U.S. History High School EOC Exam Study Guide
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
142 Terms
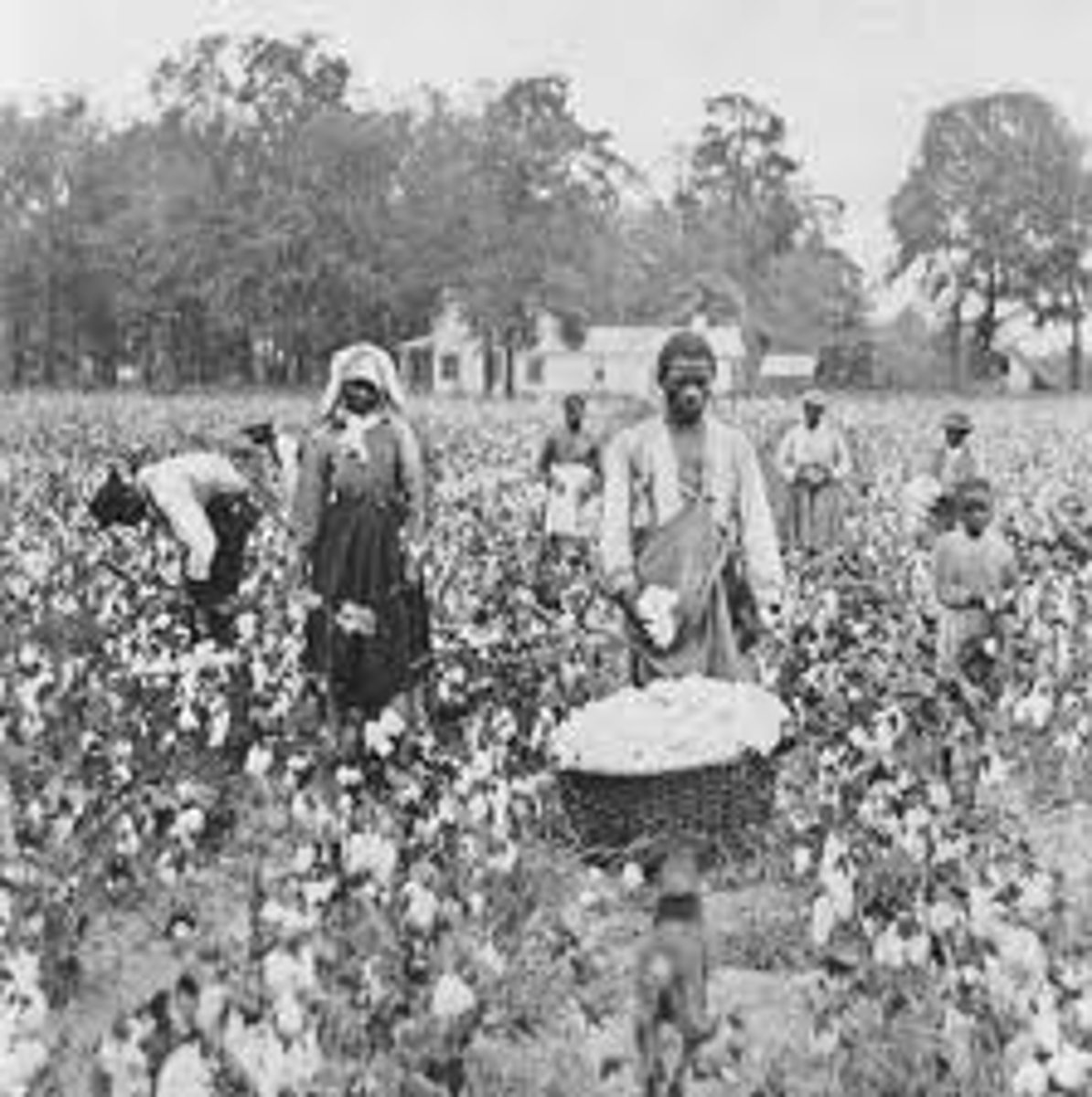
Causes of the Civil War
• Slavery
• States' rights
• Territorial claims
• Abolitionist movement
• Regional differences

Consequences of the Civil War
• Reconstruction
• Thirteenth Amendment
• Fourteenth Amendment
• Fifteenth Amendment
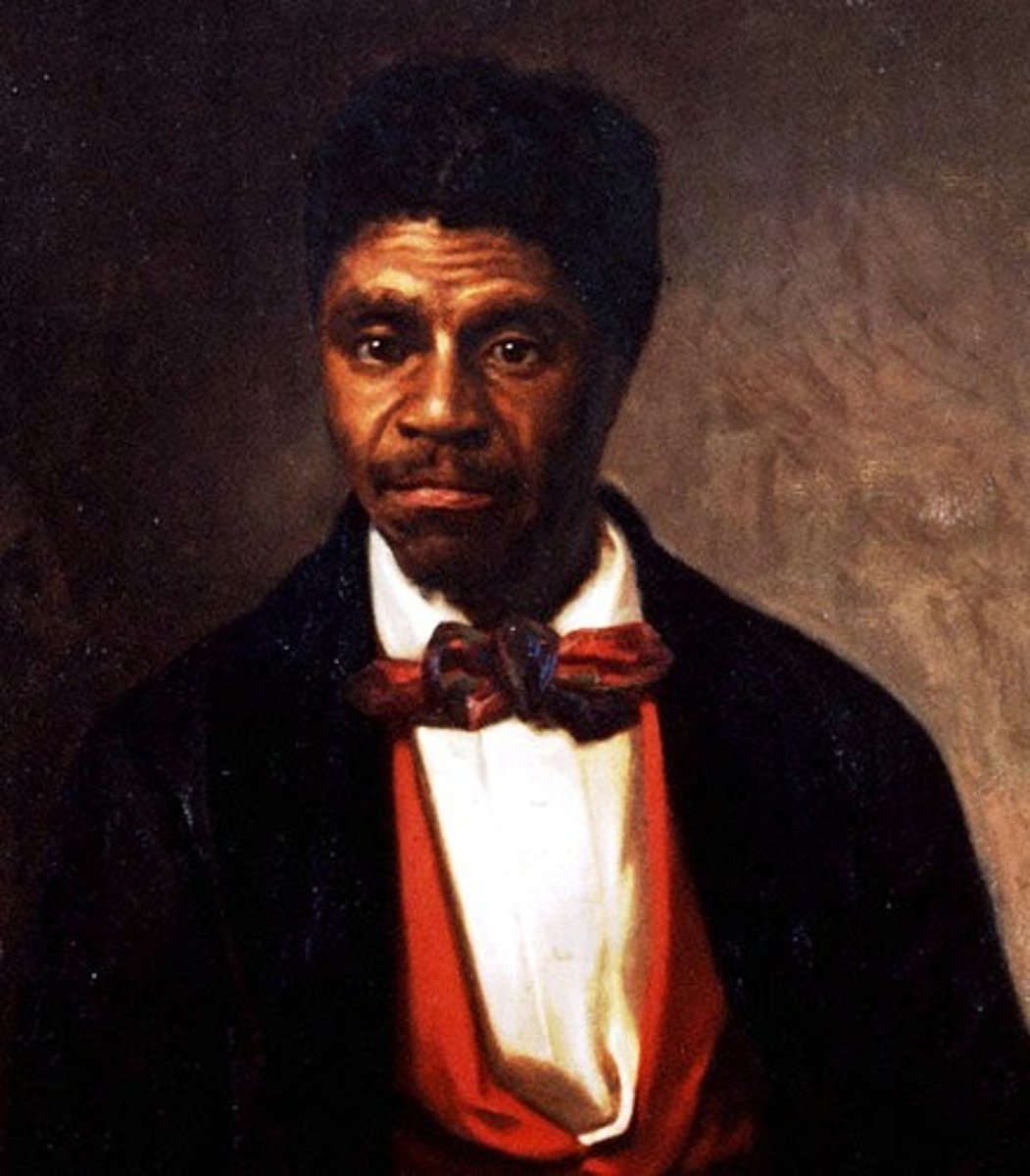
Dred Scott
A black slave, had lived with his master for 5 years in Illinois and Wisconsin Territory. Backed by interested abolitionists, he sued for freedom on the basis of his long residence on free soil. The ruling on the case was that He was a black slave and not a citizen, so he had no rights.

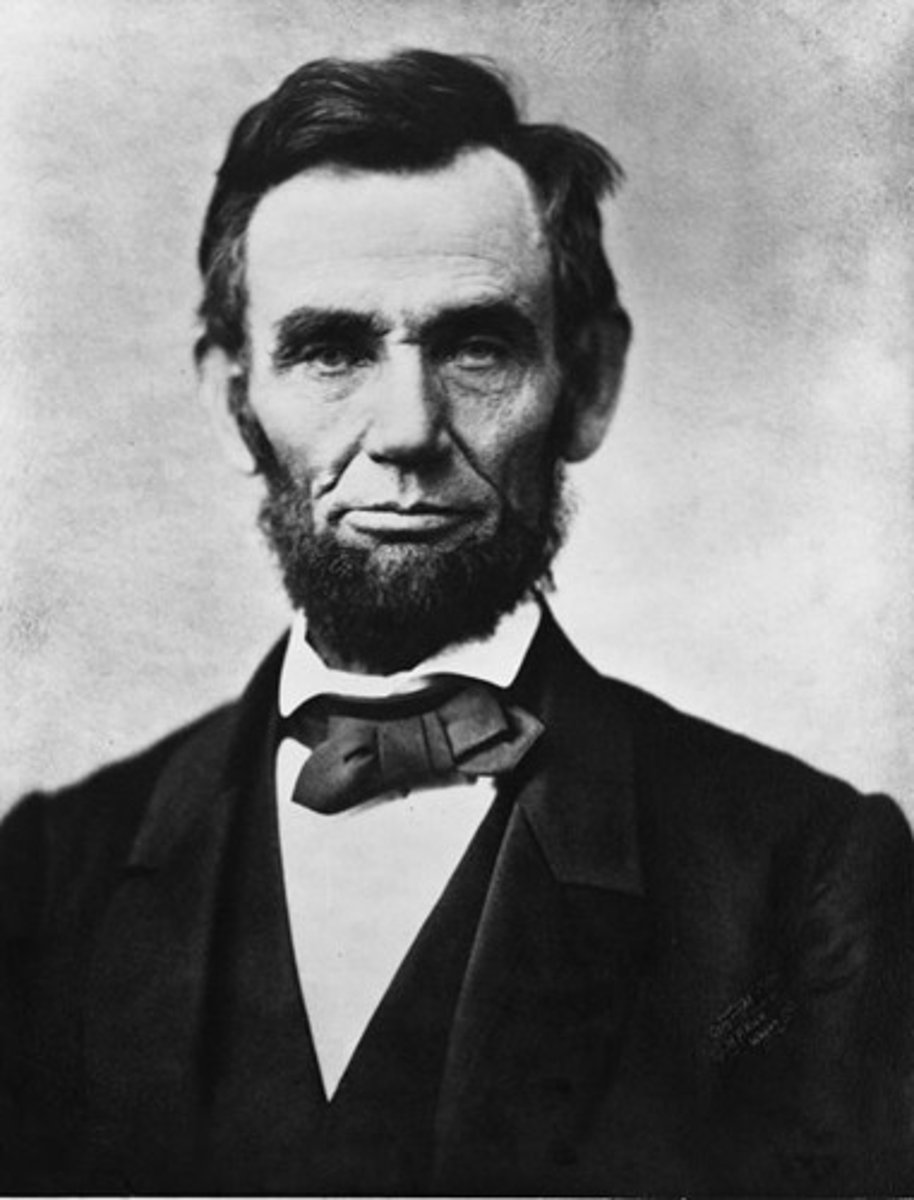
Abraham Lincoln
16th President of the United States saved the Union during the Civil War and emancipated the slaves; was assassinated by Booth (1809-1865)

Andrew Johnson
17th President of the United States; he was elected Vice President and succeeded Lincoln when Lincoln was assassinated

Jefferson Davis
President of the Confederate States of America

Frederick Douglass
United States abolitionist who escaped from slavery and became an influential writer and lecturer in the North (1817-1895)

Ulysses S. Grant
an American general and the eighteenth President of the United States (1869-1877). He achieved international fame as the leading Union general in the American Civil War.

Robert E. Lee
Confederate general who had opposed secession but did not believe the Union should be held together by force

William T. Sherman
general whose march to sea caused destruction to the south, union general, led march to destroy all supplies and resources, beginning of total warfare

Harriet Tubman
United States abolitionist born a slave on a plantation in Maryland and became a famous conductor on the Underground Railroad leading other slaves to freedom in the North (1820-1913)

Sojourner Truth
United States abolitionist and feminist who was freed from slavery and became a leading advocate of the abolition of slavery and for the rights of women (1797-1883)

Radical Republicans
Political party that favored harsh punishment of Southern states after civil war
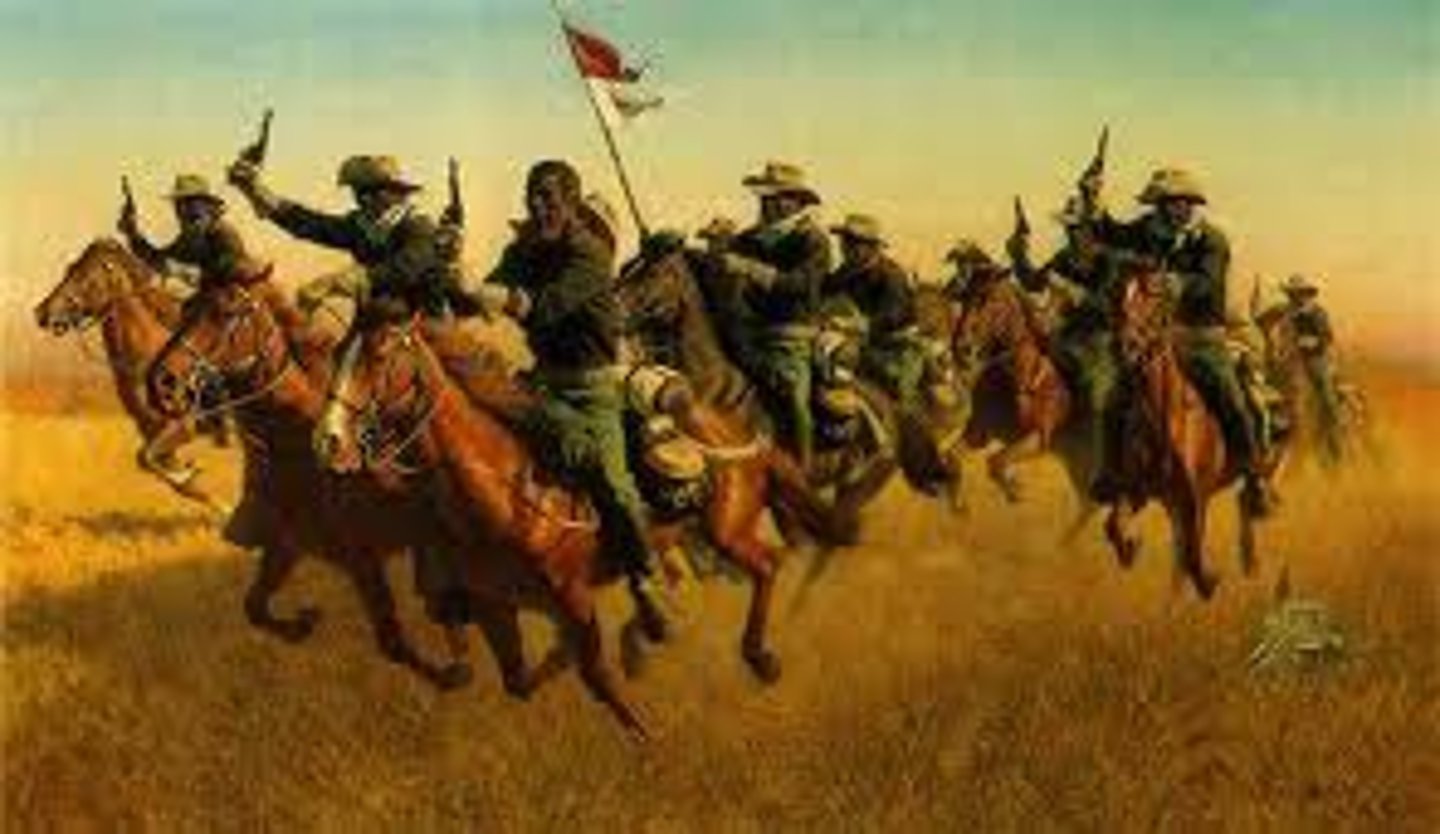
Buffalo Soldiers
Nickname for African-American soldiers who fought in the wars against Native Americans living on the Great Plains during the 1870s

