3.1 Proton transfer reactions
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Arrhenius idea about acids and bases
The Arrhenius idea about acids and bases states that acids produce hydrogen ions (H+) in aqueous solution, while bases produce hydroxide ions (OH-).
the basic idea of bronsted-lowry theory
acids donate protons and bases accept protons (hydrogen ions)
what is a Bronsted-Lowry acid?
A proton (H+) donor
what is a Bronsted-Lowry base?
A proton (H+) acceptor
conjugate acid-base pairs
the pair of species that differ by the presence and absence of one proton, the one with 1 less will be the acid and will accept protons, their roles are reversed if the reaction is reversed
what is the conjugate acid of a species?
It will have one more hydrogen and +1 more to its charge
what is the conjugate base of a species?
It will have one less hydrogen and -1 from its original charge
difference between alkali and bases?
alkali are bases that dissolve in water to form hydroxide (OH-) while bases are in general substances that give out one H+.
are polyatomic anions bases or acids?
they are bases
is the ammonium ion a base or acid?
it is an acid because it has positive charge
what does amphiprotic mean?
a substance is one which can act as both ta proton donor and a proton acceptor
difference between amphiprotic and amphoteric?
amphiprotic is only within the bronsted lowry definition of acids and bases
amphoteric is a more general, Lewis definition
what does pH measure?
concentration of hydrogen ions
pH curve shape
the equivalence point is at 7pH in standard conditions;
there is a very sharp jump because the base and acid have reached equilibrium
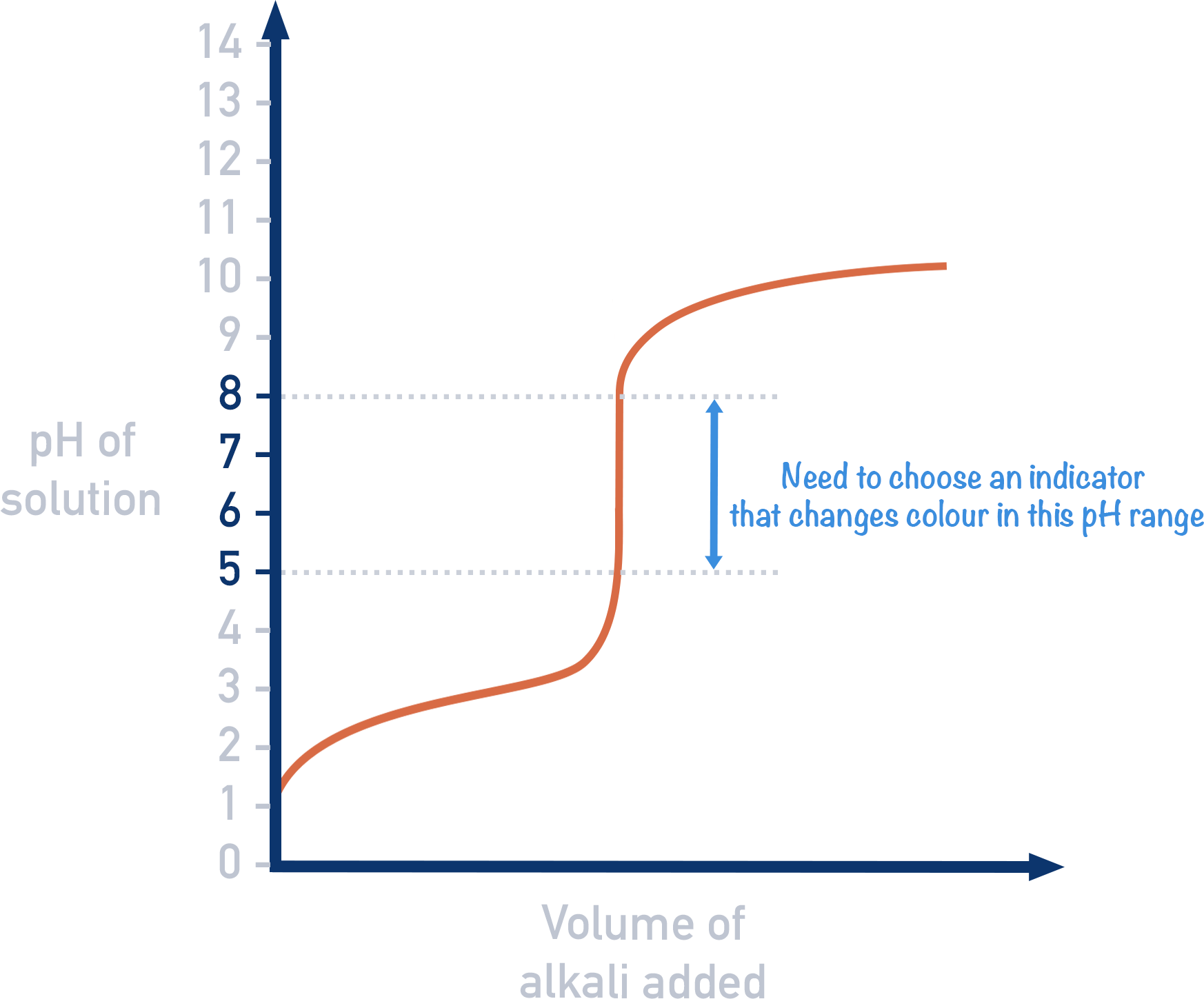
how do you find the equivalence point from a pH curve?
