Chapter 13 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
The deepest layer of the meninges is
• Dura mater
• Arachnoid
• Pia mater
• Alma mater
Pia mater
The central nervous system consists of
• Brain
• Spinal cord
• Cranial nerves
• All of the above
• All of the above except C
All of the above except C
brain and spinal cord!!!
peripheral nervous system
All neural structures outside the brain & Spinal
Cord
Sensory receptors
Peripheral nerves and associated ganglia
Motor nerves
peripheral nervous system consists of
sensory (afferent) division
approach
motor (efferent) division
exit
sensory receptors
Specialized to respond to changes in their
environment (stimuli)Activation results in graded potentials that trigger nerve impulses
Sensation (awareness of stimulus) and
perception (interpretation of the meaning of the stimulus) occur in the brain
classifications of receptors are based on
stimulus type
name indicates type of stimulus
ex) thermoreceptors
location
respond to either internal or external stimuli
structural complexity
general senses
simple
ex) touch, temp, pressure
special senses
complex
ex) vision, hearing, taste, smell
receptors that are classified by stimulus type
mechanoreceptors
thermoreceptors
photoreceptors
chemoreceptors
nociceptors
mechanoreceptors
respond to touch, pressure, vibration, stretch, and itch
thermoreceptors
sensitive to changes in temperature
touch hot item
photoreceptors
respond to light energy (e.g., retina)
chemoreceptors
respond to chemicals (e.g., smell, taste, changes in blood chemistry)
nociceptors
sensitive to pain-causing stimuli (e.g. extreme heat or cold, excessive pressure, inflammatory chemicals
receptors that are classified by location
exteroceptors
interoceptors
proprioceptors
exteroceptors
respond to environment
ex) someone taps ur shoulder, feeling the warmth of the sun
interoceptors
viscero, respond to internal
stomach growling
proprioceptors
position, movement, orientation of body parts
walking without looking at ur legs
sensation
the awareness of changes in the internal and external environment
Input comes from sensory receptors
perception
the conscious interpretation of that stimuli
This occurs in the brain
sensory integration consists of 3 levels
receptor level
sensory reception and transmission to CNS
depolarization
circuit level
processing in ascending pathways
spinal cord and brain stem (travels)
perceptual level
neuronal circuits in cerebral cortex
ex) feeling warmth of sun and recognizing its a pleasant sensation
adaption of sensory receptors
is a change in sensitivity in the presence of a
constant stimulus (bright light)
two types
phasic receptors (fast-adapting)
tonic receptors
phasic receptors
fast-adapting receptors signal the beginning or end of a stimulus, signals a change
ex) receptors for pressure, touch, and smell
(clothing)
tonic receptors
adapt slowly or not at all
ex) nociceptors and most proprioceptor
sitting in a chair and feeling the pressure of it, you don’t really notice it after a period of time but you can still maintain posture and adjust position if needed
structure of a nerve
Bundle of myelinated and unmyelinated peripheral axons enclosed by connective tissue
3 layers of connective tissue
endoneurium
perineurium
epineurium
Endoneurium
loose CT that encloses axons and their myelin
sheaths
innermost layer
Perineurium
coarse CT that bundles fibers into fascicles (binds)
Epineurium
tough fibrous sheath around a nerve
outermost layer
classifications of nerves
Most nerves are mixtures of afferent and efferent fibers:
Somatic afferent and somatic efferent
ex) hands sense something hot and responds by moving them away
Visceral afferent and visceral efferent
ex) stomach growls due to hunger and once you start to eat food the smooth muscles digest the food
Peripheral nerves classified as cranial or spinal nerves
ganglia
collections/bundles of cell bodies in PNS
nuclei
collections/bundles of cell bodies in CNS
dorsal root ganglia
sensory
sense signals related to things such as touch or pain
somatic
control voluntary movement and sensory perception
autonomic ganglia
motor
visceral
involuntary movement of muscles like heart rate and digestion
Regeneration of Peripheral Nerve Fibers vs central nerve fibers
Mature neurons are amitotic
doesn’t undergo cell division
If the soma (cell body) of a damaged nerve is intact, axon will regenerate
CNS oligodendrocytes bear growth inhibiting proteins that prevent CNS fiber regeneration
The neurotransmitter that is associated with
reward and pleasure is ...
