1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What are the major differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells have both.
List the functions of the following structures in a prokaryotic cell: cell membrane, nucleoid, plasmid, cytoplasm, ribosome, cell wall, pili, capsule, and flagella
Cell membrane: Semi-permeable barrier surrounding the cell.
Nucleoid: Region where DNA is located.
Plasmid: Circular DNA molecules that may be transferred between bacteria.
Cytoplasm: Internal fluid component of the cell.
Ribosome: Site of protein synthesis.
Cell wall: Rigid outer covering made of peptidoglycan.
Pili: Hair-like extensions for adherence to surfaces or bacterial conjugation.
Capsule: Thick polysaccharide layer for protection.
Flagella: Long, slender projections for movement.
Contrast the size of eukaryotic and prokaryotic ribosomes.
Prokaryotic ribosomes are smaller (70S) than eukaryotic ribosomes.
What is the meaning and advantages of eukaryotic cells being "compartmentalized"?
Eukaryotic cells being compartmentalized means they have membrane-bound organelles, allowing for specialized functions in different compartments, increasing efficiency and organization.
State the structural differences between plant and animal cells.
Plant cells have a cell wall and chloroplasts, while animal cells do not.
Define asexual reproduction
Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves only one parent and produces genetically identical offspring.
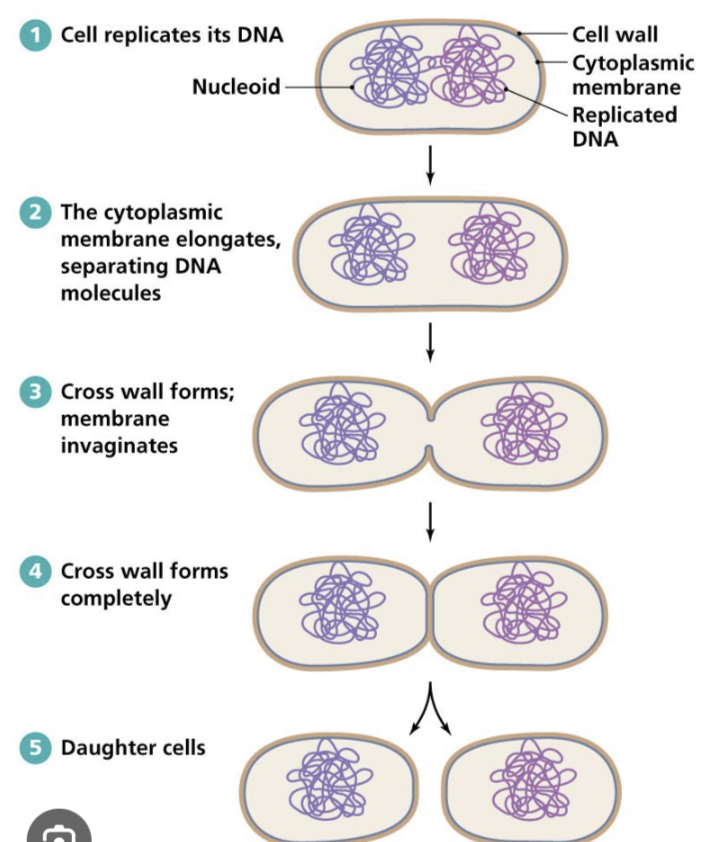
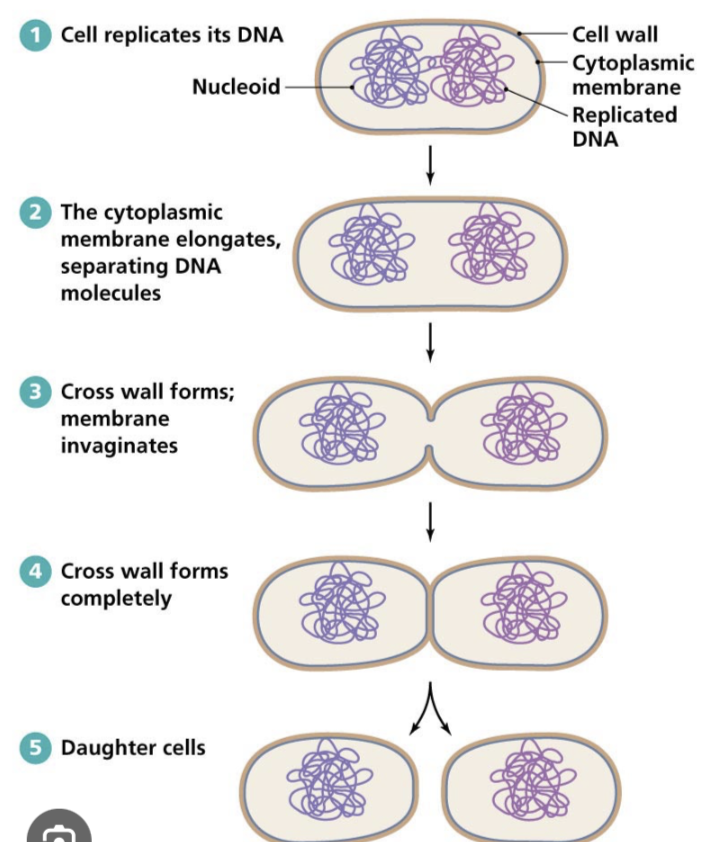
Outline the steps of binary fission. ADD ON
Binary fission is a form of asexual reproduction. Involves DNA replication, attachment of DNA loops to the membrane, elongation of the membrane, and cytokinesis, resulting in the formation of two genetically identical daughter cells.
Compare the functionality of light and electron microscopes
Electron microscopes have higher resolution and can observe much smaller objects compared to light microscopes.
State the function of an exocrine gland cell.
Exocrine gland cells secrete large quantities of digestive enzymes.
Describe the function of the following structures in an exocrine gland cell: plasma membrane, nucleus, mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vesicles, and endoplasmic reticulum.
Plasma membrane: Surrounds the cell and regulates what enters and exits.
Nucleus: Contains genetic information and controls cell activities.
Mitochondria: Produces ATP for cellular energy.
Golgi apparatus: Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins for secretion.
Lysosomes: Contain digestive enzymes for breaking down waste materials.
Vesicles: Transport materials within the cell.
Endoplasmic reticulum: Involved in protein synthesis and lipid metabolism.
State the function of a palisade mesophyll cell
Palisade mesophyll cells carry out photosynthesis in plant leaves.
Describe the function of the following structures in a palisade mesophyll cell: cell wall, plasma membrane, chloroplasts, vacuole, nucleus, and mitochondria
Cell wall: Provides support and protection.
Plasma membrane: Regulates the passage of substances in and out of the cell.
Chloroplasts: Site of photosynthesis.
Vacuole: Stores water and nutrients.
Nucleus: Contains genetic material and controls cell functions.
Mitochondria: Produces ATP for energy.