chp 5 ligand binding biochem
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
ligand
small molecule/ion that reversibly binds to a larger molecule (protein/DNA)
myoglobin
stores O2
monomer (1x subunit)
1x heme => 1 O2 binding site
common motif as hemoglobin
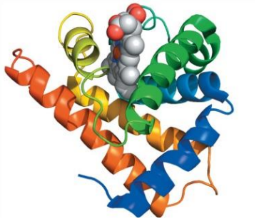
hemoglobin
tetramer (4x subunits)
4 hemes, 4 O2 binding sites
α2β
common structural motif as myoglobin
heme prosthetic group (oxygen and CO can bind)
Fractional Saturation (Y)
Y=# of occupied binding sites/total # of binding sites
=[P:L]/[[P:L]+[P]
P=protein
L=ligand
P:L=protein bound ligand
quantitative description of ligand binding (association)
P+L←→P:L
association P to L - keq [P:L]/[P][L]
association constant - ka=[P:L]/[P][L]
assumptions
[L]> > [P:L]
[L]~constant
no ICE tables
larger Ka →
more P:L
aka more saturation
kd=
[P][L]/[PL]=dissociation constant=1/ka
relationship between Y and kd
Y=L/L+Kd
kd=[L] at ½ Y
![<p>Y=L/L+Kd</p><p>kd=[L] at ½ Y </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/8a82e3ff-a2f3-41bf-9588-4f4442475f17.png)
small Kd
=> low association => high association => large Ka
cooperative binding
bind one ligand which affects affinity for binding in 2nd ligand
low affinity
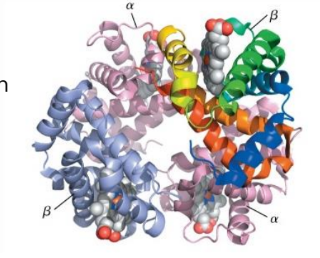
structure of hemoglobin
tetramer α2β2
cooperative binding
α-β interferences
hydrophobic interactions
H bonding
salt bridges (ionic interaction)
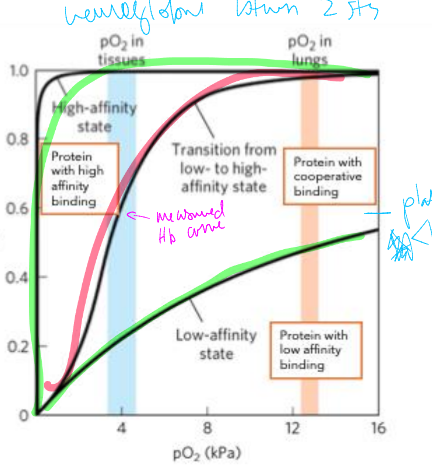
2 states of hemoglobin
T state
R state
T state
low affinity (deoxygenated) conformation
no O2 bounds
stabilized by salt bridges/ionic interactions
R state
O2 bound (oxygenated)
high affinity for O2
conformation change from T state after O2 binds \
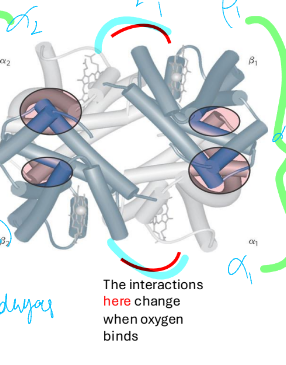
change in α1β2 and α2β1
stabilization of T state by
ion pair interactions
only present in T state
α1β2 and α2β1 salt bridge
+ O2 disrupts bridge
conformation change
T→R transition linked to
oxygen binding
in R state binding affinity for O2 higher
induced fit model : conformation change causes better ligand binding
allosteric proteins
multi-subunit proteins that undergo ligand dependent changes in binding affinity
binding a ligand at one site, affects binding to another site
if allosteric ligand =active ligand → homotopic
if allosteric ligand is not an active ligand → heterotopic
cooperativity qualitatively
proteins = dynamic
ligand binds => stabilizes conformation that favors additional ligand binding
increases affinity for ligand at additional site
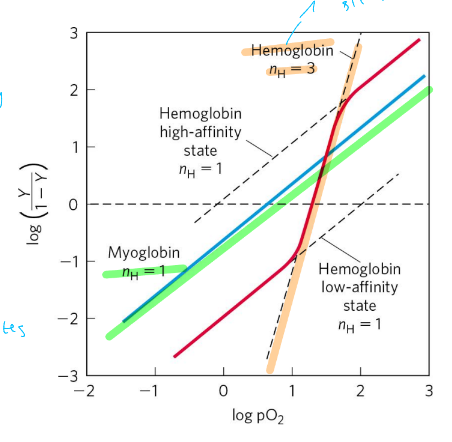
hill coefficient
(\log\left(\frac{Y}{1-Y}\right)=n\log-\log kd
n= degree of cooperativity
n=1, noncooperative
n>1 positive cooperativity
n<1 neg cooperativity
nmax=min # of binding sites in protein
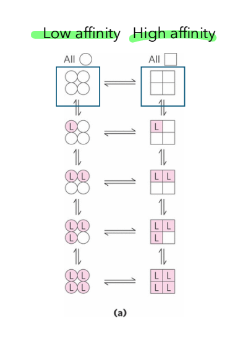
Monod Wyman Changeaux model for cooperativity
all or nothing
limitation → treats all subunits equally
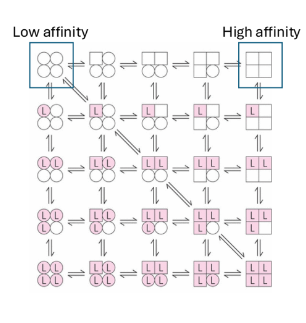
Koshland’s model for cooperativity
sequential model
change induces change
more generizable
look at subunits with independent functions
Hb also transports
H+ - pH dependent transporter
Hb binds in T state (stabilizing salt bridge found at low pH)
very important for O2 binding and release
Hb also transports, mech ??
CO2 away from respiring tissues
CO2 in T state transported out of cell tissues

biophosphoglycerate (BPG or DPG)
stabilizes T state
bind 1 BPG tetramer
high [BPG] , T-State → low affinity O2, faster release
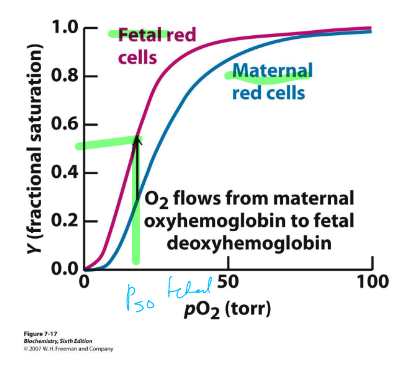
fetal hemoglobin
ɑ2ɤ2 tetramer
different than adult Hb
binds O2 with higher affinity than adult Hb
how do negative regulatory factors work together
CO2, BPG, H+ reduce O2 affinity in Hb
BPG is better at reducing O2 affinity than CO
Hb diseases
sickle cell anemia (hemoglobin aggregates and red cells distort and block capillaries
alpha thalassemia (beta chains only, forming hemoglobin that is not cooperative
beta thalassemia (alpha chains only, form insoluable aggregates resulting in few red cells—anemia)