BIOMG 3310 Quiz 1 - QUICK STUDY
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Glycine, Gly, G
Aliphatic (non-polar)
Most simple, optically inactive
Hydrogen for R
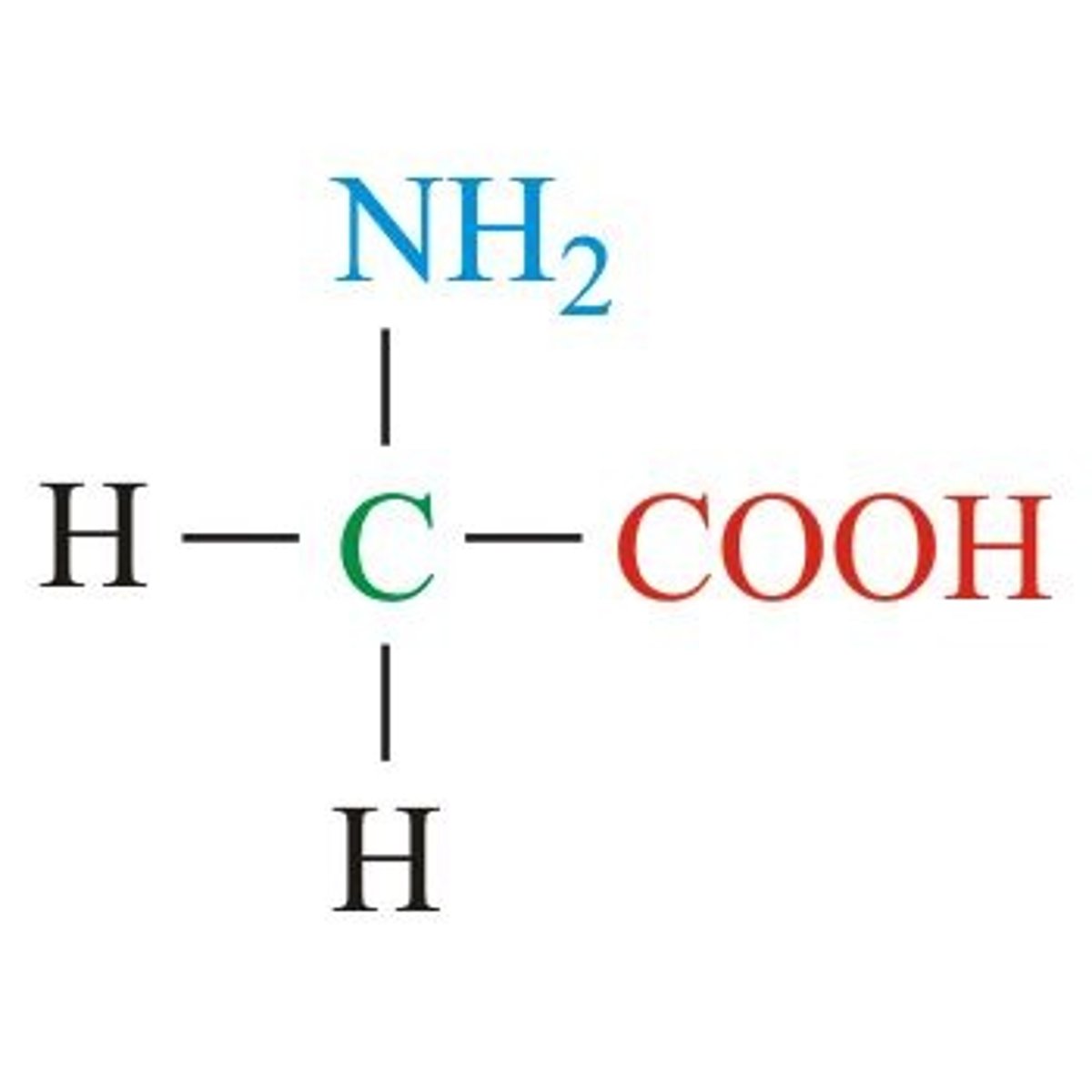
Alanine, Ala, A
Aliphatic (non-polar)
Methyl for R, a simple functional group to start just like "A" starts alphabet
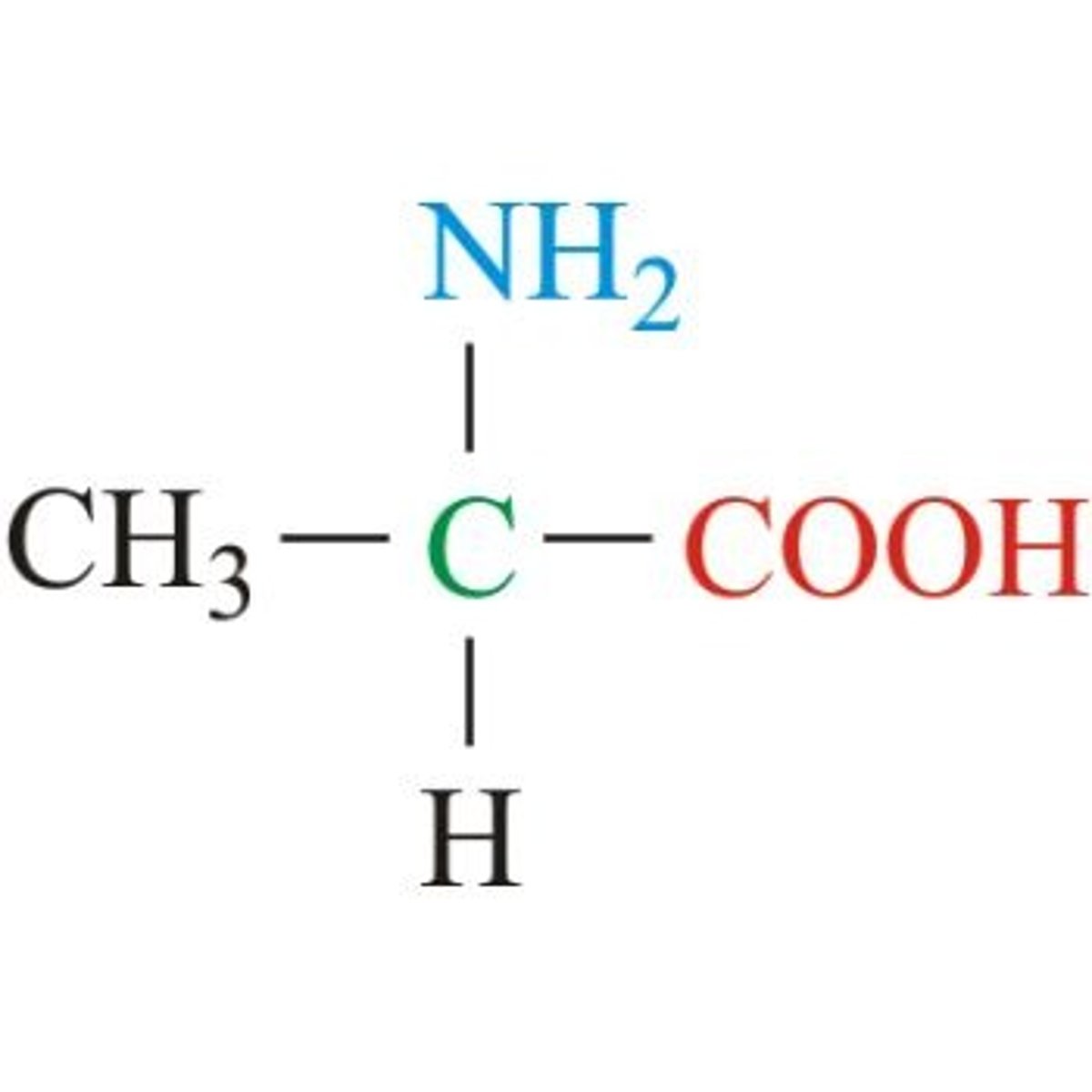
Valine, Val, V
Aliphatic (non-polar)
Simple, R shaped like a V
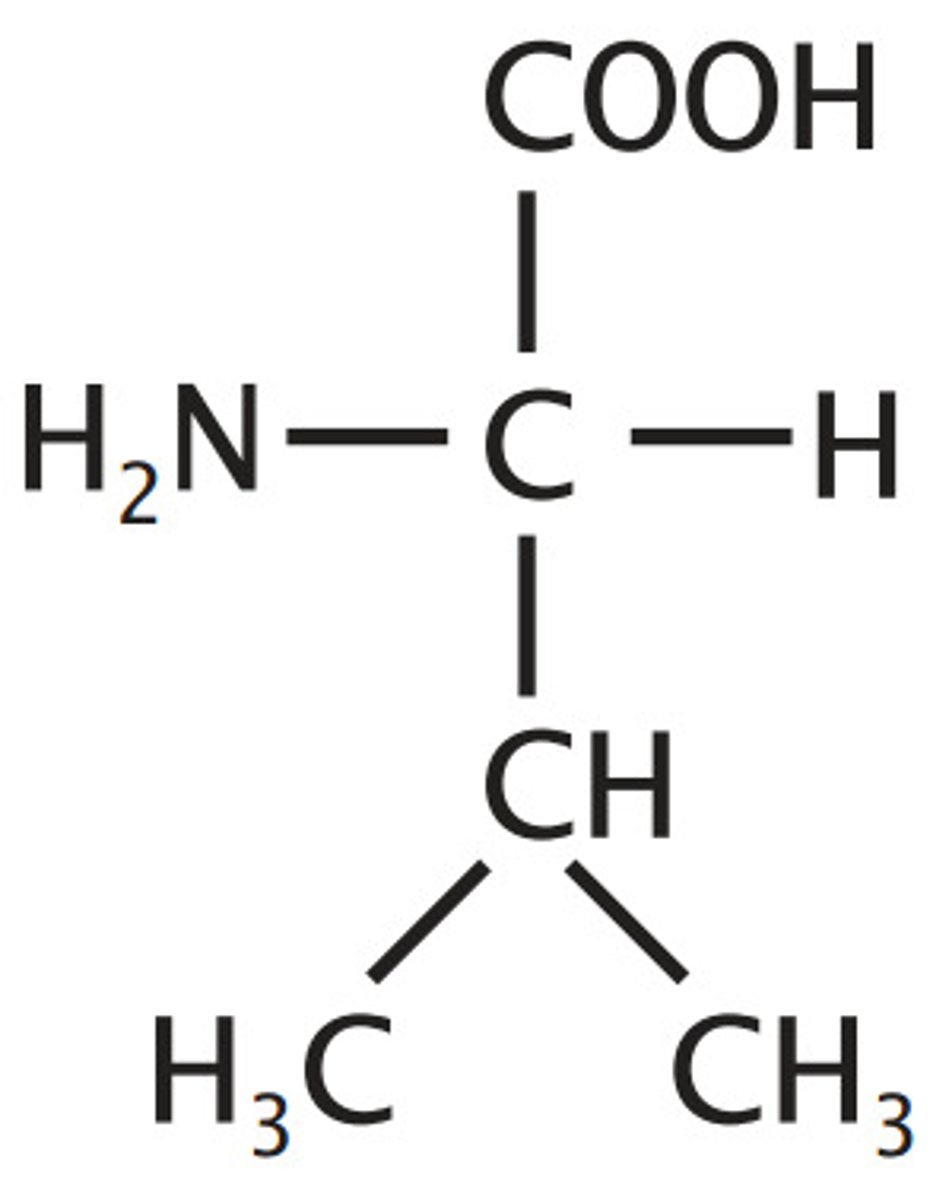
Leucine, Leu, L
Aliphatic (non-polar)
Valine extended with one methyle
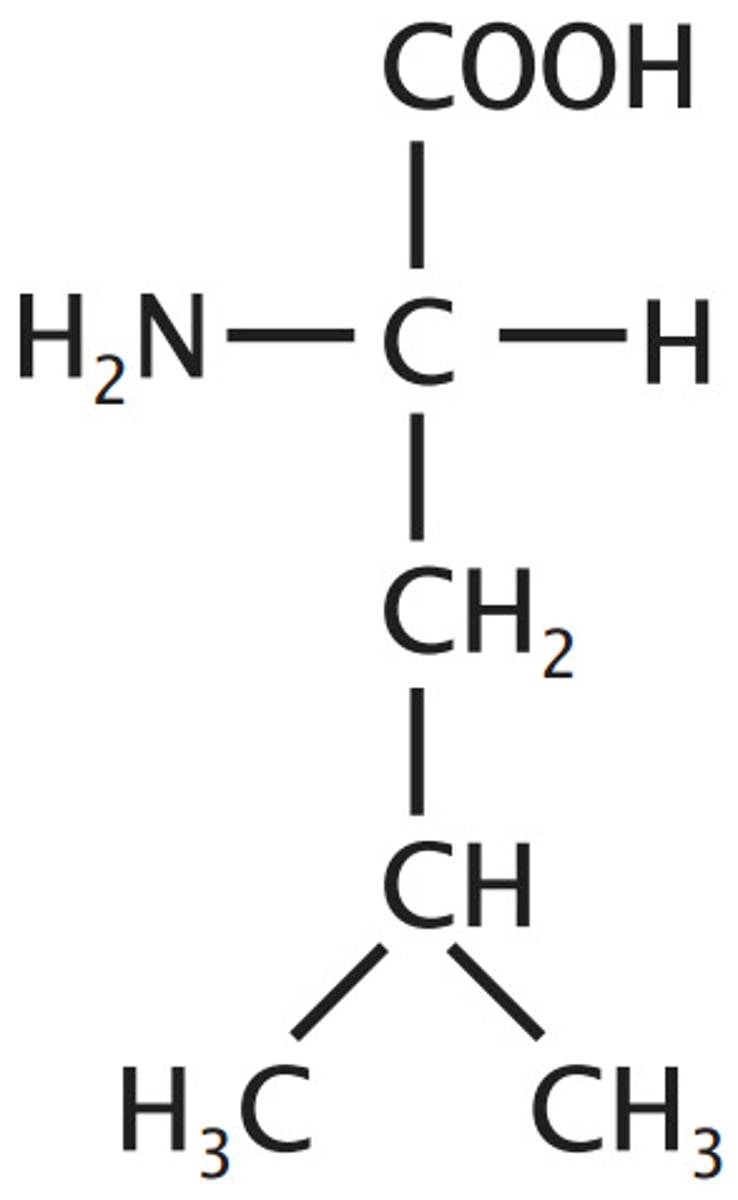
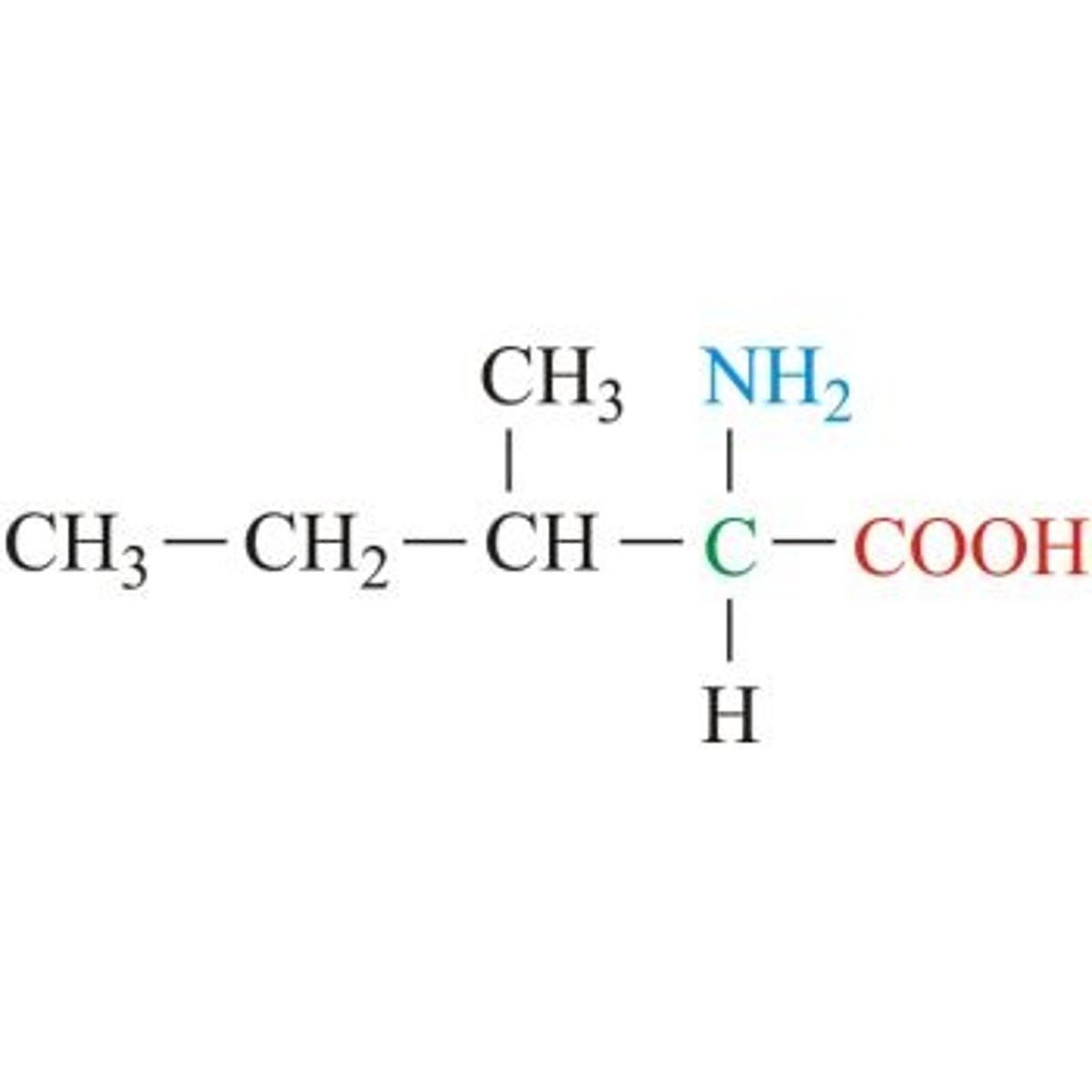
Isoleucine, Ile, I
Aliphatic (non-polar)
"Lopsided Valine"
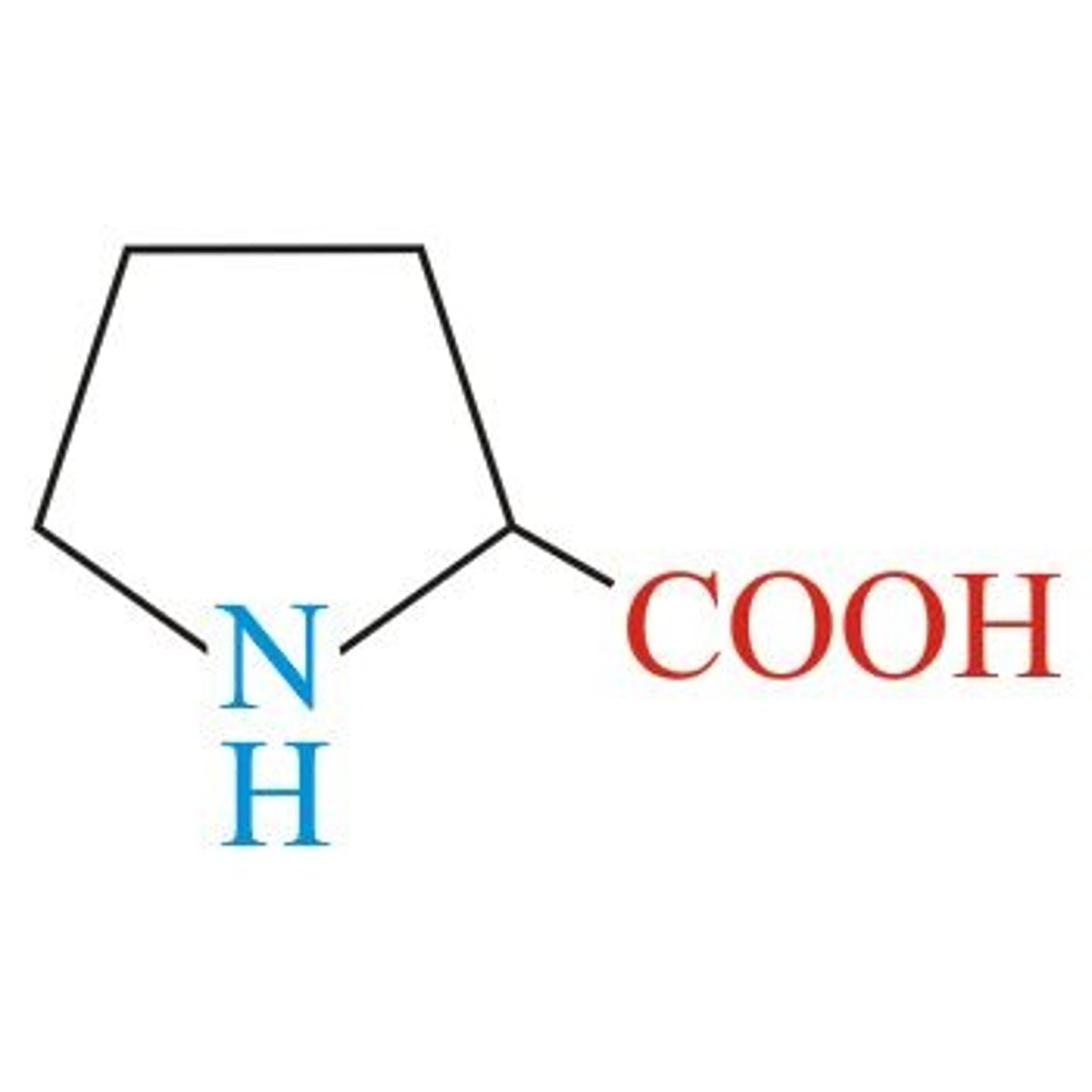
Proline, Pro, P
Aliphatic (non-polar)
3 Carbon chain to N
Special Structure found in turns
Ring-stacking!
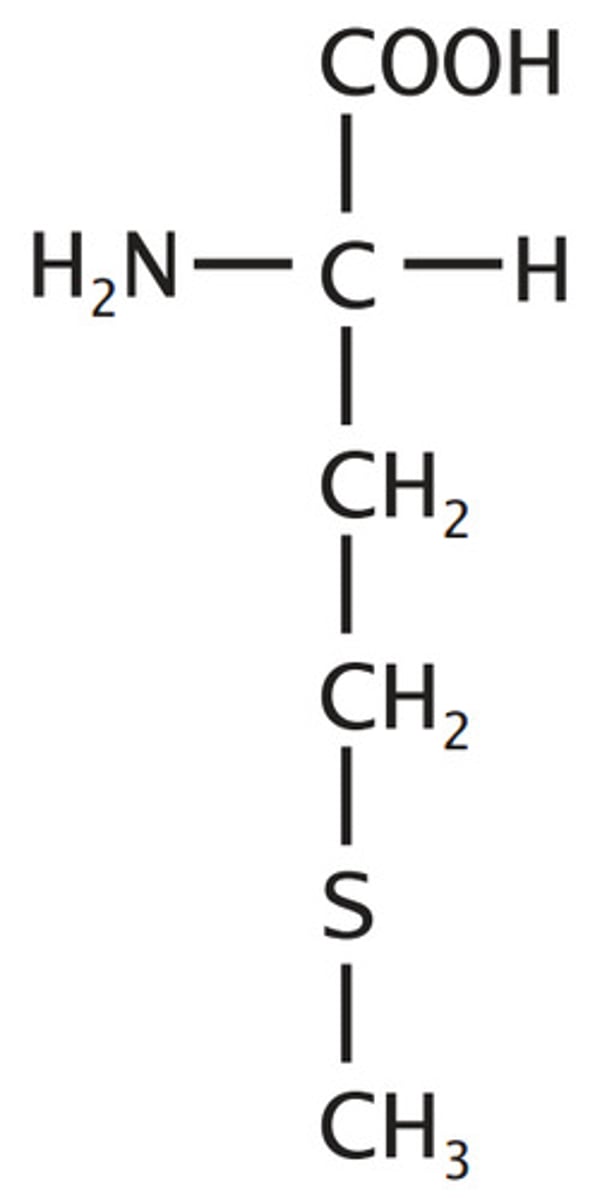
Methionine, Met, M
Sulfur Containing
Starts every protien
3 Carbons with a thioether
methyl blocked sulfhydryl
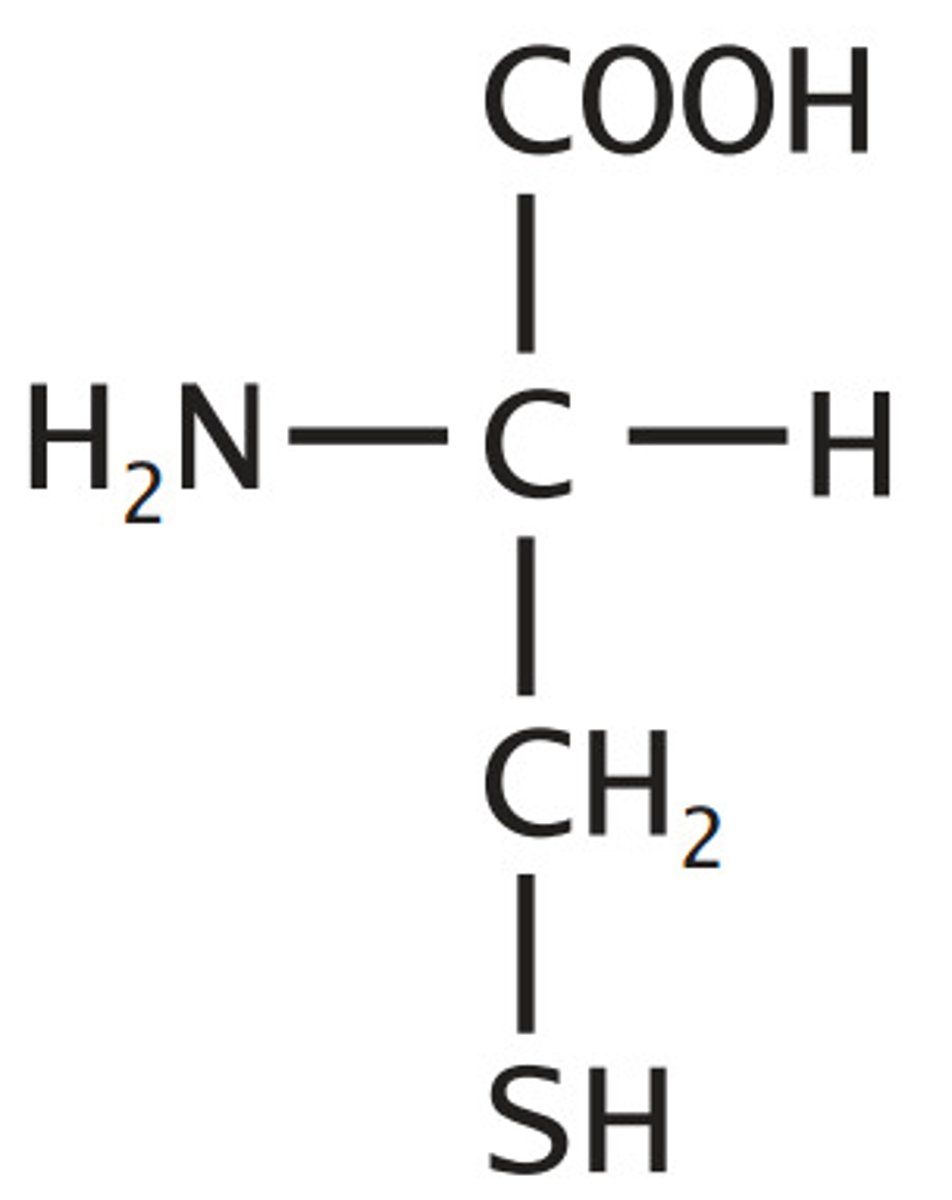
Cysteine, Cys, C
Sulfur Containing
Sulfhydryl alanine
reactive, can form disulfides
