ARDMS SPI EXAM LATEST 2024-2025 UPDATE COMPREHENSIVE QUESTIONS AND CORRECT ANSWERS| ALREADY GRADED A+/PASSED 100%
1/577
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
578 Terms
Example of nonspecular reflector
red blood cells
What happens to spatial pulse length when frequency increases?
decreases
Axial resolution is dependent on?
wavelength
Lateral resolution is dependent on?
beam diameter
Where does the beam of an unfocused transducer diverge?
Fraunhofer zone
Reverberation artifacts are a result of
two or more strong reflecting surfaces
True/False: Grating lobes are essential for the proper operation of a linear phased array.
False
True/False: Electronically steered scanners always produce higher resolution images than do mechanically steered scanners.
False
True/False: An annular array scanner uses mechanical beam steering.
True
True/False: A linear sequenced array cannot be dynamically focused.
False
registration or B-mode alignment
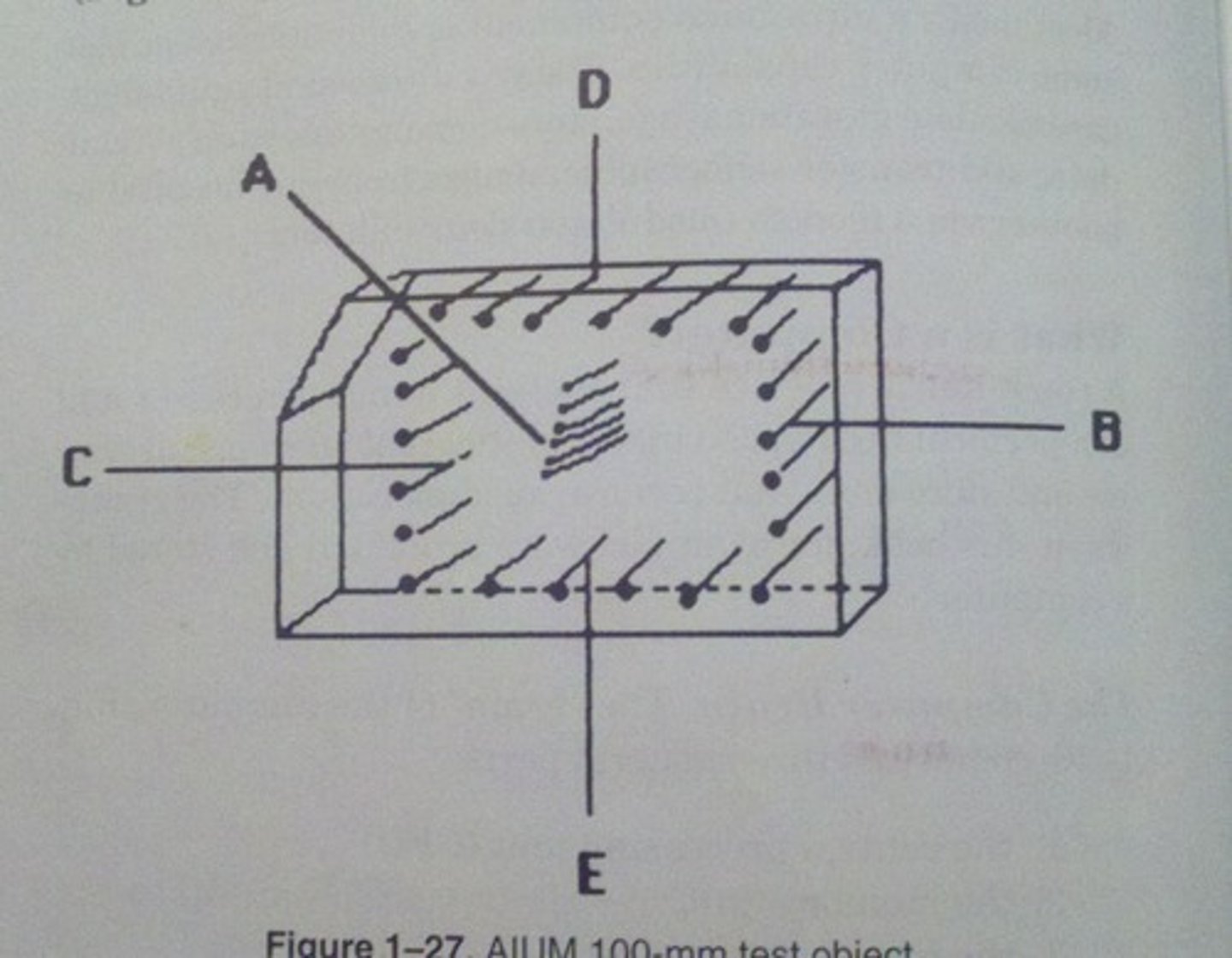
Which AIUM test object function utilizes all the groups of wires in the AIUM 100 mm test object?