The impeachment of Andrew Johnson
when the Radical Republicans tried Andrew Johnson for impeachment because he wanted to fire Edwin Stanton, the Secretary of War. The Radical Republicans passed a law called the Tenure of Office Act saying that a President cannot fire a worker "just because". President Johnson stayed in office by one vote.
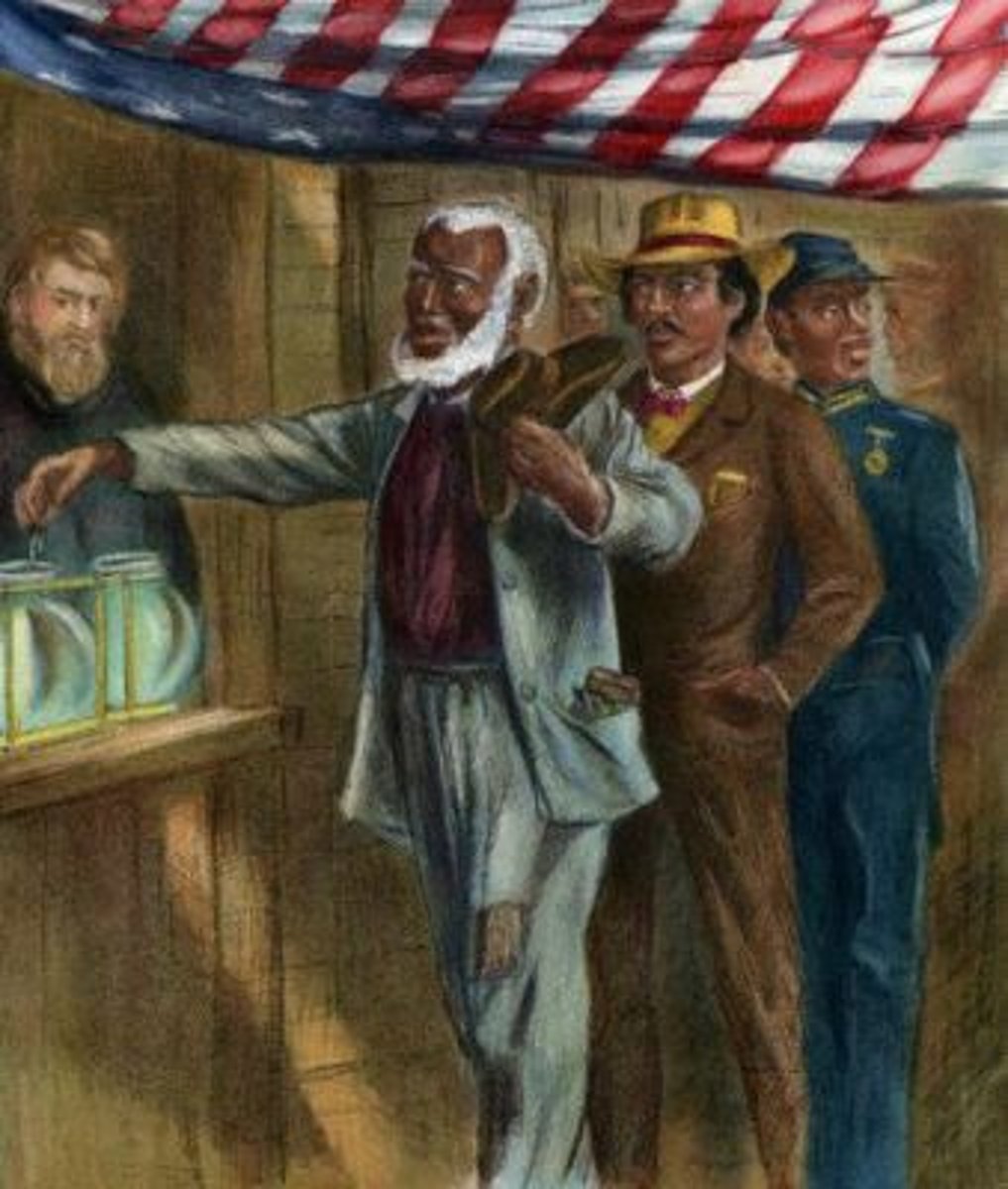
Black Legislators
Many blacks were elected to Federal offices after the Civil War
White Extremist Groups
-KKK
-Knights of the White Camellia
-The White League
-Red Shirts
-Pale Faces
13th Amendment
abolished slavery in the U.S. in 1865

14th Amendment
Declares that all persons born in the U.S. are citizens and are guaranteed equal protection of the laws regardless of race
15th Amendment
Citizens cannot be denied the right to vote because of race, color , or previous condition of servitude

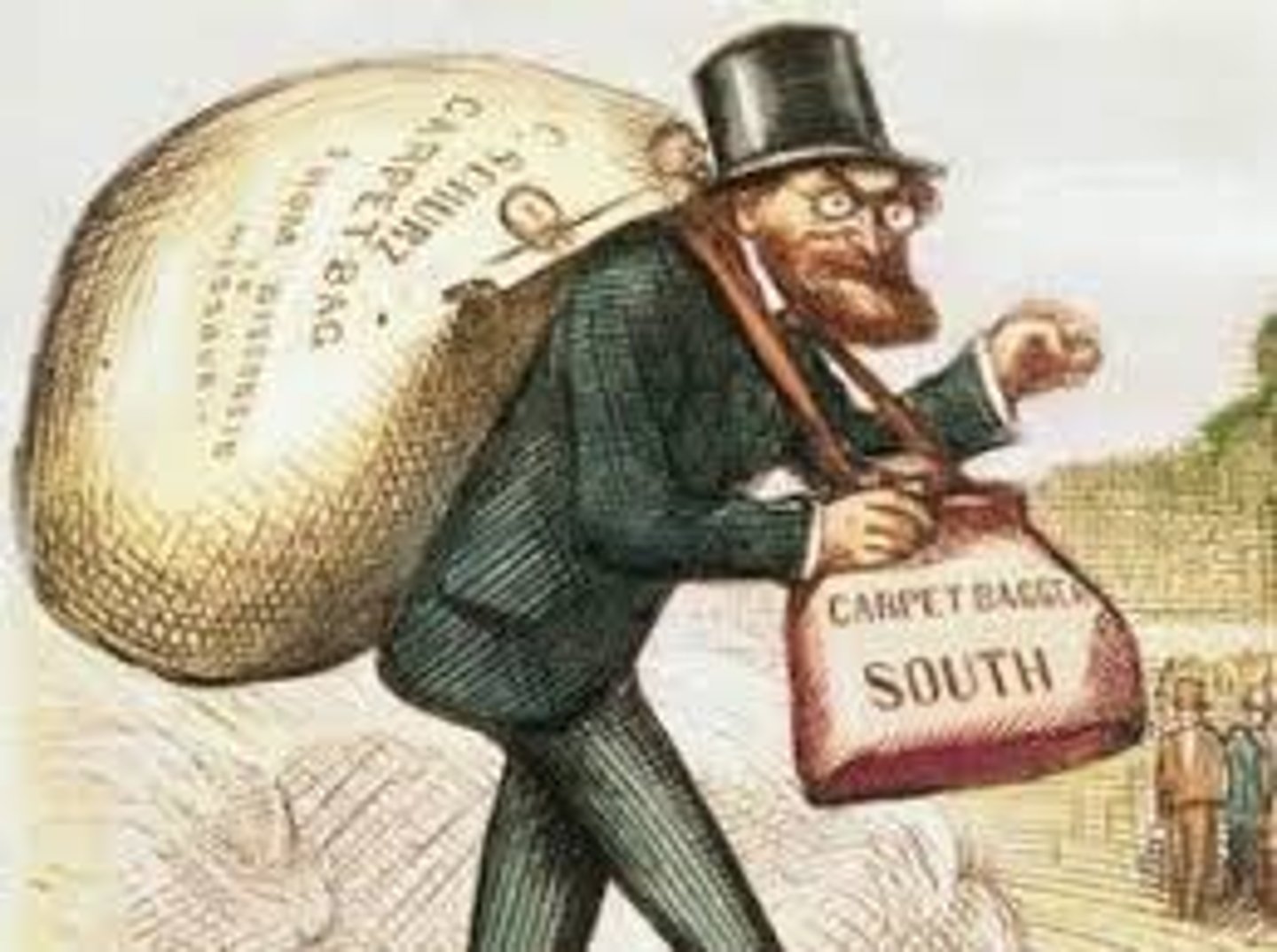
carpetbagger
Northerners who traveled south just to make money off the Reconstruction. They were called this because their suitcases were usually made from carpet.

Suffrage
the right to vote

Jim Crow Laws
The "separate but equal" segregation laws state and local laws enacted in the Southern and border states of the United States and enforced between 1876 and 1965
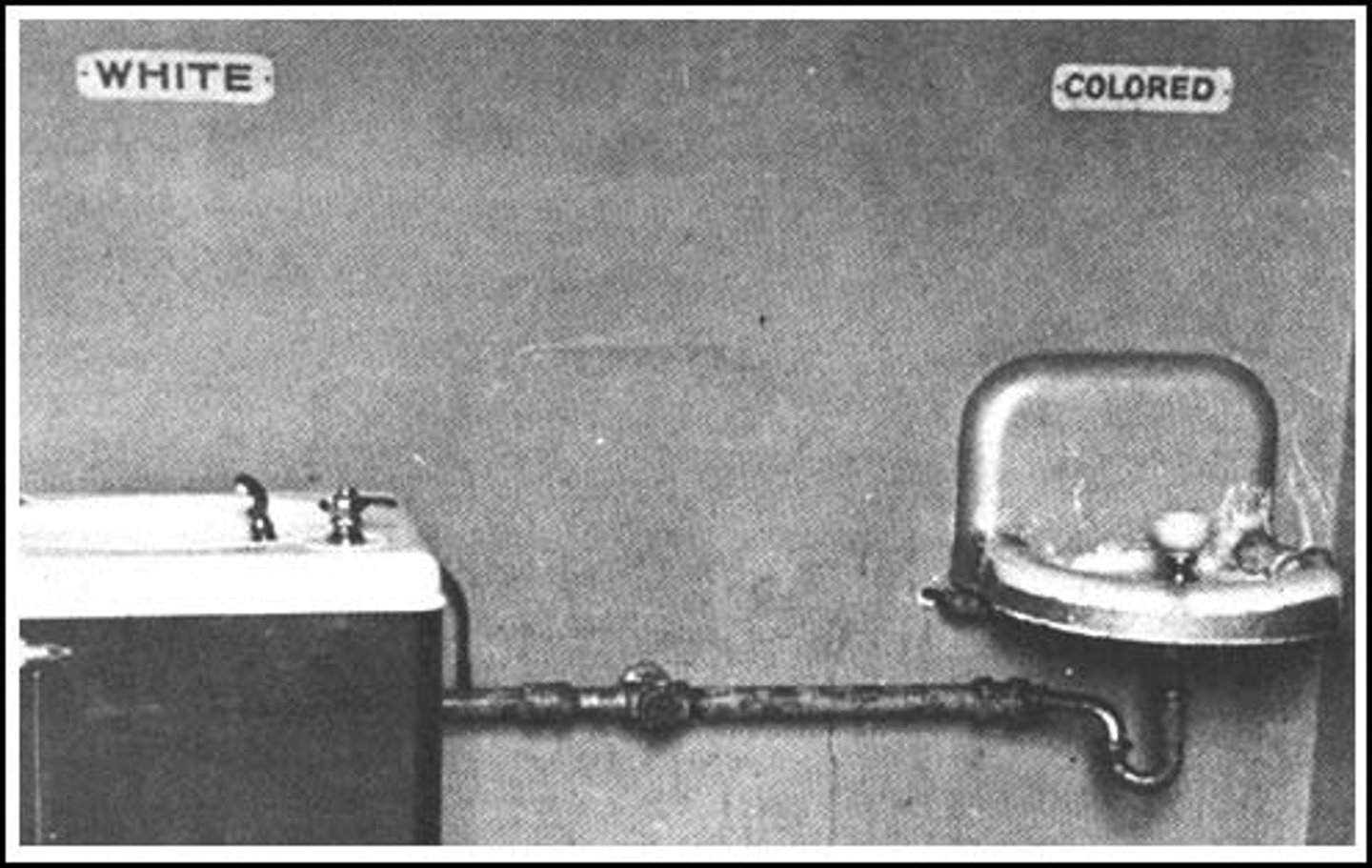
Black Codes
Southern laws designed to restrict the rights of the newly freed black slaves
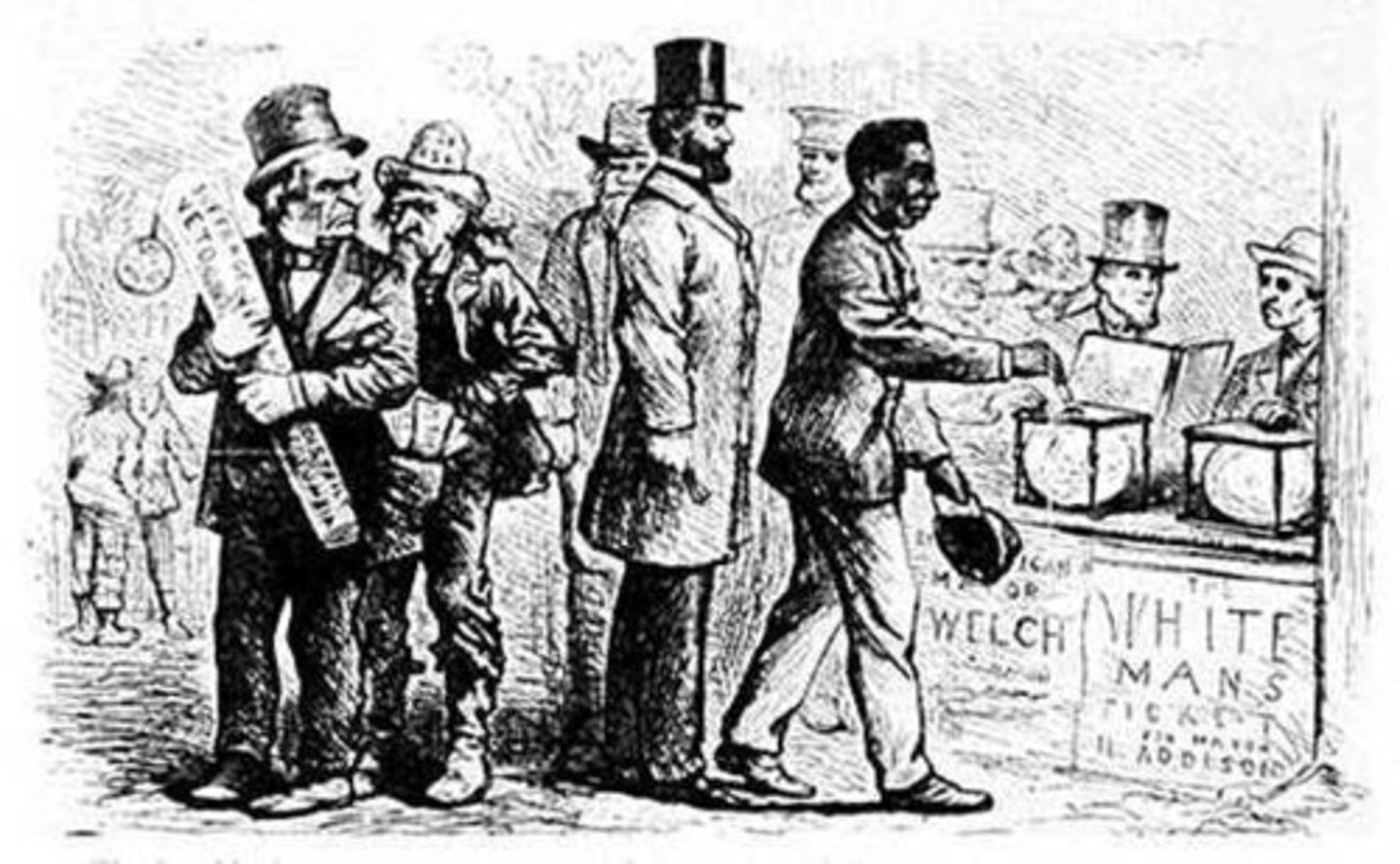

