SC120N: Plants, People, Places Final Exam Study Guide
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
drying oil -
an oil that reacts with the oxygen in the air to form a thin, waterproof elastic film
nondrying oil -
an oil that remains liquid for long time periods when exposed to air
semidrying oil -
an oil that dries slowly or only at high temperatures
auxin -
a class of plant hormones that control the growth and development of plants
phototropism -
growth toward a light source
gravitropism -
growth down in response to gravity
gibberellin -
a class of plant hormones that stimulates internode development to make plants larger
cytokinin -
a class of plant hormones that stimulates cell division and differentiation of plant organs
ethylene -
a gas that controls plant development
grafting -
a form of asexual reproduction where buds or stem cuttings from the desired variety are joined to the base of another variety
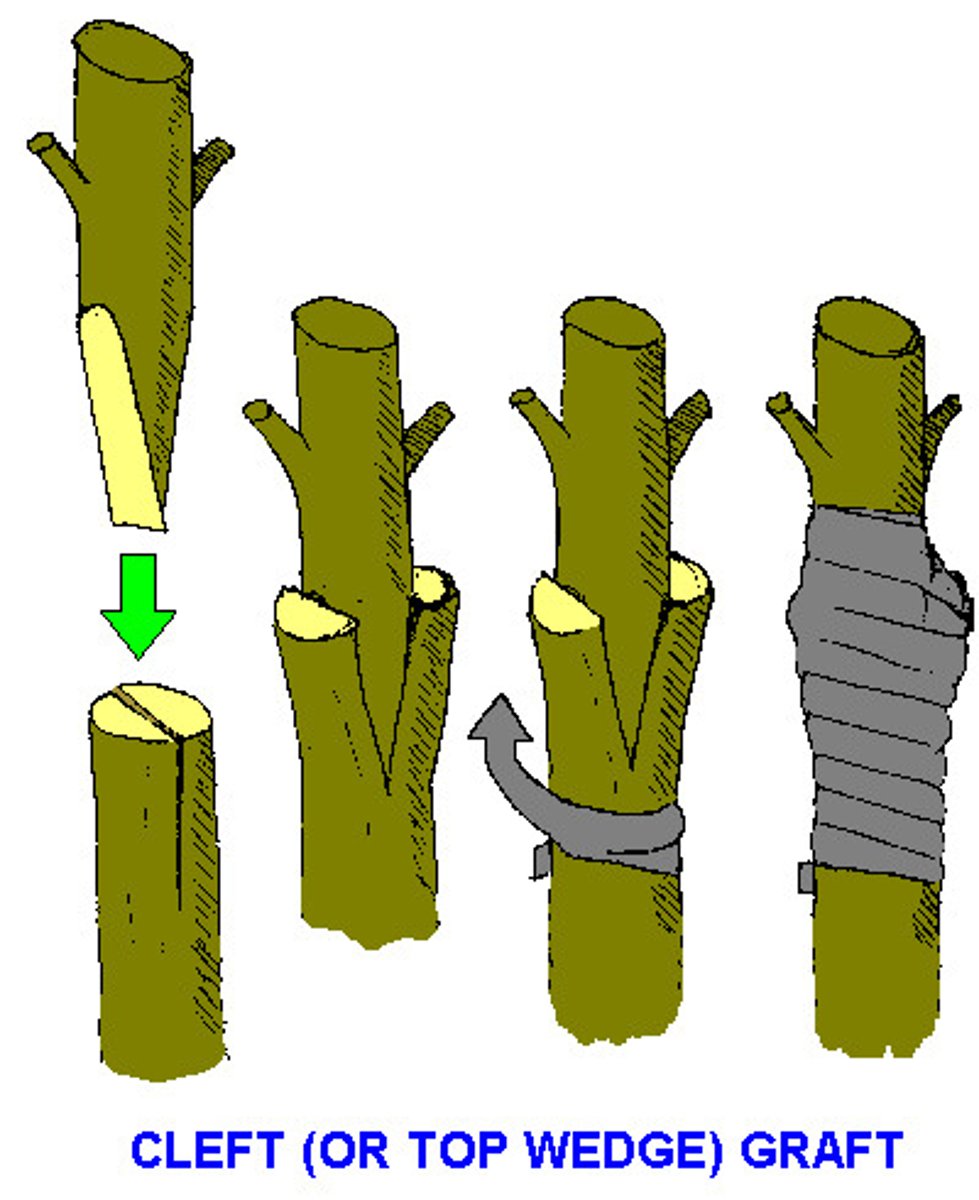
scion -
the bud or stem cutting used in grafting
rootstock -
