Cell specialisation
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
SL content
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Define the term cellular differentiation
Differentiation is the process during development whereby newly formed cells become more specialised and distinct from one another as they mature.
Define the term differential gene expression
When a cell express different genes in order to become structurally and functionally speacialized.
Define a stem cell
They are unspecialised cells
once the cell becomes specialised it loses its capacity to form alternative cell types.
What are the two key qualities of stem cells?
Self renewal – They can continually divide and replicate
Potency – They have the capacity to differentiate into specific cell types
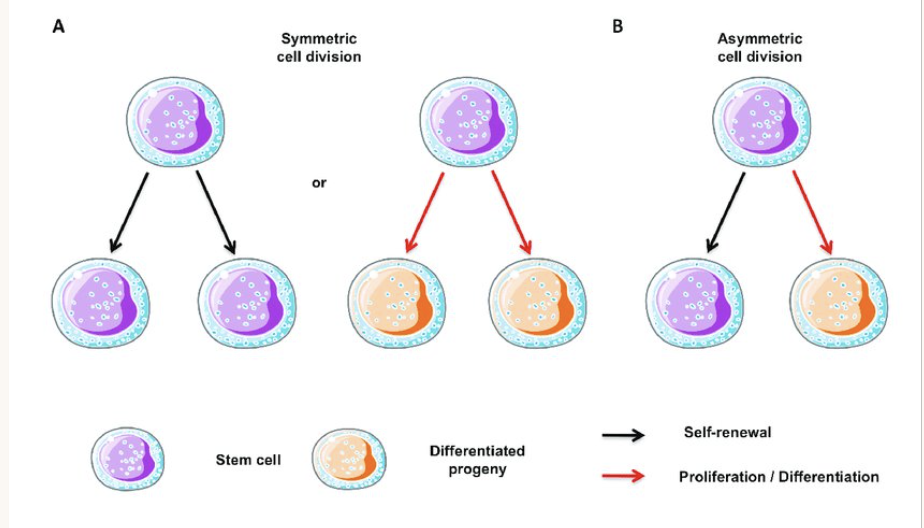
Define stem cell niche
Stem cells niches are sites within the body where adult stem cells are pooled.
Locations include the bone marrow, hair follicles, heart, intestines and brain.
They are known to be an area of tissue that provides specific environment where stem cells exist in an undifferentiated and self renewable state. And stimuli is given to determine their behaviour.
Define stimuli
Stimuli are signals such as chemicals (e.g. growth factors) or other messengers which bind to cell surface receptors of the stem cell and trigger the stem cell to stay undifferentiated or commit to a more differentiated state by causing the expression of genes.
What are two examples of stem cell niches
1: bone marrow: Hematopoietic stem cells give rise to the different types of blood cells
2: hair follicles: Hair follicles contain a range of epidermal stem cells that are involved in hair growth, skin innervation*, vascularisation and wound repair.
Define the terms totipotent, pluripotent or multipotent
Totipotent:
Whole/ It can become any body cell including placenta in placental mammals. e.g: a zygote
Pluripotent:
Many/ Can become any blood cell/ e.g the inner cell mass of a blastocyst (a cluster of dividing cells made by a fertilised egg)
Multipotent (adult):
Several/ can only form a certain number of related cells / e.g: Umbilical cords in stem cells.
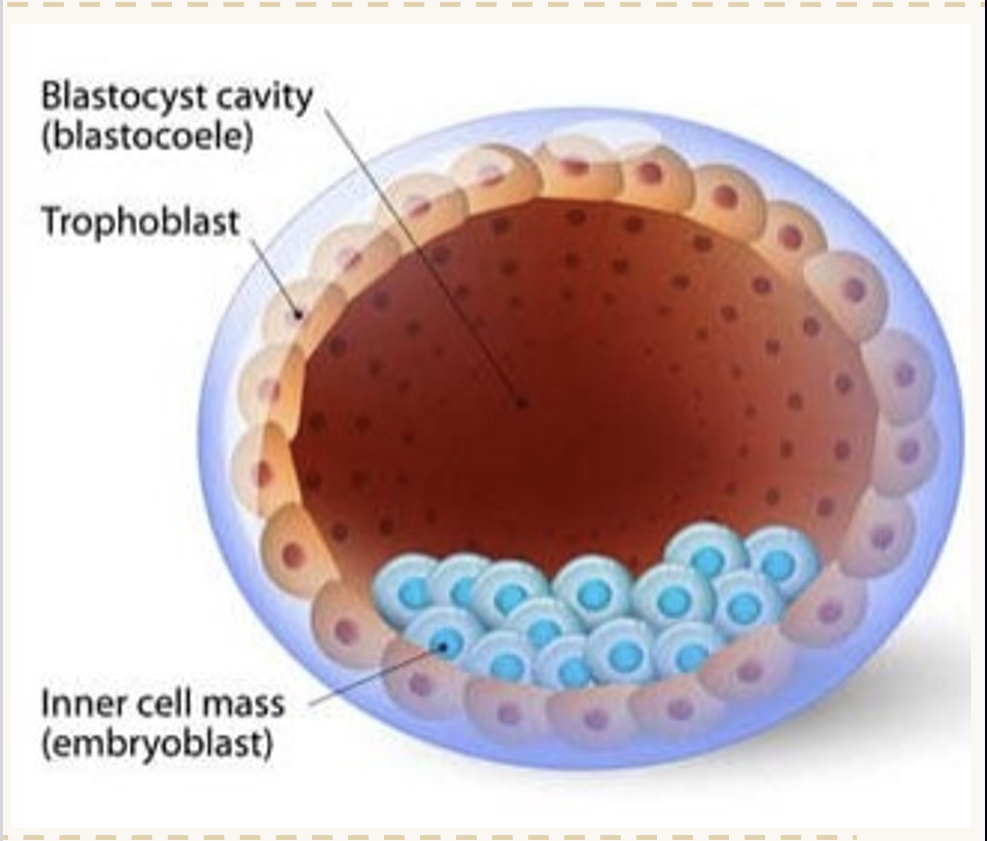
Draw a diagram of a blastocyst labelling the inner cell mass.
