Mendel's Experiments and Principles of Genetics
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Gregor Mendel
Austrian monk who worked with pea plants and provided the foundation for modern genetics.
Model Organisms
Organisms that are used to study biological processes; Mendel chose pea plants as model organisms.
True-breeding
Organisms that will produce offspring identical to themselves if they self-pollinate; also known as 'purebred'.
Hybrid
The offspring of a cross between parents with different traits.
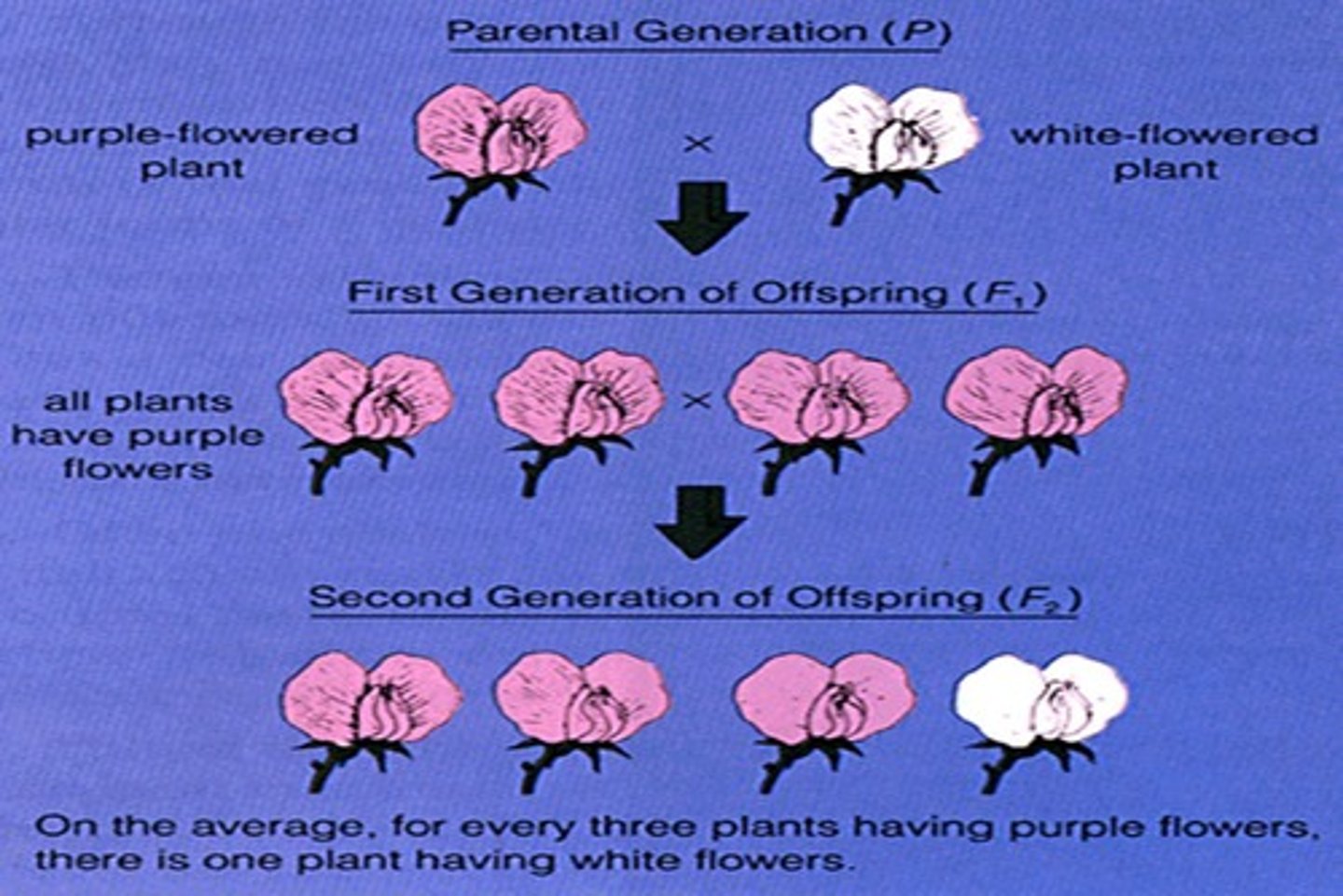
P Generation
The parents of a cross.
F1 Generation
The offspring of the P Generation; also known as 'first filial'.
F2 Generation
The offspring of the F1 Generation; also known as 'second filial'.
Cross
The mating of two organisms in genetics.