the root system used in grafting
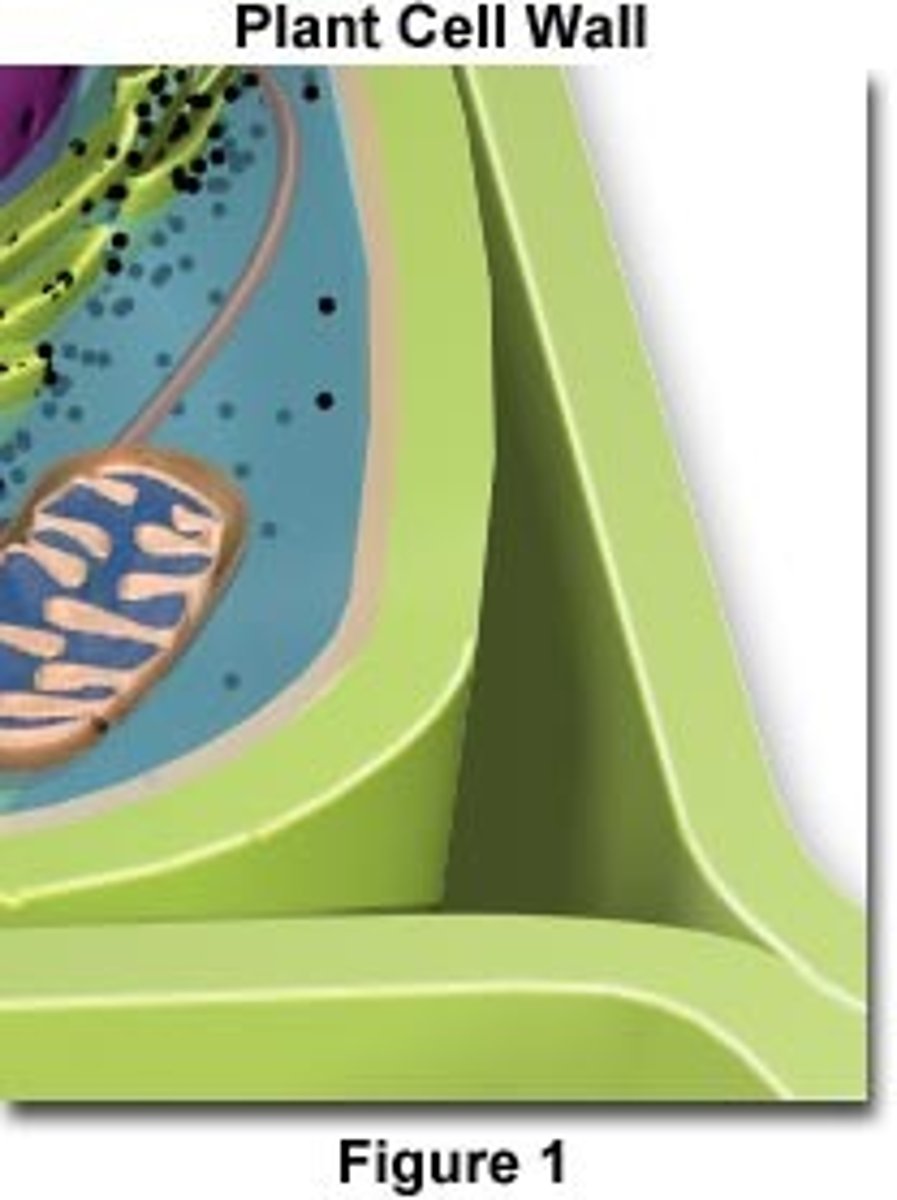
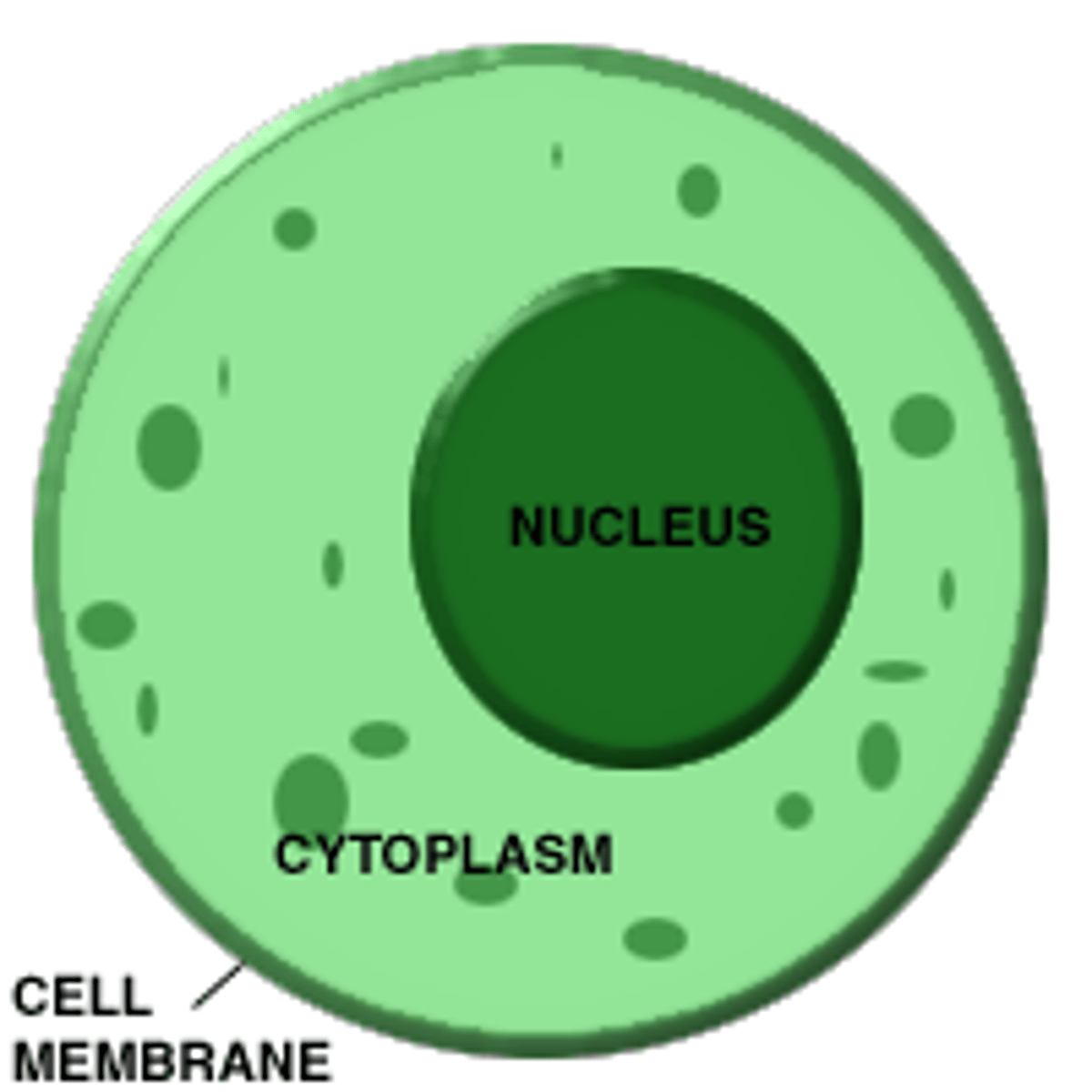
cell wall -
encloses a plant cell
cellulose -
a complex carbohydrate that provides structural support to a plant
lignin -
a complex carbohydrate that strengthens cell walls and reduces rot
pectin -
a complex carbohydrate that binds cells together
plasma membrane -
a semipermeable barrier controlling the movement of molecules in and out of a cell
protoplast -
the nucleus and cytoplasm of a cell
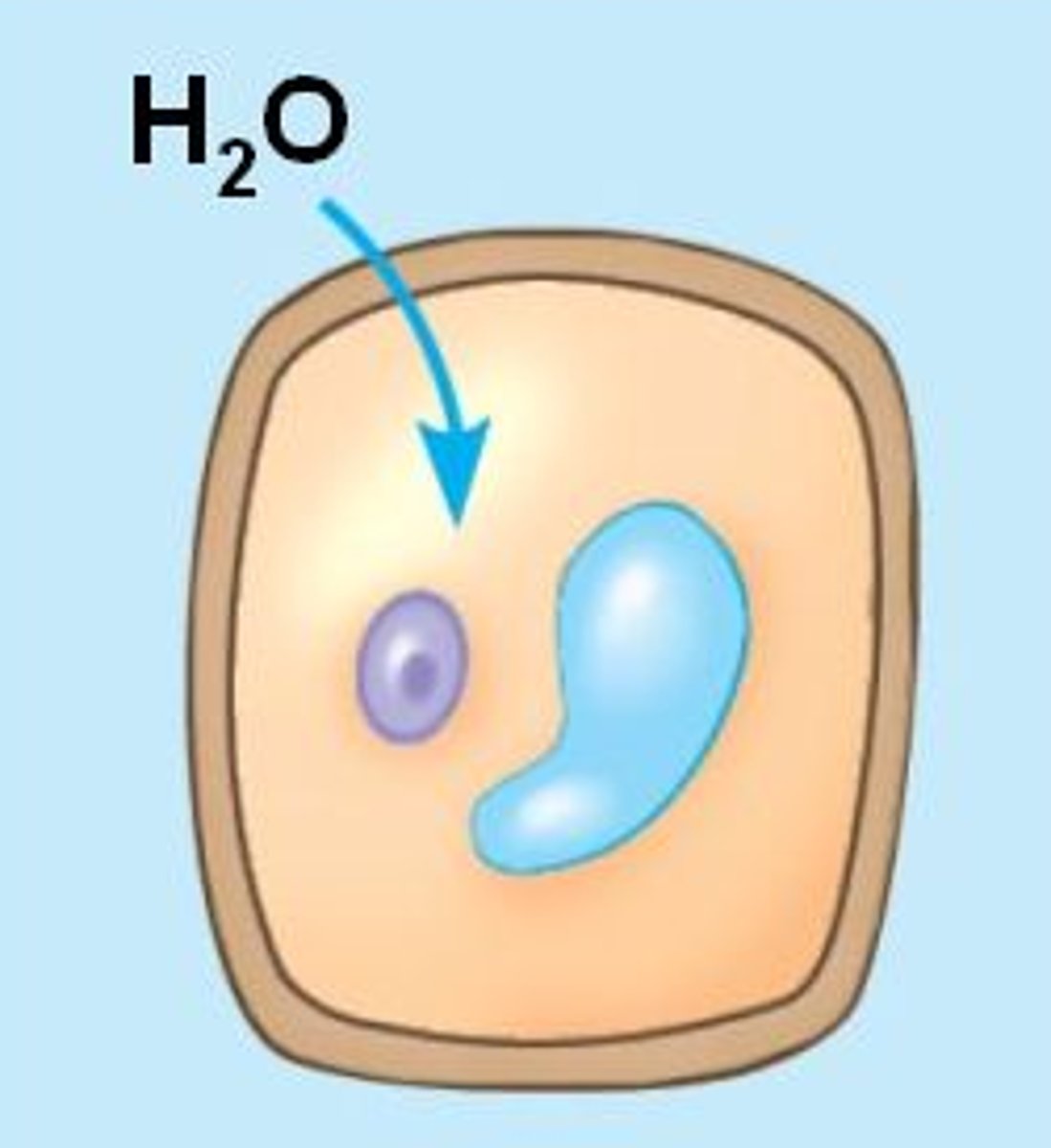
osmosis -
the movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane from areas with more water to areas with less water
turgid -
the state of a plant cell when the central vacuole fills with water, pushing the cytoplasm against the cell walls
plasmolysis -
the state of a plant cell when water has moved out of the cell, seen as a wilting plant
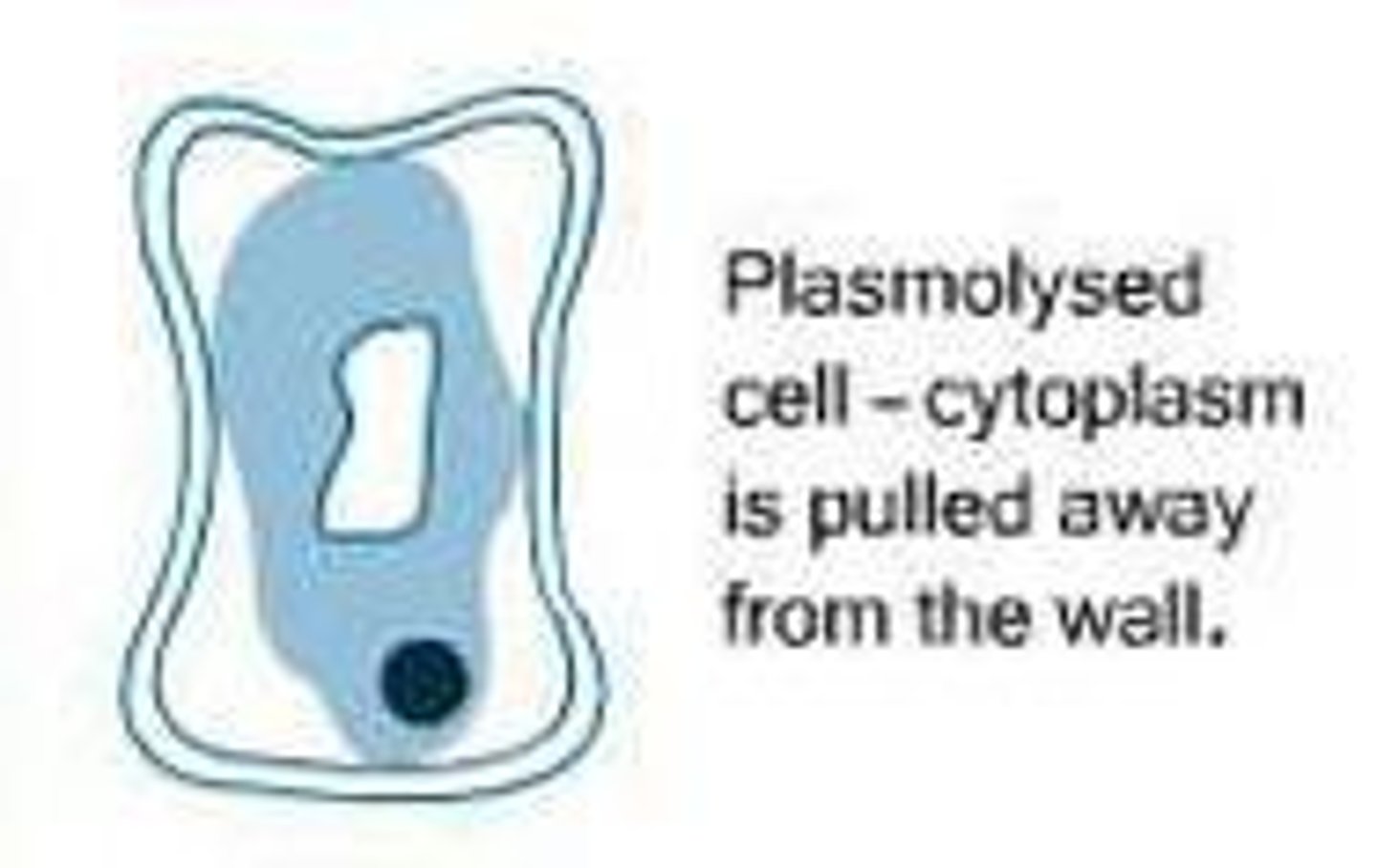
cytoplasm -
composed of various organelles distributed in an inorganic matrix consisting mostly of water called the cytosol