A. Norepinephrine
B. Serotonin
C. Dopamine
D. Acetylcholine
E. Histamine
C. Dopamine
Which statements are correct about language and the brain?
A. Wernicki’s area is related to language expression and is located in the right frontal lobe
B. Broca’s area is related to language expression and is located in the left frontal lobe
C. Wernicki’s area is related to language comprehension and is located in the left temporal lobe
D. Broca’s area is related to language comprehension and is located in the right temporal lobe
B. Broca’s area is related to language expression and is located in the left frontal lobe
C. Wernicki’s area is related to language comprehension and is located in the left temporal lobe
both are on the left hemisphere
cranial nerves
Twelve pairs (12) of peripheral nerves
associated with the brainMost are mixed in function; two pairs are purely sensory (I and II)
deal with complex sensations
what are the 12 cranial nerves
“on occasion our trusty truck acts funny— very good vehicle anyhow”
olfactory (I)
optic (II)
oculomotor (III)
trochlear (IV)
trigeminal (V)
abducens (VI)
facial (VII)
vestibulocochlear (VIII)
glossopharyngeal (IX)
vagus (X)
accessory (XI)
hypoglossal (XII)
cranial nerve I: olfactory nerve
smell just sensory
cranial nerve II: optic nerve
vision just sensory
cranial nerves I and II are just
sensory, no motor function
cranial nerves relating to eye movement (just motor)
CN 3, 4 and 6
oculomotor (III)
trochlear (IV)
abducens (VI)
cranial nerve III: oculomotor nerve
pupil constriction
all other eye movements ex) upwards
cranial nerve IV: trochlear nerve
downward and outward eye movement
cranial nerve VI: abducens nerve
outward lateral eye movements (abducts eyes)
palsy in cranial nerves III, IV and VI can result in
eye misalignment
cranial nerve V: trigeminal nerve
Sensation of face
Motor of mastication muscles
cranial nerve VII: facial nerve
Motor of face – facial expression
Sensory - taste
cranial nerve VIII: vestibulocochlear nerve
hearing and balance
trigeminal neuralgia
a type of chronic pain disorder that involves sudden attacks of severe facial pain
very painful
vestibular nerve pathology
directly affects vestibulocochlear (VIII) nerve which is responsible for balance and spatial orientation
leads to
vertigo (dizziness)
imbalance
involuntary movement of eyes
spatial disorientation
cranial nerve IX: glossopharyngeal nerve
tongue and throat” – taste & swallowing
cranial nerve X: vagus nerve
“the wanderer”
Only cranial nerve that leaves the head and neck
Involved in Parasympathetic nervous system
Help regulate the heart, lungs and abdominal viscera
cranial nerve XI: accessory nerve
moves head and neck (trapezius and SCM muscle)
SCM= sternocleidomastoid
cranial nerve XII: hypoglossal nerve
“under tongue” – moves tongue
cranial nerves XI and XII are just
motor
Neuroglial cells that protect against pathogens
in the brain are the ______.
• astrocytes
• ependymal cells
• microglia
• Schwann cells
microglia
Which cranial nerve detects sensation in the
face?
A. Cranial Nerve 4 Troclear Nerve
B. Cranial Nerve 5 Trigeminal Nerve
C. Cranial Nerve 7 Facial Nerve
D. Cranial Nerve 10 Vagus Nerve
Cranial Nerve 5 Trigeminal Nerve
facial nerve is just motor
During repolarization of the action potential
which gates are opened?
A. Voltage gated Na
B. Voltage gated K
C. Leakage channels for Na
D. Leakage channels for K
B. Voltage gated K
membrane potential going negative again
spinal nerves
31 pairs of mixed nerves named according to
their point of issue from the spinal cord
8 cervical (C1–C8)
12 thoracic (T1–T12)
5 Lumbar (L1–L5)
5 Sacral (S1–S5)
1 Coccygeal (C0)
sensory nerves enter the spinal cord vias dorsal or ventral horn?