Ionizable Group (-/neutral)
Phenylalanine, Phe, F
Aromatic
Alanine with phenyl group
y reminds of aromatics
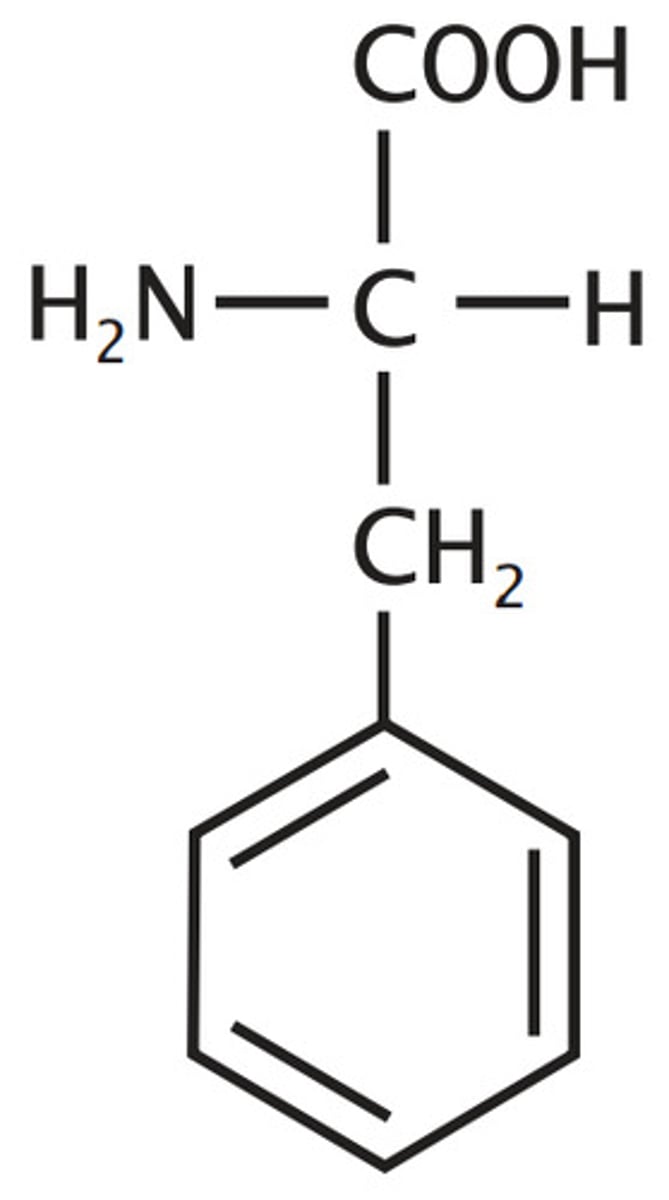
Tyrosine, Tyr, Y
Aromatic
hydroxylated
phenylalanine, one of 3 "T"s
that has "Y" in its name so it is an aromatic
Ionizable Group (-/neutral)
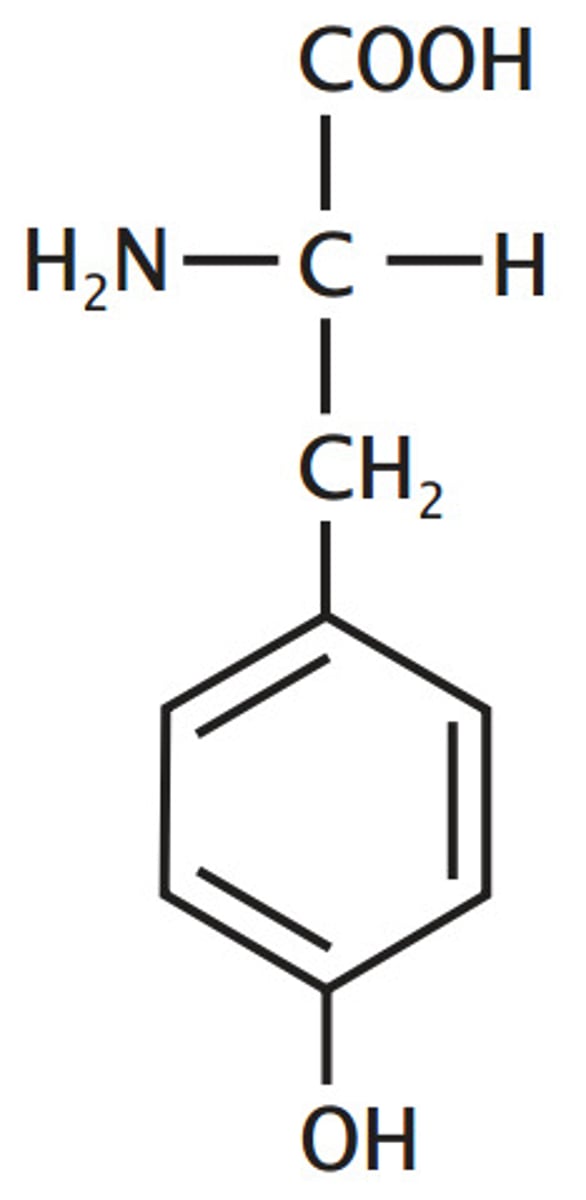
Tryptophan, Trp, W
Aromatic
one of 3 "T"s with a "Y" so it is aromatic, will
"tryp" you up because it is hard to remember,
has a 3 carbon start to N (or indole ring on methylene)
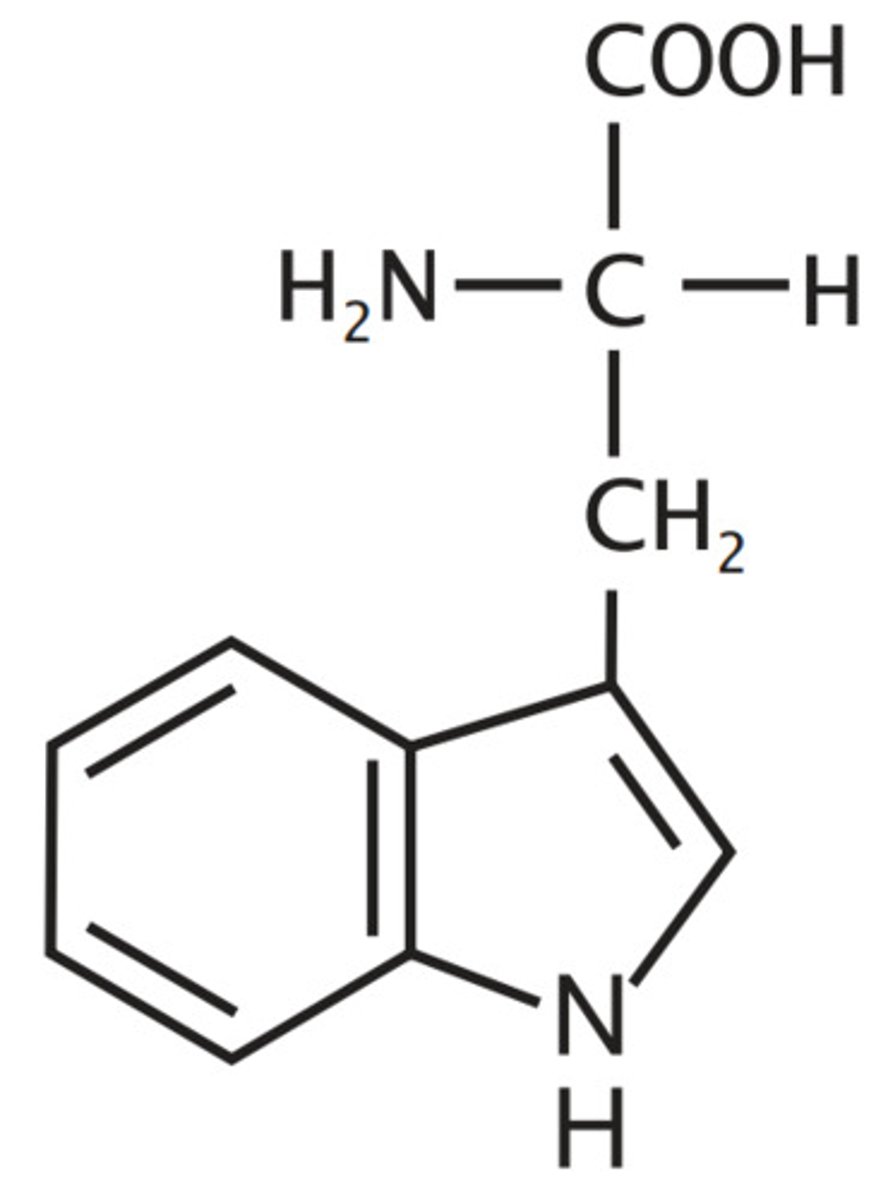
Serine, Ser, S
Aliphatic hydroxyl
"hydroxyl alanine"
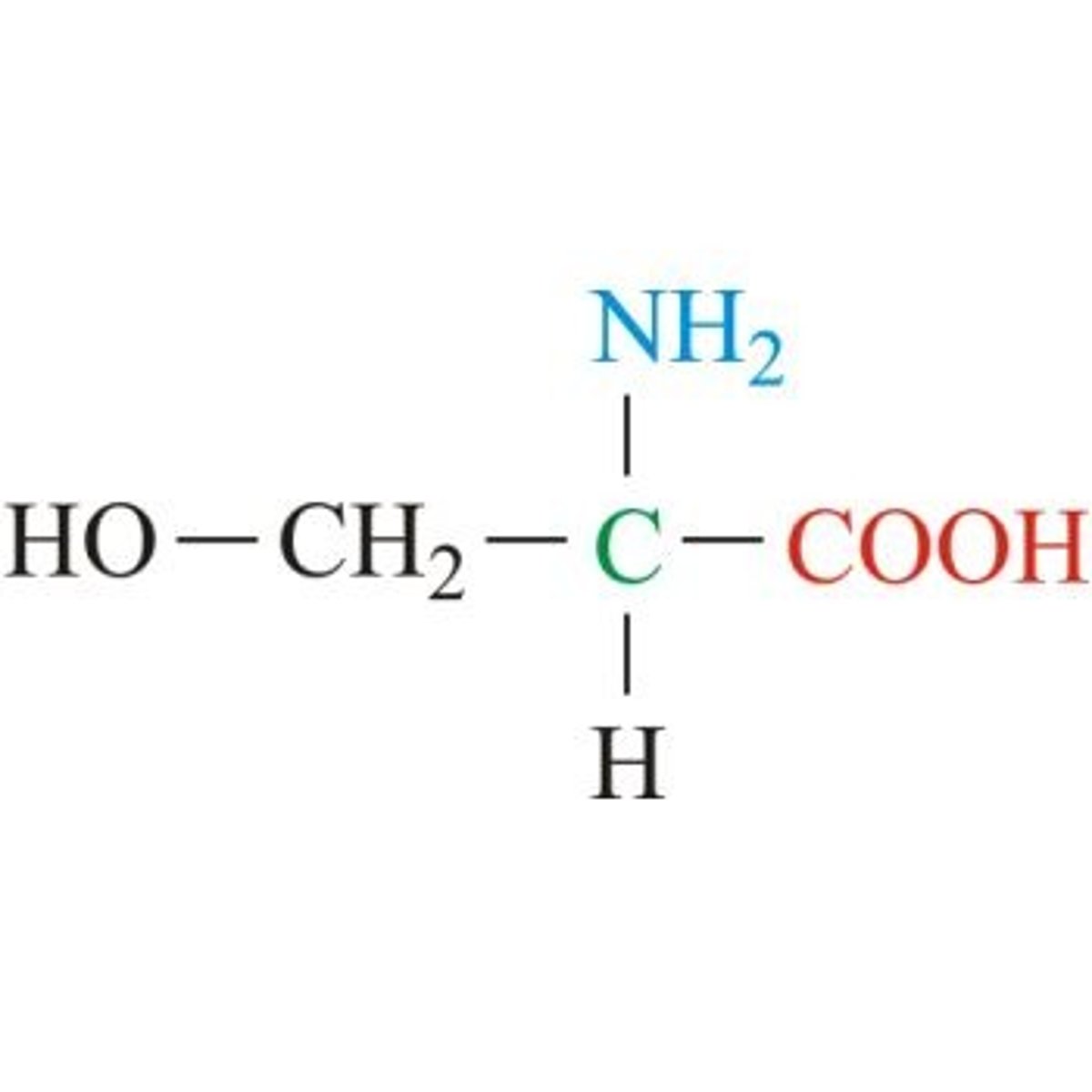
Threonine, Thr, T
Aliphatic, "threo" parts are methyl, hydroxyl, and hydrogen on a single C
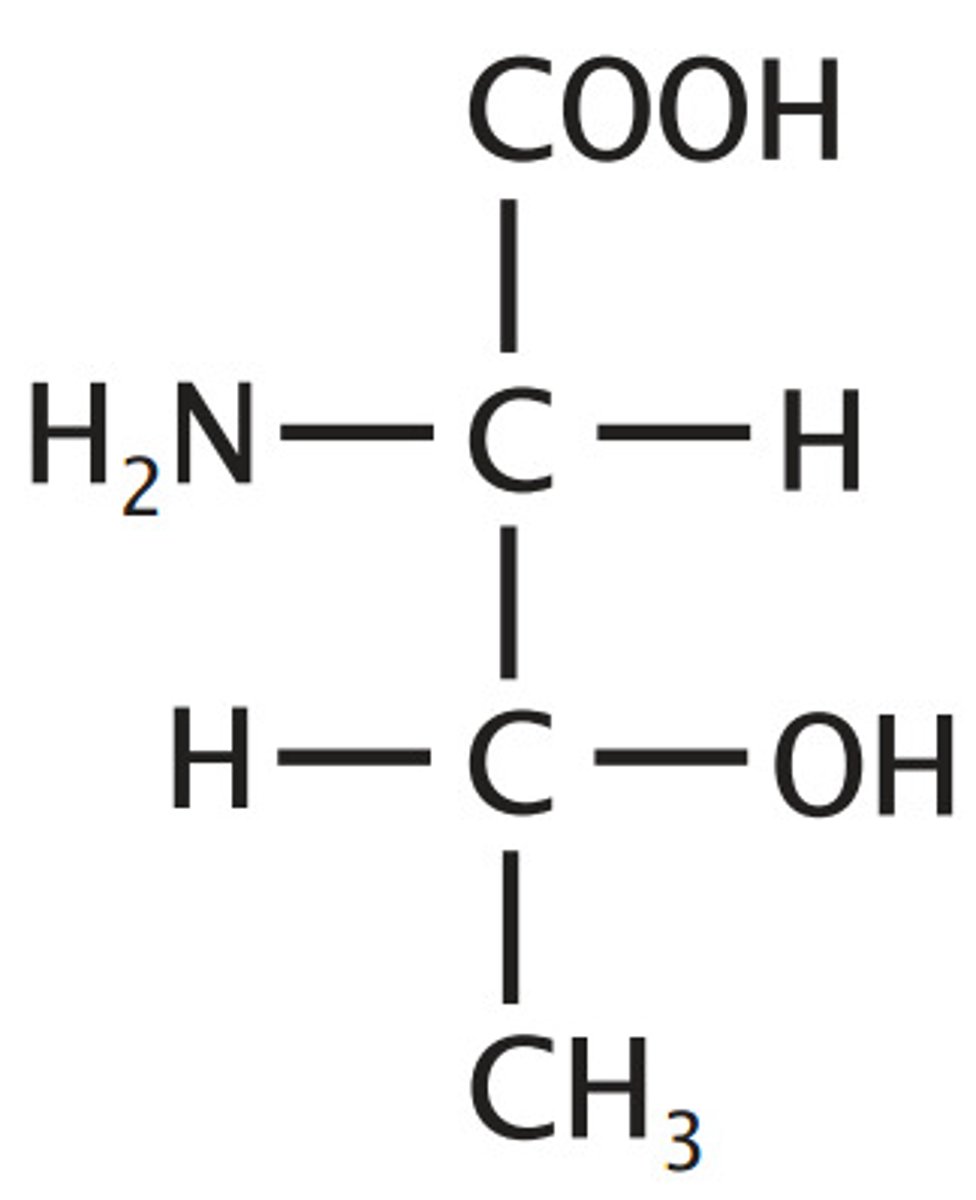
Aspartate, Asp, D
Acidic
"carboxyl alanine"
"ate" -> acidic
Ionizable Group (-/neutral)
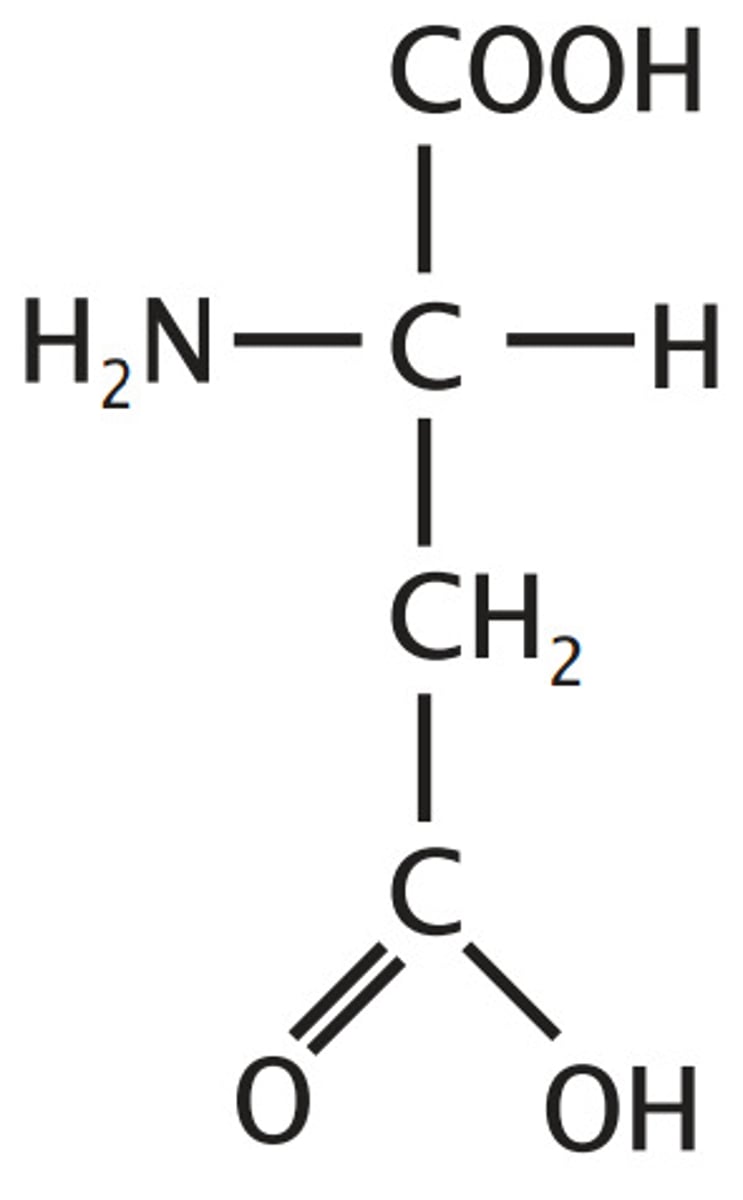
Glutamate, Glu, E
Aspartate plus one methylene, side chain length is signified by alphabetical ordering of the first letter in the names (G is after A)
Ionizable Group (-/neutral)
