Bone cells ect
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Bone
A living tissue that changes throughout life, composed of cells and a calcified extracellular matrix.
Extracellular matrix (ECM)
The non-cellular component of bone that consists of organic and inorganic parts.
Organic components of bone
33% of bone ECM, consists mainly of collagen and proteoglycans.
Inorganic components of bone
67% of bone ECM, primarily hydroxyapatite and mineral salts that contribute to bone hardness.
Collagen
A flexible protein macromolecule that provides flexibility and resistance to tension in bones.
Proteoglycans
Ground substance that surrounds collagen fibers in bone, providing structural support.
Homeostasis
The process by which bone maintains a balance between bone destruction and formation.
Osteogenic cells
Stem cells in bone that can differentiate into osteoblasts.
Osteoblasts
Bone cells that produce new bone matrix.
Osteocytes
Mature bone cells that communicate within the bone and recycle proteins and minerals.
Osteoclasts
Bone cells that remove bone matrix.
Compact bone
Dense bone tissue with an osteon structure, designed for strength.
Cancellous bone
Bone tissue with a trabecular structure that is lighter and provides support.
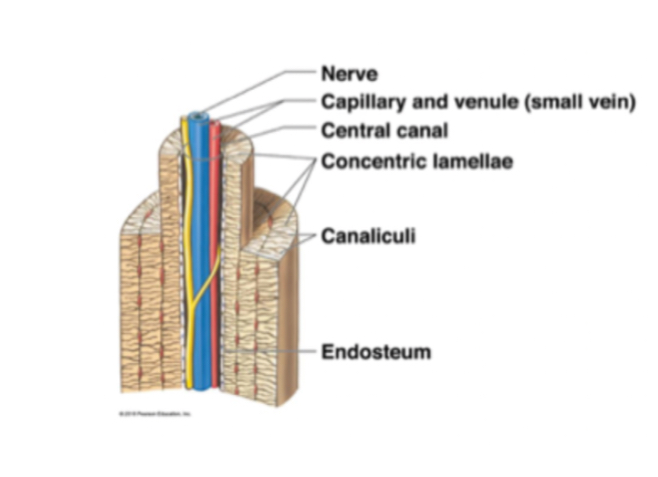
Osteon
The basic structural unit of compact bone, consisting of lamellae surrounding a central canal.
Central canal
A channel within an osteon that contains blood vessels and nerves.
Lamellae
Cylinders of ECM that form the shape of the osteon and resist forces.
Lacunae
Spaces within bone that contain osteocytes.
Canaliculi
Microscopic channels in bone that allow nutrients to travel to osteocytes.
Marrow
Soft tissue within the cavities of cancellous bone that produces blood cells.
Trabeculae
Thin structures of bone found in cancellous bone that resist force from multiple directions.
Bone mass
The amount and density of bone tissue within the skeleton.
Osteoporosis
A condition characterized by a significant imbalance in osteoblastic and osteoclastic activity, leading to weakened bones.
Cortical bone
The outer layer of compact bone that provides strength and support.
Trabecular bone
The inner structure of cancellous bone that helps distribute weight and absorb shock.
Calcium
A mineral essential for bone health and density.
Phosphate
A mineral important for bone formation and maintenance.
Mineral salts
Inorganic components that contribute to the hardness and rigidity of bone.
Remodeling signals
Chemical messages that prompt osteoblasts to build new bone and osteoclasts to resorb old bone.
Pressure and weight bearing
Factors that influence the structural adaptations in bones.
Peak bone mass
The maximum amount of bone mass achieved, typically in a person’s 20s.
Estrogen
A hormone that plays a role in regulating bone density, particularly in females.
Lacunar system
The network of lacunae and canaliculi that facilitate communication and nutrient exchange in bone.
Mechanical stress
Forces that bones encounter due to physical activity, which can stimulate remodeling.
Calcium mobilization
The process of releasing calcium from bone into the bloodstream.
Physical activity
Exercise that stimulates bone growth and density.
Skeletal system
The framework of bones that supports and shapes the body.
Calcium deficiency
Insufficient calcium intake that can lead to weakened bones and osteoporosis.
Bone structure
The arrangement and shape of bone that contribute to its function.
Bone weight distribution
How weight is supported and transmitted through bone structures.
Bone cellular activity
The processes involving osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and osteocytes in bone maintenance.
Trabecular spacing
The arrangement of trabecular bone that affects its load-bearing abilities.