Sharecropping
a system used on southern farms after the civil war in which farmers worked land owned by someone else in return for a small portion of the crops.

Effects of Reconstruction on Native Americans
• Westward expansion
• Reservation system
• The Dawes Act
• Indian Schools
• Government involvement in the killing of the buffalo
• Wounded Knee Massacre
• Sand Creek Massacre
• Battle of Little Big Horn
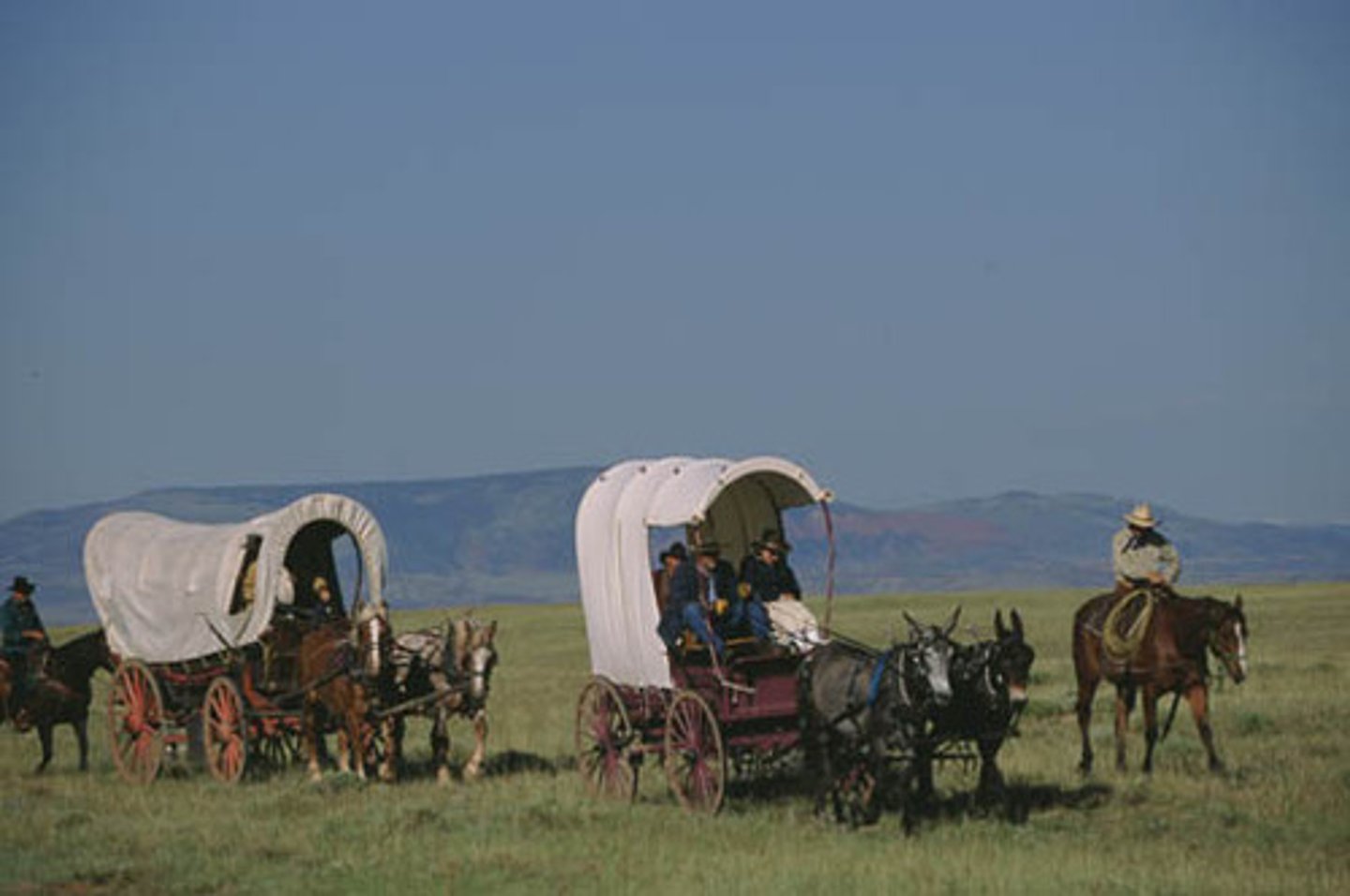
Westward expansion
territorial acquisitions as settlers began moving westward beyond the Appalachian Mountains

Reservation system
introduced in 1870, forced nations to live on barren land, it confined people so they could not support themselves in their accustomed way. It has left to the institutional of this enforced segregation.
Indian Schools
These places were created in order to forcibly assimilate Indian children to white culture. They cut their hair, converted them to Christianity, forced them to change their language and used various other ways to make Indian children act like white Americans.
The Dawes Act
Passed by Congress in 1887. Its purpose was to Americanize the Native Americans. The act broke up the reservations, gave some of the land to Native Americans.

Wounded Knee Massacre
In December 1890, Army troops captured some of Sitting Bull's followers and took them to a camp. 300 Sioux men, women, and children were killed
Sand Creek Massacre
an attack on a village of sleeping Cheyenne Indians by a regiment of Colorado militiamen on 29 November 1864 that resulted in the death of more than 200 tribal members
Battle of Little Big Horn
Sioux leader Sitting Bull led the fight against general George Custer and the 7th cavalry. The Sioux wanted miners out of the black hills, and had appealed to government officials in Washington to stop the miners. Washington doesn't listen. When Custer came to Little Bighorn rivers Sitting Bull and his warriors were ready and killed them all!
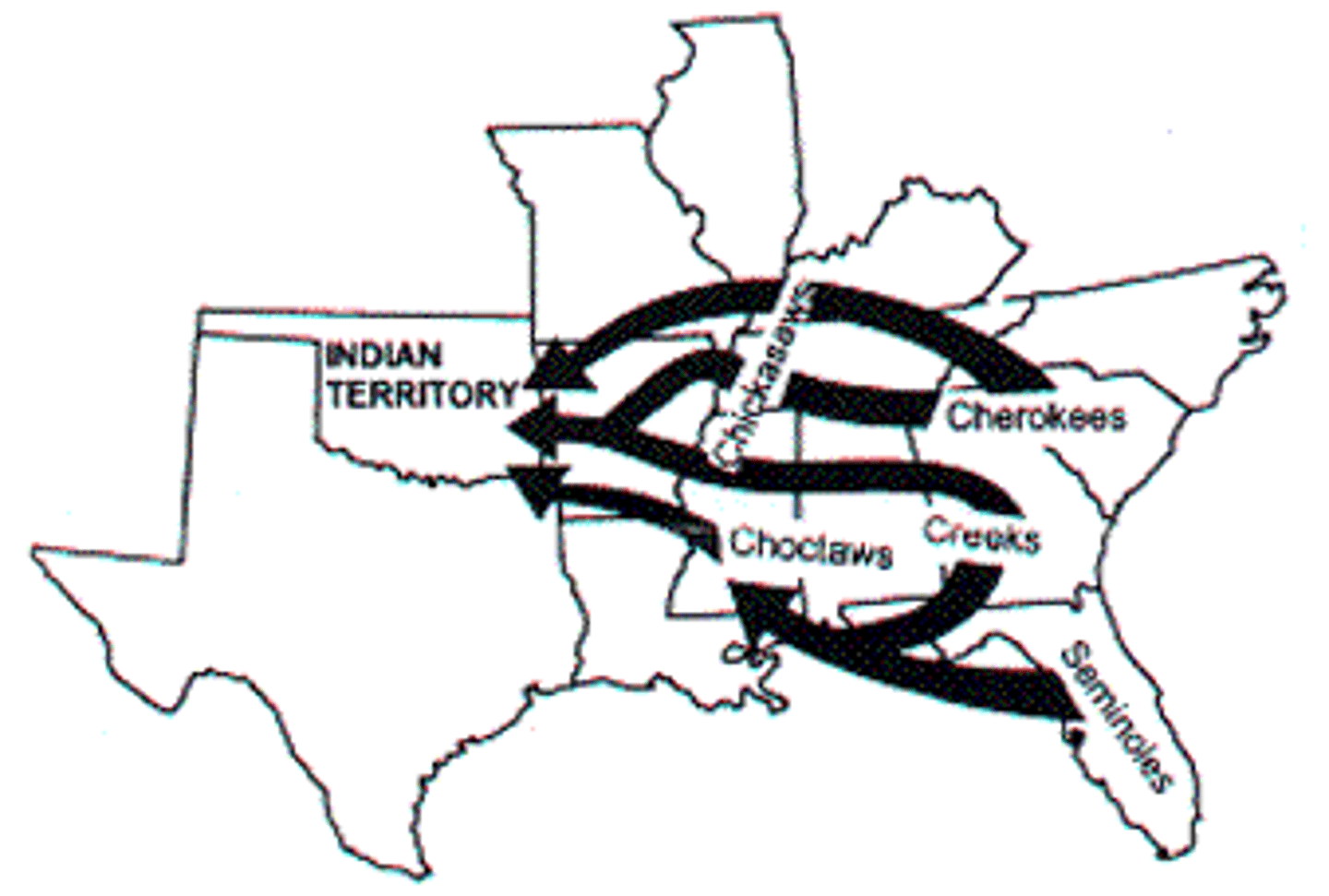
Indian Removal Act
(1830) a congressional act that authorized the removal of Native Americans who lived east of the Mississippi River
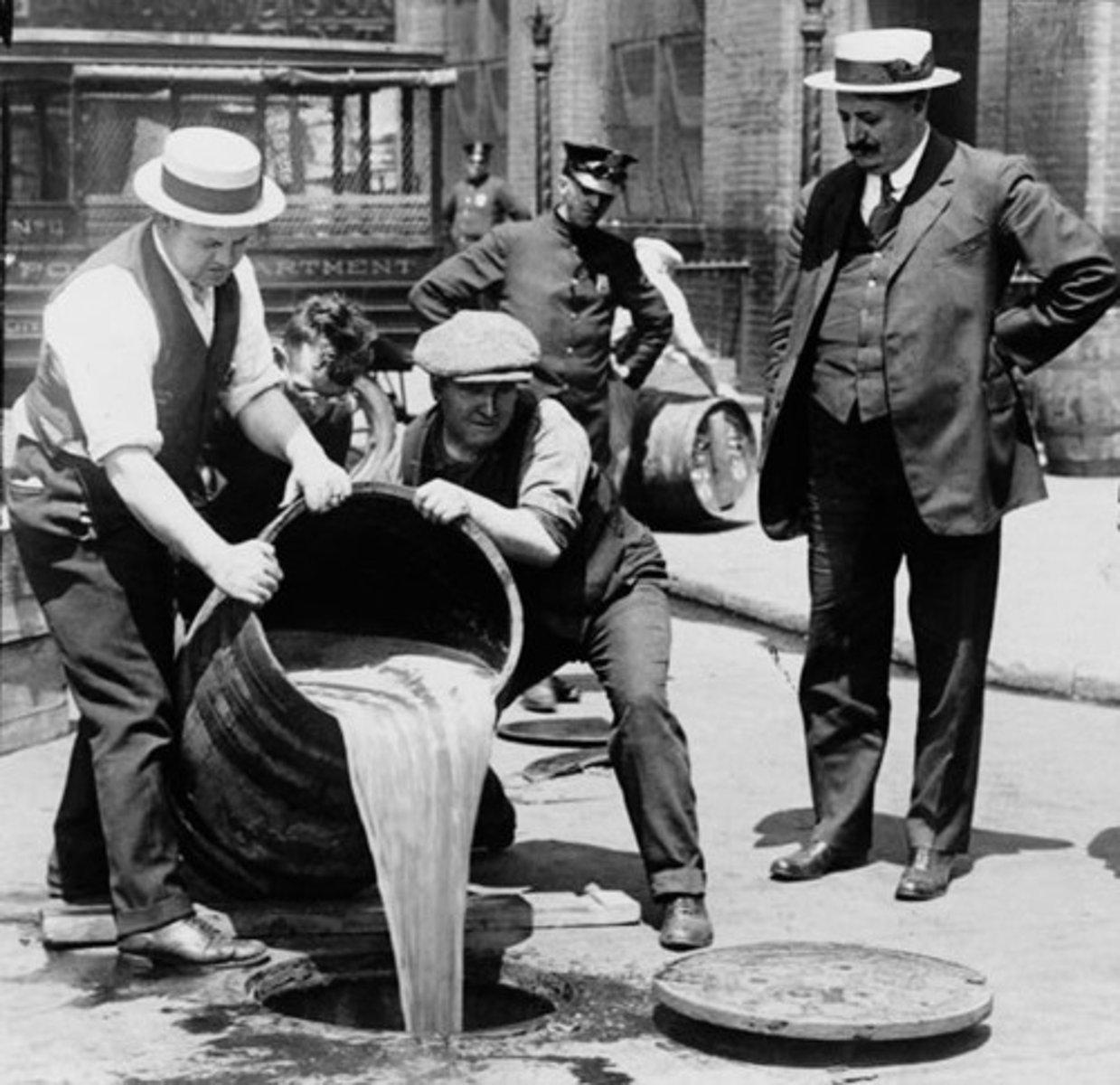
18th Amendment
Prohibited the manufacture, sale, and distribution of alcoholic beverages

19th Amendment
Amendment to the U.S. Constitution (1920) extended the right to vote to women in federal or state elections.