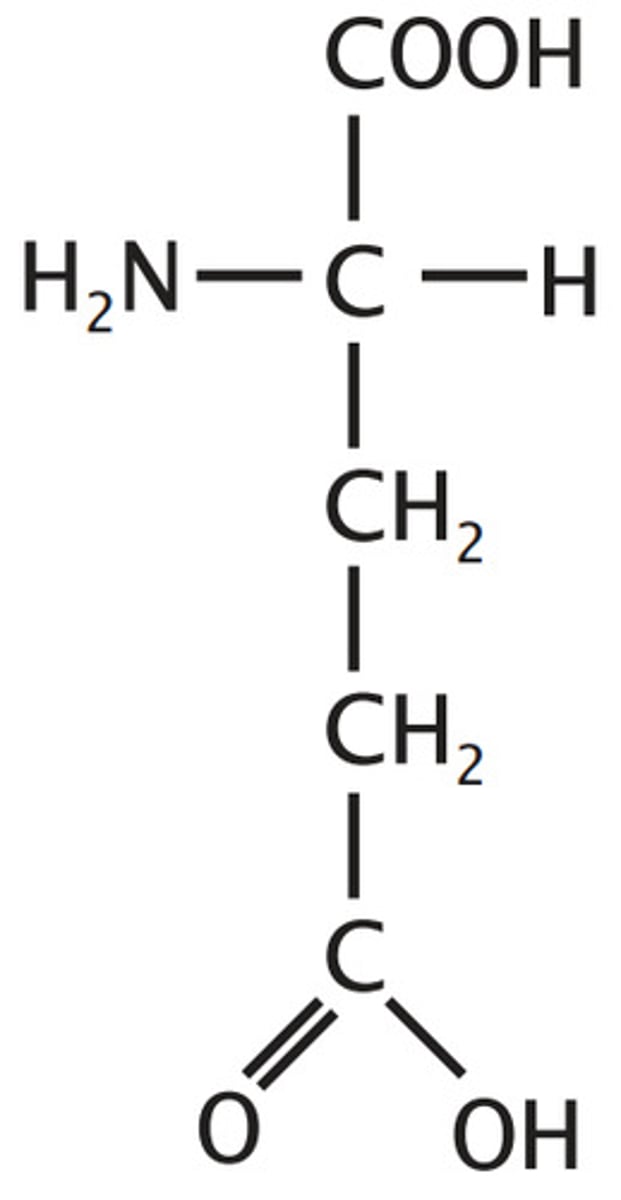
Arginine, Arg, R
Basic
3 carbon chain linked to a C full of only N's (no H's & C has 4 bonds) through an N
Ionizable Group (neutral/+)
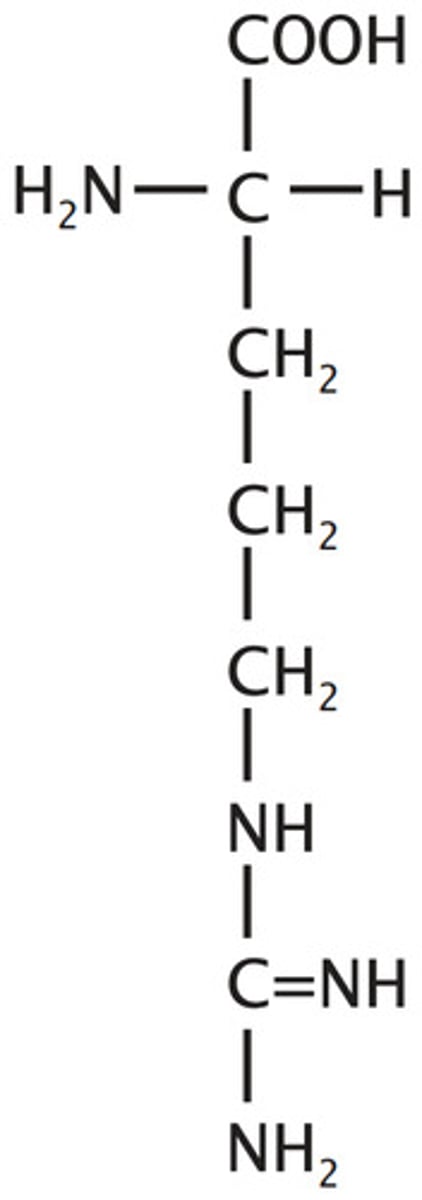
Lysine, Lys, K
Basic
3 carbon chain plus one methylene to amino, it lies ("Lys") about the 3 carbon trend
Ionizable Group (neutral/+)
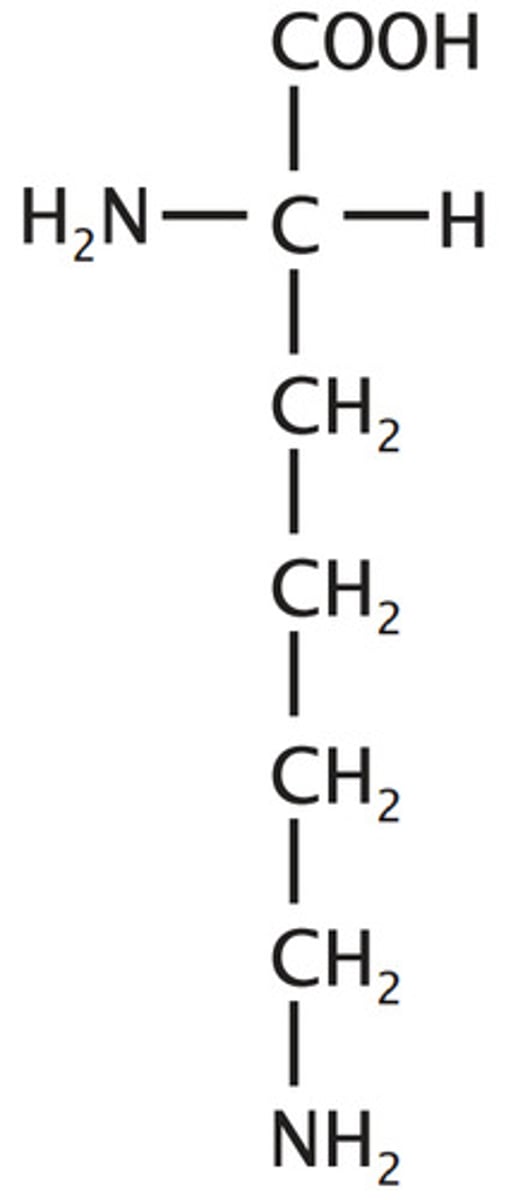
Histidine, His, H
Basic
3 carbons to N and loop back through C 'n' N
Ionizable Group (neutral/+)
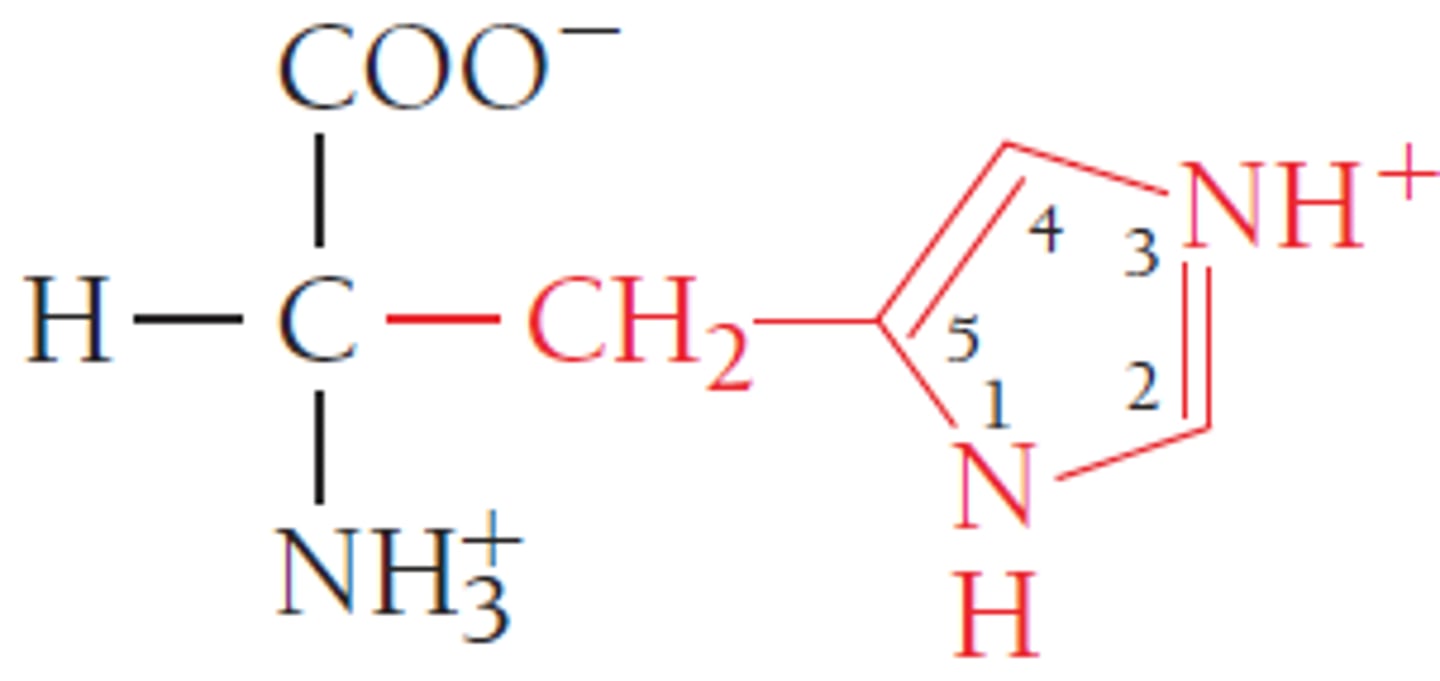
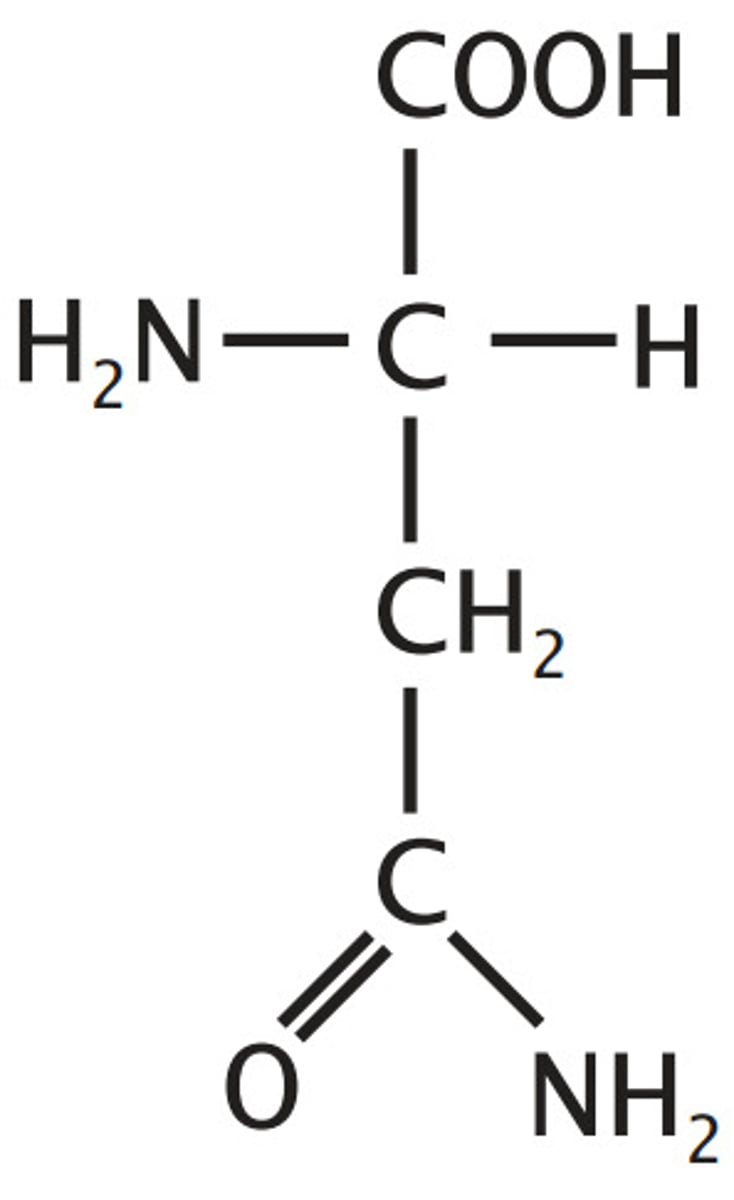
Asparagine, Asn, N
Amide derivatives of acids - loose OH for NH2 to loose charge
amide derivative of aspartate
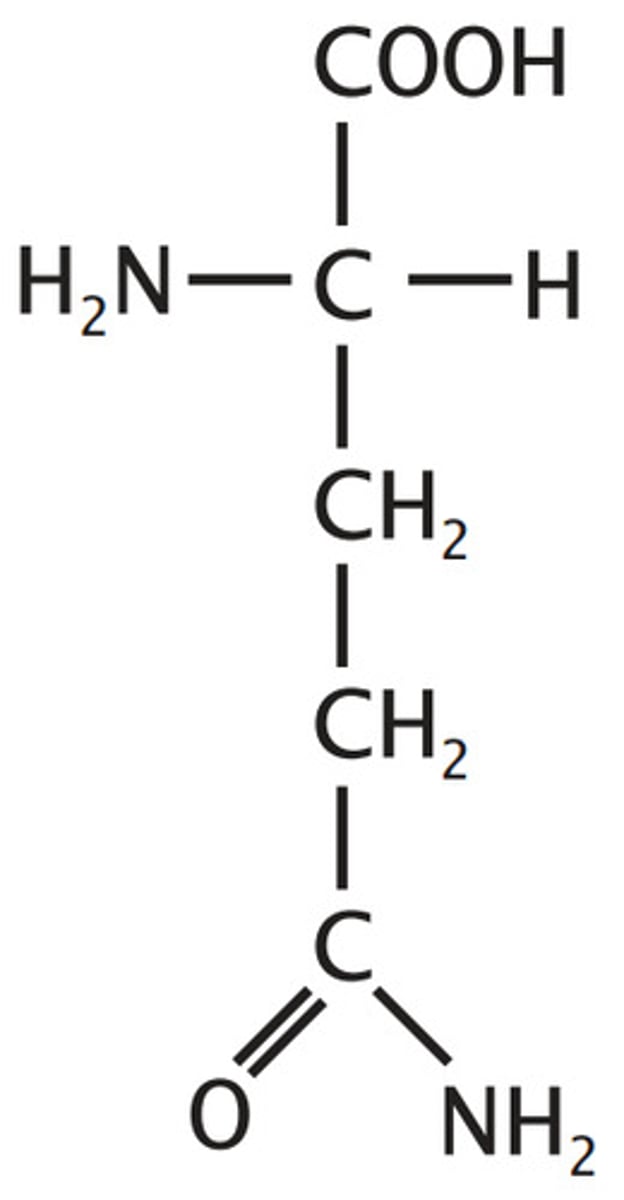
Glutamine, Gln, Q
Amide derivatives of acids - loose OH for NH2 to loose charge
amide derivative of glutamate
What are the four main categories of biomolecules?
- Lipids
- Carbohydrates
- Nucleic Acids
- Proteins
Why did natural selection result in metabolic reactions that are too slow for life?
So they can be controlled and/or regulated by catalysts.
