(Walking Gait) Biomechanics of Locomotion
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Neutral
Initial Contact
Ankle motion
Pre-tibial muscles decelerate forefoot lowering and draw the tibia forward following initial contact
Plantarflexion
Loading Response
Ankle motion
Pre-tibial muscles decelerate forefoot lowering and draw the tibia forward following initial contact
Dorsiflexion
Mid-Stance
Ankle motion
Plantar Flexors progressively increase activity throughout two phases to allow controlled forward progression of tibia. Elastic energy is stored in the Achilles Tendon.
Dorsiflexion
Terminal Stance
Ankle motion
Plantar Flexors progressively increase activity throughout two phases to allow controlled forward progression of tibia. Elastic energy is stored in the Achilles Tendon.
Plantarflexion
Pre-swing
Ankle motion
Calf muscles cease in early pre-swing. Stored elastic energy in Achilles Tendon contributes to rapid plantarflexion as the limb unloads.
Plantarflexion to Neutral
Initial Swing to Midswing
Ankle motion
Pre-tibial muscles elevate the foot to neutral by mid-swing and then maintain that posture.
Neutral Position
Midswing to Terminal Swing
Ankle motion
Pre-tibial muscles elevate the foot to neutral by mid-swing and then maintain that posture.
Knee Extension
Initial Contact
Knee Motion
Low-amplitude hamstring activity resists knee hyperextension
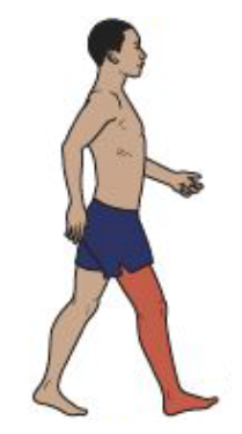
Knee flexion
Loading Response
Knee Motion
Eccentric vastii activity allows knee flexion for shock absorption but prevents collapse
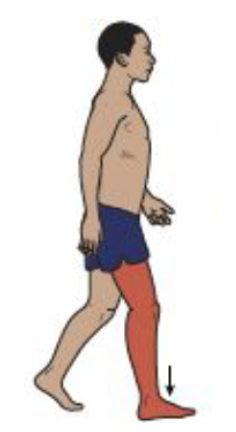
Knee extension
Mid-stance and Terminal Stance
Knee Motion
Vastii activity ceases by the middle of mid-stance
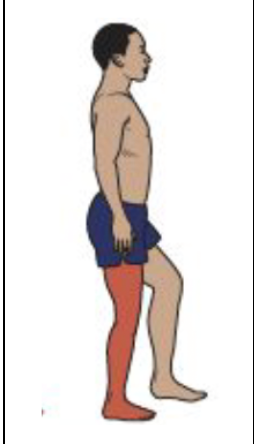
Knee flexion
Pre-swing
Knee Motion
Rectus femoris modulates the rate of knee flexion
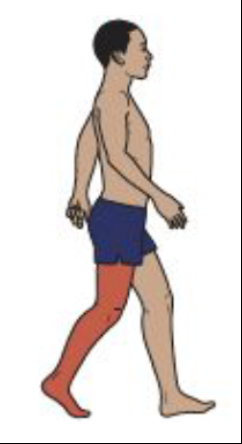
Knee flexion
Initial Swing
Knee Motion
Biceps femoris, gracilis, and sartorius contribute to knee flexion
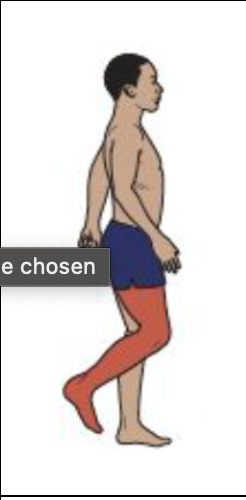
Knee flexion
Mid-swing
Knee Motion
Hamstrings modulate the rate of knee extension and thigh advancement.