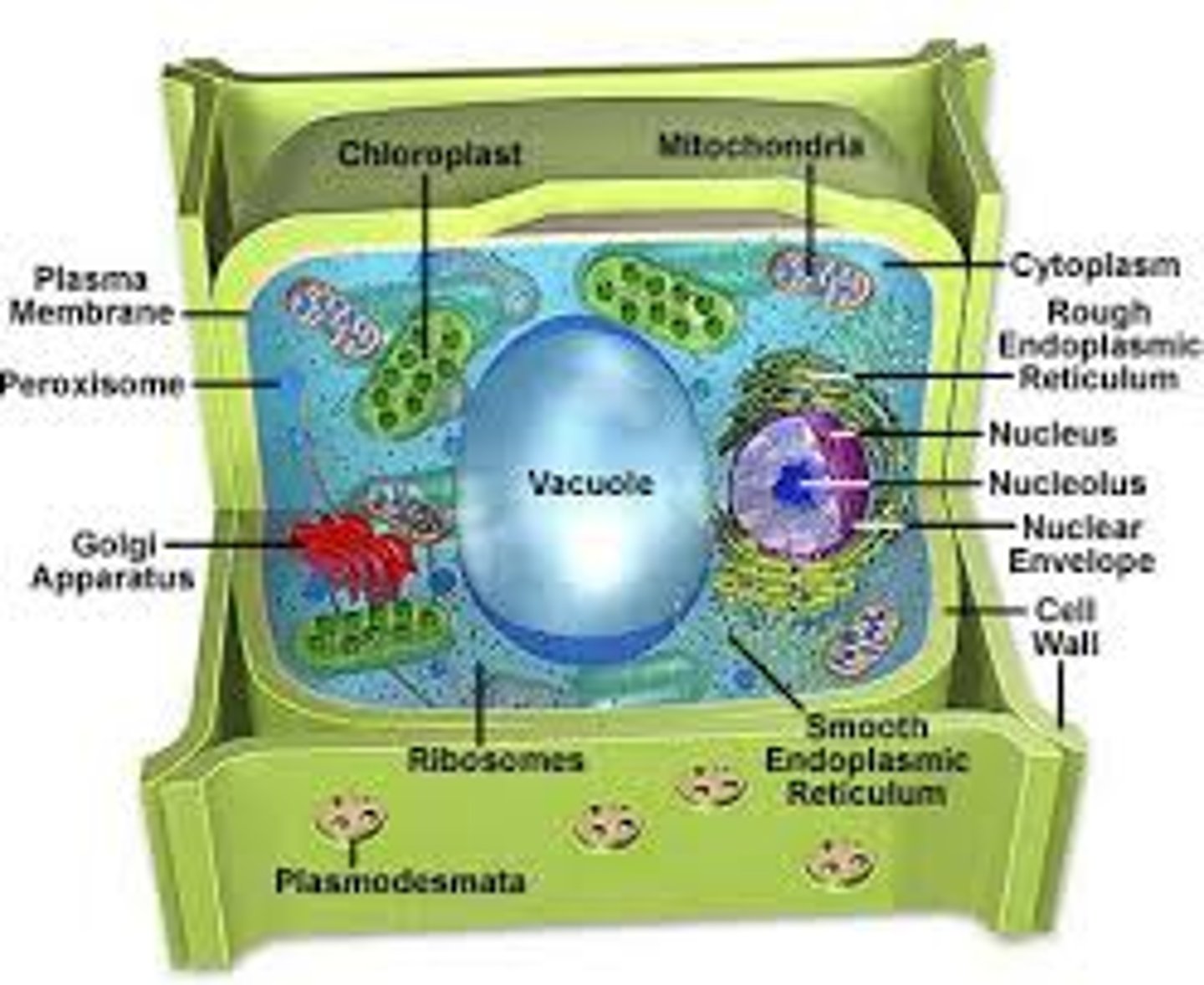
chloroplast -
a double-membrane organelle in which photosynthesis occurs, producing glucose and oxygen from carbon dioxide and water
chlorophylls -
a class of green pigments that allows for photosynthesis
carotenes -
a class of orange pigments
xanthophylls -
a class of yellow pigments
mitochondria -
a double-membrane organelle in which cellular respiration occurs, producing energy, carbon dioxide and water from the breakdown of sugar using oxygen
vegetarian -
a diet that doesn't include any any flesh
vegan -
a diet that doesn't include any animal products
macronutrient -
a nutrient the body needs in large amount in order to supply energy and cellular building blocks
micronutrient -
a nutrient the body needs in small amounts to provide optimal cellular metabolism
nutrient -
a component of food that performs a physiological function in the body
essential nutrient -
a nutrient the body needs in order to function but can't manufacture in adequate amounts and therefore must be part of the diet