dorsal horn
each spinal nerve connects to the spinal cord via
two roots
ventral roots
dorsal roots
ventral roots
Contain motor (efferent) fibers from the ventral horn motor neurons
Fibers innervate skeletal muscles
dorsal roots
Contain sensory (afferent) fibers from sensory neurons in the dorsal root ganglia
Conduct impulses from peripheral receptors
dorsal and ventral roots unite to form
spinal nerves
each spinal nerve branches into mixed rami
dorsal ramus
sensory info
larger ventral ramus
motor info
Rami communicantes (autonomic pathways) join to the ventral rami in the thoracic region
roots lie
medial to spinal nerves
either motor or sensory
rami lie
lateral to spinal nerves
mixed
All ventral rami except T2–T12 form
networks called plexuses
(cervical, brachial, lumbar, and sacral)
the back is innervated by
dorsal rami via several branches
shingles
infection on dorsal rami
cervical plexus
most superior
Formed by ventral rami of C1–C5
Innervates skin and muscles of the neck, ear, back of head, and shoulders
phrenic nerve
Major motor and sensory nerve of the diaphragm (receives fibers from C3–C5)
Irritation of phrenic nerve causes hiccups
C3,C4,C5 keeps the diaphragm alive
brachial plexus
Formed by ventral rami of C5–C8 and
It gives rise to the nerves that innervate the upper limb
Major nerves from the branches: axillary, musculocutaneous, median, ulnar and radial
brachial plexus injuries
erb’s injury
kulmpke’s paralysis
erb’s injury
stretching of upper trunk of brachial plexus
stuck in internal rotation
klumpke’s paralysis
injury to lower roots of plexus (claw hand)
hands when baby is delivered
lumbar plexus
Arises from L1–L4
Innervates the thigh, abdominal wall, and psoas muscle
Femoral nerve
Obturator nerve
Femoral nerve
innervates quadriceps and skin of anterior thigh and medial surface of leg
Obturator nerve
innervate adductor muscles (groin muscles)
inner thigh
sacral plexus
Arises from L4–S4
Serves the buttock, lower limb, pelvic structures, and perineum (lower pelvic floor)
Sciatic nerve
sciatic nerve
Longest and thickest nerve of the body
Innervates the hamstring muscles, adductor magnus, and most muscles in the leg and foot
Composed of two nerves
tibial
common fibular
sciatica
pain that travels along the sciatic nerve, often starting in the lower back and going down one leg
can be caused by
spinal stenosis
spaces within your spine narrow, putting pressure on the spinal cord and nerves
herniated disc
punctured jelly filled donut
degenerative disc disease
Dorsal roots...
• A. Are a mixture of motor and sensory fibers
• B. Contain afferent fibers only
• C. Innervate skeletal muscles
B. Contain afferent fibers only
Which nerve comes from brachial plexus?
• Musculocutaneous NN
• Sciatic NN
• Phrenic NN
• Obturator NN
• Accessory NN
Musculocutaneous NN
inborn (intrinsic) reflex
a rapid, involuntary, predictable motor response to a stimulus
splashing hot water from pot on your arm
learned (acquired) reflex
result from practice or repetition
driving skills
components of a reflex arc (neural path)
Receptor
site of stimulus action
Sensory neuron
transmits afferent impulses to the
CNS
Integration center
either monosynaptic or polysynaptic region within the CNS
Motor neuron
conducts efferent impulses from the
integration center to an effector organ
Effector
muscle fiber or gland cell that responds to the efferent impulses by contracting or secreting
spinal somatic reflexes
Integration center is in the spinal cord
Effectors are skeletal muscle
Include: stretch, flexor and crossed-extensor
how stretch reflex works
Stretch activates the muscle spindle (receptor)
Sensory neurons synapse directly with alpha motor neurons in the spinal cord
alpha motor neurons cause the stretched muscle to contract
example: Imagine you're standing on one leg and start to tip over. As your body starts to fall, the stretch reflex kicks in, quickly contracting the muscles in your ankle and leg to help you regain your balance and stay upright.