Inner cell mass: Develops into the embryo (and human)
Trophoblast: Develops into the placenta
what is the chain of events from the zygote to the blastocyst
zygote —→ morula —→ blastocyst (the first line of differentiation happens here)
Define the term Morphogen gradient
The process of early embryo differentiation is driven by the release of specialised signalling molecules* called morphogens**.
Come back to powerpoint slide 29
Define morphogen gradient
Morphogens are a group of signal molecules that diffuse from a source cell, creating different concentrations as they move from source along the body. These varying concentrations are called morphogen gradients.
What is the role of morphogen gradients in gene expression of early stage embryos
These early embryonic stem cells simply respond to different thresholds of morphogens.
Look at slides 35-38 and see how your meant to learn the range of cell sizes.
What happens when there is a lower surface area to volume ratio in a cell
Metabolism in the cell would increase exceeding the rate of exchange of vital materials and wastes.
whats the formula to calculate the surface area to volume ratio of a cube.
6a2/a3
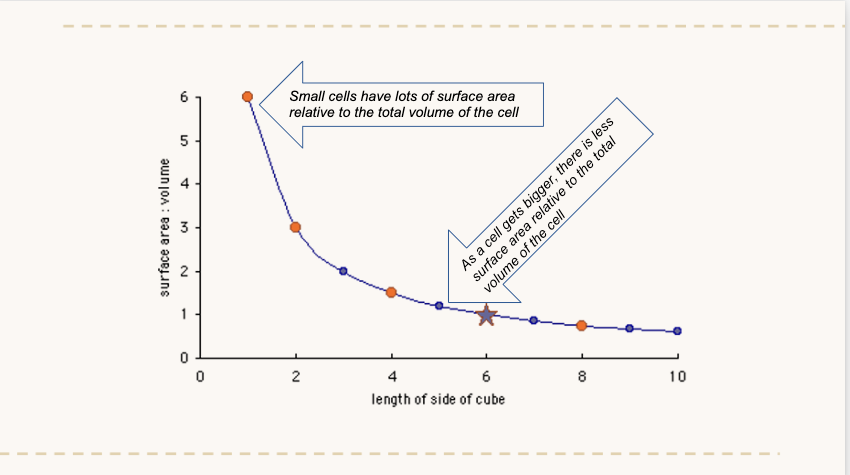
Look and understand graph.
Give examples of models used in science
Computer models
E.g. Epidemiology (study of disease spread)
Physical models
E.g. A cell model made from clay
Mathematical models
E.g. The Hardy Weinberg equation helps predict population genetics.
Living models
Using animals as models for drug/disease/etc.
What are some limitations of models in science?
Oversimplifying complex processes
Poor substitutes to study on such as rats
Why is repeated measurements important
Evaluate reliability/ reinforces strength of any conclusion made and make sure for consistent results
Define what standard deviation measures
Calculation of consistency: It determines how much spread there was across repeated trials.
Low standard deviation: High reliability
High standard deviation: Low reliability - results are too spread ouIt measures the amount of variation or dispersion of a set of values, indicating consistency in data.
What do error bars show?
Shows the standard deviation of the spread of each set of repeated trials
Whats the difference between overlapping and non-overlapping error bars?
Overlapping: Hint that there is no statistically significant difference between the levels of independent variables.
Non-overlapping: Indicate a statistically significant difference exists between the levels of your IV.
Whats the significance of using standard deviation in comparing means and spread of data.
Even if the mean is the same for two sets of data the standard deviation my differ meaning that the repeated trials that were attempted have a large spread.