its product.
What is imperfect information?
A situation where buyers and sellers do not have complete knowledge about the market.
What is product differentiation?
When firms offer different products.

Why do firms differentiate their products?
To appeal to and appear unique to customers.

Give an example of product differentiation.
Hairdressers offering different styles, cuts and services.

What does a monopolistically competitive market assume regarding the number of buyers and sellers?
It assumes a large number of buyers and sellers, all of whom are small and act independently. No single firm has market power. Price setters.

Are there barriers to entry and exit in monopolistically competitive markets?
There are no barriers to entry and exit.

What does it mean when there are no barriers to entry and exit?
New firms can easily enter the market, and firms can leave the market if they are not profitable.

What does some price-setting power allow firms in this market to do?
They can increase prices without losing all their customers. (Downward sloping demand curve)
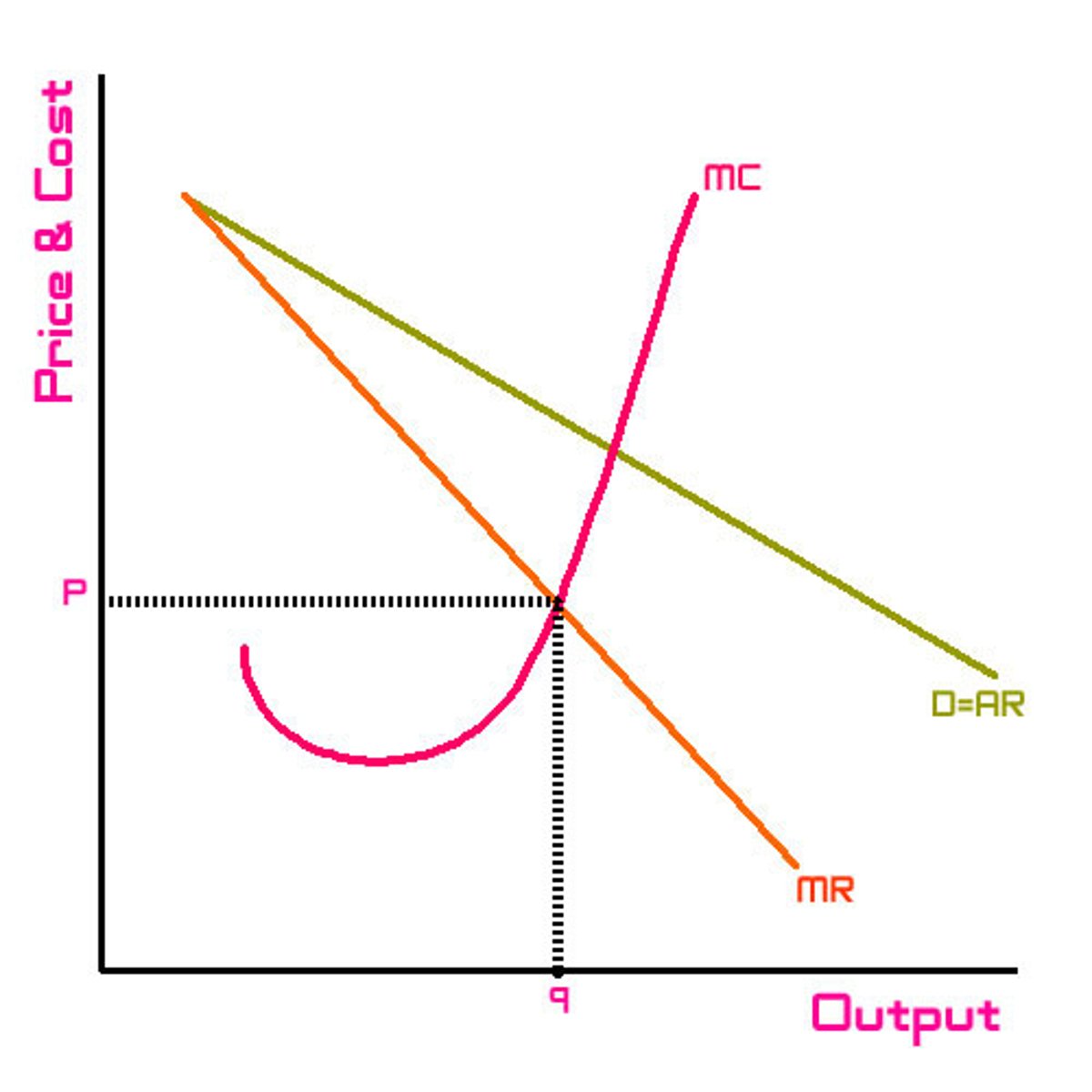
What does imperfect information mean in a market like this?
Consumers may not have complete knowledge about all products. Firms may not know all consumer preferences.

