AP Biology Unit 2- Cell Structure and Function
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
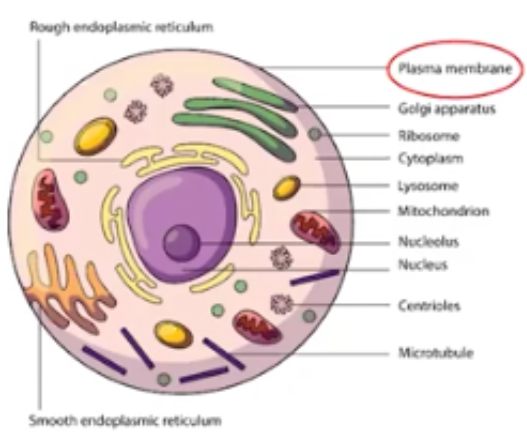
Eukaryotic Cells
Complex cells with a large variety of organelles, whose genetic information is stored in the nucleus (ex. plant)
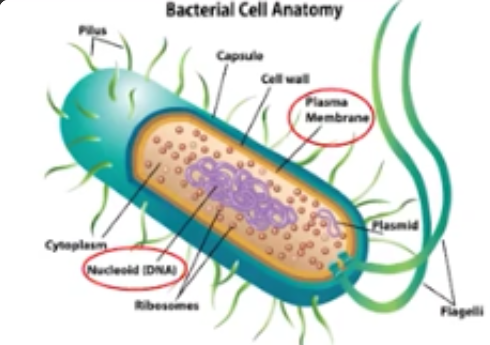
Prokaryotic Cells
Simpler cells, whose genetic information is stored in nucleoid regions (ex. bacteria)
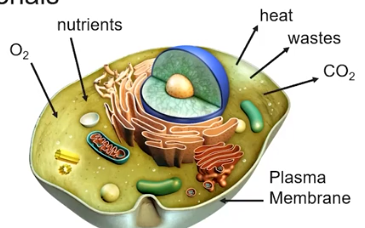
Why are cells small?
Smaller cells have a higher surface-area-to-volume and more efficiently absorb O2 & nutrients, and release heat, water, & CO2
Compartmentalization
The division of membrane-bound cells, which minimizes competing interactions and allows multiple processes to occur simultaneously
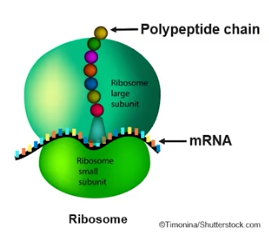
Ribsomes
Synthesis protein; two non-membrane-enclosed subunits, made out of rRNA and proteins
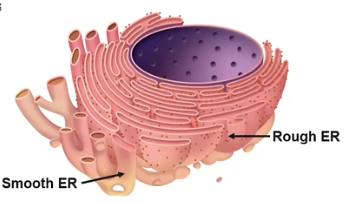
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Synthesizes, packages, and transports proteins and fats; a network of membrane tubes within the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells that provide mechanical support
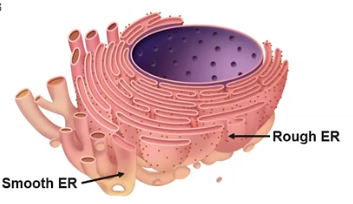
Rough ER
Packages & transports proteins, created by its attached ribosomes
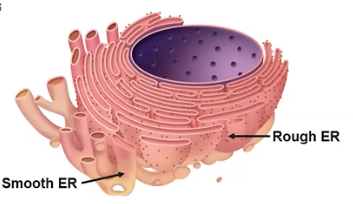
Smooth ER
Synthesizes lipids and detoxifies the cell; ER without ribosomes attached to its membrane
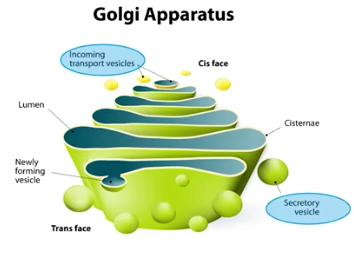
Golgi Complex
“Factory”, which chemically modifies proteins and packages them for further transport; a series of flattened membrane-bound sacs in eukaryotic cells
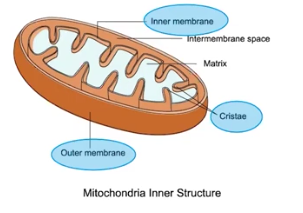
Mitochondria
Creates ATP energy; “powerhouse of the cell” that has a double membrane, a smooth outer membrane & folded inner membrane to increase the surface area
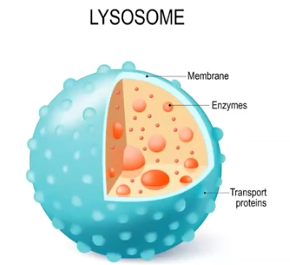
Lysosomes
Digest damaged cell parts; membrane-enclosed sacs that contain hydrolytic enzymes and can be found in some eukaryotic cells
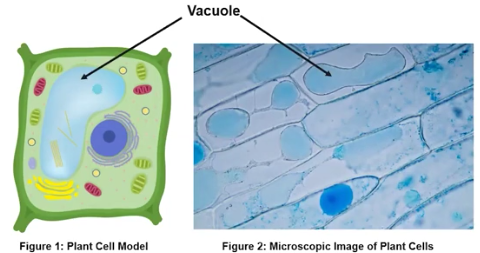
Vacuoles
Store & Release water from a cell; membrane-bound sacs in eukaryotic cells
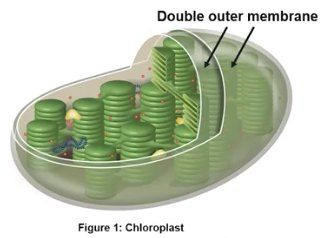
Chloroplasts
Capture sun energy & produce sugar; organelles in eukaryotic cells (algae & plants) with a double membrane that are comprised of thylakoids and the fluid region, the Stroma