carbohydrate -
organic molecules that function in energy storage
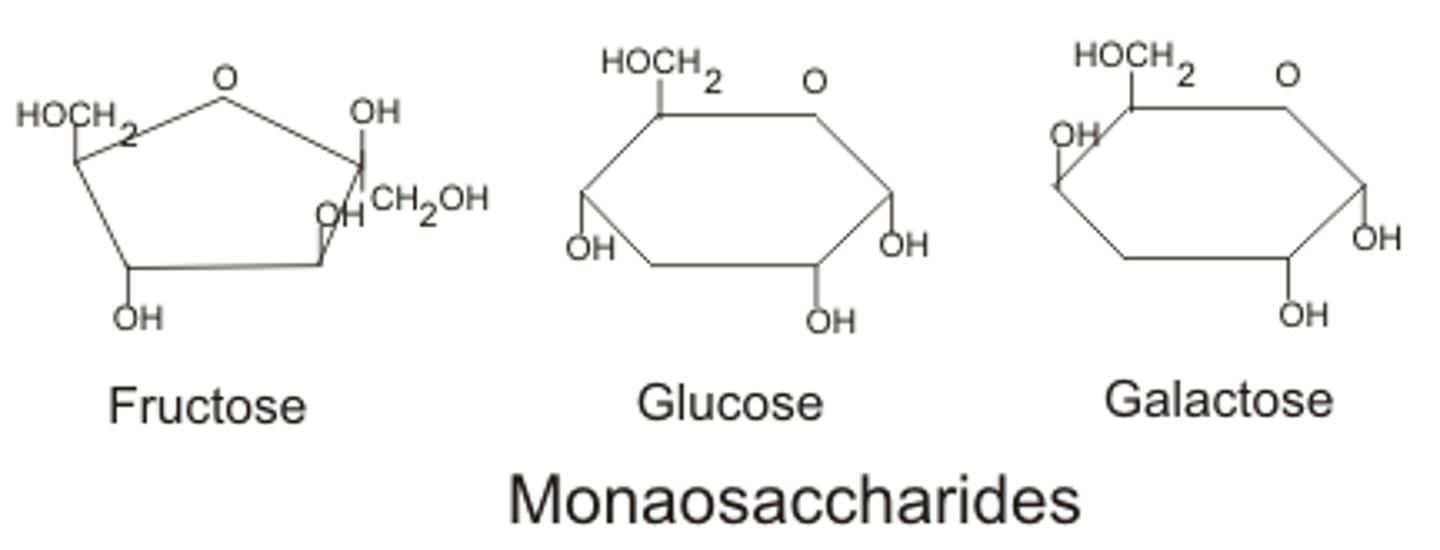
monosaccharide -
a single sugar molecule
disaccharide -
a sugar molecule containing two monosaccharides
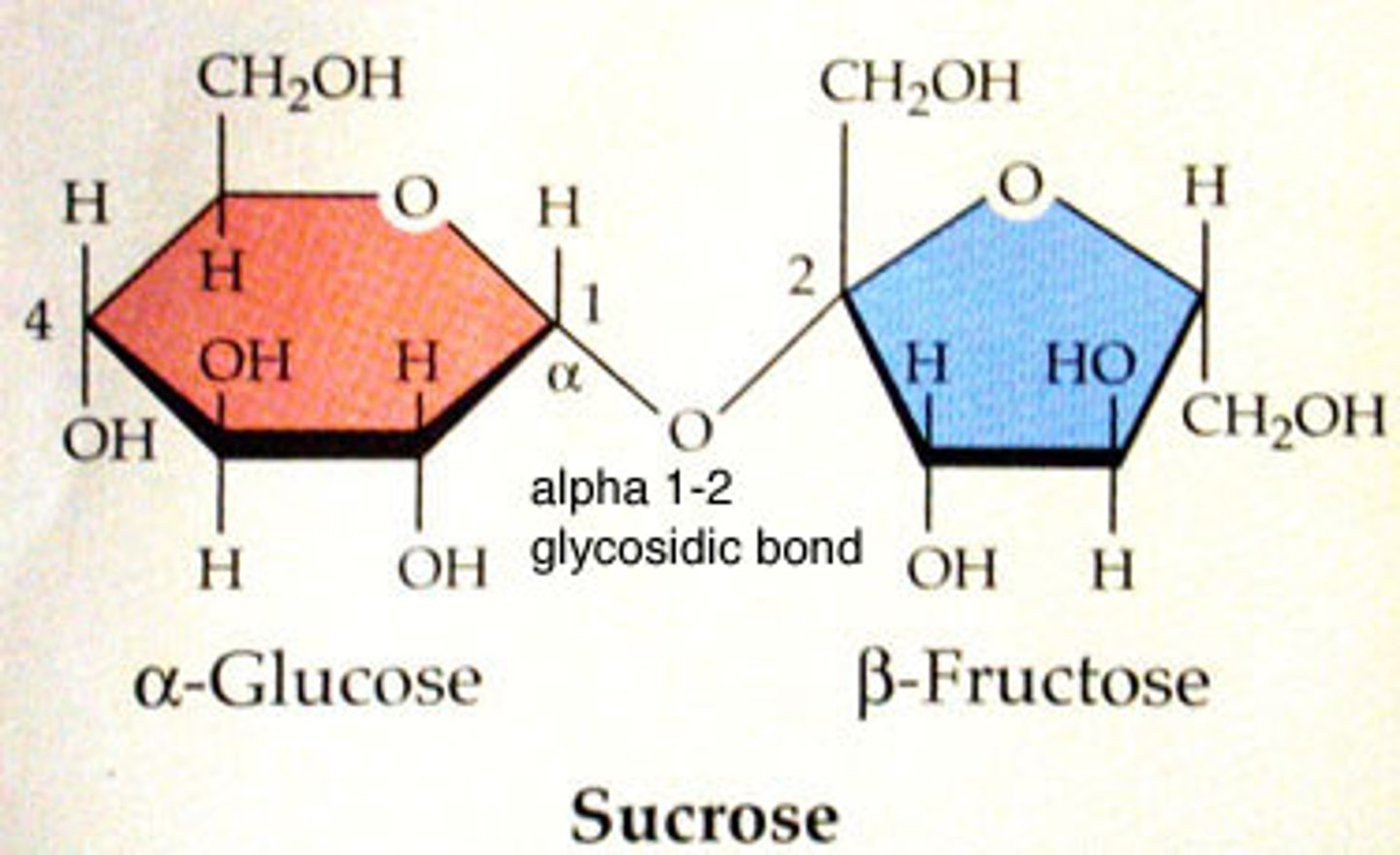
polysaccharide -
a molecule containing hundreds to thousands of monosaccharides
glycogen -
the short-term energy storage molecule of animals
starch -
the energy storage molecule of plants
fiber -
indigestible carbohydrates
protein -
an organic polymer composed of amino acids important to the structure and function of cells
complete protein -
a protein that contains all 20 essential amino acids
incomplete protein -
a protein that lacks an essential amino acid
lipids -
a diverse category of hydrophobic molecules
hydrophobic -
doesn't mix with water
saturated fat -
a triglyceride that contains all single bonds between the carbon atoms
unsaturated fat -
a triglyceride that has some double bonds between the carbon atoms
trans fat -