20th Amendment
(FDR) , change of dates for start of presidential/congressional terms
21st Amendment
Amendment which ended the Prohibition of alcohol in the US, repealing the 18th amendment

Bessemer Process
A way to manufacture steel quickly and cheaply by blasting hot air through melted iron to quickly remove impurities.

robber baron
Refers to the industrialists or big business owners who gained huge profits by paying their employees extremely low wages. They also drove their competitors out of business by selling their products cheaper than it cost to produce it. Then when they controlled the market, they hiked prices high above original price.

Thomas Edison
American inventor who developed many devices such as the phonograph, the motion picture camera, and a long-lasting, practical electric light bulb

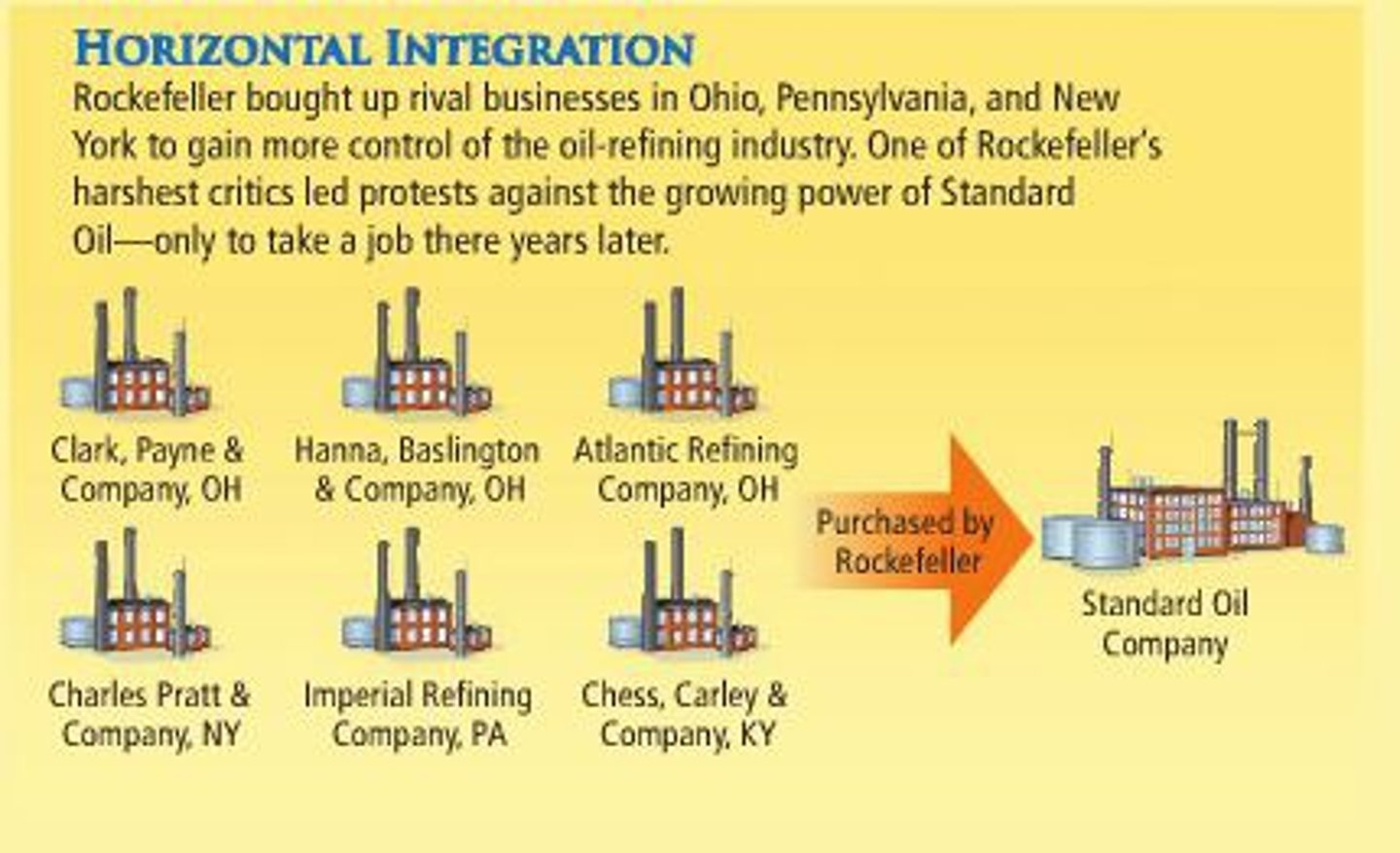
John D. Rockefeller
Established the Standard Oil Company, the greatest, wisest, and meanest monopoly known in history

Andrew Carnegie
A Scottish-born American industrialist and philanthropist who founded the Carnegie Steel Company in 1892. By 1901, his company dominated the American steel industry

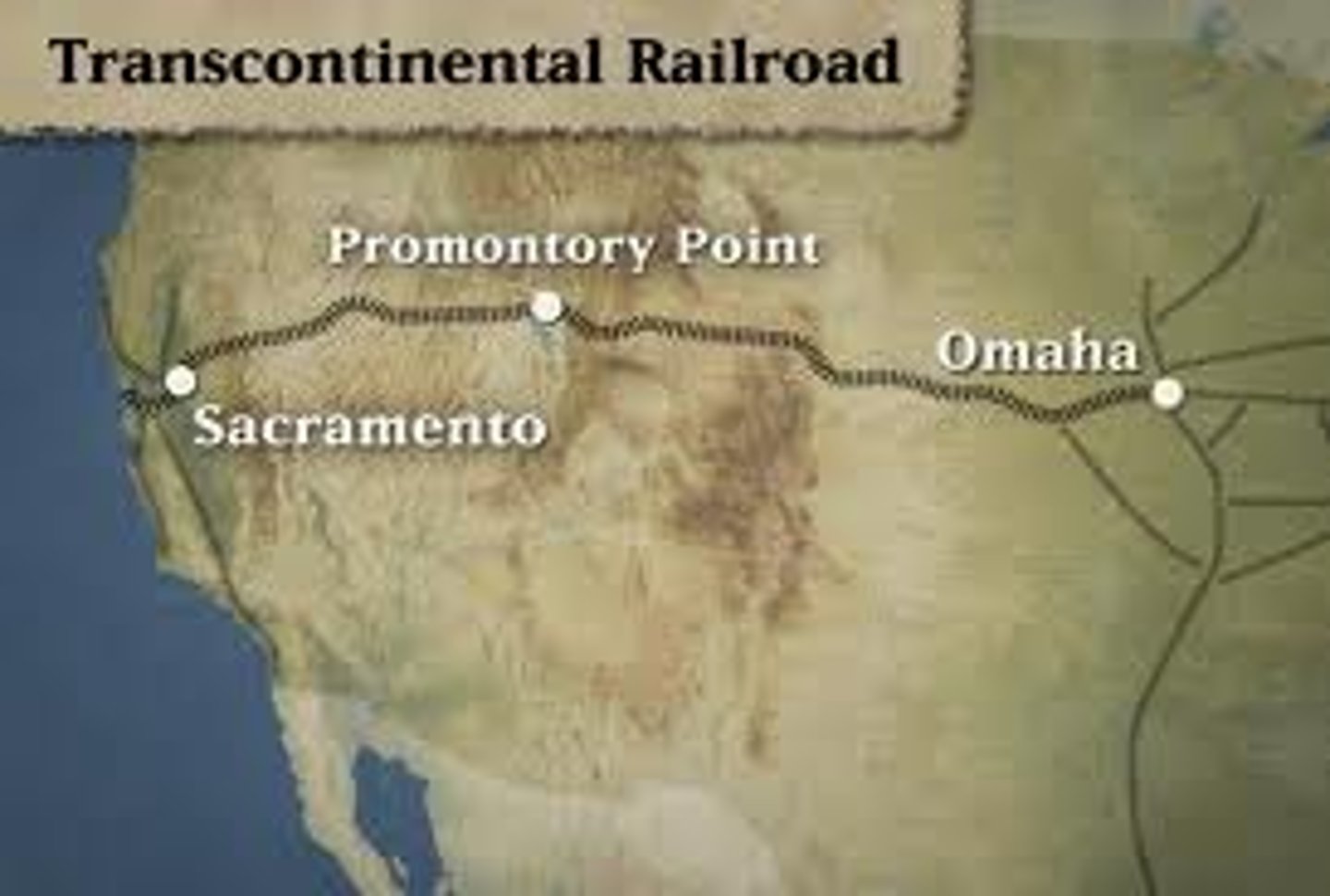
Transcontinental Railroad
Railroad connecting the west and east coasts of the continental US
Henry Ford
1863-1947. American businessman, founder of Ford Motor Company, father of modern assembly lines, and inventor credited with 161 patents.

Upton Sinclair
muckraker who shocked the nation when he published The Jungle, a novel that revealed gruesome details about the meat packing industry in Chicago. The book was fiction but based on the things Sinclair had seen.

muckraker
Journalists who searched for corruption in politics and big business

Homestead Act
Passed in 1862, it gave 160 acres of public land to any settler who would farm the land for five years. The settler would only have to pay a registration fee of $25.

Spanish American War
In 1898, a conflict between the United States and Spain, in which the U.S. supported the Cubans' fight for independence
U.S.S. Maine
Ship that explodes off the coast of Cuba in Havana harbor and helps contribute to the start of the Spanish-American War

Rough Riders
The First United States Volunteer Calvary, a mixture of Ivy League athletes and western frontiersmen, volunteered to fight in the Spanish-American War. Enlisted by Theodore Roosevelt, they won many battles in Florida and enlisted in the invasion army of Cuba.

Big Stick Diplomacy
The policy held by Teddy Roosevelt in foreign affairs. The "big stick" symbolizes his power and readiness to use military force if necessary. It is a way of intimidating countries without actually harming them.
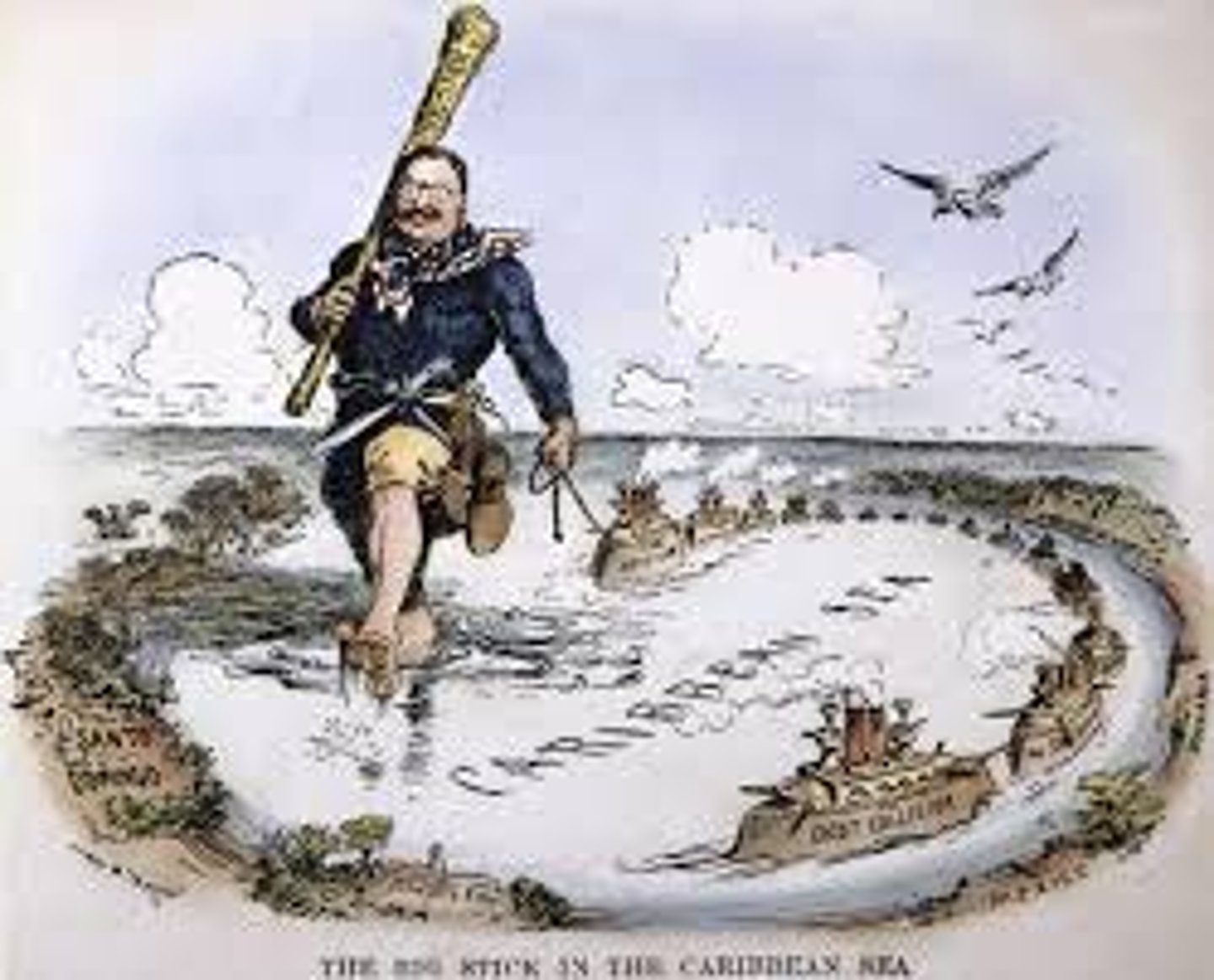

Dollar Diplomacy
Foreign Policy idea by Taft to make countries dependent on the U.S. by heavily investing in their economies

