Biology Unit 1 IHS Skavaril
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Independent variable
What the experimenter changes; x axis
Dependent variable
What is measured; y axis
Controlled variable
Variable that stays the same
What are the 8 characteristics of life
Homeostasis
Evolution (happens to species)
DNA
Metabolism
Reproduction
Cells
Growth
Stimuli
Abiotic
Non-living; does not meet all 8 characteristics of life
Biotic
Living; meets all 8 characteristics of life
What is cohesion
Attraction to itself (sticks to itself)
What is adhesion
Attraction to other substances
What is a macromolecule
Macromolecules are large organic molecules found in living things
What are the 4 main types of macromolecules
Proteins
Lipids
Carbohydrates
Nucleic Acid
Elements of proteins
Carbon
Hydrogen
Oxygen
Nitrogen
Functions of proteins
Does everything in a cell
Monomers of proteins
20 amino acids
Examples of proteins
Legumes
Biotin
Titin
ATP synthases
Elements of carbohydrates
Carbon
Hydrogen
Oxygen
(CHO ratio = 1:2:1)
Functions of carbohydrates
Energy (short term)
Structural support for cell walls
Monomers of carbohydrates
Monosaccharides
Examples of carbohydrates
Sugar
Glucose
Galactose
Elements of lipids
Carbon
Oxygen
Hydrogen
Functions of lipids
NONPOLAR
Store energy/fat (long term)
Monomers of lipids
Glycerol
Fatty acids
Examples of lipids
Butter
Oleic acid
Elements of nucleic acids
Carbon
Hydrogen
Oxygen
Nitrogen
Phosphorus
Functions of nucleic acids
Carries genetic info; also a characteristic of life
Monomers of nucleic acids
5 nucleotides
Examples of nucleic acids
DNA
RNA
What is polarity
When the molecule has one end that is positive, and another that is negative
Why is water polar
Oxygen is negative
Hydrogen is positive
The positive ends of the hydrogen is attracted to the negative ends of the oxygen
What causes surface tension
Cohesion
What causes capillary action
Cohesion and adhesion
What is the purpose of science
Solving problems
What is the minimum number of controlled variables that should be included in a well-designed scientific experiment
3
In a well-designed scientific experiment, what is the value in having repeated trials
They allow for more accurate results and to reduce the impact of errors and/or statistical outliers.
How many independent variables should a properly-designed scientific experiment have?
One
What is the control group of a well-designed scientific experiment
a trial that the independent variable is NOT applied to
What are the steps of the scientific method
Observation
Question
Hypothesis (“If…, then…, because…”)
Experiment
Analysis
Conclusion
What is the scientific method
The process by which we can ask and answer questions
Which three elements are the primary components for the molecules of life
Carbon, oxygen, hydrogen
Which two things can denature enzymes
pH/acidity changes
Temperature changes
In general, how do enzymes affect the speed of chemical reactions
Enzymes make reactions happen faster
In general, how do enzymes affect the energy of chemical reactions
Enzymes decrease the activation energy of a chemical reaction
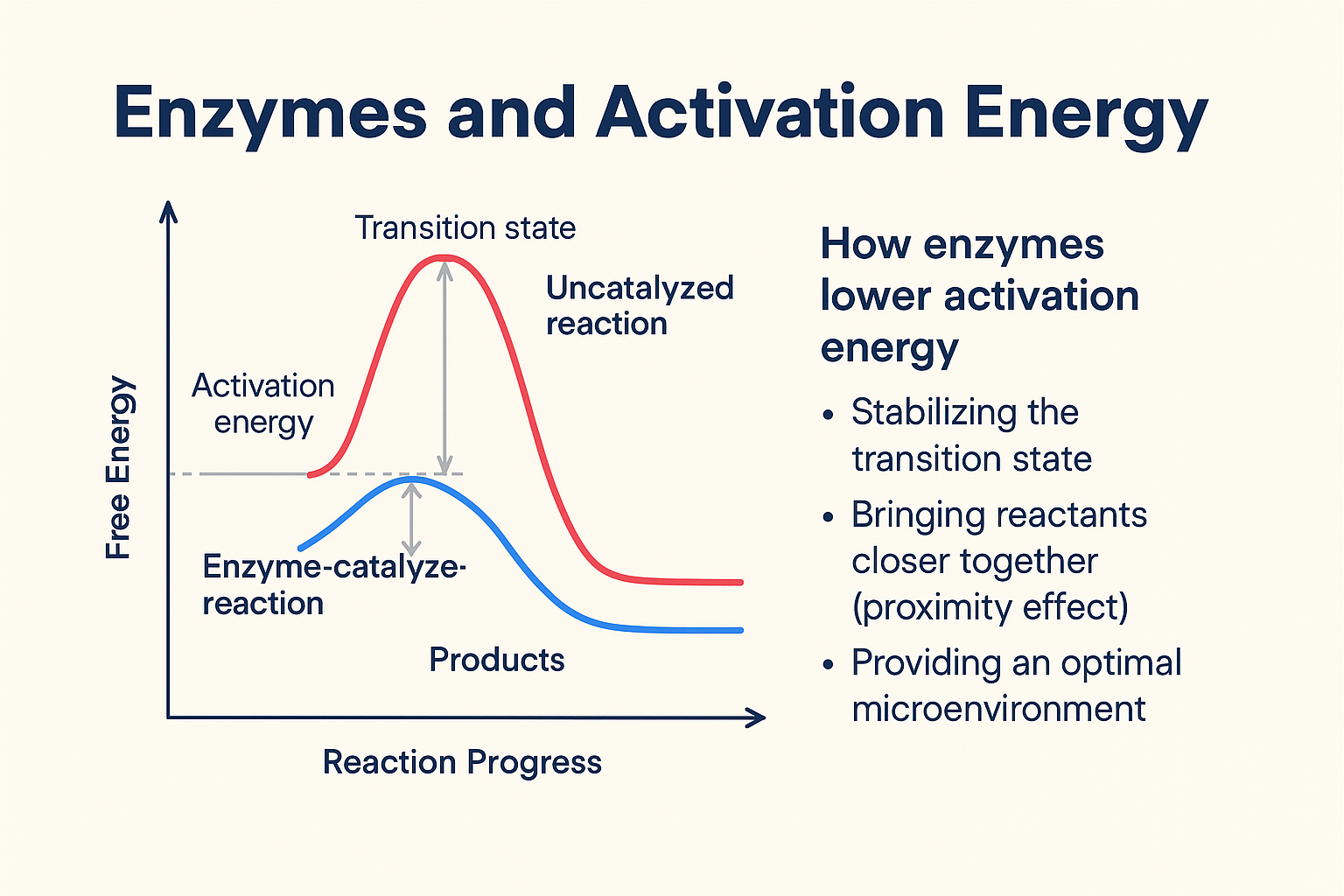
How many types of substrates will an enzyme react with
1
Enzymes are examples of what macromolecule
Protein
Structure determines function - yes or no
Yes
What body temperature is ideal for human enzymes
37 C / 98.6 F
Theory vs hypothesis
Hypothesis = backed w/ evidence. Educated guesses.
Theory = Explains how or why something exists