Thylakoids
Folded membrane components of chloroplasts, organized in stacks called grana; contain chlorophyll pigments and electron transport proteins
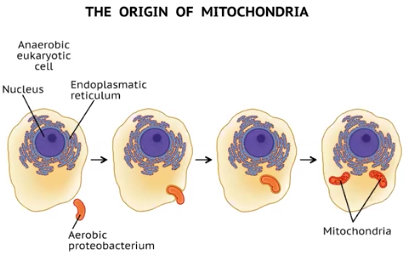
Endosymbiosis
The theorized origin of Mitochondria & chloroplasts from prokaryotic cells; To form the mitochondria, an anaerobic proteobacterium was engulfed by an archaeon cell, forming a symbiont relationship. Eventually, the proteobacterium gained independence and became the mitochondria. The same process occurred with photosynthetic prokaryotes to create Chloroplasts.
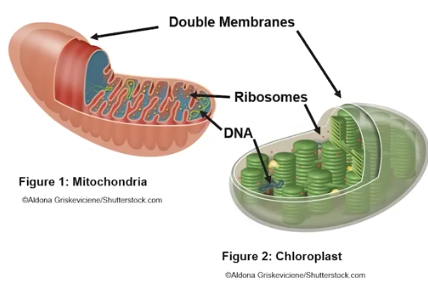
Evidence of Endosymbiosis
Both Mitochondria & Chloroplasts have properties of prokaryotic cells: 1) double membranes 2) DNA genetic info. 3) ribosomes
Cell Membrane
Creates a boundary between the cell interior and outside, controlling the transportation in & out of the cell; made up of phospholipids
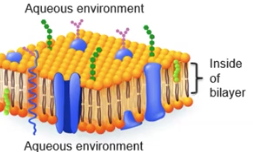
Phospholipids
Amphipathic, with a hydrophilic, nonpolar head, and hydrophobic fatty acid tail wedged inside; Spontaneously form a bi-layer in an aqueous environment
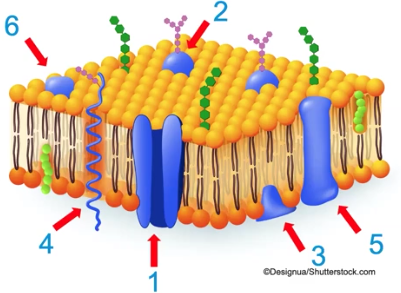
Fluid Mosaic Model of Cell Membranes
The structural framework of a cell membrane, consisting of a mosaic of protein molecules in a fluid bilayer of phospholipids, steroids, and carbohydrates; held together by hydrophobic interactions
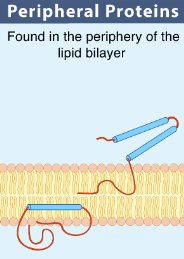
Peripheral Proteins
Embedded protein, loosely bound to the membrane surface, that interacts with the hydrophilic regions of the phospholipid bilayer
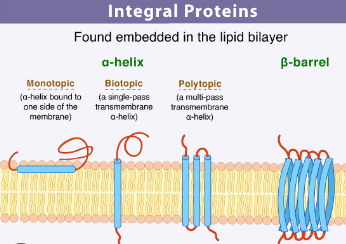
Integral Proteins
Embedded proteins, that span the membrane and penetrate the hydrophobic interior of the bilayer
Glycoproteins
Carbohydrates attached to embedded proteins
Glycolipids
Carbohydrates attached to lipids
Cell Walls
Comprised of complex carbohydrates, they act as a structural boundary and permeable barrier for PLANT cells; protect and maintain the shape of the cell, prevent cellular rupture, aid the plant in standing upright, & provide plasmodesmata
Selective Permeability
The cell membrane’s ability to allow some molecules through, while blocking others; caused by the presence of phospholipids, making the plasma hydrophobic. Small non-polar molecules can freely pass, while large polar molecules and ions cannot.
