CS L3
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key concepts related to infectious disease control, including definitions and principles.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Epidemic disease
A disease acquired by many hosts in a given area in a short time.
Pandemic disease
A worldwide epidemic.
Primary prevention
Actions taken prior to the onset of disease to remove the possibility of its occurrence.
Passive surveillance
Monitoring based on readily available data reported by healthcare providers.
Active surveillance
Involves periodic field visits to identify new cases of disease.
Basic reproduction rate (R0)
A measure of how many people each sick person will infect on average.
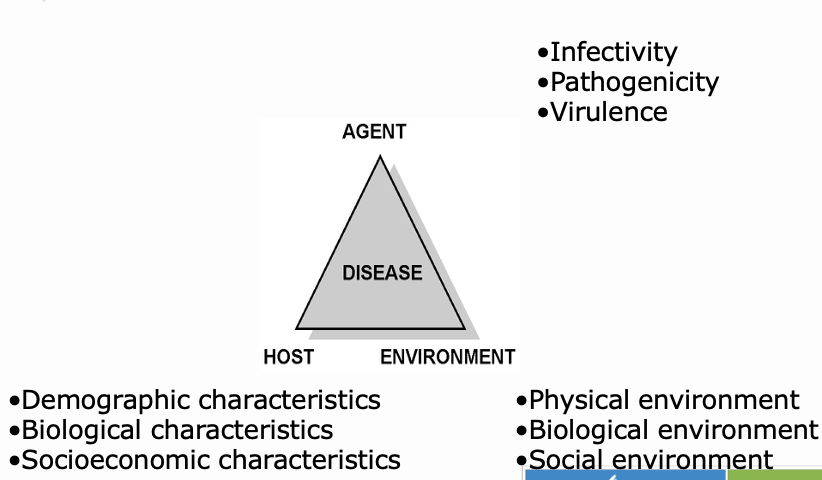
Infectivity
The ability of an agent to infect a host.
Virulence
The ability of an agent to cause disease, often measured by the severity of the disease it causes.
Quarantine vs Isolation?
Quarantine: Restriction of movement for well individuals who may have been exposed to a contagious disease.
Isolation: Separation of ill persons with contagious diseases from those who are healthy.
EPI (Expanded Programme on Immunization)
A WHO initiative to provide universal access to routine immunizations.
Define infection and IF diseases
Infection → when a micro-organism is present in a host where it is not normally found
IF disease → when this causes infection
Notifiable diseases
Diseases that must be reported to health authorities when diagnosed.
Cholera, TB and E.coli are examples of?
Bacteria
HIV, HPV and Hepatitis are examples of ?
Viruses
Malaria and Giardia are examples of ?
Protozoa
Helminths and Fungi are..?
Multicellular / Metazoa
What defines the 4 types of cases ?
Index → first case identified in pop
Primary → the case that brings the infection into a population
Secondary → infected by primary
Tertiary → infected by secondary
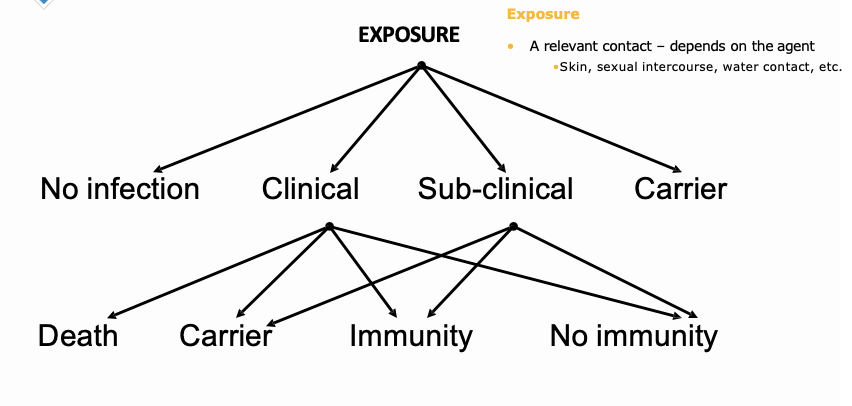
How does exposure look for clinical and subclinical cases ?
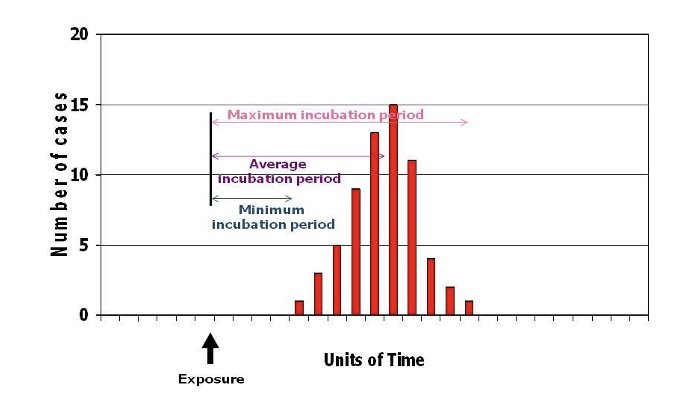
What type of disease is most likely occurring like this?