Foramina
Small openings in bone that allow blood vessels and nerves to pass.
Skeletal remodeling
A continuous process of bone tissue renewal that adapts to physical stress.
Osteogenic processes
Biological mechanisms through which bone is formed and maintained.
osteon
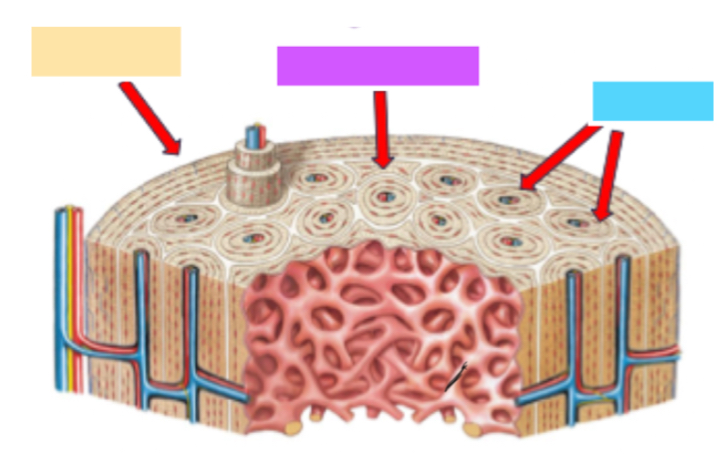
Circumferential lamellae
Yellow
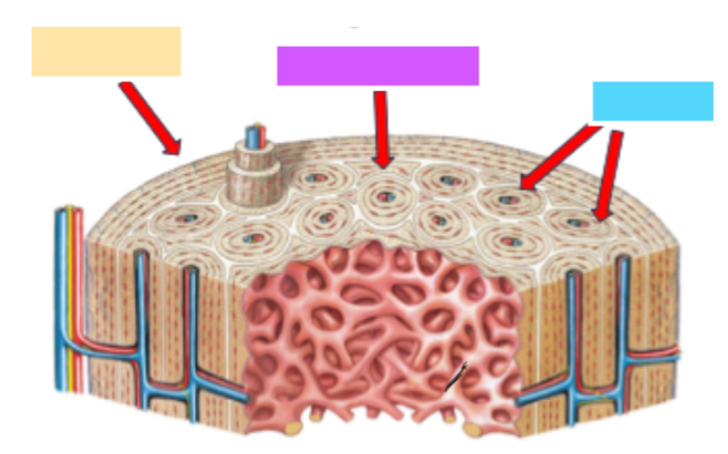
Interstitial lamellae
Purple
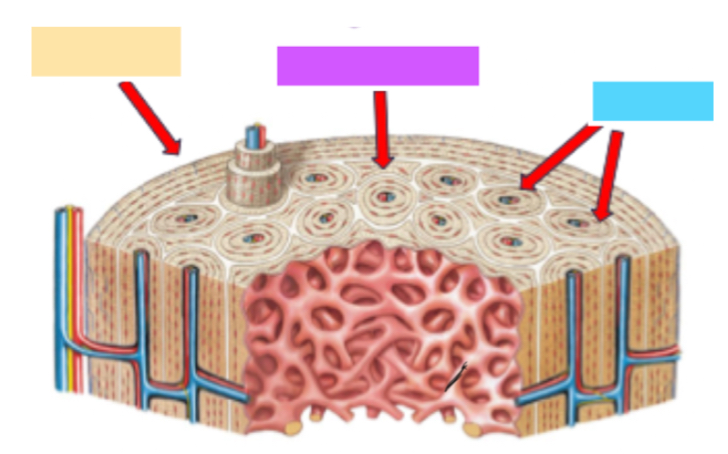
Osteons
Blue
Osmosis
Movement of water across a semi-permeable membrane to equalise solute concentration
Hypertonic
Higher concentration in ECM than ICM
Isotonic
Equal concentration inside and outside of cell
Hypotonic
Lower concentration in ECM than ICM
Chemical gradient
Uneven distributions of molecules
Electrical gradient
Uneven distribution of charges across the membrane
Turgid
Plant cell has a lower concentration in the ECM than ICM
Plasmolysed
Plants have a higher conc of solute in the ICM than the ECM
Flaccid
When plant cells have equal concentration of solute inside and outside the cell
What state do plant cells want to be in - turgid, flaccid, or plasmolysed
Turgid