all stretch reflexes are _____ and _____
monosynaptic (1 synpase)
ipsilateral (same side)
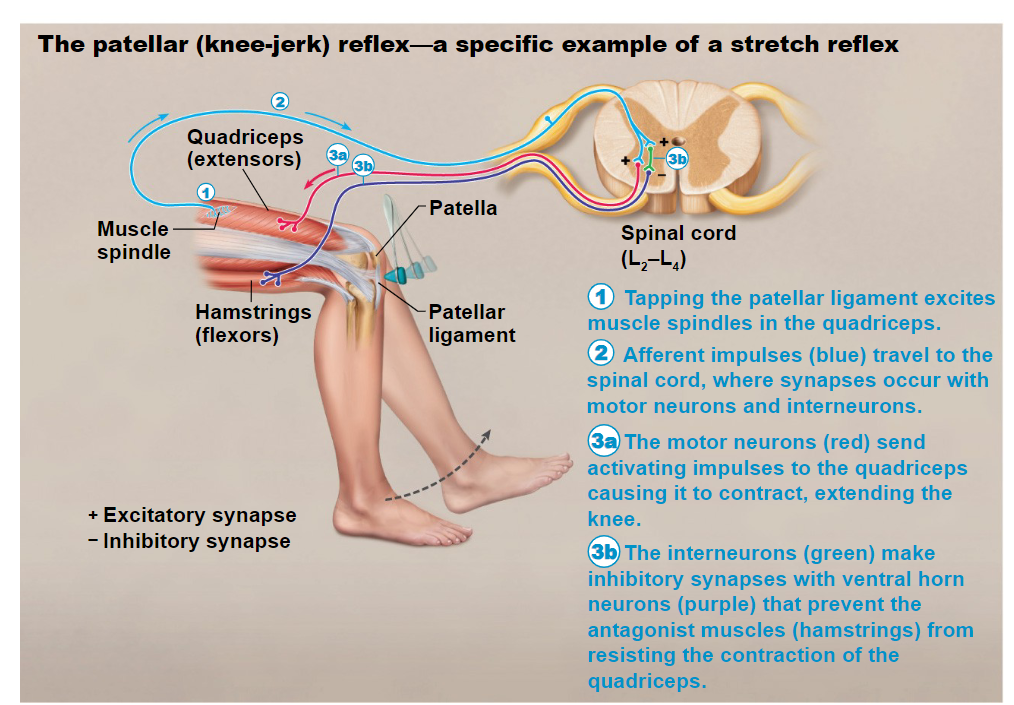
patellar (knee-jerk) reflex
tapping the patellar ligament excites
muscle spindles in the quadriceps.Afferent impulses (blue) travel to the
spinal cord, where synapses occur with
motor neurons and interneurons.The motor neurons (red) send
activating impulses to the quadriceps
causing it to contract, extending the
knee.The interneurons (green) make
inhibitory synapses with ventral horn
neurons (purple) that prevent the
antagonist muscles (hamstrings) from
resisting the contraction of the
quadriceps
abnormal stretch reflexes
dampened reflex
abnormal kick
flexor (withdrawal) reflex
initiated by a painful stimulus
Causes automatic withdrawal of the
threatened body partIpsilateral (same side) and polysynaptic (multiple)
However descending signals from brain can override flexor reflexes. Ie: pin prick
crossed extensor reflex
lower extremities
Occurs with flexor reflexes in weight-bearing limbs to maintain balance
Consists of an ipsilateral flexor reflex and a contralateral extensor reflex
The stimulated side is withdrawn (flexed)
The contralateral side is extended
plantar reflex (Babinski reflex)
helps diagnosis stroke
Stimulus: stroking lateral aspect of the sole of the foot
Normal Response: downward flexion of the toes
this goes away as you age, people who experienced a stroke have this reflex again
Tests for function of corticospinal tracts
Which cranial nerve is the exception and travels
to the thoracic and abdominal cavities?
• Trochlear (4)
• Trigeminal (5)
• Vestibulocochlear (8)
• Vagus (10)
Vagus (10)
Quickly lifting your foot and leg after stepping on
a rock is an example of a(n) ________.
• Learned reflex
• Flexor withdrawal reflex
• Superficial reflex
• Stretch reflex
Flexor withdrawal reflex
CN IV: trochlear
superior oblique (top muscle at angle)
move eye inferior (down) and laterally (out)
CN IV: abducens
lateral rectus
move eye laterally (side)
CN III: oculomotor
superior rectus
superior and medial
inferior rectus
inferior and medial
medial rectus
medial
inferior oblique
superior and lateral