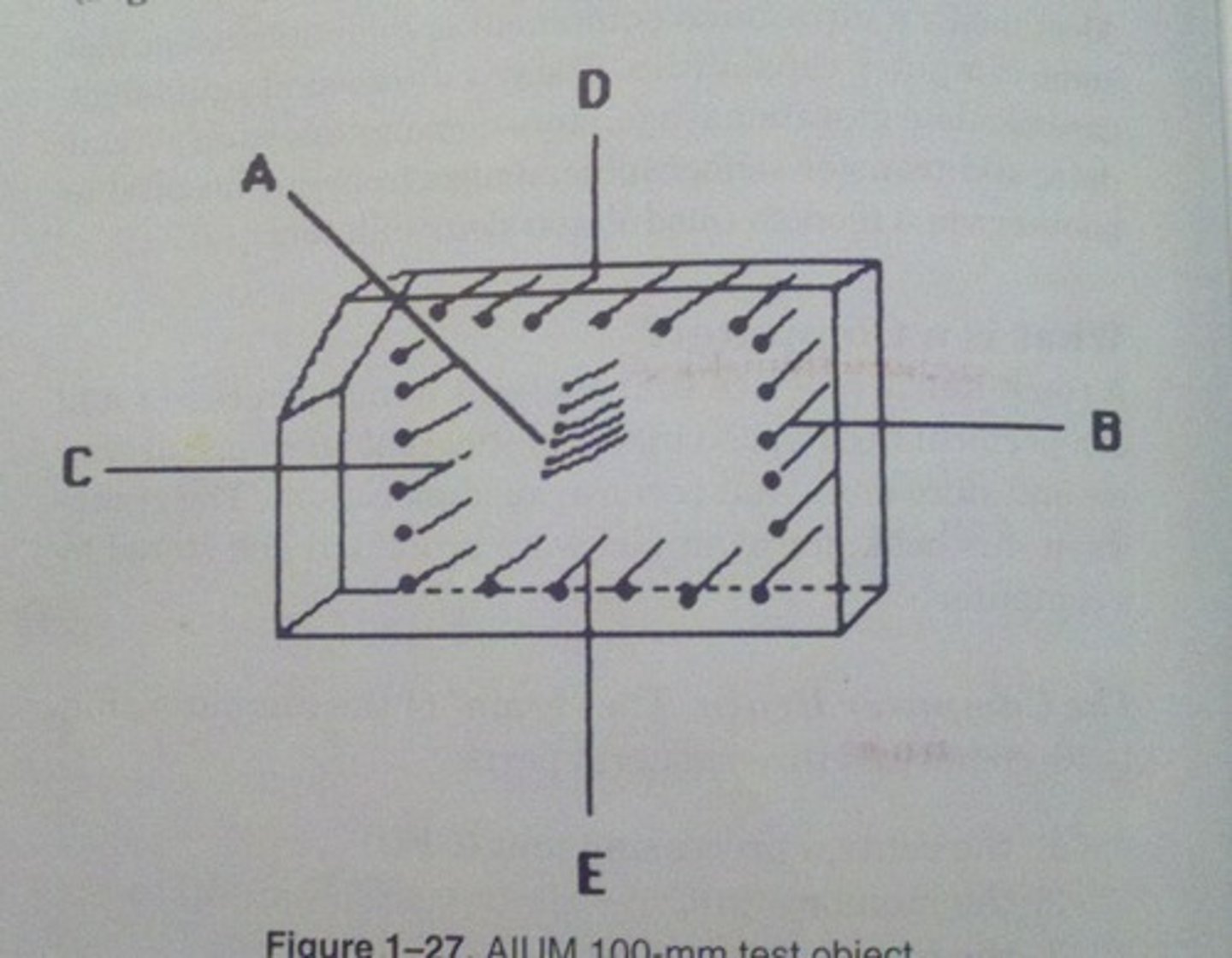
axial resolution
Which AIUM test object function utilizes the A group of wires in the AIUM 100 mm test object?
