Vas week 2 : Waveforms exercise
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
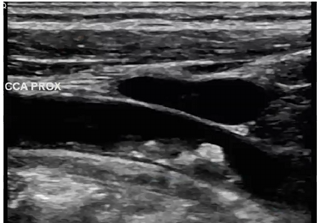
We can describe plaque as
Select two sonographic characteristics
Irregular
heterogenous
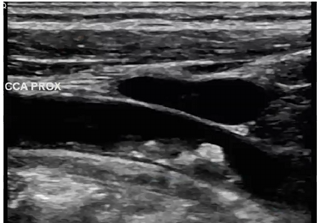
In this image, what structure is anterior to proximal CCA
portion of the IJV
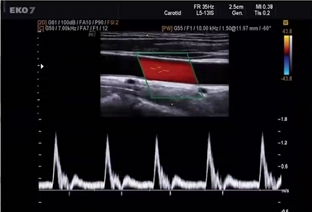
Pt presents with c/o syncope. you obtain this waveform in CCA. is waveform normal? does this waveform help explain pt symptoms
it is normal
No because there is nothing wrong here. Syncope is a posterior circulation problem while the CCA has nothing to do with posterior circulation
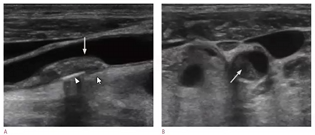
identify 3 sonographic characteristics to describe plaque
smooth
slightly heterogenous
calcification posterior wall
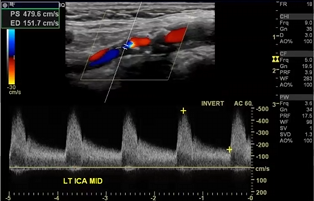
considering velocities and plaque,
where will we find tardus parvus waveform
Mid to distal ICA (will always be distal to the stenosis)
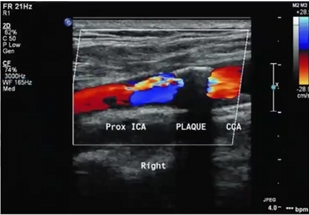
How would you describe this plaque
calcified
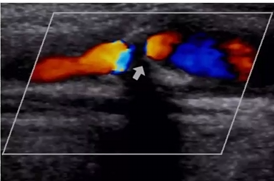
study color flow just distal to shadowing produced by calcified plaque. what is occurring with color? what is a cause for this color finding and possible diagnosis? can we make this diagnosis with color doppler only? how will we confirm what we believe is occurring with color doppler?
Aliasing
speeds exceeding Nyquist limit, stenosis
No, we need speed measurements
use PW to walk the sample gate through narrowing to find the peak velocity. then get velocities proximal, distal and at return to laminar
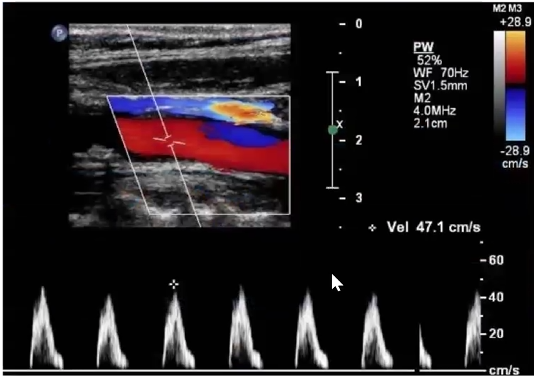
Pt admitted with stroke symptoms. Carotid ultrasound ordered and you obtain this image of cca.
is this a normal carotid artery waveform? why or why not.
what does this waveform indicate?
does this finding explain patient stroke symptoms?
no it is not because there is no end diastolic flow.
That there is an obstruction distal to this sample. this is a pre stenotic waveform
distal obstruction
yes it does
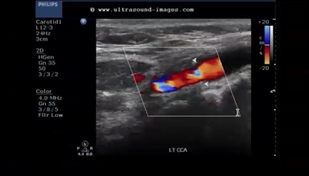
After reviewing image, please answer following questions:
what is the white arrows indicating
which sonographic terms will you use to describe?
how will you optimize image?
how will you determine if plaque is hemodynamically significant?
if plaque is hemodynamically significant, where will we find a tardus parvus waveform?
Plaque
heterogenous, and smooth
steer color box in the right direction, decrease the depth, open up the vessel
walk sample gate through narrowing and find the highest PSV. then grab velocities at prox, distal, and return to laminar
distal to the narrowing or stenosis. beyond the sample valume