Organic Chemistry: Alkenes, Alkynes, Aromatics, and Isomerism
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
What are alkenes?
Compounds that contain a carbon−carbon double bond.
What are alkynes?
Compounds that contain a carbon−carbon triple bond.
What is the general formula for alkenes?
C_nH_(2n)
What is the general formula for alkynes?
C_nH_(2n-2)
What type of bonds do alkenes and alkynes contain?
Multiple bonds (double bonds for alkenes and triple bonds for alkynes).

What are the physical properties of alkenes and alkynes?
They have low melting and boiling points, are insoluble in water, and are nonpolar.
Why are alkenes and alkynes called unsaturated hydrocarbons?
Because they contain fewer than the maximum number of hydrogen atoms per carbon atom.
What suffix identifies an alkene in IUPAC nomenclature?
The suffix -ene.
What suffix identifies an alkyne in IUPAC nomenclature?
The suffix -yne.
What is the first step in naming an alkene or alkyne?
Find the longest chain that contains both carbon atoms of the double or triple bond.
What is the second step in naming an alkene or alkyne?
Number the carbon chain from the end that gives the multiple bond the lower number.
What is the third step in naming an alkene or alkyne?
Number and name the substituents and write the name.
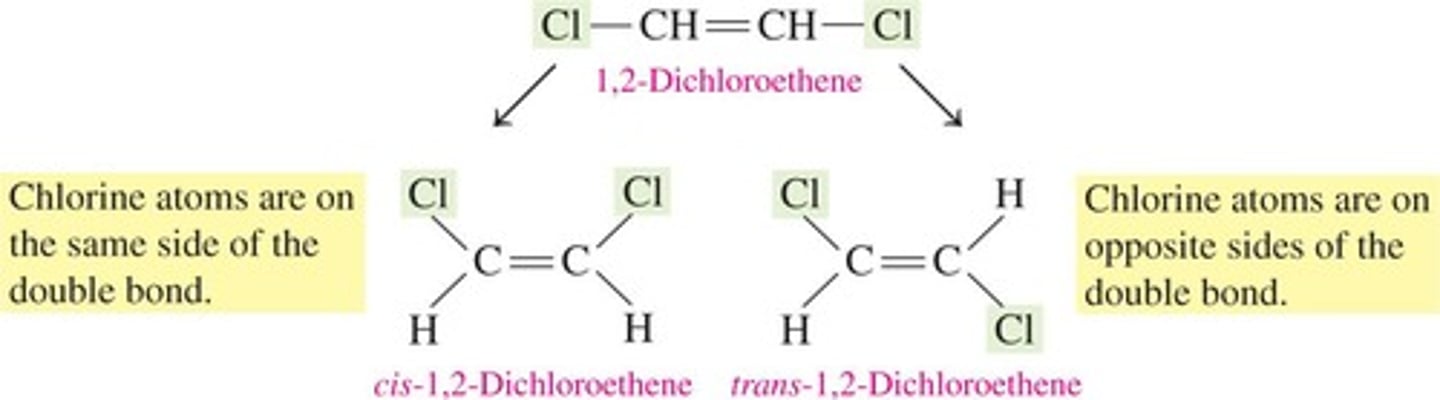
What are stereoisomers?
Isomers that differ only in the 3-D arrangement of atoms.
What is a characteristic of cis-trans isomers?
They have restricted rotation around the carbon atoms of a double bond.
What are saturated fatty acids?
Fatty acids with no double bonds in their long hydrocarbon chains.
What are unsaturated fatty acids?
Fatty acids with one or more double bonds in their long hydrocarbon chains.
What happens to the melting point of fatty acids as the number of double bonds increases?
The melting point decreases.
What are the two most commonly used synthetic birth control drugs?
Ethynylestradiol and norethindrone.