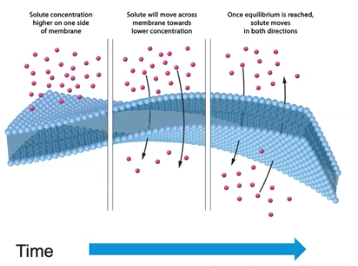
Concentration Gradients
Occurs when a solute is more concentrated in one area than another and a membrane separates the two; formed by the selective permeability of membranes
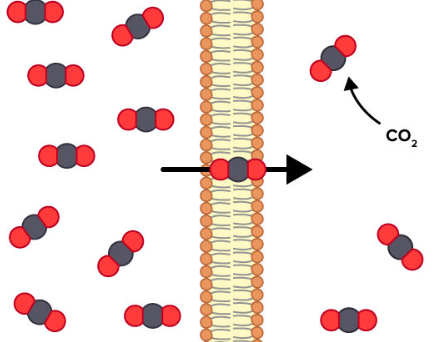
Passive Transport
The net movement of molecules from high to low concentration, without metabolic energy needed
Diffusion
The movement of molecules from high to low concentrations, where small nonpolar molecules pass freely
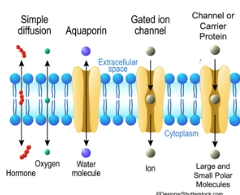
Facilitated Diffusion
The movement of molecules from a high to low concentration through transport proteins, which allows hydrophilic molecules and ions to pass through the membrane
Channel Proteins
A transport protein and hydrophilic tunnel, that only allows some molecules to pass through
Carrier Proteins
A transport protein that alters its shape to move a molecule through the channel protein tunnel
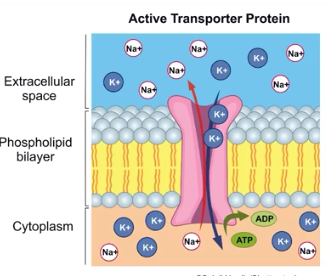
Active Transport
The net movement of molecules from low to high concentration, using metabolic energy and carrier proteins called pumps.
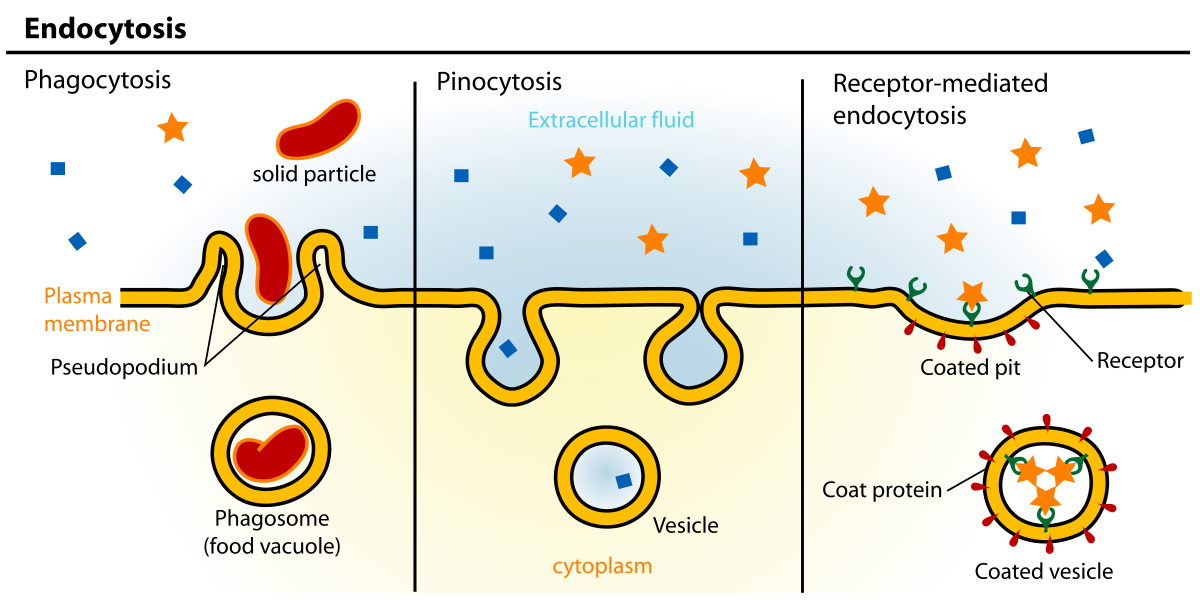
Endocytosis
The movement of large molecules into the cell membrane, where new vesicles use energy to take in molecules.