the midpoint of the straight vertical line, which is 7 at standard conditions
when do indicators change colour?
at the end point when the pH is equal to the pKa
pH of a salt that is formed from a strong acid and strong base
neutral pH = 7 at standard conditions
pH of a salt that is formed with a weak acid and a strong base
more alkali start and end pH > 7
pH of a salt that is formed with a strong acid and a weak base
more acidic and end at pH < 7
how to choose a suitable indicator
pKa of the indicator should be as close as possible to the pH at the equivalence point of a titration and in the equivalence range
what happens to the equilibrium we increase H+ concentration in an indicator solution
as per chateliers principle, equilibrium will shift towards reactants
what happens to the equilibrium we decrease H+ concentration in an indicator solution
as per chateliers principle, equilibrium will shift towards products
difference between acid base titrations and in redox titration?
acid base:
proton transfer
redox:
electron transfer
may change colour themselves but not always
similarities between redox and acid base titrations?
both change colour at the equivalence point
strong acid and strong base has the equivalence range of:
3 - 11 pH
strong acid and weak base has the equivalence range of:
3- 7 pH
weak acid and strong base has the equivalence range of:
7 - 11pH
a buffer
a solution resistant to changes in pH on the addition of small amount of acid or alkali
why do we put a small amount of indicator only?
Indicator is slightly acidic so it will change the pH of the sample
how do buffers work? what are they made of?
are a micture of two solutions, composed so that they contain a pair of conjugate base-acid pair
acidic buffers are made from
a weak acid and a solution of a salt from a strong alkali, need to be conjugate:
E.g. CH3COOH(aq) and NaCH3COO(aq) The following equilibria exist
CH3COOH(aq) ⇌ CH3COO-(aq) + H+(aq) equilibrium lies to the left
NaCH3COO(aq) → Na+(aq) + CH3COO-(aq)
what is a strong base? examples
it is a salt made with a group 1 or group 2 metal hydroxides except for Mg(OH)2 and Be(OH)2
strong acid examples?
acid that dissociates fully into H+ and A-
HCl, HBr, HI, HNO₃, H₂SO₄ (first dissociation), HClO₄.
what if H+ or OH- is added to an acid buffer?
H+ will react with the base in hte buffer to form salt
OH- will react with the acid in the buffer to from salt again:
Addition of acid (H+):
H+ will react with the base CH3COO- to form CH3COOH
CH3COO-(aq) + H+(aq) ⇌ CH3COOH
Addition of base (OH-):
OH- will react with the acid CH3COOH to form CH3COO- and H2O
CH3COOH(aq) + OH-(aq) ⇌ CH3COO-(aq) + H2O(l)
basic buffers are made of
mixing a weak base with the salt of a strong acid, which are congugate pairs
how do H+ and OH- react in an basic buffer
the H+ reacts with the weak base:
Addition of acid (H+):
H+ will react with the base NH3 to form NH4+
NH (aq) + H+(aq) ⇌ NH +(aq) 34
Addition of base (OH-):
OH- will react with the acid NH4+ and form NH3 and H2o
NH4++(aq) + OH-(aq) ⇌ NH3(aq) + H O(l)
how do we figure out the number of moles to make a buffer?
we need to find the ratio which produces excess weak acid or base depending of the type of buffer and salt
approximations to do calculations of an acidic buffer
initial concentration of weak acid = eq concenration of salt
initial concentration of salt = eq concentration of salt
factors that influence buffers
dilution: dillution does not change the pH, but can change its buffering capacity
temeperature: affects the values of Ka and Kb so it affects the pH