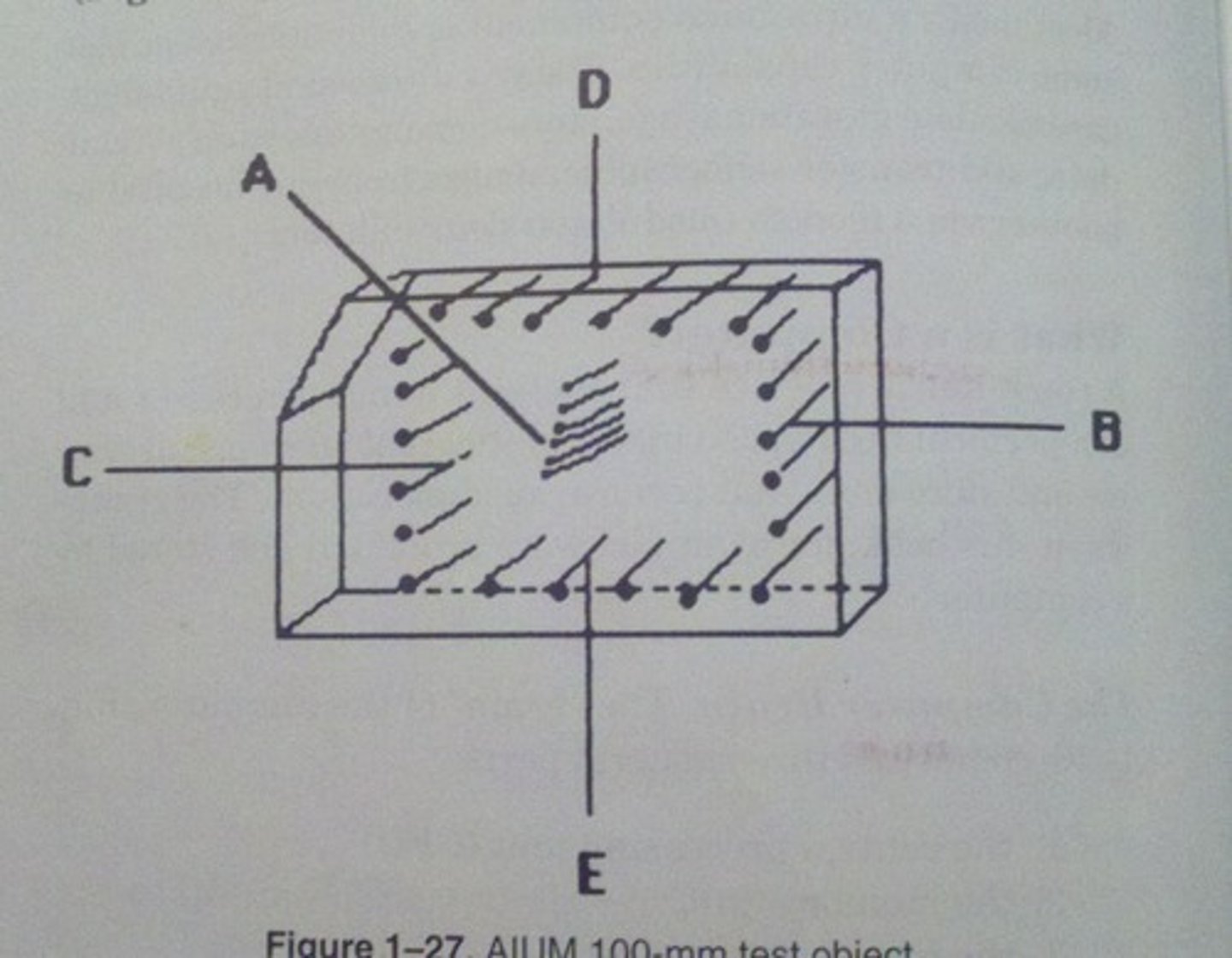
lateral resolution
Which AIUM test object function utilizes the B group of wires in the AIUM 100 mm test object?