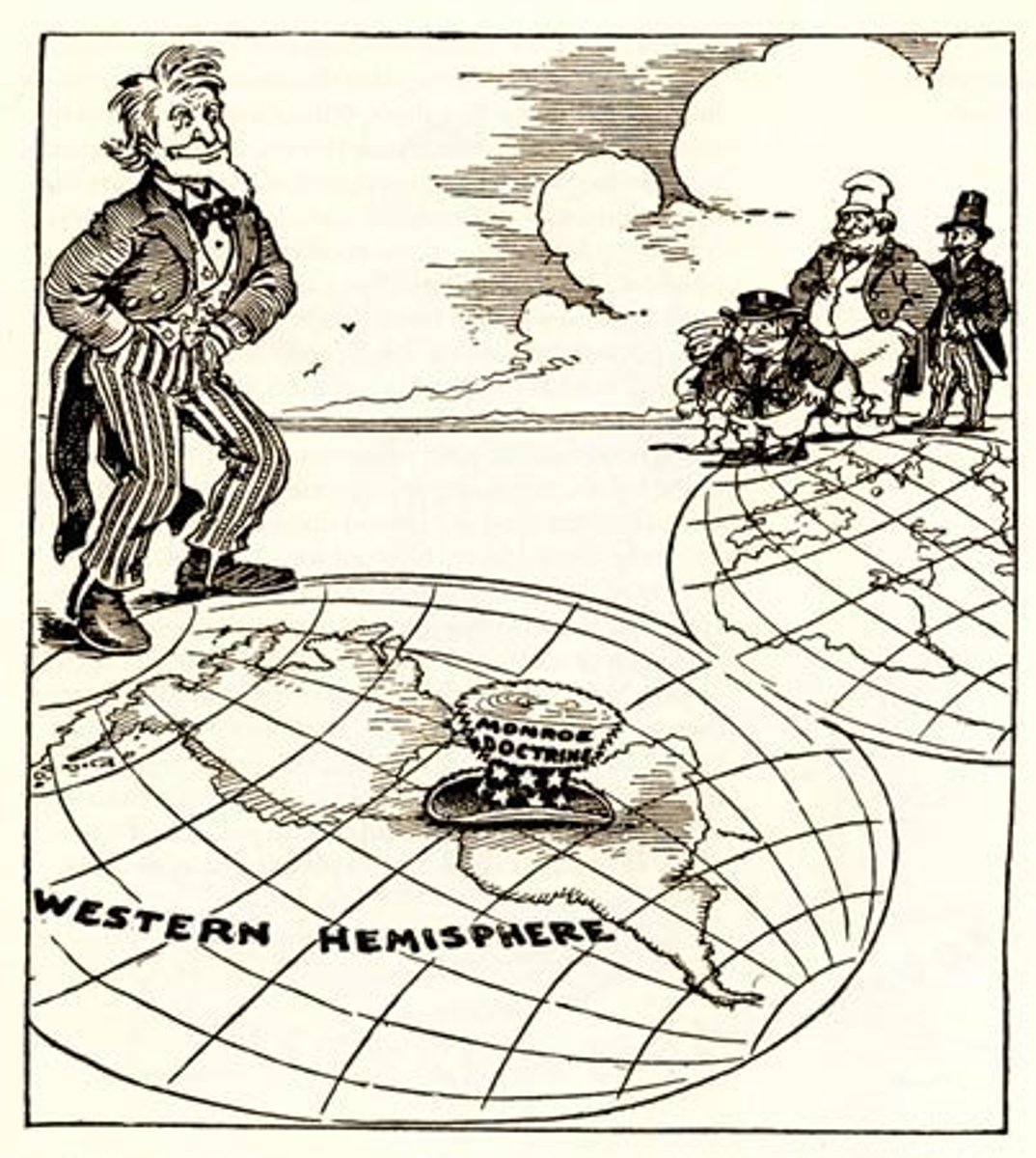
Monroe Doctrine
(1823) A political policy of the United States by President James Monroe that states the Western Hemisphere is closed to European interference.
Manifest Destiny
A notion held by a nineteenth-century Americans that the United States was destined to rule the continent, from the Atlantic the Pacific.

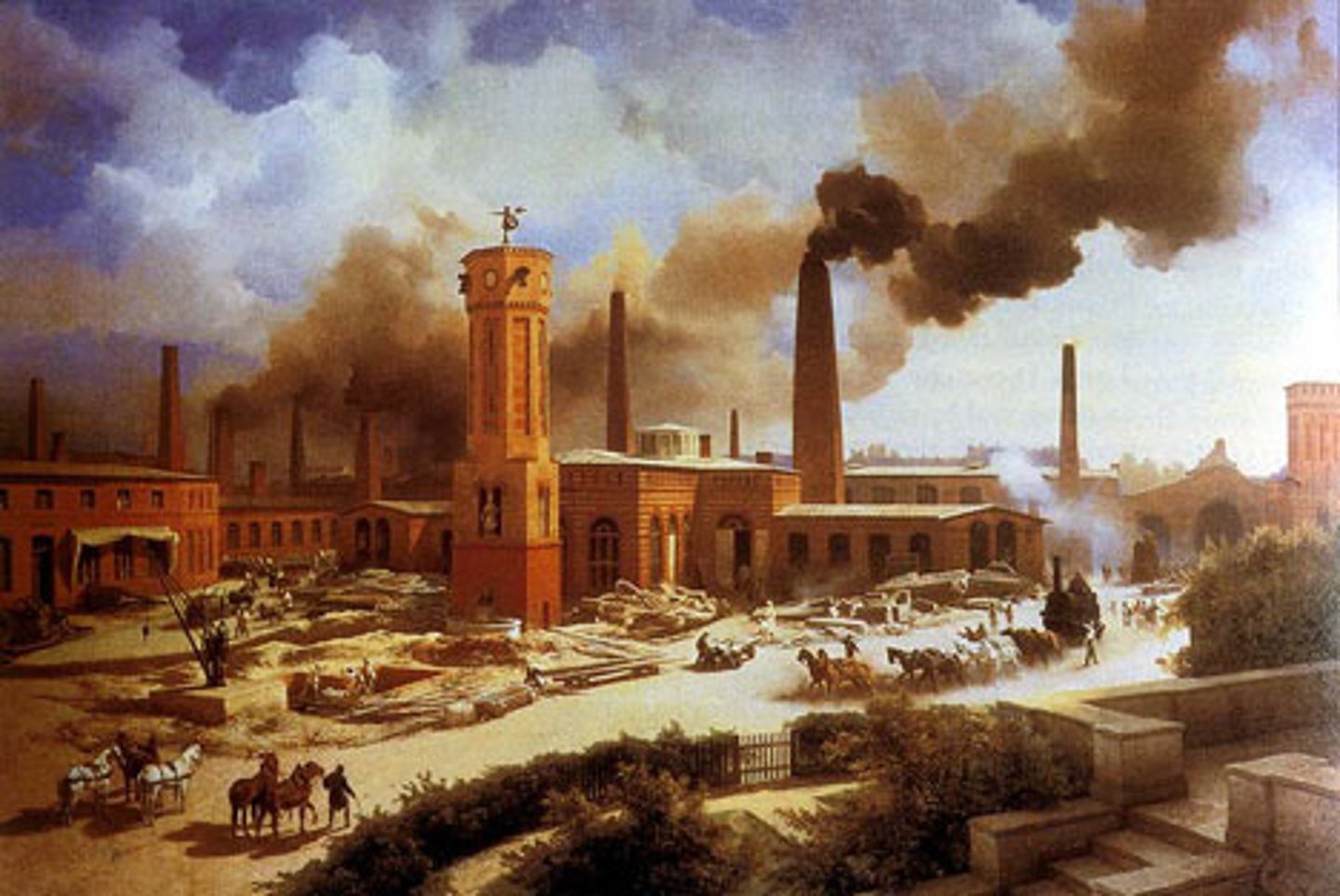
Second Industrial Revolution
(1871-1914) Involved development of chemical, electrical, oil, and steel industries. Mass production of consumer goods also developed at this time through the mechanization of the manufacture of food and clothing. It saw the popularization of cinema and radio. Provided widespread employment and increased production.

mass production
Process of making large quantities of a product quickly and cheaply

easy credit
People could purchase things off of credit which before they would have had to save up for years
installment buying
A consumers buys products by promising to pay small, regular amounts over a period of time
buying on margin
Purchasing stock with a little money down with the promise of paying the balance at sometime in the future

Black Tuesday
October 29, 1929; date of the worst stock-market crash in American history and beginning of the Great Depression.

Great Depression
(1929-1939) The dramatic decline in the world's economy due to the United State's stock market crash of 1929, the overproduction of goods from World War I, and decline in the need for raw materials from non industrialized nations. Results in millions of people losing their jobs as banks and businesses closed around the world. Many people were reduced to homelessness, and had to rely on government sponsored soup kitchens to eat. World trade also declined as many countries imposed protective tariffs in an attempt to restore their economies.

New Deal
A series of reforms enacted by the Franklin Roosevelt administration between 1933 and 1942 with the goal of ending the Great Depression.
Causes of World War I
Militarism
Alliance System
Assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand
Imperialism
Nationalism

militarism
A policy of glorifying military power and keeping a standing army always prepared for war

alliances
agreements between nations to aid and protect one another
imperialism
A policy in which a strong nation seeks to dominate other countries politically, socially, and economically.

nationalism
A strong feeling of pride in and devotion to one's country
Effects of World War I
New weapons invented, tons of casualties, France destroyed, Treaty of Versailles, Germany had to take responsibility and pay reparations, "Lost Generation"

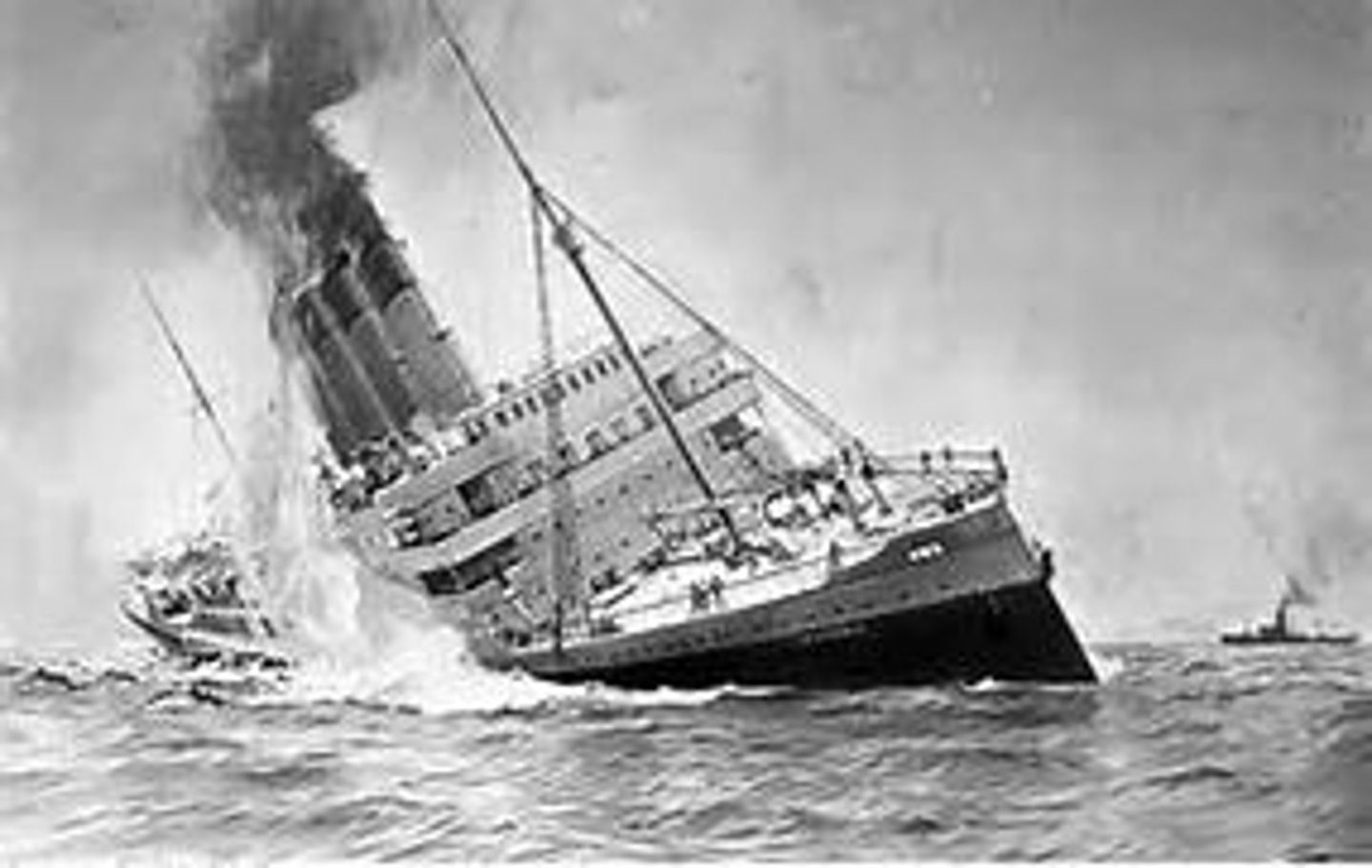
Lusitania
A British passenger ship that was sunk by a German U-Boat on May 7, 1915. 128 Americans died. The sinking greatly turned American opinion against the Germans, helping the move towards entering the war.

Zimmerman Note
1917 - Germany sent this to Mexico instructing an ambassador to convince Mexico to go to war with the U.S. It was intercepted and caused the U.S. to mobilized against Germany, which had proven it was hostile

