eye notes
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
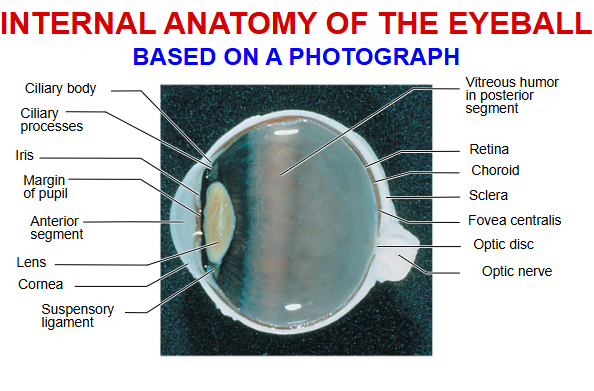
sclera
support, protection and movement
cornea
main refractive (light-bending structure)
choroid
blood supply and light absorption
ciliary body and muscles
after shape of lens for focusing
iris and pupil
regulation of amount of light entering eye
pigmented layer
absorb light, vitamin A storage
neural layer
photoreception and vision
macula lutea, fovea
area of maximal visual acuity
optic disc
site where optic nerve exits
conjuctiva
lubrication and protection of eyeball
lens
refractive structure: focusing
suspensory ligaments
connect lens to ciliary body
aqueous humor in anterior segment
nourishment and ocular pressure
vitreous humor in posterior segment
support of retina and ocular pressure
photoreceptors
rods and cones
rods
non color vision
rods
high sensitivity; function in dim light
rods
low acuity
rods
more numerous
rods
mostly in peripheral retina
rods
visual pigment : Rhodopsin
cones
colour vision
cones
low sensitivity ; function in bright light
cones
high acuity
cones
less numerous
cones
mostly in central retina
cones
visual pigment : photospins ( blue, green, red)
image fornation
refraction of light
accomodation of lens
constriction of pupils
convergence of eyes
refraction
bending of light rays at junction between two transparent substances with different densities
osteogenic cells
undifferentiated cells
divide and become osteoblasts
inner layer of periosteum and endosteum
osteoblasts
immature bone cells
form and secrete ecm
osteocytes
mature cells no longer secreting ecm
main cells in bone
cells lie within lacunae
osteoclasts
very large cells with several nuclei
derived from fusion of monocytes
mostly in endosteum
function in bone resorption
diaphysis
bone shaft
epiphysis
end of long bone
metaphysis
growth (epiphyseal) plate region
articular cartilage
hylaine cartilage over joint surfaces
reduces friction and absorbs shocks
medullary cavity
yellow bone marrow cavity
endosteum
inside lining of medullary cavity
bone cells
periosteum
tough membrane covering bone
outer fibrous layer made of ct
inner osteogenic layer
protects and nourishes bone
attatchment point for ligaments
compact bone tissue
strongest bone tissue
makes up frame of long bones
resists stress produced by weight and movement
provides support and protection
osteons
repeated units
concentric lamellae around central canal
osteocytes
located in lacunae
communicate via canaliculi
spongy bone tissue
light bone tissue inside a boen
protected by compact bone
area of low stress from many directions
ends of long bones
inside of flat and short bones
supports and protects bone marrow
trabeculae
spongy bone
latticework of thin plates
concentric lamellae with osteocytes in lacunae
three types of cartilage
hylaine, fibrocartilage, elastic cartilage
hyaline cartilage
support and reinfoece resist compressive stress
location of hyaline cartilage
covers ends of long bones in joint cavities,; costal cartilage of rivs; cartilage of nose, trachea and larynx
fibrocartilage
tensile strength allows it to absorb comprehensive shock
location of fibrocartilage
intervertebral discs, pubic symphsis; menisci of knee joint
elastic cartilage
maintains shape of a structure while allowing great flexibility
location of elastic cartilage
supports the external ear, epigilotis
5 major types of bone
long, short, flat, irregular, sesamoid
axial skeleton
80 bones
midline bones
appendicular skeleton
126 bones
along limbs
vertebral collumn
26
cervical -7
thoracic - 12
lumbar - 5
sacrum- 5
coccyc, 4
synarthrosis
non-moveable
amphiarthrosis
slightly moveable
dairthrosis
freely moveable