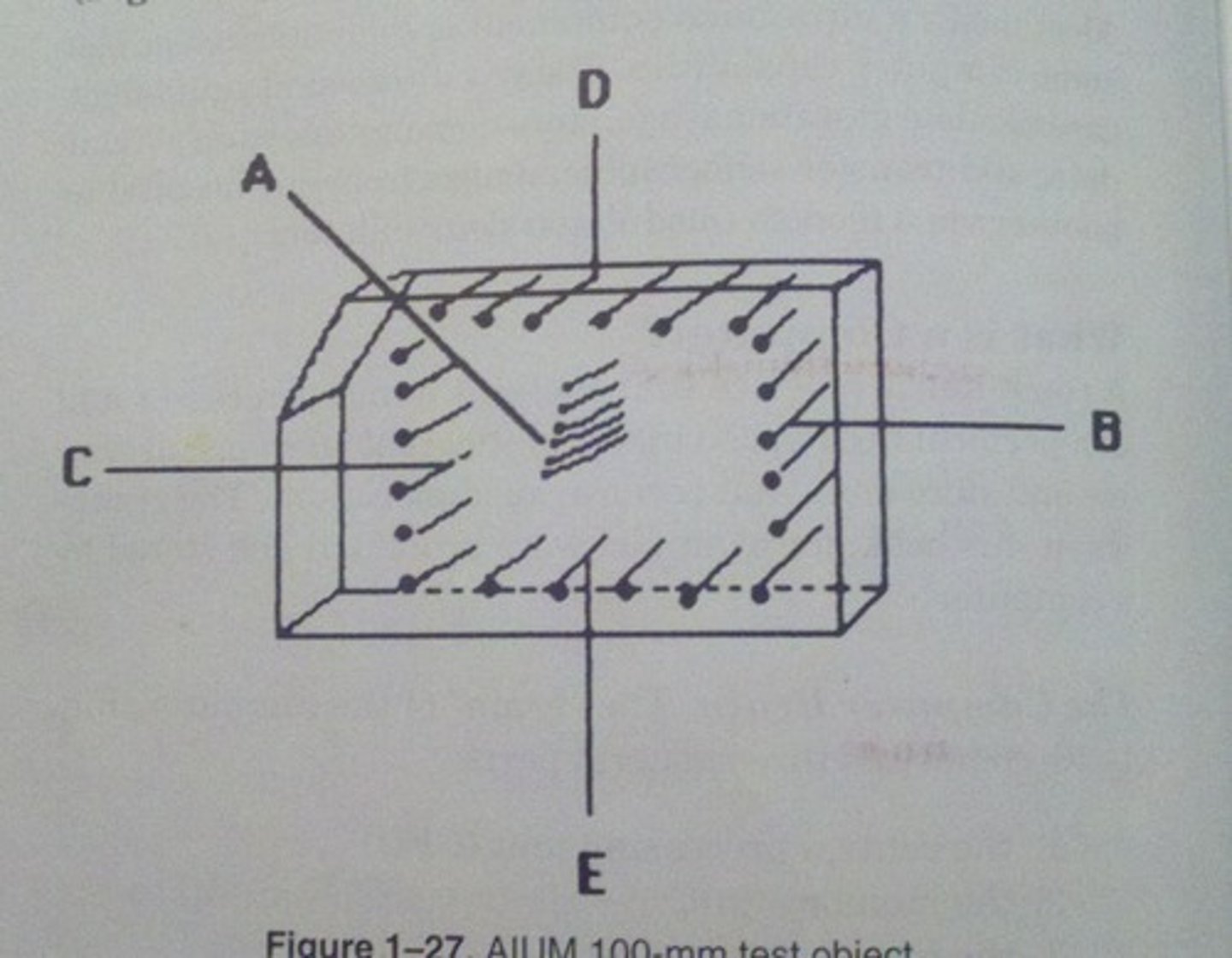
dead zone
Which AIUM test object function utilizes the D group of wires in the AIUM 100 mm test object?
