Lecture 1
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
The basics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Anatomy
Study of body structures
What does structure mean in relation to anatomy?
Shape, size, color, location
Gross anatomy
-Surface
-Regional
Microscopic Anatomy
-Smaller scale structures
-See info through a microscope
Physiology
-Study of body functions
-Cell, Systemic, Pathology
What does functions mean in the terms of physiology?
What the body does in the terms of actions in the body
Why are anatomy and physiology closely related?
The structure is directly related to its function
EX: Bicycle wheel; The shape/ location (structure) is related to how it rolls (function)
Using the heart, describe how its structure is closely related to its function
-Function of the heart= pumps blood in the body through blood vessels
-Structure of the heart= heart is a muscle, the muscle tissue around the heart is dependent to its ability to pump blood
Muscular wall, hollow chamber, direct connection to blood vessels= how the hearts structure is related to its functions.
Levels of organization
Atom—>Molecule—>Macromolecule—>Cells—>Tissue—>Organs—>Organ system—>Organism
Homeostasis- Stable, internal state
Regulatory process that counteracts changes to maintain a constant state
-Includes a set point, receptor/sensor, control center, and effectors
Internal environment
Fluid that surrounds your cells (Interstitial fluid)
What does a set point mean in Homeostasis?
Normal range
What does a receptor/sensor mean in Homeostasis?
Notice when set point is not right, then communicates with CC
What does a control center mean in Homeostasis?
Processes info from receptor then sends info to effector
What does a effector mean in Homeostasis?
helps bring back situation to set point
Negative Feedback
Response counteracts the change
-EX: Body temp drops, response has body temp rise
3 Examples of substances in the blood that are maintained at specific levels
Glucose, sodium, calcium
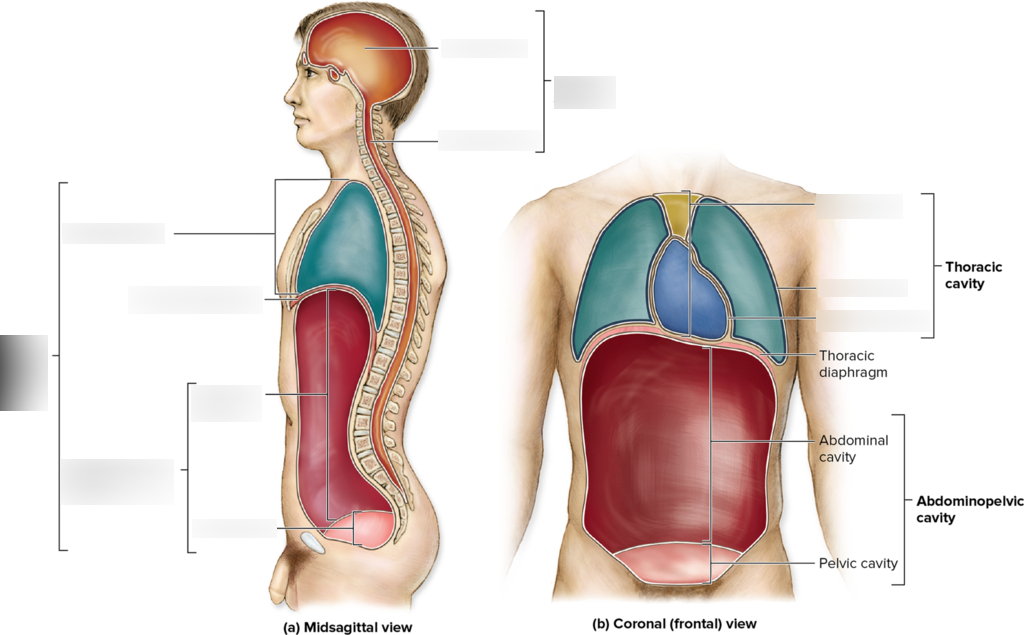
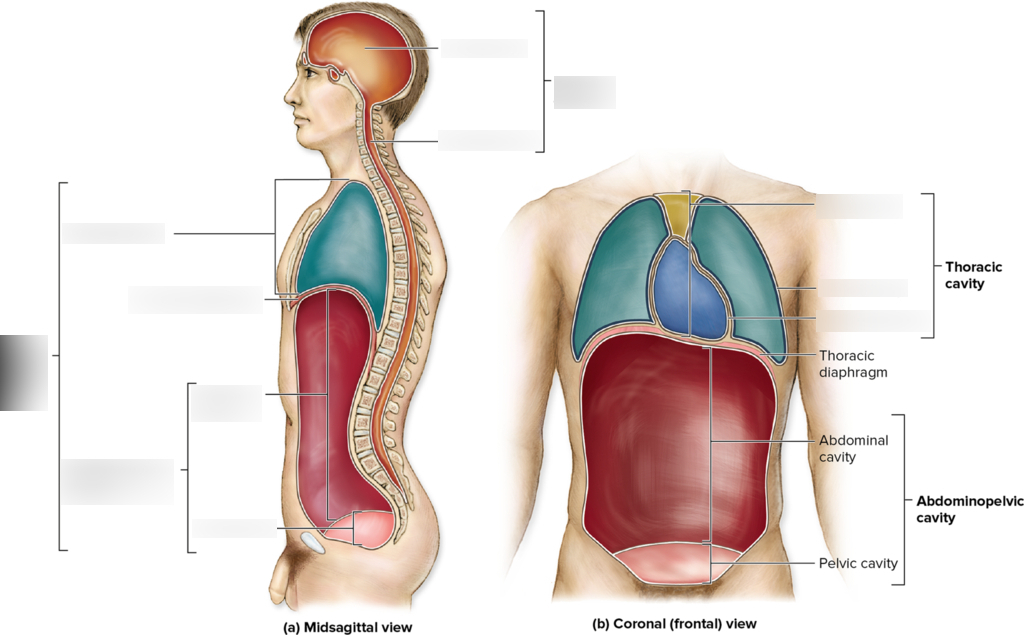
Human Body Cavities
-Posterior Aspect
-Cranial Cavity (Brain)
-Vertebral Cavity (Spinal Cord)
Ventral Cavity
-Thoracic Cavity
—Mediastinum
—Plural
—Pericardial
-Diaphragm
-Abdominopelvic Cavity
—Abdominal
—-Pelvic
Diaphragm
Separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominopelvic cavity
Thoracic Cavity
Hollow space in the chest containing the thoracic organs
Abdominopelvic Cavity
Space between the diaphragm and the pelvic outlet
Contains the abdominal and pelvic organs
Abdominal Cavity
Includes the stomach, liver, spleen, etc
Pelvic Cavity
Include portion of large intestines, urinary bladder, internal reproductive organs
Mediastinum
Contains the heart, esophagus, thymus
What cavities are in the thoratic and abdominalpelvic cavity?
Viscera
Parietal
membrane attached to the wall of a cavity
Visceral
Membrane that is interior (covers an internal organ)
Pariental pleura
Serous membrane that covers the inner surface of the thoracic cavity wall
Pleural cavity
Potential space between the visceral and parietal plural membranes
What is the membrane in the abdominopelvic cavity called?
Peritoneal membranes