APES - Unit 6
1/43
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Fossil Fuels
A fuel derived from biological material that became fossilized millions of years ago.
Nonrenewable Energy Resource
An energy source with a finite supply, primarily the fossil fuels and nuclear fuels.
Nuclear Fuel
Fuel derived from radioactive materials that give off energy.
Commercial Energy Sources
An energy source that is bought and sold.
Subsidence Energy Sources
An energy source gathered by individuals for their own immediate needs.
EROEI
Energy Return On Energy Investment
100 J EROEI = 100J / 5 J = 20
Energy Carrier
Something that can move and deliver energy in a convenient, usable form to end users.
Turbine
A device that can be turned by water, steam, or wind to produce power.
Electrical Grid
A network of interconnected transmission lines that joins power plants together and links them with end users of electricity.
Combined Cycle
A power plant that uses both exhaust gases and steam turbines to generate electricity.
Capacity
In reference to an electricity-generating plant, the maximum electrical output.
Capacity Factor
The fraction of time a power plant operates in a year.
Cogeneration
The use of a fuel to generate electricity and produce heat. Also known as combined heat and power.
Combined Heat and Power
The use of a fuel to generate electricity and produce heat. Also known as co generation.
Coal
A solid fuel formed primarily from the remains of trees, ferns, and other plant materials preserved 280 million to 360 million years ago.
The largest coal reserves are found in the United States, Russia, China, Australia, and India. The countries that are currently producing the greatest amounts of coal are China, the United States, India, and Australia.
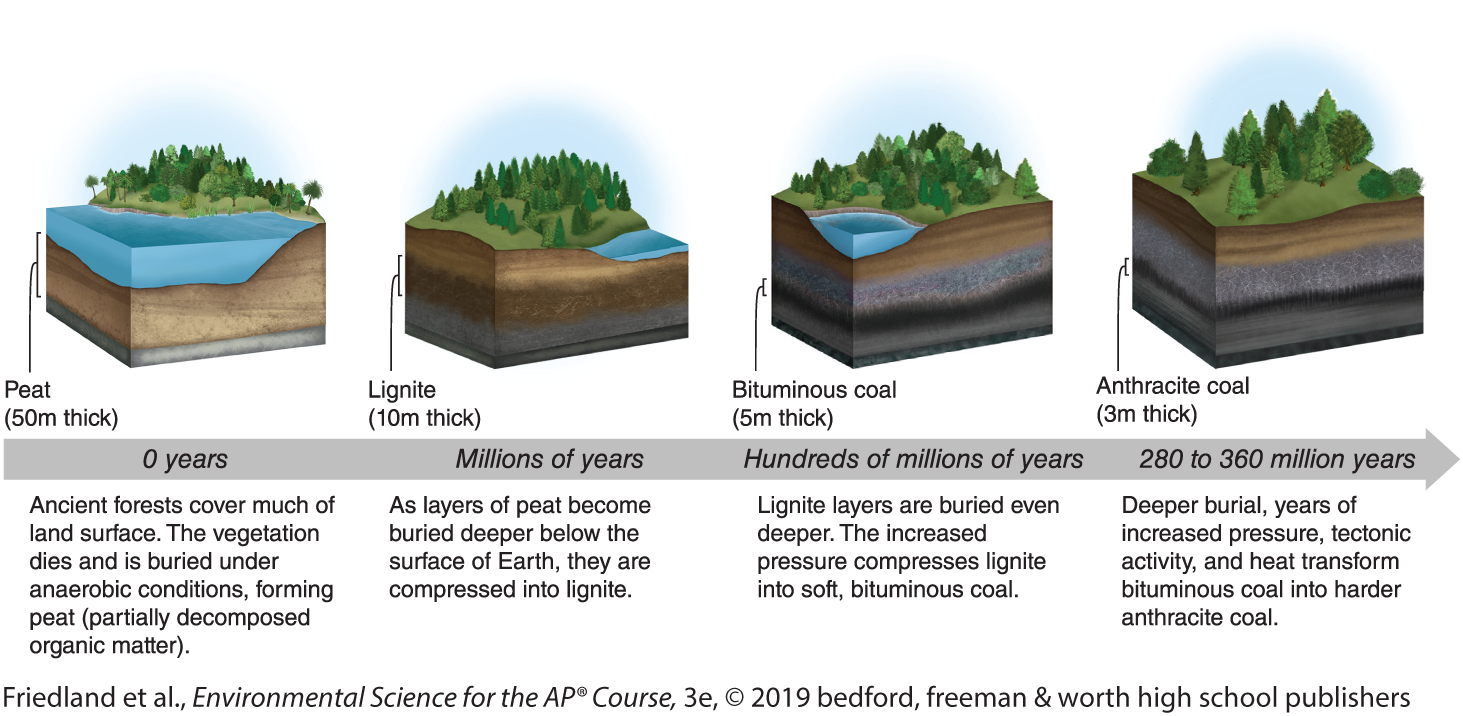
Coal Formation Process
Starts off as peat, then Lignite, then Bituminous, then Anthracite
Advantages of Coal
Because it is energy-dense and plentiful, coal is used to generate electricity and in industrial processes such as making steel.