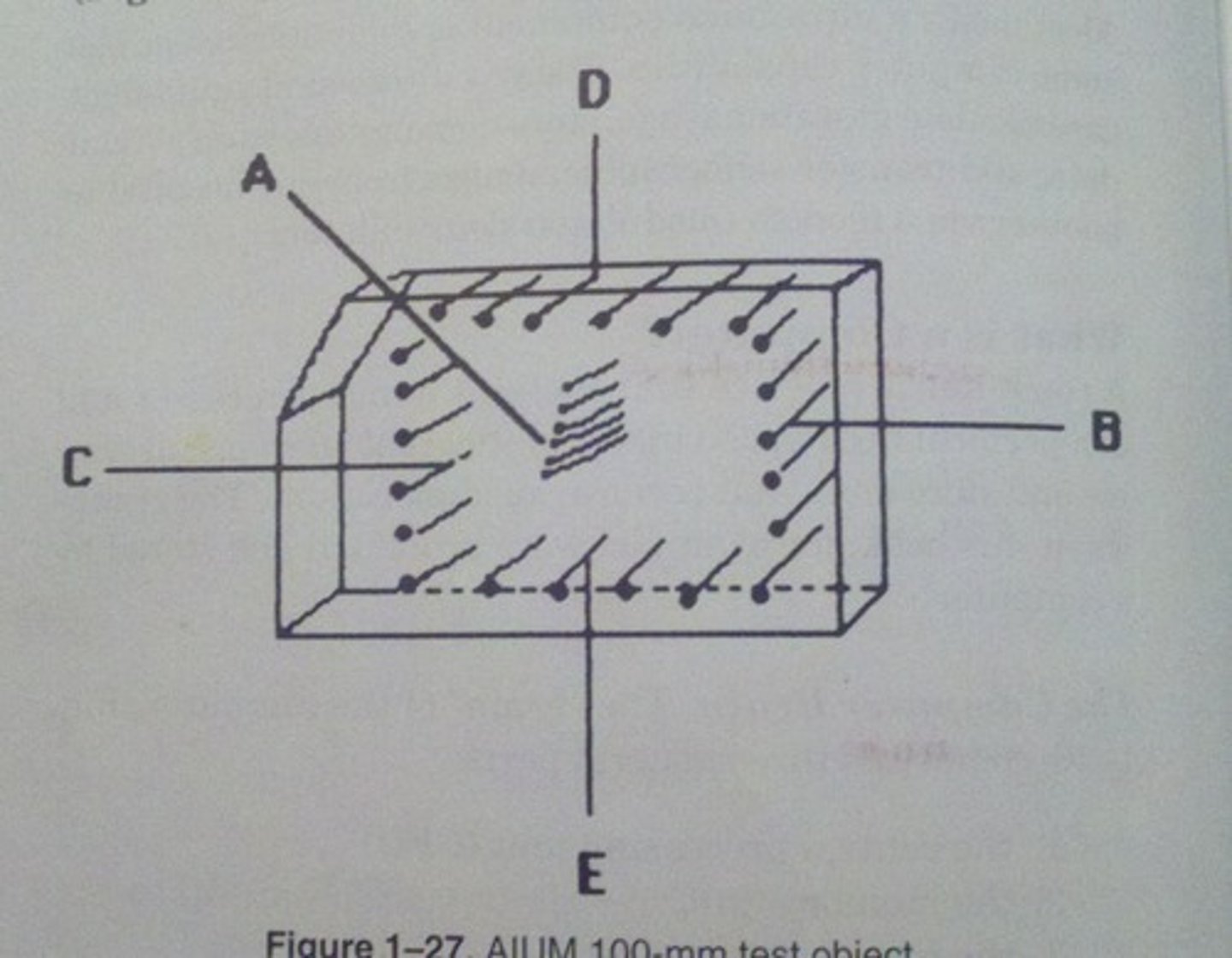
depth calibration
Which AIUM test object function utilizes the C or E groups of wires in the AIUM 100 mm test object?
