Research
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Gaining Stream
Groundwater recharges stream
Losing Stream
Stream recharges groundwater
Characteristics of a healthy stream
Flows retain much of their natural quantities and variability
Sediments eroded and re-deposited
Substrate, water temp and water quality remain within normal ranges
Streams are connected…
Longitudinally from source to mouth
Laterally with riparian zones, floodplains, and landscapes
Vertically with groundwater sources
What characteristic of a stream often determines the velocity of its currents?
The slope or gradient
Reach
A section of stream with several runs, pools, and riffles
What does sediment deposition form along inner banks of streams?
Point bars
Sinuosity
The amount of curving or bending occurring in a stream (Channel distance/straightline downvalley distance)
Riffles
Areas of turbulent water
Examples of primary producers growing on rocks and rubble in streams
diatoms
cyanobacteria
green algae
water moss
Algae that grows on other algae is called
Epiphytic
Runs
Habitat areas that lead into or out of riffle areas
Pools
areas where the water has slowed down, containing much of the organic matter and sediments (areas of decomposition)
Substrate types from smallest to largest
clay < silt < muck < sand < gravel < cobble < boulder
Sites with the greatest heterogeneity of substrates have the
highest diversity of macroinvertebrates
Sandy bottom areas are low in production because they offer little
Substrate for the periphyton
Solid bedrock is directly exposed to currents thereby
Limiting the number of organisms that can remain attached
Gravel and cobble bottoms which are associated with fast streams support the most abundant life because
They have the greatest surface area for periphyton
They provide stability and protected areas for insect larvae
Embeddedness
The extent to which rocks (gravel, cobble, boulders) and snags are covered or sunken into the silt, sand or muck of the stream bottom
The more embedded, the more ___ the living conditions of creatures
unavailable
Observations of embeddedness should be taken in the ___ and ___ portions of riffles
Upstream and central
Hyporheic zone
The zone between the stream water and the groundwater
In slow water, rather than periphyton, what is the primary producer?
Phytoplankton
The basin or watershed of a stream can also be called the
Catchment
Ohio Ecoregions
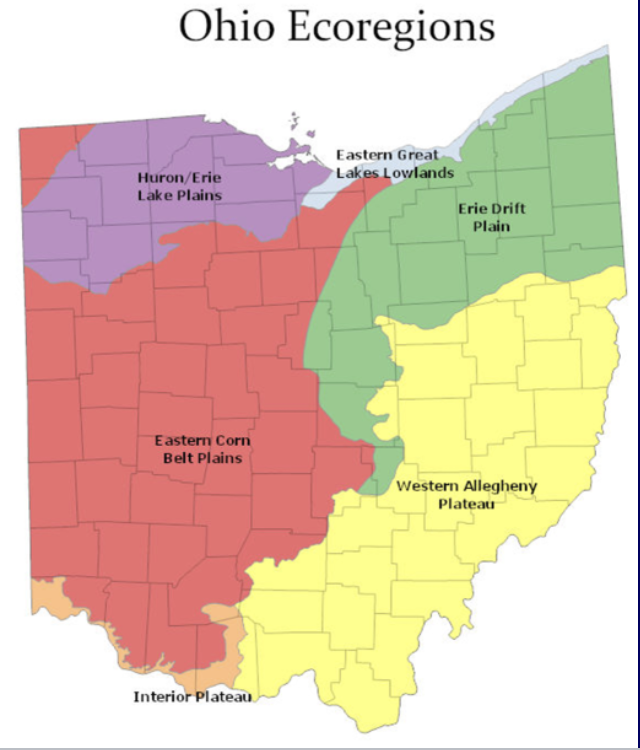
HELP
Huron/Erie Lake Plains
EGLL
Eastern Great Lakes Lowlands
ECBP
Eastern Corn Belt Plains
WAP
Western Allegheny Plateau
IP
Interior Plateau
Older name for Erie Drift Plain
Erie/Ontario Lake Plain