Anatomy L5 - Neural crest cells
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Neural crest cells
ectodermal derivative
formed dorsal area of NT
BMPs difine the region that will become NCC
Migrate and diffrentate into different cells
Form glial and neurons of parasympathetic, sympathetc and sensory NS
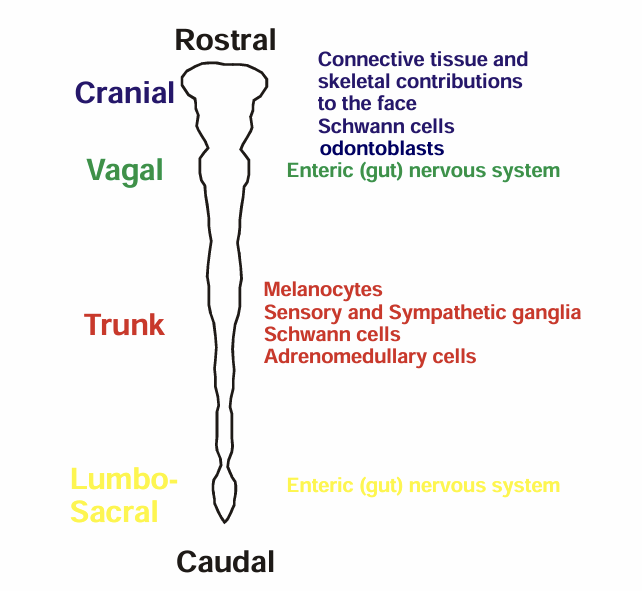
Fate of the Neural Crest Along the Rostro-caudal axis
When NCC migrate away form Neural tube…
they undergo a epithilial mesenchymal trasition (EMT)
When these cells migrate away they get exposed to different signals causing them to lineage restrict and become a certain type of cell
NCC that remain in the sclerotome become…
Dorsal root ganglia which then lineage restrict to form proprioceptive sensory neurons
NCC that migrate Dorsal lateraly become….
melonocytes of skin
NCC that migrate ventralateraly form..
go to doral aorta and form adrenal medulla cells
Where do NCC enter the somite
enter theough anterior portion of somite
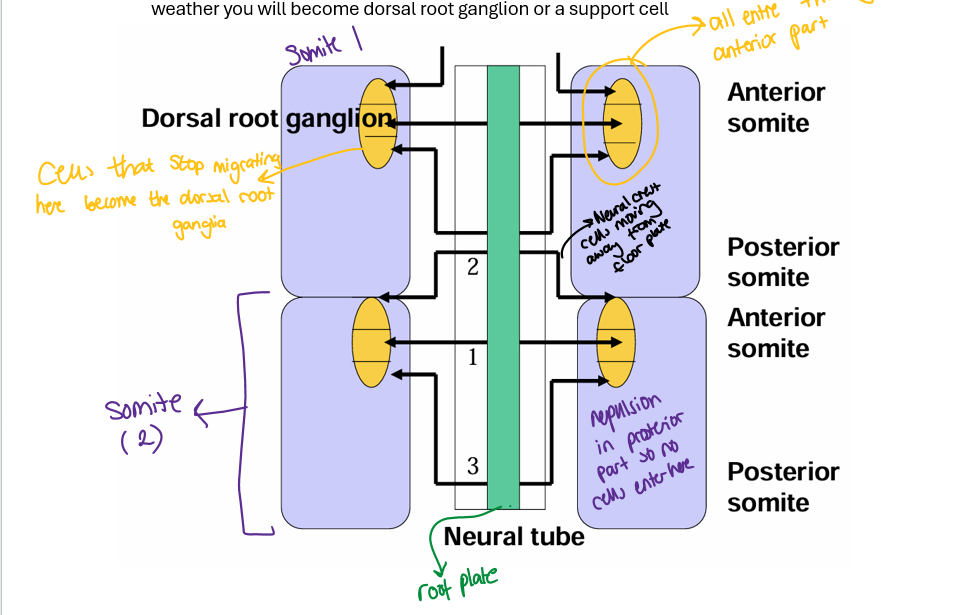
NCC that continus to move through somite become…
support cells for PNS e.g Schwann cells
Proprioceptive Sensory Neurons
Tap on muscle in knee causes small elongation of muscle which then causes the sensory neuron to fire an action potential causing motor neuron to then also fire an action potential which then leads to contraction of the muscle
What gives rise to Schwann cells
A subset of glial cells (from the neural crest) give rise to these myelinating Schwann cells
How schwan cells made
Swhann cell precursers migrate until find axon
axon tells it what to do
Glial growth factor expressed by motor neuron and neurons in periphery ganglia stimulate proliferationa and diffrentation