The technological demands of surface mining are relatively small and the economic costs are low.
It can be transported to power plants and factories by train, barge, or truck.
Disadvantages of Coal
The sulfur content of coal typically ranges from 0.4 to 4 percent by weight.
Trace metals such as mercury, lead, and arsenic are also found in coal.
Combustion of coal results in the release of these elements, which leads to an increase of sulfur dioxide and other air pollutants, such as particulates, in the atmosphere.
Chemical spills and resulting ash causes pollutions and affects humans health.
Coal is 60 to 80 percent carbon. When it is burned, most of that carbon is converted into CO2 and energy is released in the process and it contributes to the increasing atmospheric concentrations of CO2 .
Petroleum
A widely-used fossil fuel that occurs in underground deposits, composed of a liquid mixture of hydrocarbons, water, and sulfur.
Petroleum is formed from the remains of ocean-dwelling phytoplankton (microscopic algae) that died millions of years ago. Petroleum forms and fills the pore spaces in the rock. The less dense petroleum migrates upward toward the highest point in the porous rock and trapped in nonporous rock.
The natural gas often associated with petroleum is even less dense, so it migrates to the absolute highest point in the dome, above the petroleum.
After drilling and extraction via pumps, the petroleum must be transported to a refinery, by pipeline or by supertanker.
Crude Oil
Liquid petroleum removed from the ground.
Petroleum Accumulation Underground
Formed between a layer of sandstone and shale, which are the shale source rock and the shale cap rock.
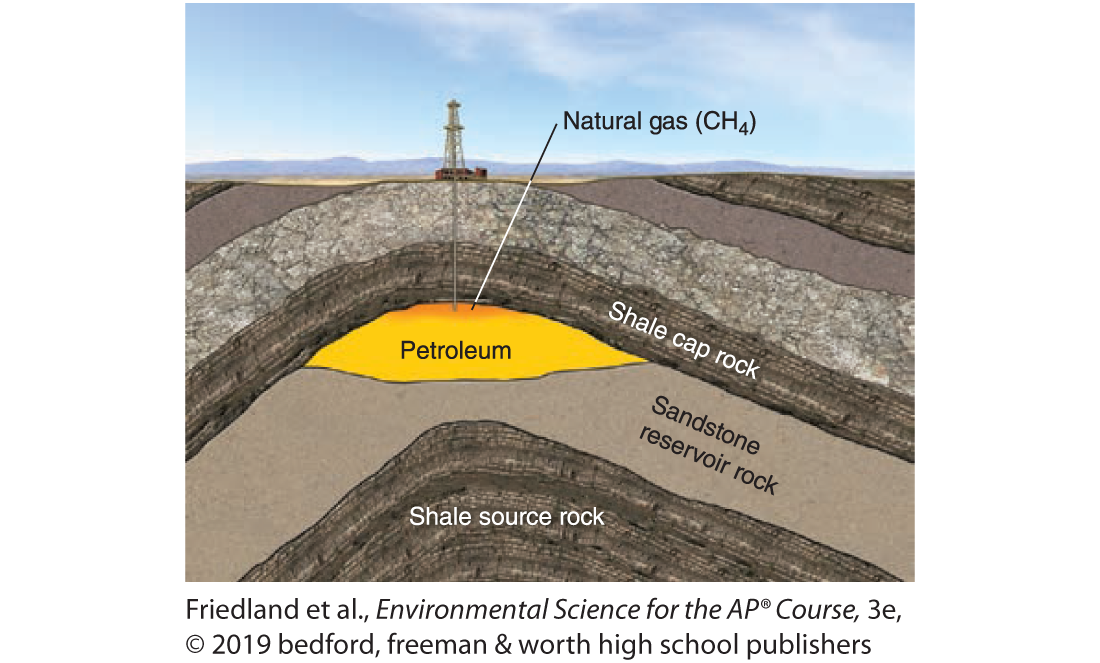
Petroleum Is Found In
US uses petroleum the most out of all fuels. However most of it is imported
The top petroleum-producing countries are Saudi Arabia, Russia, the United States, Iran, China, Canada, and Iraq, in roughly this order. These seven countries account for approximately one-half of worldwide oil production.