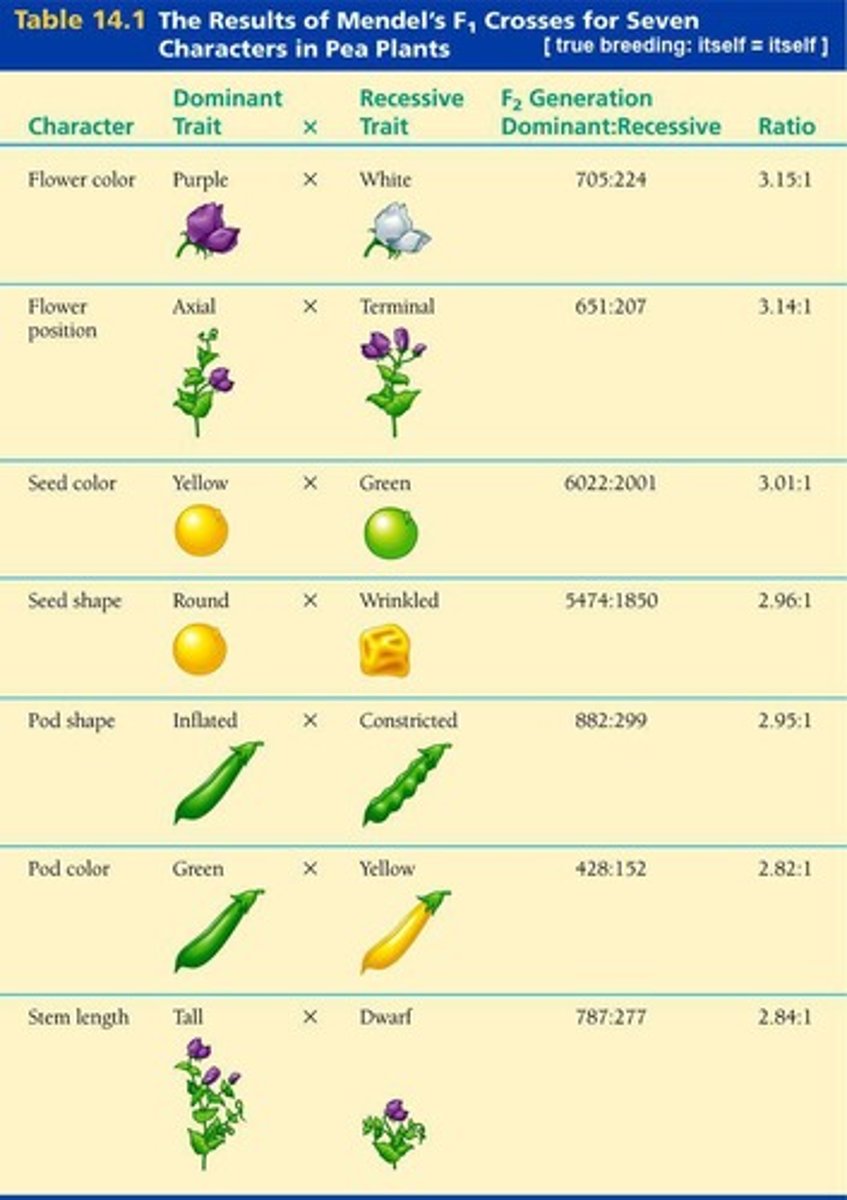
3:1 Ratio
The ratio of purple to white flowers observed in the F2 Generation after Mendel's experiments.
Genes
Factors that are passed from one generation to the next and determine inheritance.
Alleles
Different forms of a gene, such as brown eyes vs. blue eyes.
Principle of Dominance
Some alleles are dominant while others are recessive; dominant alleles will mask the recessive ones.