A point source infection (ex. a single meal had by many people)
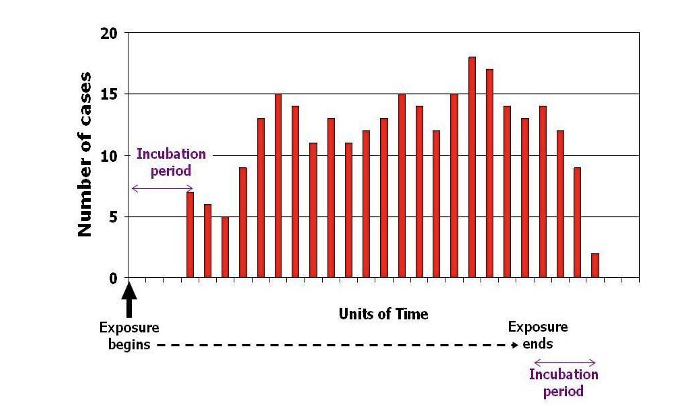
What type of infection does this curve represent ?
Continuous source - not confined to one period / point of time
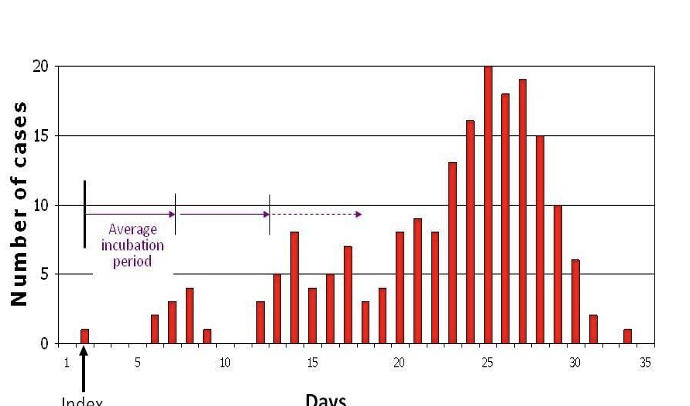
What type of infection does this curve represent ?
Propagated → not a common source but HUMAN TO HUMAN transmission ex. Mumps
What are the characterises of the factors of the EPI triangle ?
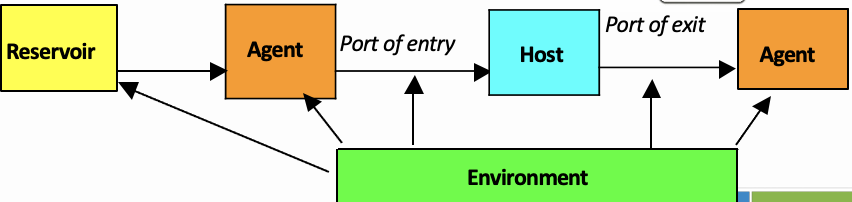
What does the adequate chain of transmission ?
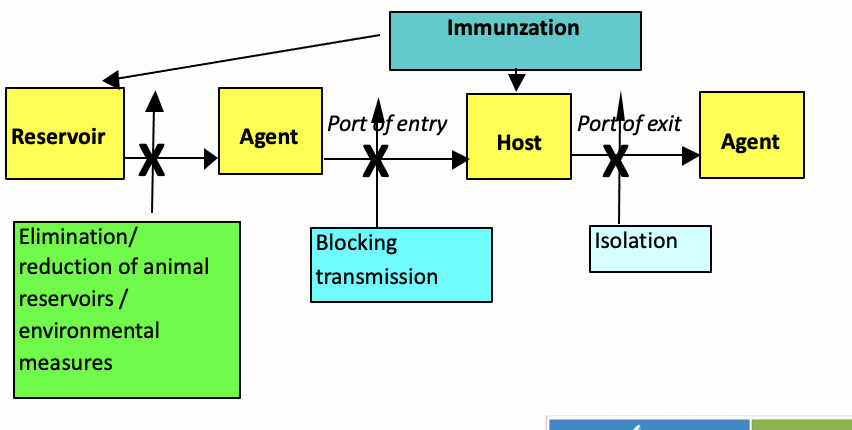
What does the adequate chain of transmission look like with intervention strategies ?
Name 4 limitations of passive surveillance
Dependant on many actors
Inadequate lab facilities
limited access to health facilities
local outbreaks may be missed
Name pros and cons of active surveillance ?
Pros:
Reporting is more accurate
Local outbreaks are generally identified
Cons:
More difficult to develop for routine work, always different
More expensive to maintain
Potentially invasive of privacy
What actions should be taken when a notifiable disease is in Group A1&2?
Isolation of patient
Examination
Observation and quarantine of contacts
What measures should be taken for a Group B1 and B2?