What happens to axial resolution when spatial pulse length is decreased?
improves
How much will a 3.5 MHz pulse be attenuated after passing through 2 cm of soft tissue?
3.5 dB
Propagation speed errors result in
improper axial position
Enhancement is caused by
weakly attenuating structures
The Doppler shift frequency is
directly proportional to the velocity of the reflector
The number of frames per second necessary for a real-time image to be flicker free is
more than 15
True/False: The SPTA intensity will always be larger than the SATA intensity.
True
The intensity of the ultrasound beam is usually greater at the focal zone because of
the smaller beam diameter
If the amplitude is doubled, the intensity is
quadrupled
The attenuation for soft tissue is
increased with tissue thickness
The acoustic impedance of the matching layer
can be chosen to improve transmission into the body
True/False: In a pulse-echo system, the quality factor should be made as large as possible.
False
True/False: The beam diameter is constant in the near zone.
False
The operating frequency is dependent on
thickness of the crystal
The period of an ultrasound wave is
the time of one wavelength
The dynamic range of a system is
the ratio of smallest to largest power level that the system can handle
True/False: The intensity of an ultrasonic beam can be measured with radiation force balance.
True
Increasing the pulse repetition period
increases the maximum depth that can be imaged
Ultrasound bioeffects
are not confirmed below 100 mW/cm² SPTA
True/False: No refraction can occur at an interface if the media impedances are equal.
False
True/False: Smaller transducers always produce smaller beam diameters.
False
True/False: The ultrasound beam profile can be measured with a hydrophone.
True
True/False: The pulsed-Doppler system yields better depth resolution than the continuous wave (CW) system.
True
True/False: The gray-scale display was made possible when digital scan converters replaced analog scan converters.
False
True/False: Videotape recorders operating at 30 frames per second cannot be used with mechanical real-time units because the fram rate is too slow.
False
True/False: Linear phased array scanners need no form of mechanical focusing because focusing is performed electronically.
False
True/False: The fram rate of real-time scanners depends on the number of lines used to form the image.
True
True/False: It is not possible to steer an annular phased array electronically.
True
True/False: The near zone length should be kept as short as possible.
False
What percentage of intensity of an ultrasound pulse incident on an interface of 0.25 and 0.75 rayls is reflected?
25%
Axial resolution can be improved by using
higher frequency transducers
When particle motion of a medium is parallel to the direction of a wave propagation, the wave being transmitted is called a
longitudinal wave
The wavelength in a material having a wave velocity of 1500 m/s emplying a transducer frequency of 5 MHz is
0.3 mm
The factor that determines the amount of reflection at the interface of two dissimilar materials is
difference in acoustic impedances
The equation that describes the relationship among propagation, wavelength, and frequency is
λ = c/ƒ
What three things can occur when an ultrasonic beam reaches the interface of two dissimilar materials?
reflection, refraction, mode conversion
The acoustic impedance of a material is
equal to the product of density and velocity
The average velocity of ultrasonic waves in soft tissue is
1540 m/s
True/False: Receiver-angle values in CW Doppler analysis do not influence the final Doppler shift.
False
Refraction occurs because of difference in ______ across an interface between two materials
wave velocity
Reflection factor at an interface between two materials depends primarily on the change in ______ across the interface.
acoustic impedance
The velocity of sound waves is primarily dependent on
medium and mode of vibration
Increasing the frequency of an ultrasonic longitudinal wave will result in ______ in the velocity of that wave.
no change
The change in direction of an ultrasonic beam, when it passes from one medium to another, in which elasticity and density differ from those of the first medium is called
refraction
A long near zone can be obtained by
using a higher frequency transducer
If a 2 MHz frequency is used in human soft tissue, the wavelength is approximately
0.75 mm
The ratio of particle pressure to particle velocity at a given point within the ultrasonic field is
impedance
What is the following formula used to determine?