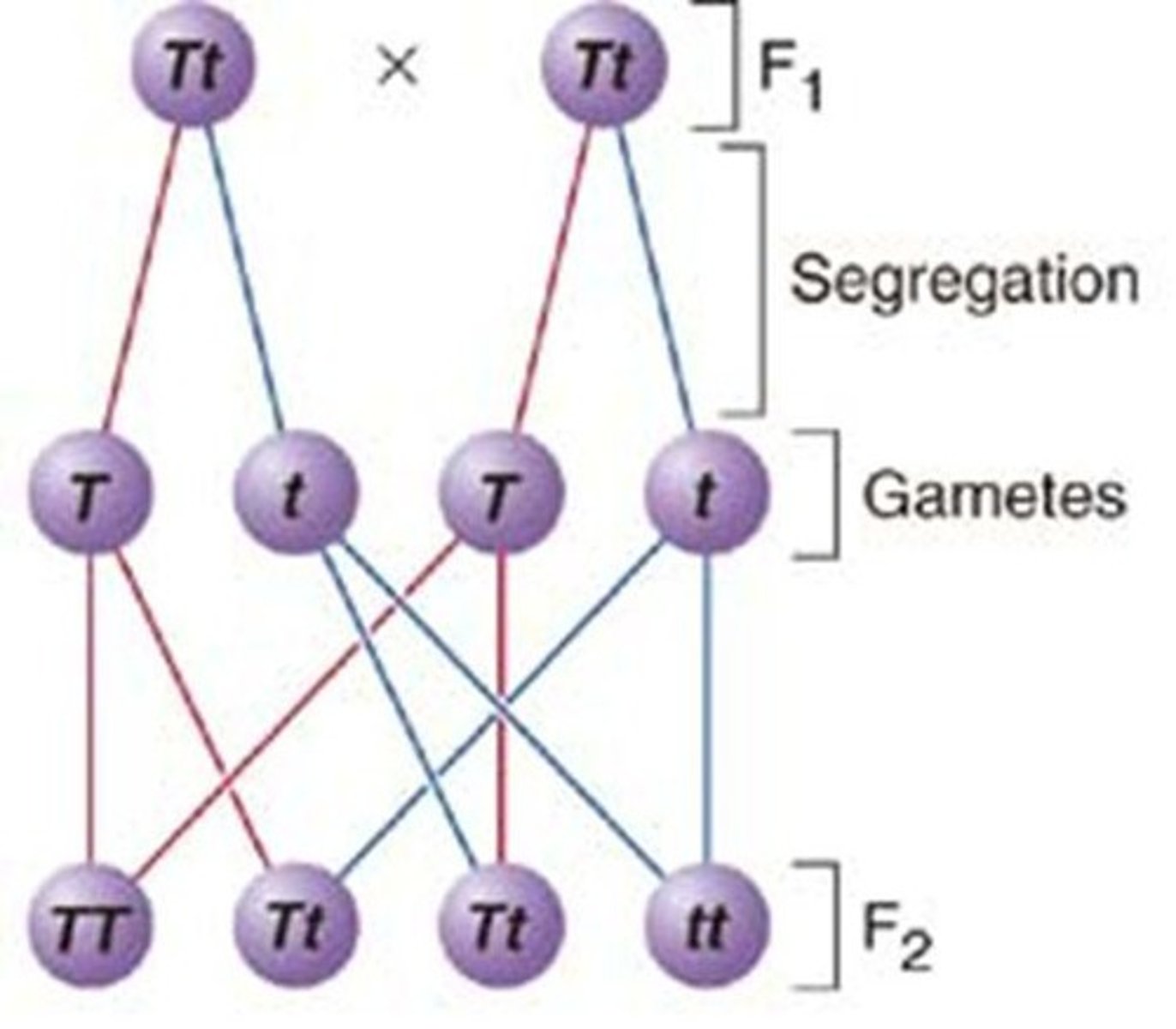
Principle of Segregation
Alleles will separate from each other during meiosis, ensuring each gamete receives only 1 allele.
Principle of Independent Assortment
Genes and the chromosomes they are attached to assort without influence on each other.
Pea Shape
One of the 7 traits Mendel followed; can be Round or Wrinkled.
Pea Color
One of the 7 traits Mendel followed; can be Yellow or Green.
Pod Shape
One of the 7 traits Mendel followed; can be Inflated or Constricted.
Pod Color
One of the 7 traits Mendel followed; can be Yellow or Green.
Flower Color
One of the 7 traits Mendel followed; can be Purple or White.
Flower Position
One of the 7 traits Mendel followed; can be Axial or Terminal.
Plant Height
One of the 7 traits Mendel followed; can be Tall or Dwarf.