acts like saturated fats but are chemically unsaturated
vitamin -
an organic compound the body need for metabolic purposes but can't manufacture in adequate amounts
mineral -
inorganic compounds the body needs for metabolic purposes
major mineral -
the body contains >5g of each and should consume >100mg per day
trace mineral -
the body contains <5g of each and needs <20mg per day
heartwood -
the center of a trunk made up of secondary xylem and darker in color than the sapwood
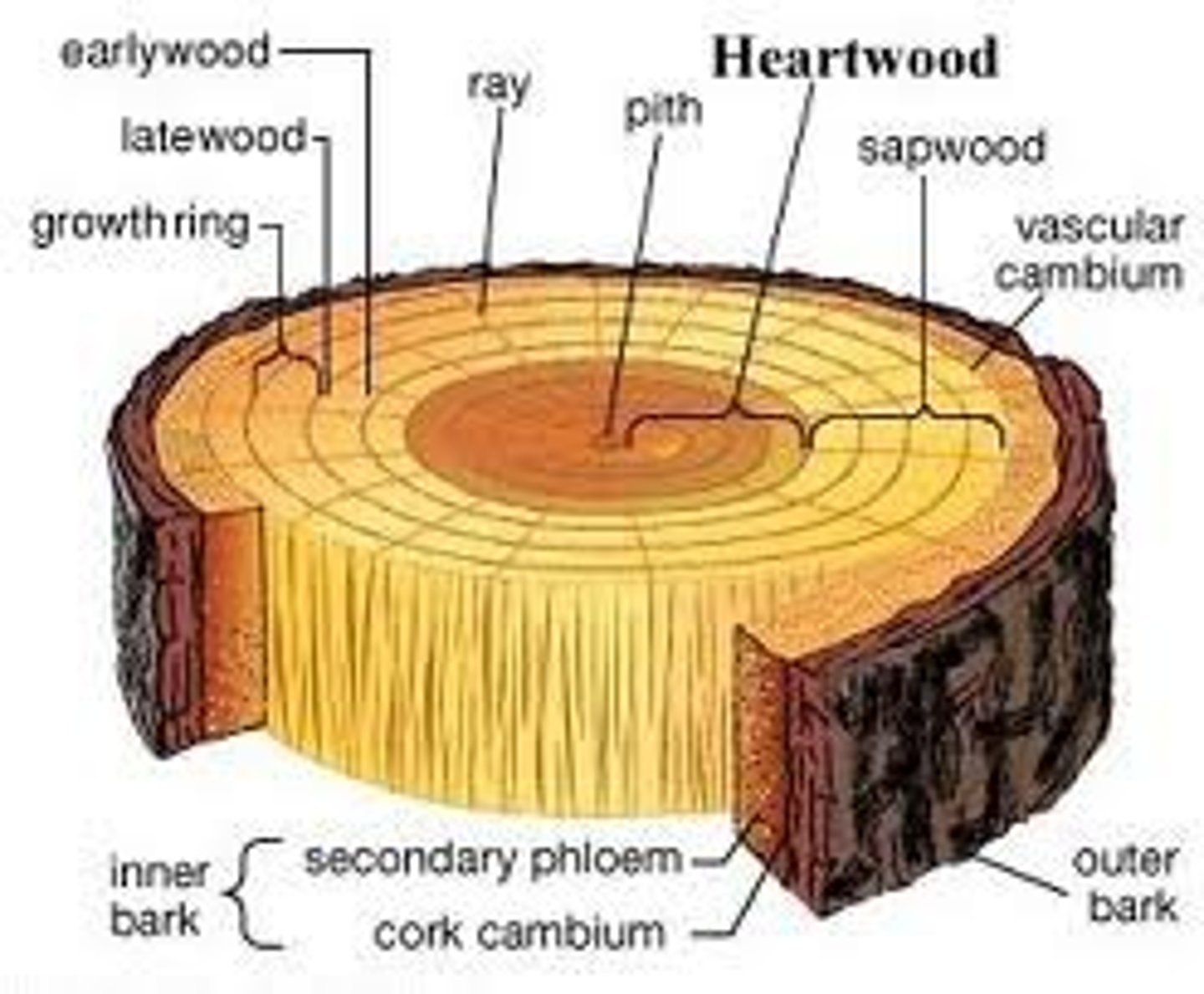
sapwood -
the lighter colored wood surrounding the heartwood that provides support and transport of nutrients
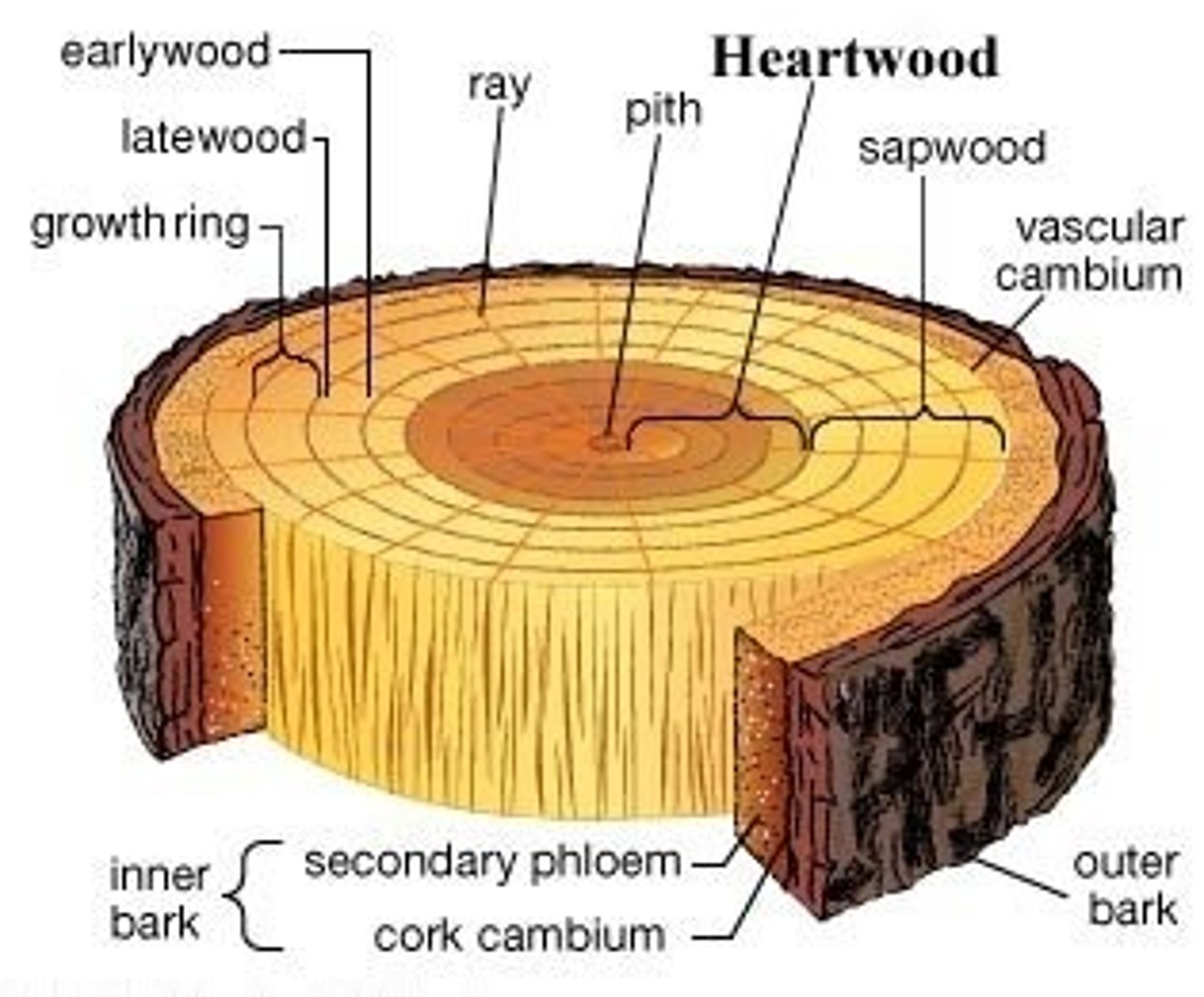
pulp -
a watery suspension of cellulose-rich plant material
resins -
chemical produced by plants as protection from herbivory and decomposition
cork -
material produced by the cork cambium of trees as the epidermis of the trunk is replaced by the periderm
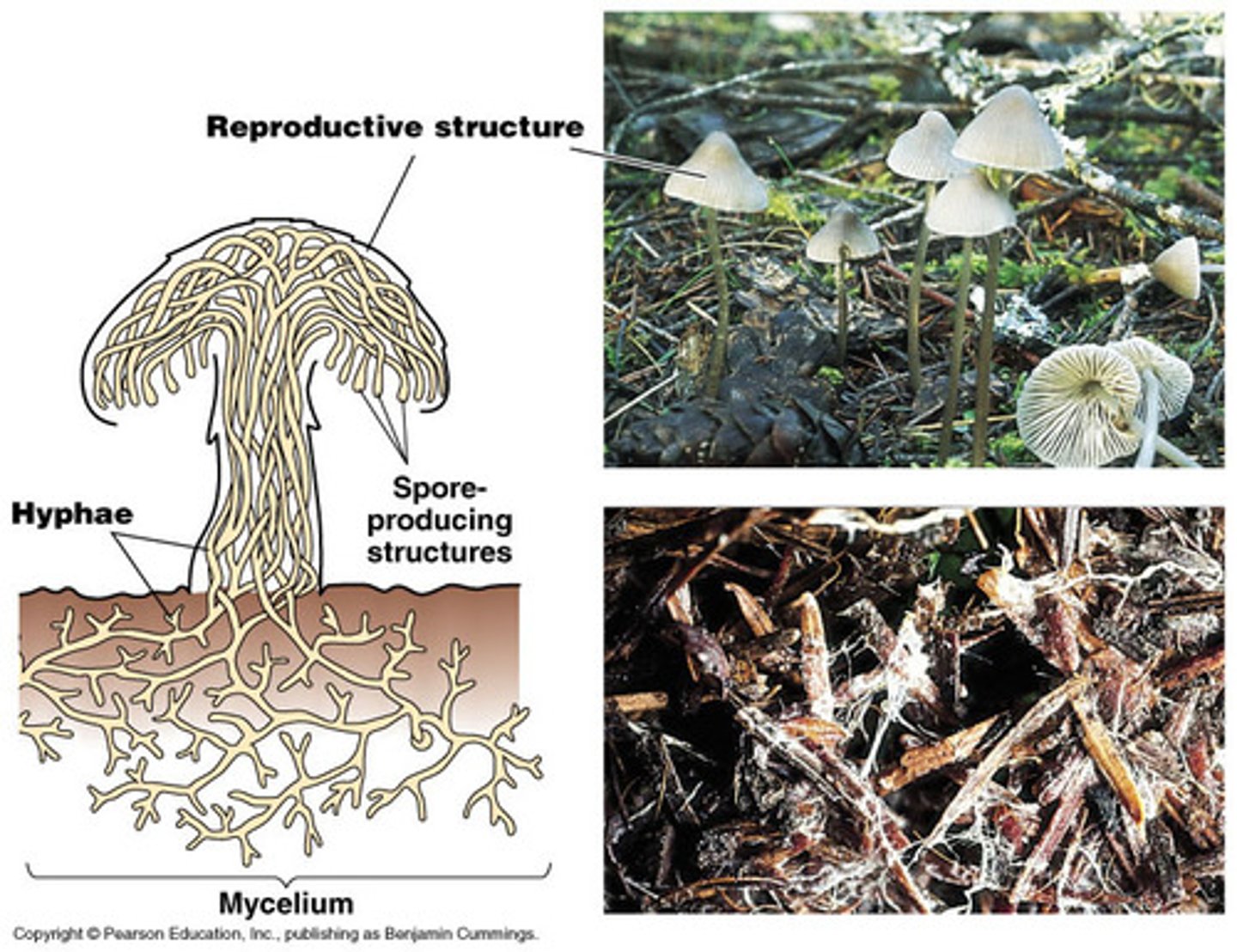
hyphae -
small, thread-like filaments that make up most visible fungi