(2 × velocity of reflector × original frequency) / velocity of sound
Doppler shift frequency
The principle that states that all points on a wavefront can be considered as point sources for the production of sperical secondary wavelets was postulated by
Huygens
A 10 dB difference in signal intensity is equivalent to a _______ difference.
tenfold
The level below which signals are not transmitted through an ultrasound receiver system is the
threshold, negative, reject level
Gray-scale systems typically use _____ as a means of signal dynamic range reduction.
compression
The strength of the echo is related to the height of the deflection on the oscilloscope for the ____ display.
A-mode
What are methods of restricting the dynamic range of the signal?
suppression, rejection, compression
Most of the scan converters currently in use are of the _____ type?
digital
The fraction of time that pulsed ultrasound is actually on is the
duty factor
The ability of an imaging system to detect weak reflections is called
sensitivity
What image shape is produced by a linear sequenced array transducer?
rectangular
The major factor in determining the acoustic power output of the transducer is the
magnitude of the voltage spike
Two primary mechanisms that produce tissue biological effects are
thermal and cavitational
The _____ relates bandwidth to operating frequency.
quality factor, Q Factor
The extraneous beams of ultrasound generated from the edges of individual transducer elements and not in the direction of the main ultrasonic beam are called
side lobes
The product of the period and the number of cycles in the pulse is the
pulse duration
The substance typically used as a matrix on the imaging surface of an analog scan converter tube is
silicon oxide
Specular reflection occurs when
the reflector surface is small and smooth as compared with wavelength
The refractive index of water is slightly altered when a sound beam passes through it, thus causing compression and rarefaction of the water molecules. The phenomenon is the basis for the _____ technique of beam measurement.
Schlieren
Artifacts appearing as parallel, equally spaced lines are characteristic of
reverberation
An increase in reflection amplitude from reflectors that lie behind a weakly attenuating structure is called
enhancement
The amount of dispersion in the far field of an ultrasound beam can be decreased by
using a larger diameter transducer
Longitudinal or axial resolution is directly dependent on
spatial pulse length
The transducer _____ is equal to the ratio of the operating frequency to the frequency bandwidth.
Q factor
The technique that uses an optical system to produce a visible image of an ultrasonic beam is the _____ technique.
Schlieren
Which of the following is the least obstacle to the transmission of ultrasound?
A. MUSCLE
B. FAT
C. BONE
D. BLOOD
blood
The ratio of the largest power to the smallest power that the ultrasound system can handle is the
dynamic range
Ultrasound waves in tissues are called _____ waves.
longitudinal
axial resolution
The row of wires in the middle are used to check

scan C
Which of the diagrams shows correct arm registration?

dead zone
The row of wires on top is used to check?

call for service
While using the AIUM test object to test an articulated-arm scanner you obtain an image similar to scan A. You should

horizontal caliper check
The row of wires on the bottom is used to check for

Which of the following CANNOT be checked when the AIUM test object is scanned from the top only?
A. AXIAL RESOLUTION
B. LATERAL RESOLUTION
C. VERTICAL DISTANCE CALIBRATION
D. HORIZONTAL DISTANCE CALIBRATION
lateral resolution
What parameters CANNOT be evaluated by the AIUM test object?
gray scale, dynamic range
Scanning a test object from three sides without erasing would be used to check
registration
When using the AIUM test object, which of the following should be kept constant for comparisons?
A. OUTPUT POWER
B. TGC
C. REJECT
D. TRANSDUCER MHz & FOCUS
all the above
Which of the following type(s) of ultrasound machine can be used with AIUM test object?
A. LINEAR ARRAY
B. STATIC SCANNER
C. PHASED ARRAY
D. ANNULAR ARRAY
E. SECTOR SCANNER
all the above