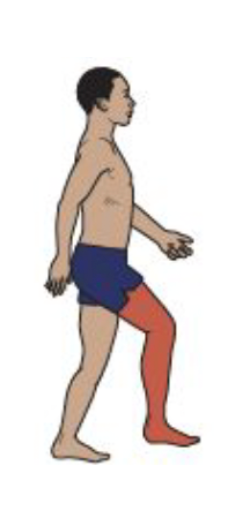
Knee extension
Terminal Swing
Knee Motion
Hamstrings continue the activity and vastii becomes active in preparation for the demands of initial double limb stance.
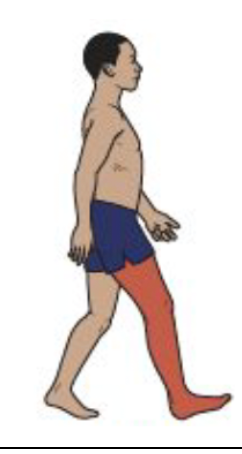
Hip flexion
Initial Contact and Loading Response
Hip Motion
Single joint hip extensors and abductors contract vigorously to stabilize the pelvis and trunk over the femur. Hamstring activity is diminishing.
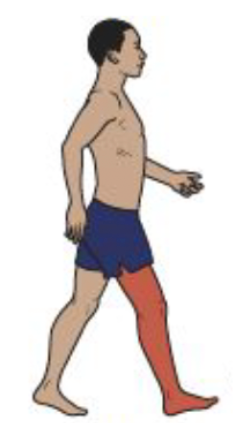
Neutral
Mid-stance
Hip Motion
Residual hamstring activity assists with hip extension at the beginning of the phase. Low-level abductor activity stabilizes the pelvis.
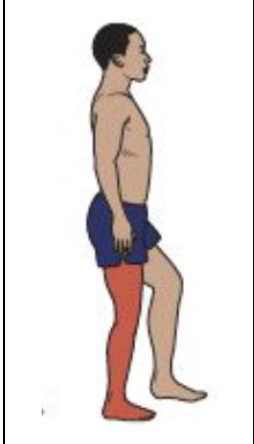
Hip extension
Terminal Stance
Hip Motion
Low amplitude tensor fascia latae activity
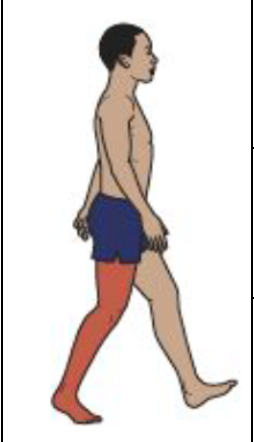
Hip extension
Pre-swing
Hip Motion
Rectus femoris assists with early thigh advancement
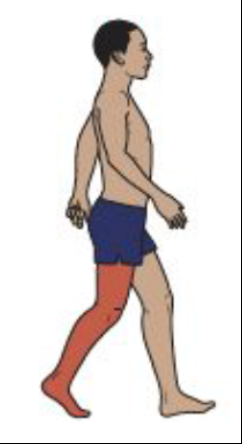
Hip flexion
Initial Swing
Hip Motion
Iliacus, adductor longus, gracilis, and sartorius actively advance the thigh
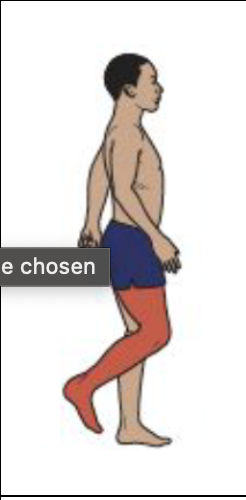
Hip flexion
Mid-swing
Hip Motion
Increasing hamstring activity at the end of the phase restrains further thigh advancement
Hip flexion
Terminal swing
Hip Motion
Hamstrings continue activity to control thigh posture; single joint hip extensors and abductors rapidly increase in activity to prepare for demands of the next phase of gait.