Treaty of Versailles
Treaty that ended WW I. It blamed Germany for WWI and handed down harsh punishment.
vertical integration
Practice where a single entity controls the entire process of a product, from the raw materials to distribution
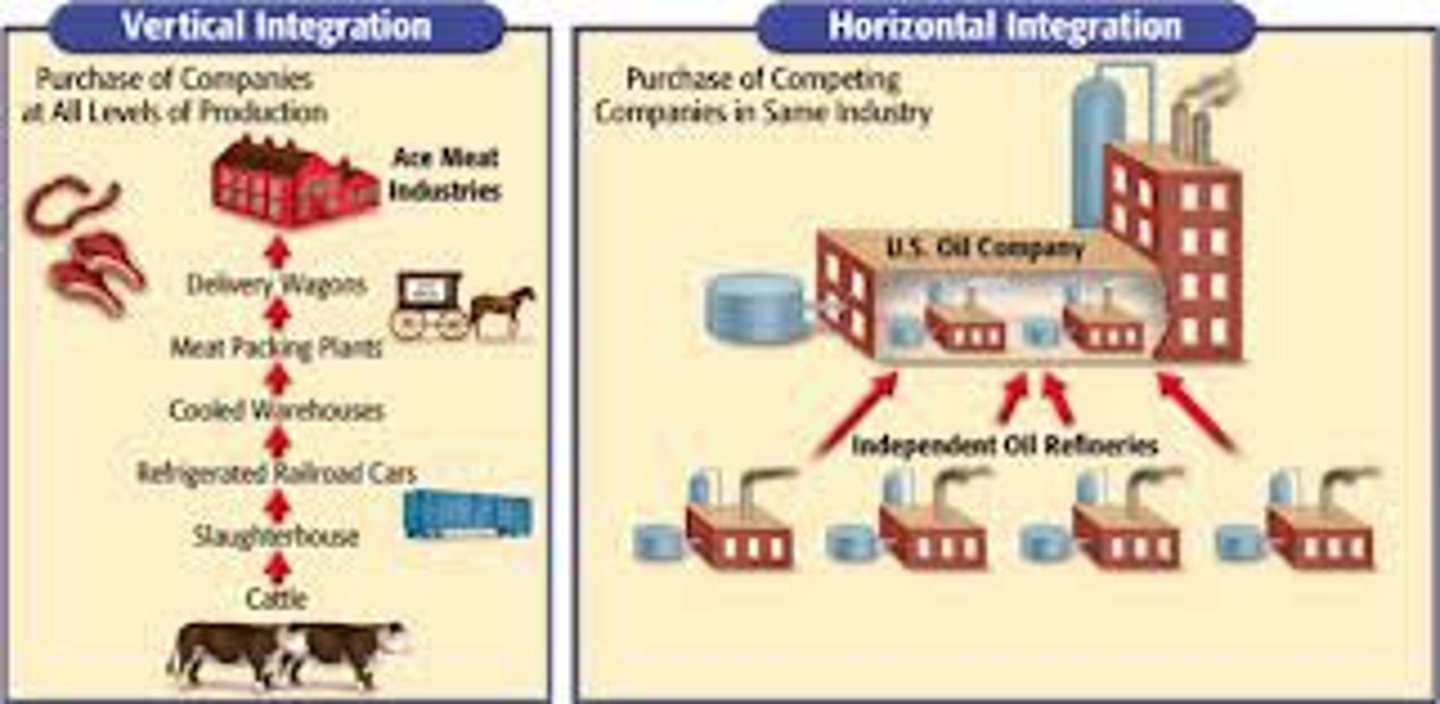
horizontal integration
Absorption into a single firm of several firms involved in the same level of production and sharing resources at that level
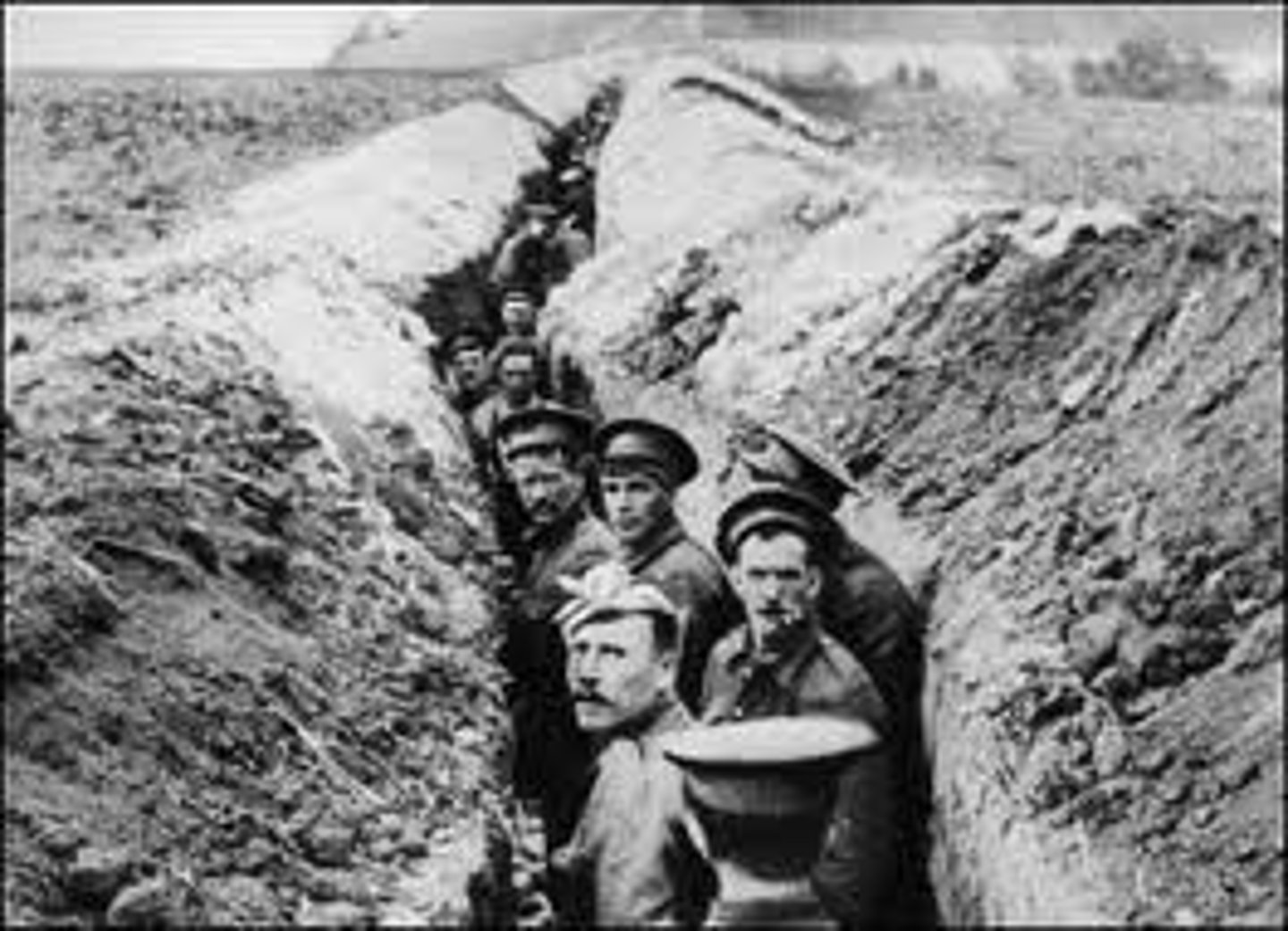
trench warfare
Fighting with trenches, mines, and barbed wire. Horrible living conditions, great slaughter, no gains, stalemate, used in WWI.

Chinese Exclusion Act
(1882) Denied any additional Chinese laborers to enter the country while allowing students and merchants to immigrate.

monopoly
A market in which there are many buyers but only one seller.

Taft-Hartley Act
1. outlawed "closed shops and required union leaders to sign loyalty oath 2. required 80 day cooling off period before strike
unions
An association of workers, formed to bargain for better working conditions and higher wages.

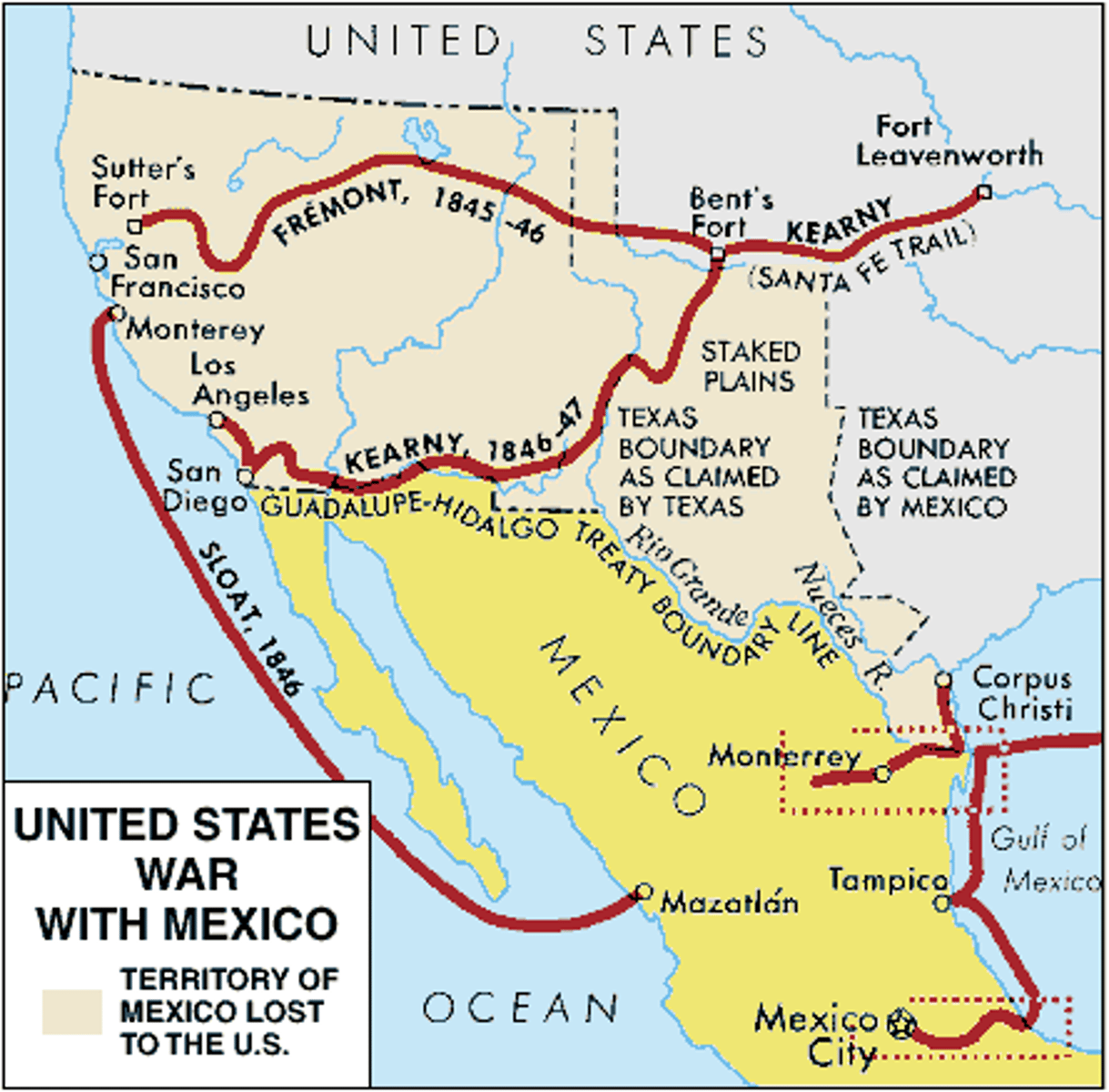
Mexican-American War
(1846-1848) The war between the United States and Mexico in which the United States acquired one half of the Mexican territory.
flapper
Young women of the 1920s that behaved and dressed in a radical fashion
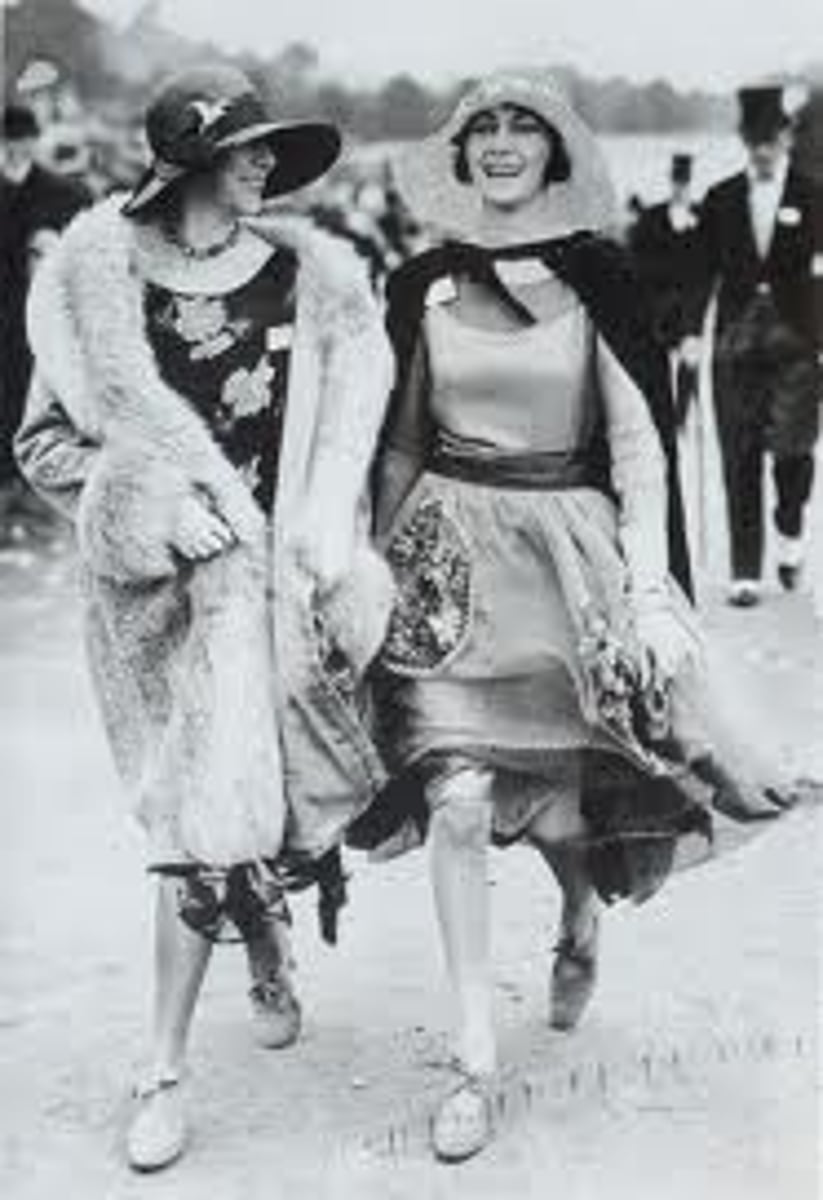

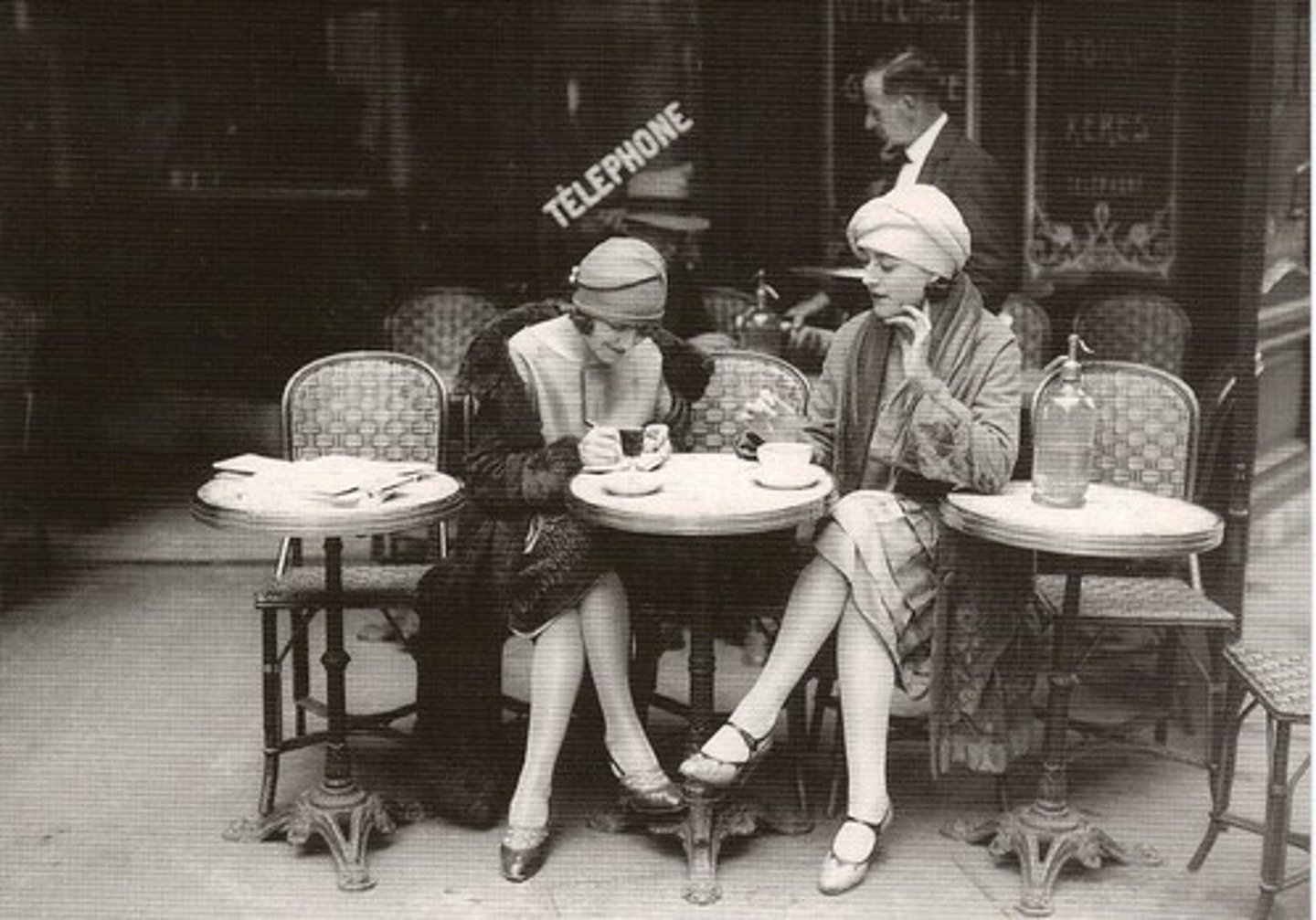
Roaring Twenties
the decade of the 1920's which got this nickname because of the times prosperity and excitement

urbanization
An increase in the percentage and in the number of people living in urban settlements.

