b5 - Genes, inheritance and selection
1/48
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
whats a gamete
reproductive cells (egg in female and sperm in males)
whats a chromosome
a long,thin molecule of DNA
whats a gene
A short section of DNA that codes for a protein, and therefore contribute to a characteristic.
whats an allele
Different forms of the same gene- can be called variants
whats a dominant allele
only one copy of it is needed for it to be expressed
whats a recessive allele
Two copies are needed for it to be expressed
what does it mean if an organism is homozygous
a genotype where the 2 alleles for the characteristic are the same (AA) or (aa)
what does it mean if an organism is heterozygous
a genotype where the 2 alleles needed for the characteristic are different (Aa)
whats a genotype
a collection of all the genes an organism has
whats a phenotype
The visible characteristics in the individual, e.g. eye colour
whats a genome
entire genetic material of an organism
whats discontinuous variation
variation that produces distinct categories (e.g eye colour or blood groups)
whats continuous variation
variation that cannot be places into distinct categories and creates a spectrum (e.g. height and weight)
what 2 things can variation be as a result of
genetics - variation is caused by differences in the genotype ( the genetic information)
environmental- conditions in which it lives
what causes variation
mutations in the gentic code
what does mutation mean
the sequence of DNA bases in the gene is changed which produces a genetic variant
whats the effect of mutation on the phenotype
most have no effect on the phenotype, some influence phenotype and a very few determine phenotype
why do some mutations only have a small influence on the organisms phenotype
some characteristics e.g. eye colour are controlled by more than one gene
a mutation in one of the genes may change the eye colour a but but the difference wont be huge
describe how a mutation in a coding DNA sequence could be detrimental
the mutations may change the sequence of amino acids in the protein which will change its structure
this may affect the protein, particularly in specific molecules like enzymes and antibodies
whats an example of when a mutation has a dramatic affect on the phenotype
cystic fibrosis
variant deletes the bases that controls the movement of salt and water in and out of cells properly
leads to excess mucus production in lungs + digestive system
whats sexual reproduction
where genetic information from two organisms (mother and father) combine to produce offspring which are genetically different to either parent
sexual reproduction causes genetically __________ cells
different
whats a haploid cell
a cell that only has half the normal amount of genetic material
whats a diploid cell
a cell with the full number of chromosome (genetic material) - 46 chromosomes ( 23 pairs)
how many divisions are their in meiosis
2
how many cells does meiosis produce
4 haploid cells which are all genetically different from each other
where does meiosis occur
in sex organs - testes in males and ovaries for females
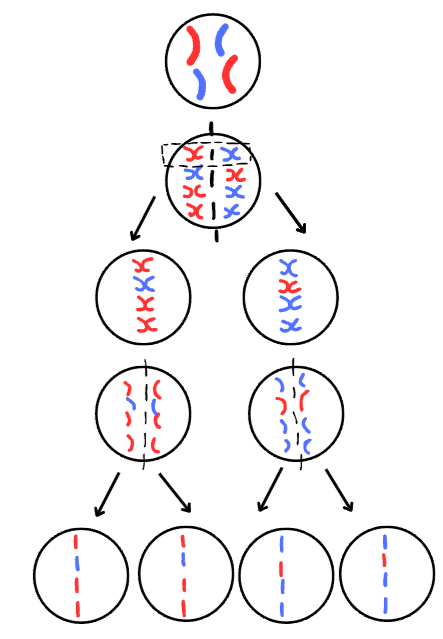
whats the process of meiosis
chromosomes double to create x shaped chromosomes
line up in random male and female pairs
splits down the middle and pairs are pulled apart
x shaped chromosomes pulled apart
produces 4 gamete cells
give 1 advantage and disadvantage of sexual reproduction
advantage - introduces variation
disadvantage - it is slower and produces a limited amount of offspring
how are dominant alleles represented in a punnet square
using uppercase letters
how are recessive alleles represented in a punnet square
use lowercase version of the same letter as the dominant allele
what are the chromosomes that determines the sex
males : have an x and a y chromosome - y chromosome causes male characteristics
females : have 2 x chromosomes - lack of y chromosome causes female characteristics
whats asexual reproduction
only 1 parent so offspring genetically identical to that parent
happens by mitosis
the new cell has exactly the same genetic information as the parent cell
bacteria, some plants and animals reproduce asexually
give 1 advantage and 1 disadvantage of asexual reproduction
advantage - it produces a lot of offspring quickly
disadvantage - it does not introduce variation so all offspring are susceptible to the same environmental pressures as the parents
what 3 advancements have improved classification
use of microscopes
studies of biochemistry
DNA evidence
how has DNA sequencing helped improve classification
Studies of DNA sequences of different species show that the more similar the base sequences in the DNA of two species, the more closely related those two species are (and the more recent in time their common ancestor is)
Classification based on this information is called molecular phylogeny
what are the 2 types of classification
artificial - using observable features
natural - using evolutionary relationships
whats artificial classification
used comparisons of observable and non-evolutionary features to group organisms
Observable characteristics include things like whether they give birth to live young or lay eggs etc
The less scientific nature of these methods means they are not considered to be the best way of classifying organisms
whats natural classification systems
is based on evolutionary relationships between organisms
Organisms are categorised using information about common ancestors and common structural features
ceated by carl linnaeus
He named organisms in Latin using the binomial system
categorises organisms based on their structure and characteristics
he created 7 different groups
kingdom
phylum
class
order
family
genus
species
whats the binomial naming system
every species has a binomial name made up of 2 parts: the genus name and the species name
what are the 2 rules in the binomial naming system
both names should be written in italics
all letters should be lower case except the first letter of the genus name (‘Homo sapiens’)
what are the 3 advantages of using the binomial naming system
each species has a unique name which avoids confusion
allows scientists from different parts of the world to discuss species
can show how closely related organisms are ( as many related organisms often have the same genus name )
whats the process of natural selection
populations are naturally varied die to random genetic mutations
some genetic variants make characteristics that are better suited to a particular environment (advantageous phenotype)
these organisms survive and reproduce passing on the successful genes
whats evolution
a change in the inherited characteristics of a population over time, through a process of natural selection
what affects the speed at which a species evolves
how quickly it reproduces because the inherited characteristics are passed on to future generations more quickly
how can evolution create new species
a species phenotype changes so much that an entirely new species if formed
happens when two populations of species are separated with a physical barrier
conditions on each side of the barrier will be slightly different so the phenotype that will be beneficial will be different for each population
whats are 2 pieces of evidence for evolution
fossils
antobiotic resistance
how can fossils be used to see evolution
is any trace if animals/ plants that lived a long time ago
can tell us about what organisms looked like
by arranging fossils in chronological order, we can see the gradual changed in organisms
how does antibiotic resistance happen
bacteria can sometimes develop random mutations i their DNA which can cause the bacteria to become resistant to the antibiotic
when antibiotic is used, all bacteria with resistance survive and the rest are killed
the population containing the resistant bacteria then begins to grow