In the short run, where do firms maximise profits?
Where MC = MR. They can earn supernormal profits.
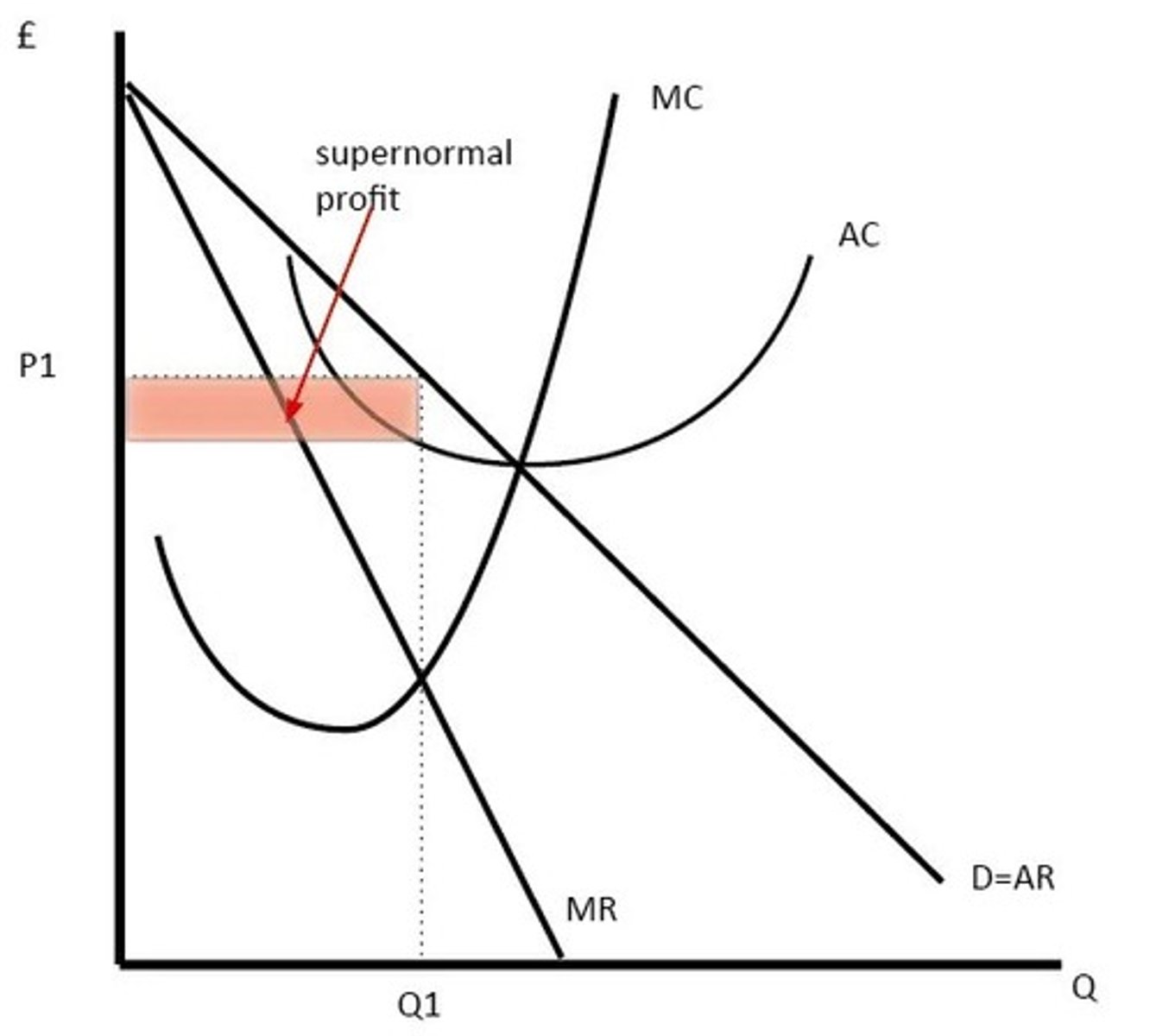
In the long run, what do new firms do?
New firms are attracted by profits. This increases supply, reduces demand for existing firms, and leads to normal profits in long run.

What is an advantage of monopolistically comeptitive markets regarding choice?
Consumers have many options.

What is an advantage of monopolistically competitive markets regarding realism?
More reflective of real-world markets.

What is an advantage of monopolistically compeititve markets regarding efficiency?
Dynamic efficiency - supernormal profits could drive innovation
What is a disadvantage of monopolistically competitive markets regarding allocative inefficiency?
P > MC in short and long run. Resources are not allocated optimally.
What is a disadvantage of monopolistically competitive markets regarding productive inefficiency?
Firms do not operate at the minimum of the AC curve.
What is a disadvantage of monopolistically competitive markets regarding X-inefficiency?
Firms may not minimise costs due to lack of competition.
Do any firms in monopolistic competition have significant market power?
No.
What happens in the long run?
In the long run, new firms enter the market because supernormal profits made by existing firms attract them. This increases the market supply, reducing demand for individual firms' products. The average revenue (AR) curve shifts to the left, indicating a decrease in demand. This process continues until all firms earn only normal profits.
In the long run, if existing firms are earning supernormal profits, what will happen to their average revenue (AR) curve and why?
It will shift to the left because new firms entering the market will decrease the demand for existing firms' products
Why is dynamic efficiency limited in monopolistic competition?
Firms earn normal profits in the long run.
What does a lack of supernormal profit restrict?
It restricts investment in innovation.

Regarding innovation, how does perfect competition differ from perfectly competitive markets?