United Nations
An international organization formed after WWII to promote international peace, security, and cooperation.

League of Nations
A world organization established in 1920 to promote international cooperation and peace. It was first proposed in 1918 by President Woodrow Wilson, although the United States never joined the League. Essentially powerless, it was officially dissolved in 1946.

Wilmot Priviso
1846 - stated that no territory gained from Mexico would allow slavery. Never became a federal law, but was endorsed by most of the legislatures of the free states Symbolized the issue of slavery in the territories
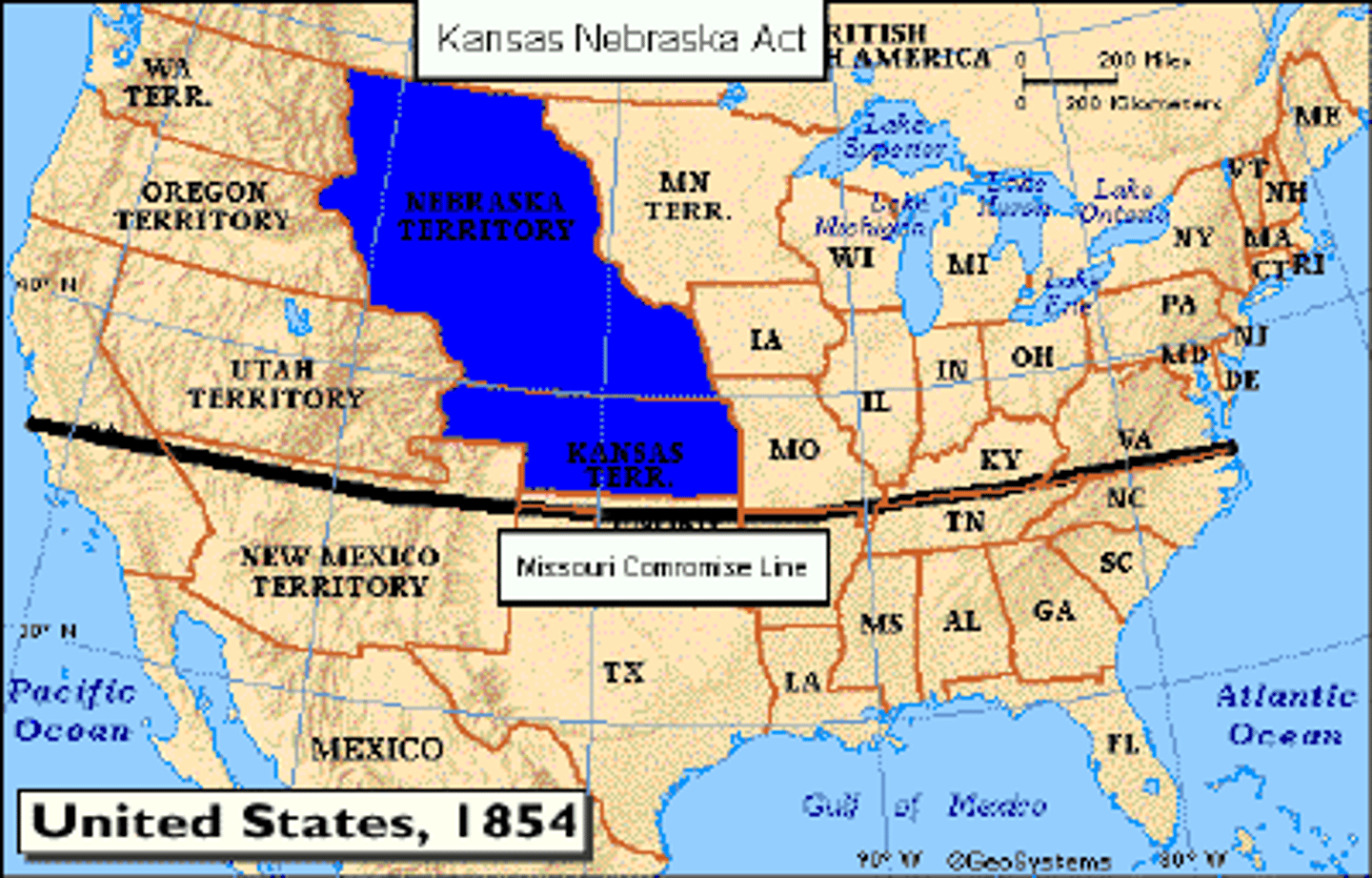
Kansas-Nebraska Act
1854 - Created Nebraska and Kansas as states and gave the people in those territories the right to chose to be a free or slave state through popular sovereignty.
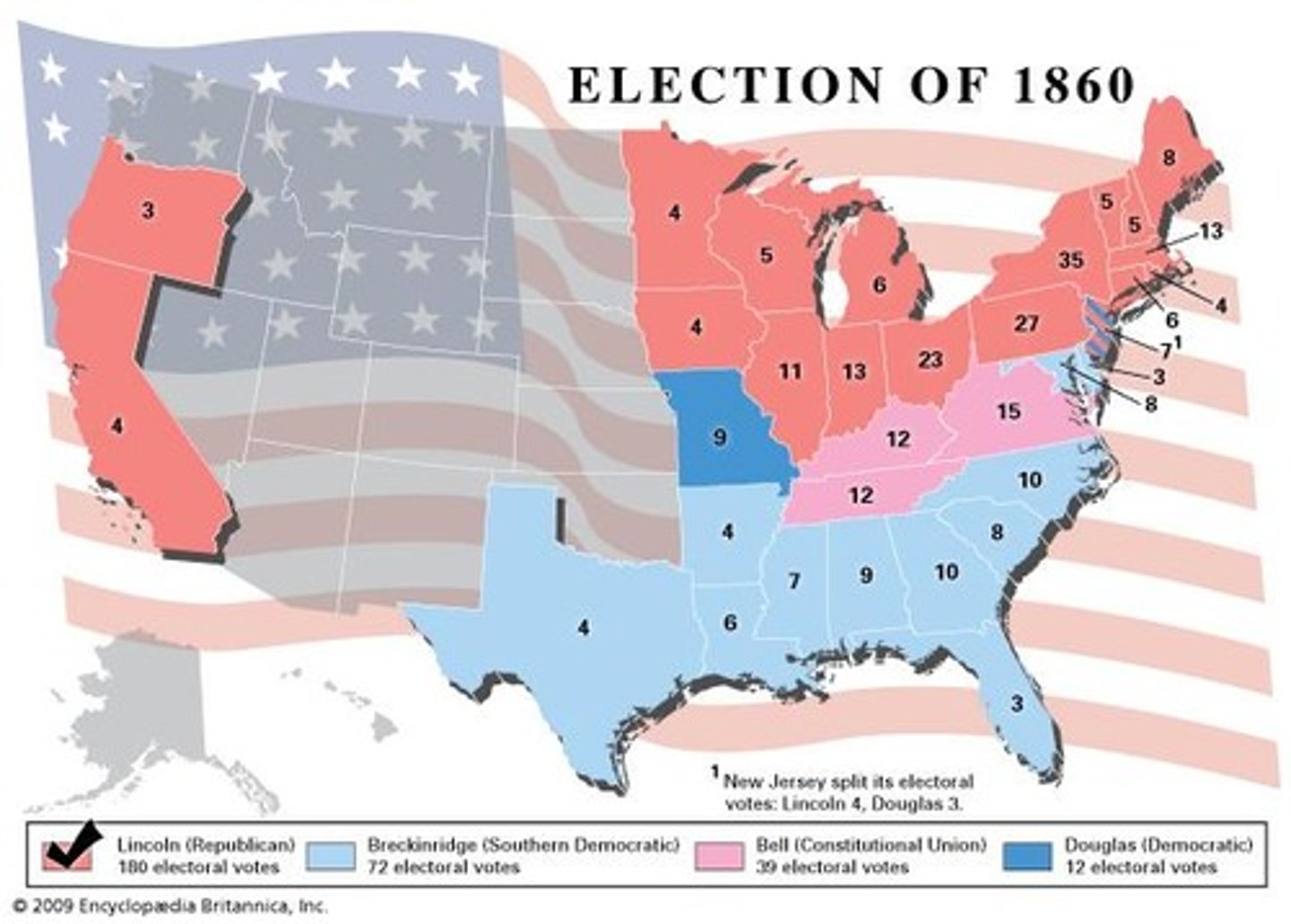
Election of 1860
Presidential Election that ended with Abraham Lincoln as President, the Southern states began to secede forming the Confederate States of America with Jefferson Davis as their President.
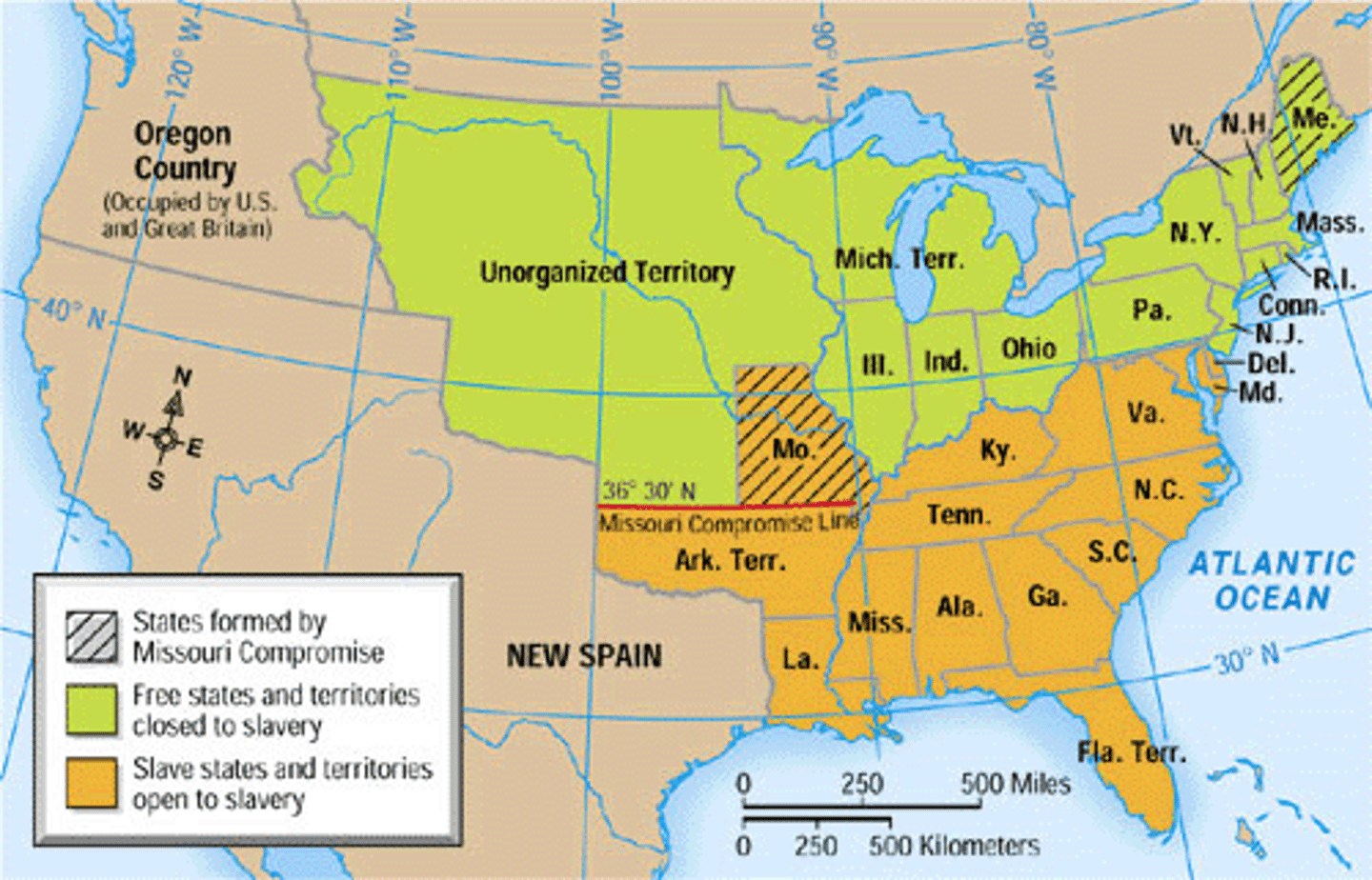
Missouri Compromise
Allowed Missouri to enter the union as a slave state, Maine to enter the union as a free state, prohibited slavery north of latitude 36˚ 30' within the Louisiana Territory (1820)
Bleeding Kansas
A sequence of violent events involving abolitionists and pro-Slavery elements that took place in Kansas-Nebraska Territory. The dispute further strained the relations of the North and South, making civil war imminent.

John Brown's Raid
1859. Harpers Ferry - attempt by white abolitionist John Brown to start an armed slave revolt by seizing US Arsenal at Harpers Ferry in Virginia. defeated by detachment of US marines led by Robert E. Lee. Within 36 hours most of Browns men were either killed or captured.

Gilded Age
..., A name for the late 1800s, coined by Mark Twain to describe the tremendous increase in wealth caused by the industrial age and the ostentatious lifestyles it allowed the very rich. The great industrial success of the U.S. and the fabulous lifestyles of the wealthy hid the many social problems of the time, including a high poverty rate, a high crime rate, and corruption in the government.