Phagocytosis
A form of endocytosis where the cell takes in large particles
Pinocytosis
A form of endocytosis where the cell takes in extracellular fluid containing dissolved substances
Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis
A form of endocytosis where the receptor proteins on the cell membrane are used to capture target molecules
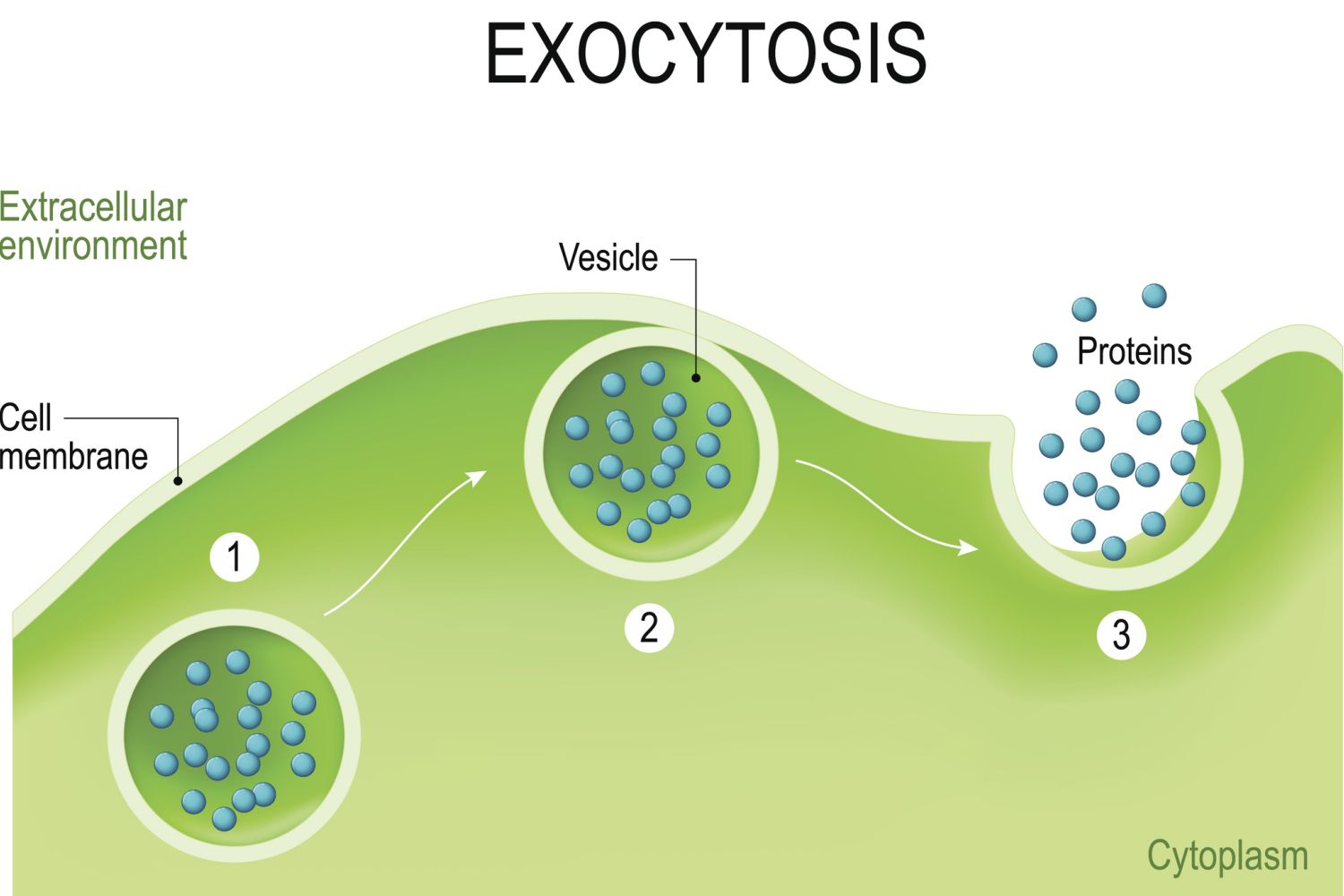
Exocytosis
The movement of large molecules out the cell membrane, where internal vesicles use energy to fuse with the plasma membrane and release molecules.
