Lecture 3.2 - Protists
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A compilation of key vocabulary terms related to protists, their characteristics, roles, and classifications in biological systems.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Protists
A diverse group of eukaryotic microorganisms that are not classified as plants, animals, or fungi.
Euglena
A protist commonly found in pond water, known for its flagellum and photosynthetic abilities.
Excavata
A clade of protists characterized by a feeding groove and can be predatory heterotrophs, photosynthetic autotrophs, mixotrophs, or parasites.
Giardia intestinalis
A flagellated unicellular eukaryote that is parasitic in the human intestine, causing giardiasis.
Mixotrophs
Protists that combine photosynthesis and heterotrophic nutrition.
Diatoms
A major group of unicellular algae that are a key component of phytoplankton, known for their glass-like walls.
Brown algae
Multicellular algae that are typically found in marine environments and store carbohydrates as laminarin.
Dinoflagellates
A group of protists that possess flagella and are known for causing 'red tides' due to their bloomed populations.
Apicomplexans
A group of almost wholly parasitic protists, including those that cause diseases like malaria.
Plasmodium
The genus of protists that causes malaria in humans, characterized by a complex life cycle involving mosquito and human hosts.
Rhodophyta
A group of red algae which are mostly marine and known for their distinctive pigments.
Chlorophyta
Green algae that are most plant-like and often live in freshwater environments.
Unikonta
A clade that includes protists closely related to fungi and animals, including amoebozoans.
Symbiotic relationships
Interactions between different species where at least one benefits, such as the relationship between corals and zooxanthellae.
Phytoplankton
Aquatic protists responsible for about 30% of global photosynthesis, including diatoms and dinoflagellates.
Parasite
An organism that lives in or on another organism (its host) and benefits at the host's expense.
Most nutritionally diverse of all eukaryotes include
Photoautotrophs
Heterotrophs
Mixotrophs
Photoautotrophs in protists
Contain chloroplasts
Heterotrophs in protists
Absorb organic molecules or ingest larger food particles
Mixotrophs in protists
Combine photosynthesis and heterotrophic nutrition
Supergroups of rotists
Excavata
SAR
Archaeplastida
Unikonta
Clade excavata
Can be predatory heterotrophs, photosynthetic autotrophs, mixotrophs and parasites
Giardia
Parasite shed in faeces
Giardia protection
Has a protective outer shell → can survive outside the body for long periods and is resistant to chlorine disinfection
SAR clade
Diverse monophyletic group of protists defined by DNA similarities
Stramenopiles
A group within the SAR clade, characterized by hair-like structures on their flagella, including diatoms and brown algae.
Diatoms
Single-celled algae known for their glass-like cell walls made of silica, contributing to oceanic primary production.
Brown algae
A group of large, multicellular marine algae, often ranging in color from olive green to brown, that play a vital role in coastal ecosystems and food webs.
Alveolates
Membrane-enclosed sac under the plasma membrane
Dinoflagellates
a group of single-celled organisms characterized by two flagella and can be photosynthetic or heterotrophic; some species can cause red tides.
Dinoflagellates can produce…
Toxins, and can contaminate invertebrates and fish
Apicomplexans
a group of parasitic protists that utilize apical complex structures to invade host cells, including the species that causes malaria.
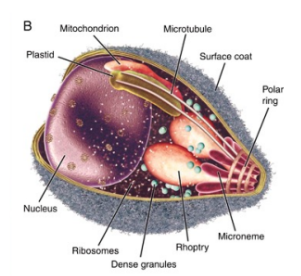
Name
Apicomplexans
Plasmodium
a genus of apicomplexan parasites that are responsible for causing malaria in humans. They are transmitted through the bite of infected Anopheles mosquitoes.
Malaria
a disease caused by Plasmodium parasites, transmitted through the bites of infected Anopheles mosquitoes.
Rhodophyta (red algae)
a division of red algae, characterized by their ability to perform photosynthesis using chlorophyll a and accessory pigments. Red algae are primarily found in marine environments.
Chlorophyta (green algae)
a division of green algae that are primarily freshwater organisms, utilizing chlorophyll a and b for photosynthesis. They play a significant role in aquatic ecosystems and are important for oxygen production.
Unikonta
Includes protists that are closely related to fungi and animals as well as fungi and animals
Amoebozoans
a group of protists characterized by their irregular shapes and ability to move using pseudopodia. They are often found in moist environments and include organisms like amoebas.
Symbiotic protists
are protists that live in close association with other organisms, often providing benefits to their hosts, such as nutrient acquisition or protection.
Phytoplankton percentage of photosynthesis
30% all photosynthesis - includes diatoms, dinoflagellates, multicellular algae and other aquatic protests
Parasitic protists
are protists that obtain nutrients and energy by living on or inside a host organism, often causing disease or harm to the host.