Compare the size scale of biochemistry relative to the universe.
Biochemistry: Atoms/chemistryUniverse: Measured in lightyears
Explain why humans and plants need each other to exist.
Interdependent processes of human metabolism (produces CO2 and H2O) and plant photosynthesis (produces carbs and O2).Plants need CO2 and H2O; humans need carbs and O2.
Compare the conditions of Earth and the core of a star. Justify why one is suitable for nuclear fusion and the other for chemical bond formation.
Earth isn't as hot as the core of stars so the temperature is suitable for chemical bond formation, whereas the hot temperature at the core of stars allows nuclear bond formation.
Justify the truth of the statement, "We are made of stardust".
Nuclear fusion in star cores produces the lighter elements that we are made of, such as hydrogen.
Memorize the equation that expresses pH in terms of [H+].
pH = -log10 [H+]
Memorize the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation in both log and inverse log forms.
10^(pH - pka) = [unprotonated/protonated]
Determine the dominant charge form of an ionizable group, given its pKa value and the pH.
pH < pKa → protonated
pH > pKa → unprotonated
pH = pKa → equally protonated/unprotonated
Protonated: + / 0 (His, Lys, Arg)
Unprotonated: 0 / - (Asp, Glu)
Describe the formation of a peptide bond (what specific groups are involved, what are the reactants, and what are the products).
COO- loses an oxygen, NH3+ loses 2 hydrogens. The product is a peptide and H2O
Describe the thermodynamic basis for the hydrophobic interaction (what type of energy is the driving force).
Water entropy is the driving force. If protein is folded, water has more opportunity to make H-bonds with other water molecules. Polar AAs are on outside of folded protein chain, nonpolar AAs are on the inside.
Isozyme/isoenzyme/isoform
From the same organism, catalytically and structurally similar enzymes, but AA sequence is slightly different (example: LDH and CPK)
Define "primary structure" and explain why it is important and what it can be used for
The AA sequence that can be used to eventually determine the 3D shape of a protein.
Define homolog