Progressive Era
Period of reform from 1890s-1920s. Opposed waste and corruption while focusing on the general rights of the individual. Pushed for social justice, general equality, and public safety. Significant in this movement included trust-busting, Sherman Anti-trust Act, President Theodore Roosevelt, Upton Sinclair's "The Jungle", Pure Food and Drug Act and Meat Inspection Act of 1906.`

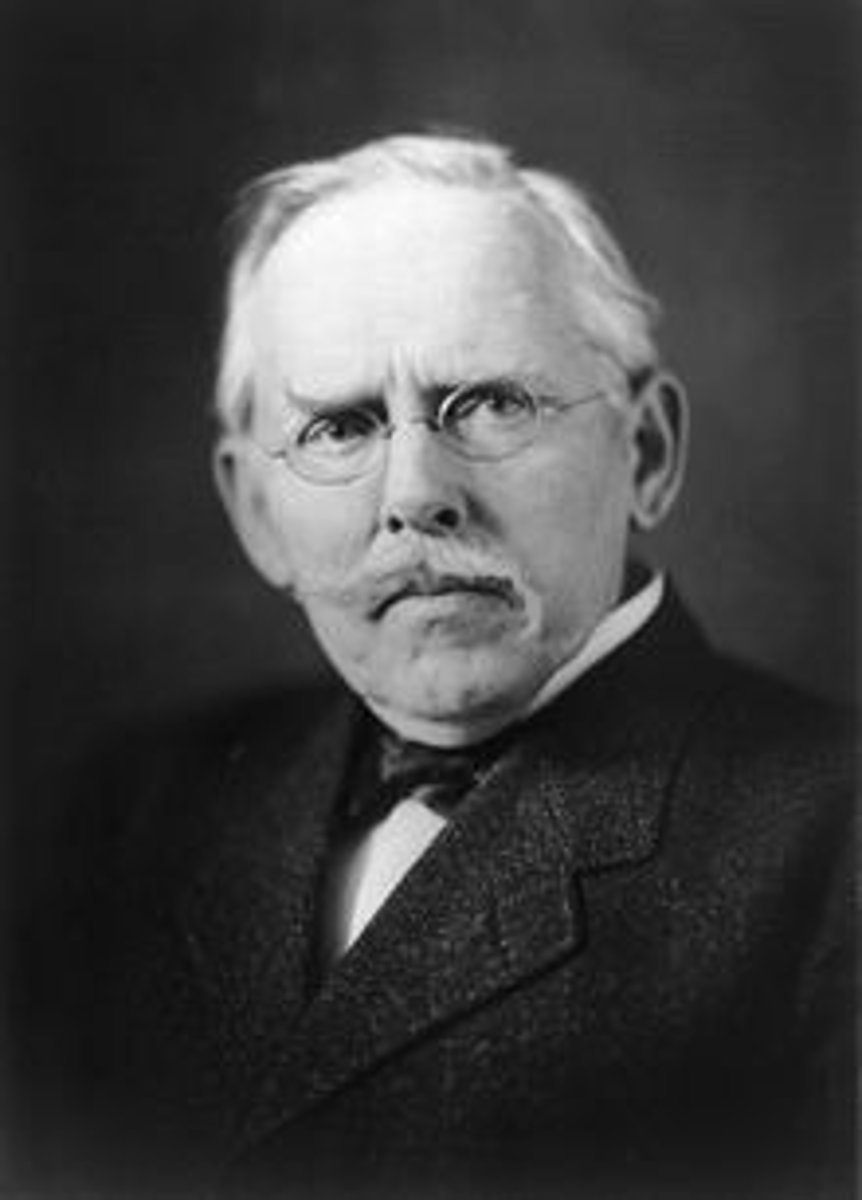
Jane Addams
1860-1935. Founder of Settlement House Movement. First American Woman to earn Nobel Peace Prize in 1931 as president of Women's International League for Peace and Freedom.
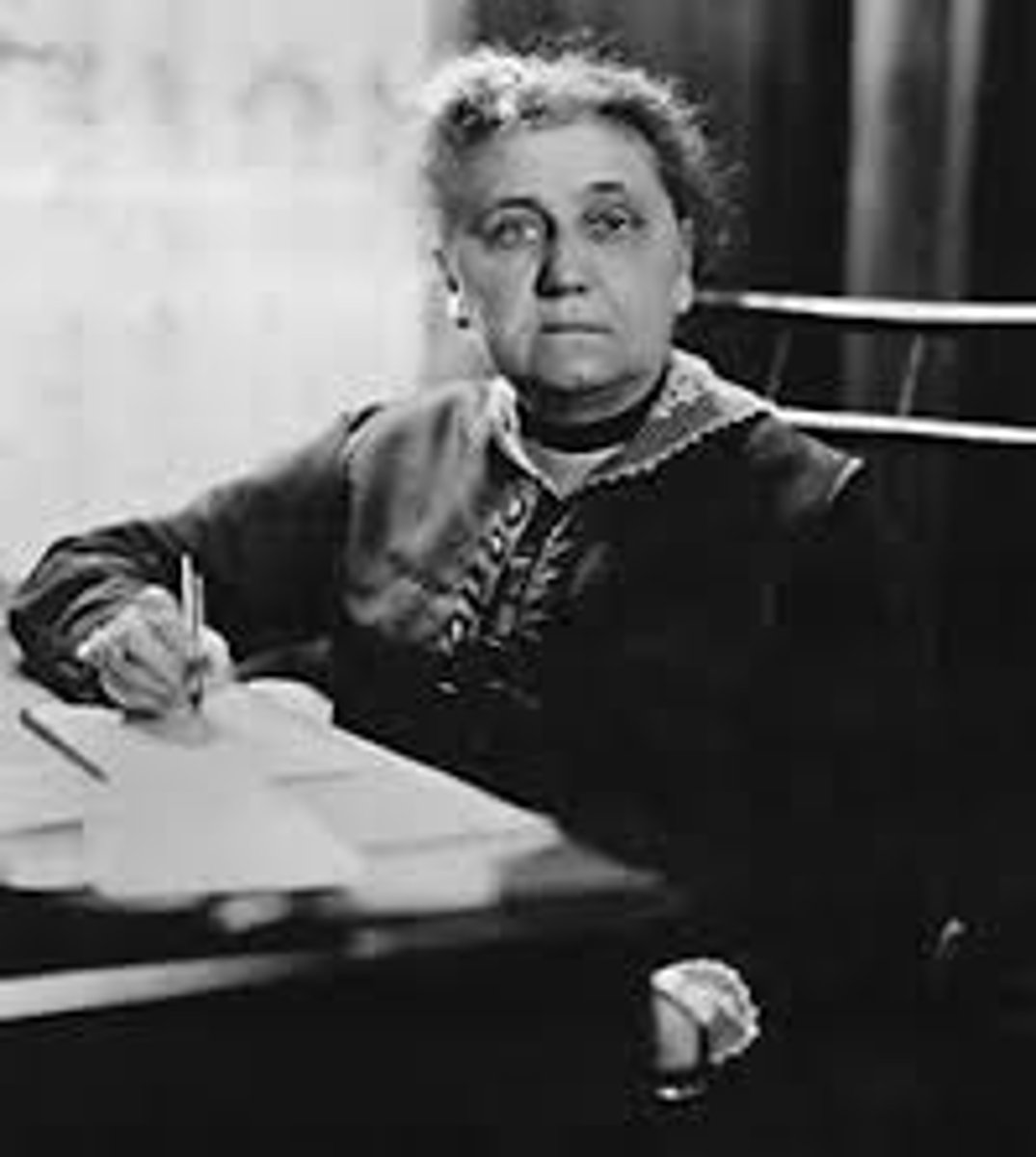

Jacob Riis
A Danish immigrant, he became a reporter who pointed out the terrible conditions of the tenement houses of the big cities where immigrants lived during the late 1800s. He wrote How The Other Half Lives in 1890.

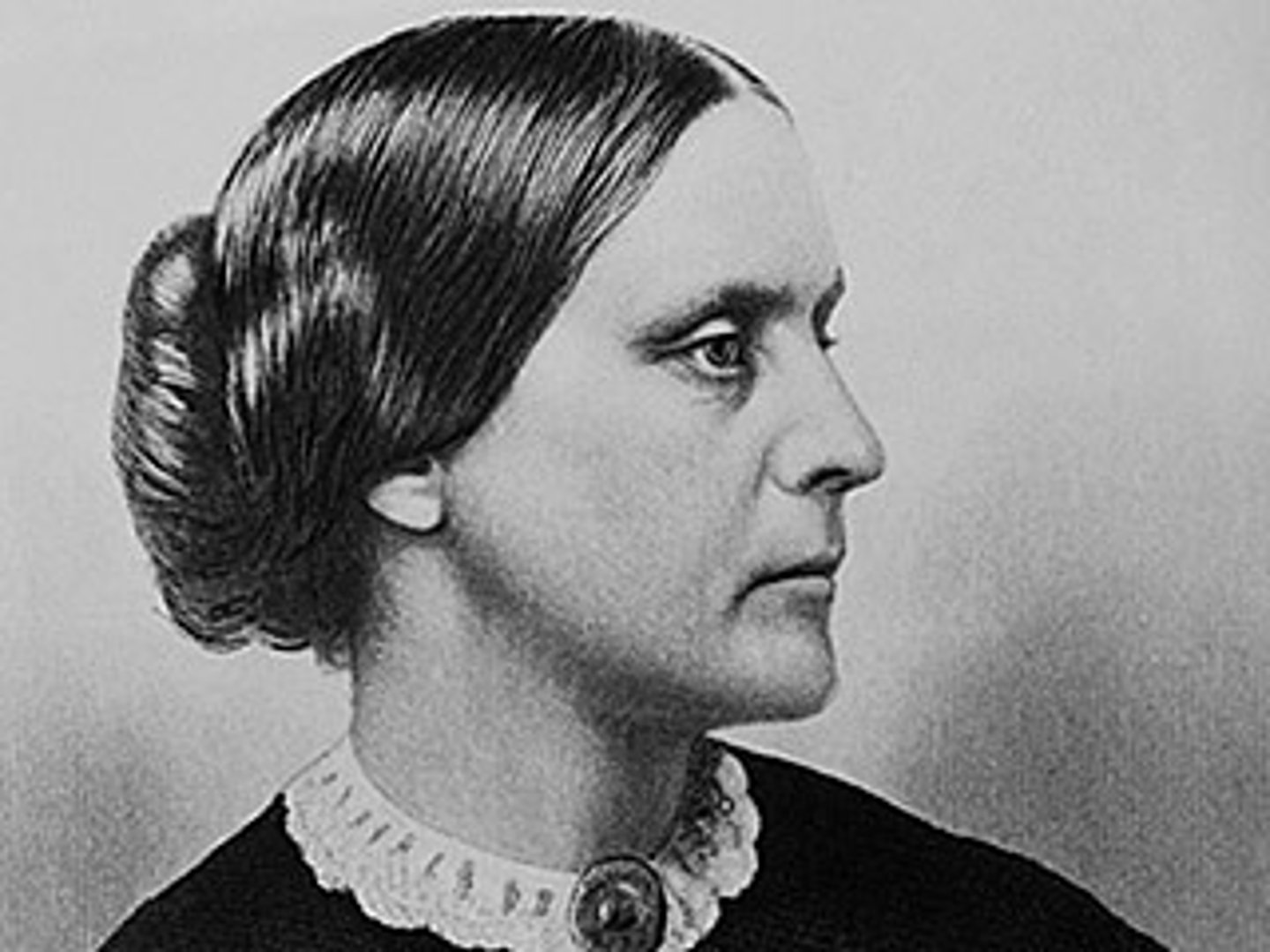
Susan B. Anthony
social reformer who campaigned for women's rights, the temperance, and was an abolitionist, helped form the National Woman Suffrage Association

Social Gospel
reform movement that emerged in the late nineteenth century that sought to improve society by applying Christian principles
populism
the political doctrine that supports the rights and powers of the common people in their struggle with the privileged elite
Populist Party
U.S. political party formed in 1892 representing mainly farmers, favoring free coinage of silver and government control of railroads and other monopolies
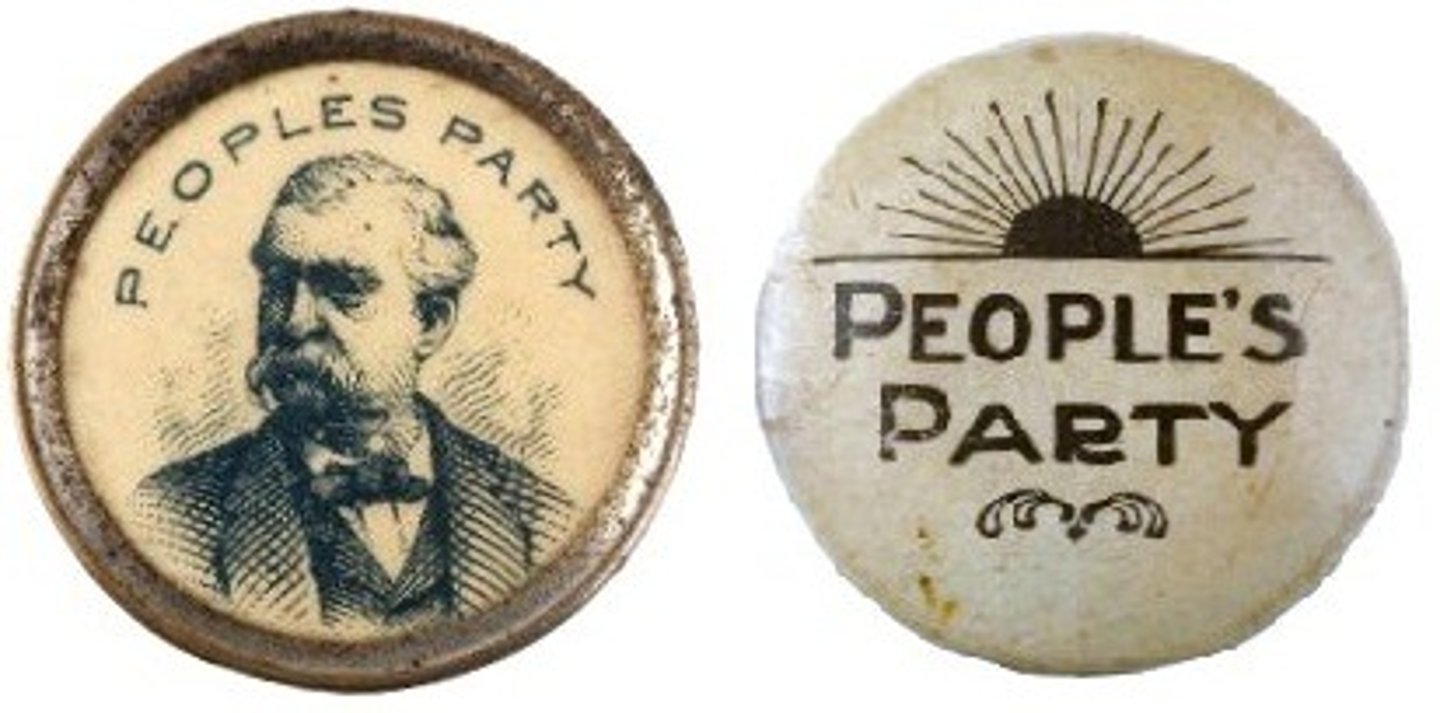

William Bryan Jennings
Populist Leader, democratic candidate, writes crossing of gold speech; prosecutor in the "Scope's Monkey Trial"