chitin -
a nitrogen-containing polysaccharide that provides support to the cell wall of fungi
mycelium -
a collective mass of hyphae
parasite -
an organism that obtains nutrients from a living host, causing harm to the host
mutualistic symbiont -
an organism that obtains nutrients from a living host but provide a benefit to that host
saprobe -
an organism that obtains nutrients by breaking down non-living organic matter, a decomposer
protoplasmic toxin -
a chemical that destroys the liver and kidney cells
neurotoxin -
a chemical that negatively affects the central or autonomic nervous systems
gastrointestinal irritant -
a chemical that causes nausea, vomiting, cramps or diarrhea
We typically consume the _____ of the soybean plant.
seeds
T/F: The majority of soy is grown for human consumption.
True
Ethiopia
Coffee was originally domesticated in
seeds-
The _____ of the coffee plant is used to make coffee
Which of the following is NOT part of the coffee depulping process?
Roasting the beans
3 multiple choice options
T/F: Soybeans are commonly consumed raw
False
Purple
Anthocyanin produces this color in plants:
central vacuole-
You find tannins in the _____ of the plant cell
False, only dicots
T/F: Monocots can be grafted
T/F: Starch is a carbohydrate
True
This fat should be eliminated from your diet because it has a negative impact on cholesterol levels
Trans fats
The four steps of curing vanilla beans (in order)
Killing, Sweating, Drying, Conditioning
T/F: Vanilla gets its flavor from essential oils in the fruit
True
T/F: Soy is a complete protein source
True
_____ are the most diverse type of gymnosperm because they have the most species
Conifers
True
Hemp and marijuana come from the same species of plant
T/F: The lignin in the cells of conifers can degrade paper made from conifer pulp
True
T/F: The grapes native to North America are typically picked as table grapes
False
distillation-
Liquor has to be made through what process?
Fly agaric mushrooms produce this hallucinogenic
Ibotenic Acid
Aflotoxin
fungal poison (mycotoxin), produced by the mold Aspergillus flavus, which grows on nuts, grains and peanuts--can be toxic in high doses
Psilocybin
Causes hallucinations and is produced by Teonanacatl (Psilocybe)
Fungal Infections
Ringworm and yeast infections are both:
T/F: Mycellium can be used to produce building materials and clothing
True
T/F: Gymnosperms are seed-bearing and can produce flowers
False, they are non-flowering
What are the four groups of gynmosperms?
Gnetophytes, Ginkgo, Cycads, Conifers
T/F: The roots, stems, and seeds of cycads are good sources of starch
True, but toxins must be soaked out of the plant
True
T/F: Conifers are monoecious
monoecious
having male and female reproductive organs in the same plant or animal
secondary xylem (early and late wood)
main component of wood
T/F: Softwoods are angiosperms
False, Hardwoods are angiosperms, softwoods are conifers
T/F: Most softwood is used for lumber
True
True
T/F: Most bananas cultivars are sterile triploids
Deities associated with olives
Athena, Elaea, Aristaeus