two genes with sequence similarity, regardless of function, share a common ancestor
Define paralog
related genes in the same species
Define ortholog
genes in different species with clear similarity in sequence and function
Understand why the comparison of primary structures of orthologs provides evolutionary relationships among organisms.
Orthologs descend from a common ancestor but are found in different species, which can help draw connections back to evolution.
Describe bioinformatics.
Uses large datasets to better understand how life works
What is AlphaFold?
It is a protein folding prediction algorithm that represents a significant step forward in protein folding prediction; recent advancements in 3D protein structure prediction.
List three main ways the atomic-level 3D structure of proteins can be determined.
- X-ray diffraction of protein crystals
- NMR of protein dissolved in buffer.
- Cryo electron microscopy
Describe light.
light is an electromagnetic wave produced by an oscillating electric field that produces mutually perpendicular oscillating electric fields and magnetic fields
Describe "the phase problem"
the loss of crucial phase information during a diffraction experiment (like X-ray crystallography), making it impossible to directly determine the structure of a molecule from the measured diffraction intensities alone
What are the six categories of non-covalent interactions?
1. Hydrogen bonds
2. Electrostatic (ion pair, salt bridges)
3. Disulfide bonds (covalent, think cystine)
4. Weak and weakly covalent bonds (ion-dipole, dipole-dipole, and London dispersion forces (van der waals))
5. Ring stacking (w/ Proline!)
6. Hydrophobic Interactions
Hydrogen bonds
form between backbone atoms of the polypeptide chain to stabilize alpha-helices and beta-sheets (secondary structures)
Electrostatic bonds
interaction of amino acids based on their charge
Disulfide bonds (covalent)
tertiary and quaternary structure
cysteine
London Dispersion Forces
stabilize the hydrophobic interior of globular proteins by attracting nonpolar side chains
Dipole-Dipole forces
(alongside hydrogen bonds) attract polar uncharged side chains
Ion-dipole forces
occur between charged amino acids and polar groups or water, contributing to protein folding and function in aqueous environments
Ring-stacking
dipole-dipole interaction between two aromatic groups
Hydrophobic interactions
drive protein folding by forcing nonpolar (hydrophobic) amino acid side chains to cluster in the protein's interior, away from water, creating a stable, hydrophobic core
ionizable groups in amino acids
1. terminal carboxyl group
2. terminal amino group
3. Asp and Glu acids
4. His
5. Cys
6. Tyr
7. Lys
8. Arg
terminal amino
(unprotonated/protonated) = (neutral/+)
terminal carboxyl
(unprotonated/protonated) = (-/neutral)
If pH >>> pKa
H+ is "off" (deprotonated)
If pH <<< PKa
H+ is "on" (protonated)
If pH = Pka
[unprotonated] = [protonated]
rate = 1/2
condensation reaction
forms peptide bond
hemoglobin
tetramer that transports oxygen
myoglobin
monomer that stores oxygen; allows transport of oxygen to mitochondria
prosthetic groups
non-amino acid group covalently bonded to protein
holoprotein
protein with a prosthetic group (the WHOLE protein)
Apoprotein
just the protein itself (no prosthetic group)