AP HUMAN GEOGRAPHY UNIT 1 VOCAB
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Place
Specific point on Earth, distinguished by a particular characteristic
Every one has its own unique location
Space
refers to the physical gap or interval between two objects or places
Scale
relationship between PORTION of earth being studied and earth as a WHOLE
ex. national, global, local
scale of analysis
the relative size of the map or lens we choose to use to observe geographical phenomena
Region
area on earth defined by one or more distinctive characteristic.
Can be cultural, geographical, or both.
ex: latin america, sub-saharan africa
Absolute Location
Position on Earth's surface using the coordinate system of longitude (that runs from North to South Pole) and latitude (that runs parallel to the equator)
Relative Location
the relationship of a place to other places
Cartography
the science of mapmaking
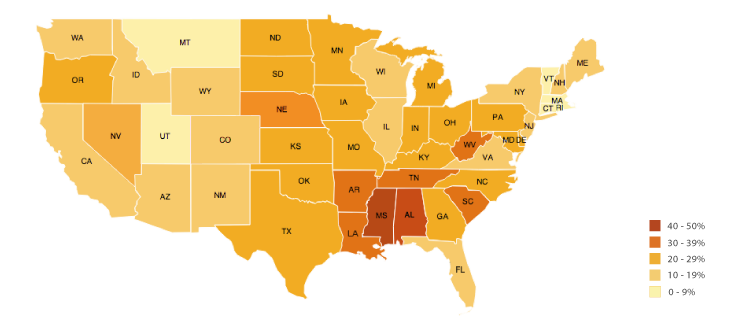
Choropleth
a thematic map in which areas are shaded or patterned in proportion to the measurement of the statistical variable.
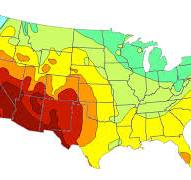
Isoline
connects with lines all the places that have particular values
ex: topographic map
Reference maps vs. Thematic maps
reference maps contain places and regions you can visit inside a country while thematic maps all have themes
reference map
contains places and regions you can visit inside a country
shows us where in the world something is
thematic maps
have themes such as temperature or religions in a region
GIS
Geographic Information System
A computer system that stores, organizes, analyzes, and displays geographic data.
Each type is stored in a layer. Can superimpose layers on top of each other to compare data
Data is acquired through photogrammetry, remote sensing, and many other ways
GPS
A system that determines the precise position of something on Earth through a series of satellites, tracking stations, and receivers.
Photogrammetry
the process of making surveys and maps through the use of aerial photographs
Remote Sensing
A method of collecting data or information through the use of instruments that are physically distant from the area or object of study.
Distance Decay
as the distance between two places increases, the interaction between those two places decreases
Time-space compression
The reduction in the time it takes to diffuse something to a distant place, as a result of improved communications and transportation system
Density
Frequency- how often does something occur in a given area
Concentration
how close or far apart things are in a given area
Pattern
arrangement of objects in space
Could be a geometric, linear, or irregular.
How things are arranged on the ground-street grids
Network
chain of communication/interaction that connects places
help explain phenomena such as travel patterns, and diffusion (spread) of religions, languages, all other ideas.
Cultural Landscape
Combination of physical, economic, and cultural features that define an area may determine how we “make up” regions.
Formal/Uniform Regions
Regions with distinct, defined areas that cannot be debated. Formally agreed upon regions.
Ex: Saharan Africa, Middle East
Functional/Nodal Regions
focused on a center point that connects other areas culturally and/or economically
Ex: Wall Street, Down the shore, School district
Vernacular/Perceptual Regions
No distinct political/ drawn boundaries
Ex: North/South/Central Jersey
Sustainability
the use of earth’s resources in ways that ensure their availability in the future
Renewable vs. Non-Renewable resources
Renewable: a natural resource which will replenish to replace the portion depleted by usage and consumption
Non-renewable: a natural resource that cannot be readily replaced by natural means at a pace quick enough to keep up with consumption
Cultural Ecology
The study of human-environment relationships
Environmental Determinism
you are a product of the world around you- it determines how you act and behave
Most modern geographers, BUT NOT ALL, reject this
Environmental Possibilism
we can alter things around us to live the way we want to live
Why/how maps get distorted; reliability of maps
because of their scale.
When trying to make a map of the entire world, many details can be left out
Different map projections often mess up the shape, distance, and relative size of areas
ex: the Mercator projection.
why is every map different
they don’t all use the same scale to project areas.
All project the size of the Earth in a different way, making them all different.
Some (thematic) are also used for completely different things like showing how much of something is in an area.
mercator pros and cons
it is good for sailing; however, it is still disproportionate
Robinson map
Shows the entire world at once but compromises both area and angles, especially at the poles
Goode map
provides an effective alternative to portraying global area relationships on the Mercator map and number of map projections is limitless; but, its distorted in terms of shape, distance, direction, or land area and impractical because of cutouts
Winkel map
Reasonably accurate shapes and sizes of countries but land masses closer to the poles still enlarged
Gall-Peters map
The only ‘area-correct’ map of its time, longitude and latitude is very accurate; but, Galled the cartographic community in the 1980s and not PERFECTLY accurate
Importance of geographic data & its influence on decision making
used at all scales for personal, business and organizational, and governmental decision making purposes
ex: census data and satellite imagery
global scale of analysis
shows the world at one level of data, usually not that useful (almost impossible to use)
ex: climate change
regional scale of analysis
shows data by continents or world regions
Ex: Southeast Asia, Sub-Saharan Africa
national scale of analysis
shows data for one or more countries
local scale of analysis
shows data at subnational level
Ex: states within the United States
ratio scale
example: 1:500,000 → 1 unit on the map (given by the key of the map… could be an inch, cm, foot, etc.)= 500,000 of the same unit on Earth itself
written scale
describes the scale in words.
ex: 1 centimeter equals 1000 miles
graphic scale
includes a bar line marked to show distance on the Earth’s surface. Need to measure with a ruler, a straightedge or even your fingers!
Larger vs. smaller ratio scales; usefulness of “zoomed in” or “zoomed out” maps
Maps at smaller scales (more zoomed out) are ideal for global & regional levels of analysis
Maps at larger scales (more zoomed in) are ideal for local scale of analysis
factors that make up cultural landscapes
Trees, buildings, pathways, site furnishings, water bodies – basically any element that expresses cultural values and the history of a site.
global regions
ex: Latin America, Eastern Asia, Indian subcontinent, North Africa, Sub-Saharan Africa, etc.
national regions
ex: Northwest/New England, Southeast, Southwest, Midwest, West
local regions
Could be counties of NJ. Or, on an even smaller scale, regions of Bergen County itself! (example: Northern/Southern Bergen county.)
How humans interact with their environments AND factors that determine this
Sustainability, use of natural resources, and land use all display
Humans…
Adapt to their environment
Modify their environment if needed
Depend on the environment
3 pillars of sustainability
Environment: → conservation/preservation
Social: → consumer (human) choices about which resources to use and how
Economic: → do the price of goods that humans pay reflect their environmental costs? (ex: oil)