Electrochemical Gradient
A type of concentration gradient that relies on membrane potential, that becomes polarized by the movement of ions
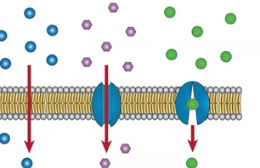
Cotransport
A secondary active transport that uses energy from an electrochemical gradient to move ions
Symport
Two different ions transported in the same direction
Antiport
Two different ions transported in opposite directions
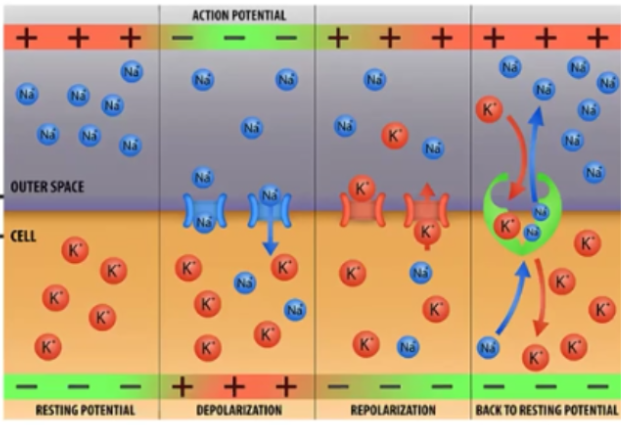
Na+/K + Pump
Establishes a gradient of sodium and potassium and creates cell membrane potential
Osmosis
The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane, where large water molecules can travel via aquaporins.
Tonicity
The measurement of the concentration of solute between two solutions, inside and outside the cell
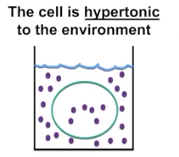
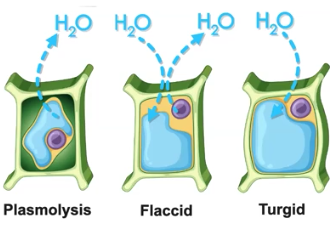
Hypertonic
More solute & less solvent; results in Plasmolysis (process of water leaving plant cells) and shriveled animal cells
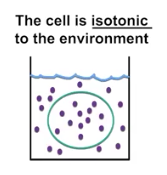
Isotonic
Equal concentration of solute & solvent; results in a flaccid solution and normal animal cell
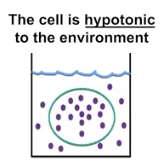
Hypotonic
Less solute & more solvent; results in Turgid solution (water rushing into a plant cell) and lysed animal cell
Osmolarity
Using osmosis to find the concentration of a cell
Osmoregulation
The regulation of water balance and homeostasis in a cell, which contributes to the survival of plant and animal cells
Water Potential
The measure of water’s movement through osmosis. The more negative the water potential, the more likely the water will move into the area: Ψ = ΨS + ΨP ΨS= solute potential, ΨP= pressure potential (bars)
Solute Potential
Impacts the water potential and can be equivalent to it in open systems: ΨS= -iCRT
i= ionization constant (sucrose=1, NaCl=2)
C= molar concentration
R= pressure constant (0.0831 L Bars/mol K)
T= temperature in celsius +273 = Kelvin
Components of an Effective Graph
Title
Labeled Axis with Units
Scaling
Identifiable Lines or Bars
Trend Line
Line Graph
Reveals trends or progres, and tracks changes over time or concentrations

Scatter Plot
Used to determine the relationship between two different things that may not be linear
Histogram
Shows the distribution of a data set in evenly spaced intervals
Bar Graph
Compares multiple groups of each other
Box and Whisker Plot
Shows the variability & ideal for comparing mean of distributions
Dual Y
Shows the relationship between two dependent variables