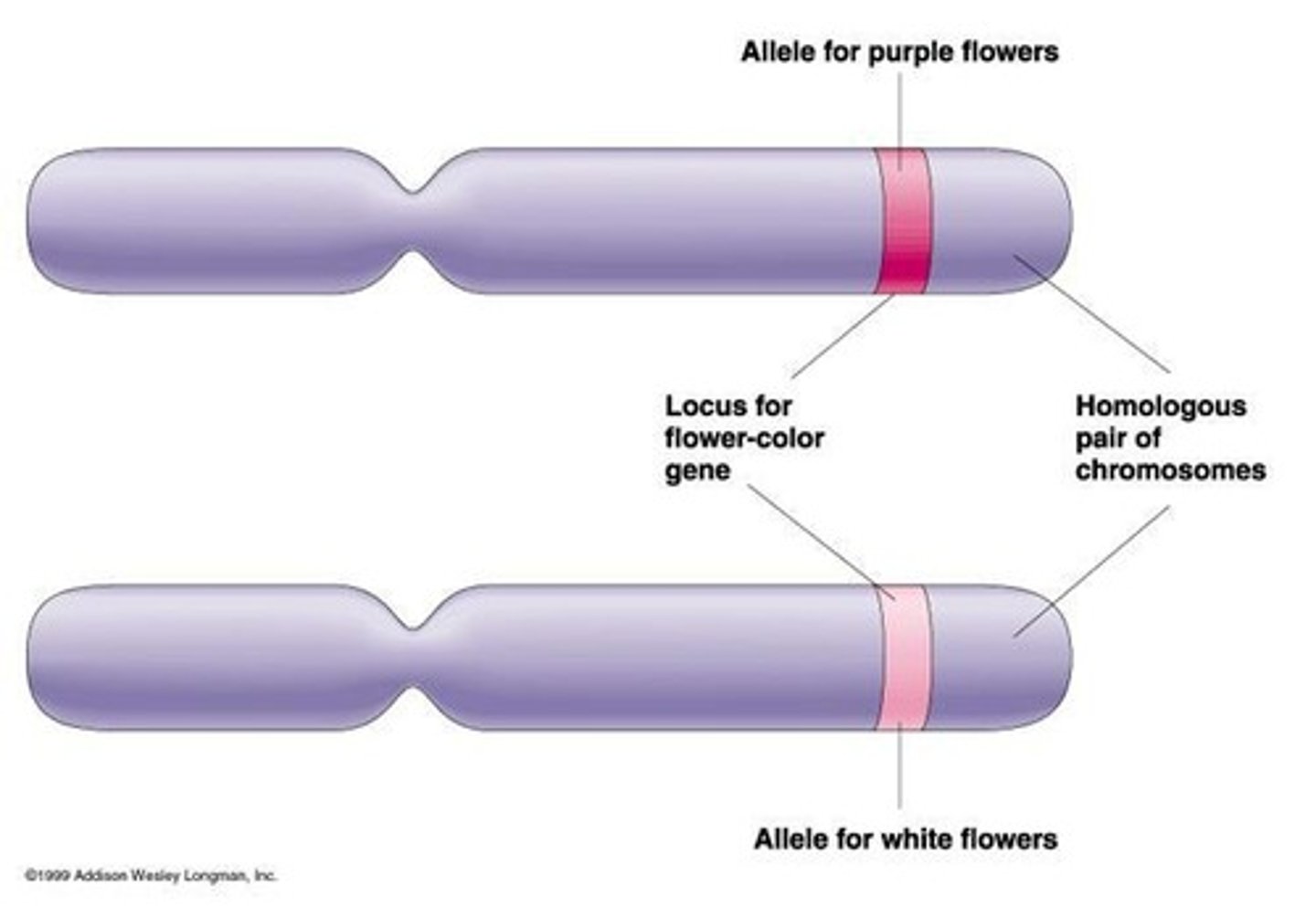
Gene
A heritable factor that has a specific characteristic and a specific locus on a pair of homologs.
Alleles
Alternative forms of a gene
Dominant Allele
The allele that is expressed; usually represented by a capital letter
Recessive Allele
The allele that is only expressed if the dominant allele is absent; usually represented by a lowercase letter
Homozygous
Having 2 of the same allele; BB or bb; sometimes called 'purebred'
Heterozygous
Having 2 different alleles; Bb
Genotype
The genetic makeup of the organism; BB, Bb, or bb
Phenotype
The physical appearance of the trait; brown or blue eyes
Monohybrid Cross
A cross showing the inheritance of only one trait
Dihybrid Cross
A cross showing the inheritance of two traits
Genome
All the genetic material in an organism
Punnett Square
A grid system for predicting the possible genotypes that result from a cross; deals with probability
Testcross
A cross between an organism of unknown genotype with an organism of the recessive genotype; allows scientists to determine if the organism of unknown genotype is homozygous dominant or heterozygous
F1 Offspring
Offspring resulting from the first cross; used to determine genotypes and phenotypes
F2 Offspring
Offspring resulting from crossing two F1 individuals; used to determine genotypes and phenotypes
Phenotypic Ratio
The ratio of different phenotypes in the offspring
Genotypic Ratio
The ratio of different genotypes in the offspring
Segregation
The process by which alleles separate during gamete formation
Fertilization
The union of gametes to form a new organism
Mendel's Principles
Fundamental concepts that describe the inheritance of traits
Flower Color in Peas
Purple (P) is dominant to white (p)
Plant Height in Peas
Tall Plants (T) are dominant to Dwarf Plants (t)