All measures expect quarantine of contacts
B2: Only expulsion from workplace
Can the government enforce measures for Group C diseases?
No
Give 2 examples of diseases that are in Group A2?
Small pox, Ebola
Examples of Group B1 and B2 diseases
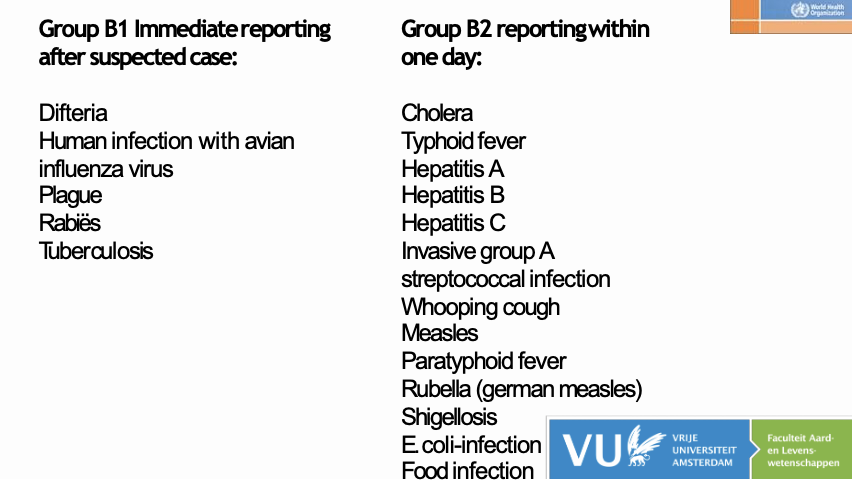
Examples of Group C diseases

In what phases of disease is primary, secondary or tertiary prevention most appropriate?
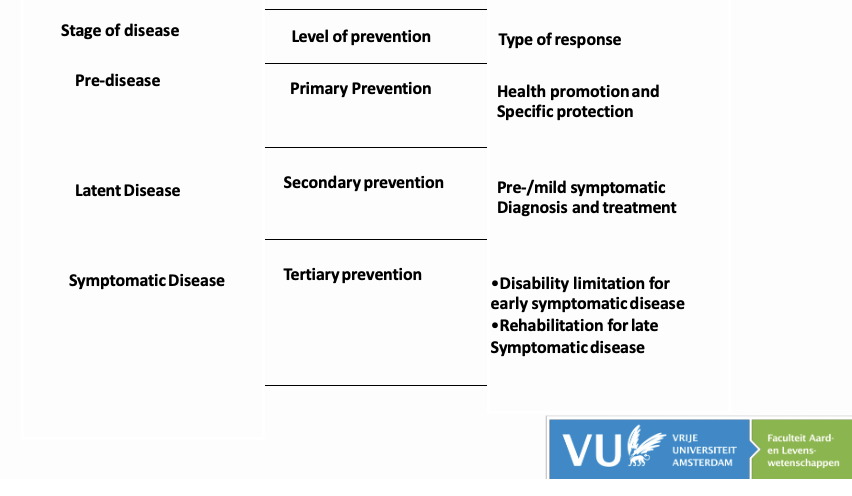
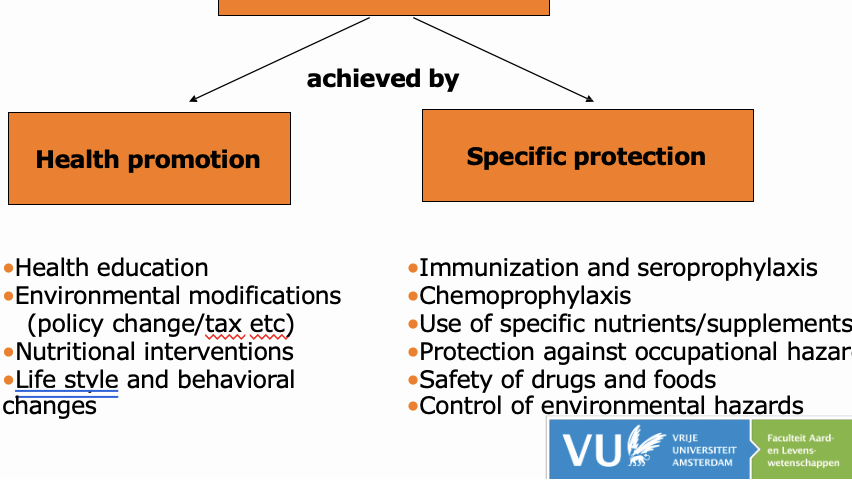
Primary prevention is achieved by two things, what are they?
Health promotion and specific protection
Ex: EPI, Vaccinations or use of prophylactic medicines / education (for non vaccine preventable diseases)
Describe the two main factors of secondary prevention and name 3 diseases for which screening is most important in prevention
Screening and treatment
Ex. Cervical, breast cancer and rubella or TB