Advantages of Petroleum
Because petroleum is a liquid, it is extremely convenient to transport and use. It is relatively energy-dense and is cleaner-burning than coal.
Oil produces only about 85 percent as much CO2 as coal.
It is an ideal fuel for mobile combustion engines such as those found in automobiles, trucks, and airplanes.
Disadvantages of Petroleum
Some oil naturally escapes from the rock in which it was stored and seeps into water or out onto land. However, commercial oil extraction has greatly increased the number of leakage and spillage events.
The largest oil spill in the United States until 2010 was the Exxon Valdez oil tanker accident in 1989.
Larger oil spills have occurred elsewhere in the world. For example, during the 1991 Persian Gulf War, approximately 912 million liters (240 million gallons) of petroleum were spilled.
Study found that roughly 85 percent of the oil entering marine waterways came from runoff and not direct spills.
Pipelines could possible have an issue, but nothing extremely direct.
There is also a continued debate about the ethics of extracting oil on animals and humans.
Many developing countries, oil flaring—the burning off of excess natural gas—takes place close to homes. Crude oil covers the ground where people walk, sometimes in bare feet.
Natural Gas
Natural gas is 80 to 95 percent methane ( CH 4 ) and 5 to 20 percent ethane, propane, and butane. Because natural gas is lighter than oil, it lies above oil in petroleum deposits .
Sometimes found with petroleum and sometimes alone.
Used in the US for electricity generation and industrial processes.
Natural gas is also used to manufacture nitrogen fertilizer, and it is used in homes as an efficient fuel for cooking, heating, and operating clothes dryers and water heaters.
Compressed natural gas can be used as a fuel for vehicles, but because it must be transported by pipeline, it is not accessible in all parts of the United States
Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG)
which is similar to natural gas, but in a liquid form, is a slightly less energy-dense substitute.
LPG can be transported via train or truck and stored at the point of use in tanks. This fuel is available practically everywhere in the United States and is used in place of natural gas and for portable barbecue grills and heaters.
Overall, natural gas and LPG supply 29 percent of the energy used in the United States.
Advantages of Natural Gas
In the US, roughly one-half of homes use natural gas for heating.
Compared with coal and oil, natural gas contains fewer impurities and therefore emits almost no sulfur dioxide or particulates during combustion. Natural gas emits only 60 percent as much CO2 as coal.
In some locations where natural gas pipelines are not present, LPG is used although it is slightly less convenient.
Disadvantages
Unburned natural gas—methane—that escapes into the atmosphere is itself a potent greenhouse gas that is 25x worse than CO2. And it does leak often during extraction.
While natural gas when combusted releases the least carbon dioxide of all the fossil fuels, unburned natural gas—methane—that escapes into the atmosphere is itself a potent greenhouse gas that is 25 times more efficient at absorbing infrared energy than CO 2 . Natural gas that leaks after extraction is a suspected contributor to the steep rise in atmospheric methane concentrations that was observed in the 1990s. While natural gas is referred to as the “clean” fossil fuel, extraction and use still lead to environmental problems (FIGURE 35.6).