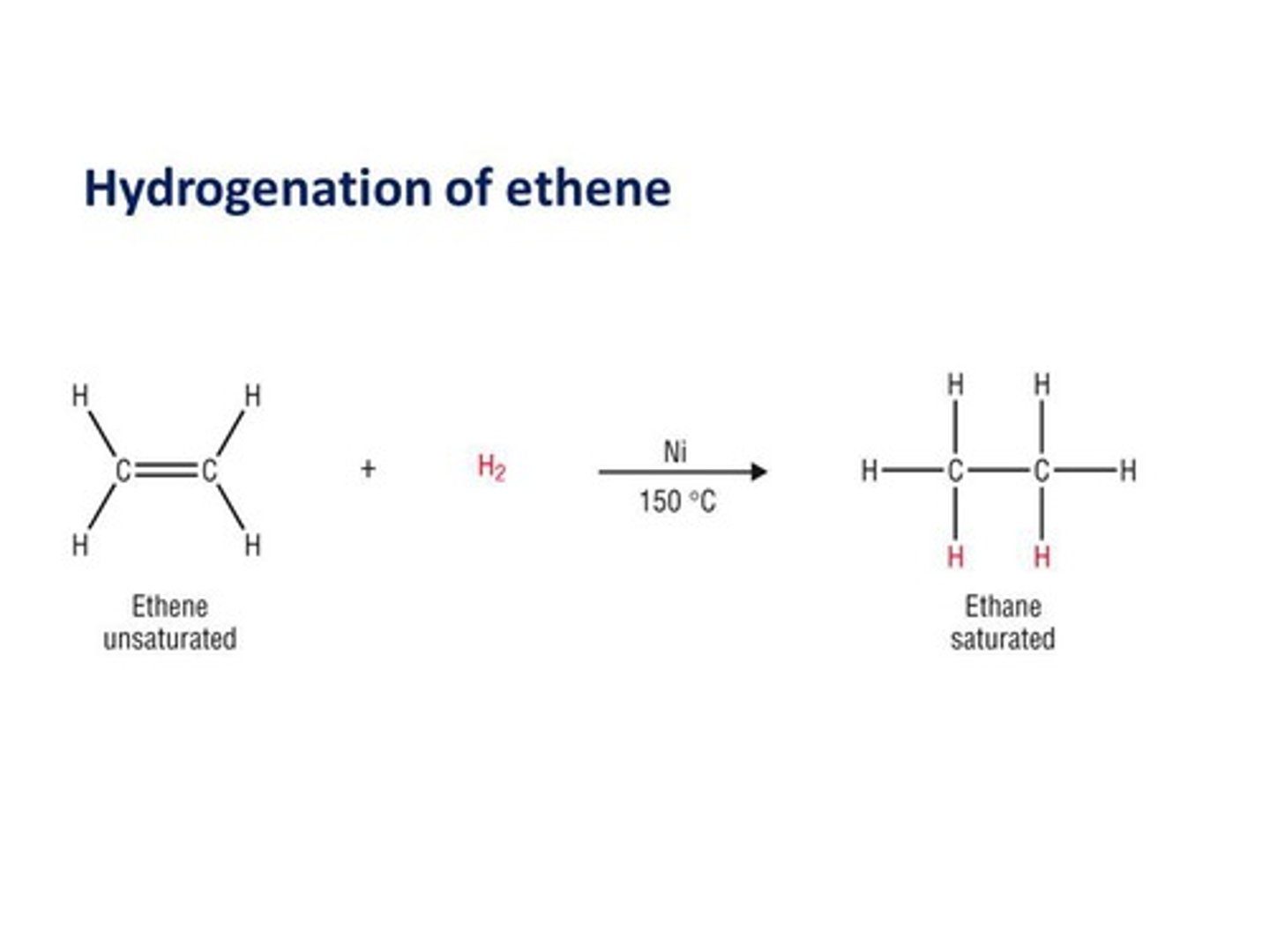
What is hydrogenation?
The addition of hydrogen to an alkene, resulting in the formation of an alkane.
What is hydration in the context of alkenes?
The addition of water to an alkene, forming an alcohol.
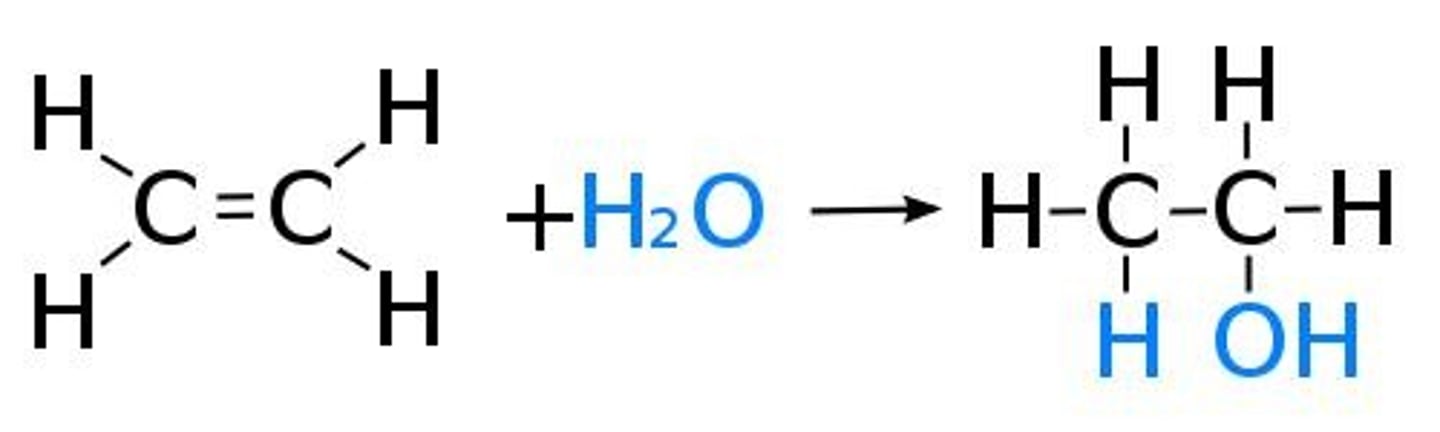
What does Markovnikov's rule state?
The hydrogen atom bonds to the less substituted carbon atom in an asymmetrical alkene.
What is the process used to create margarine from unsaturated fatty acids?
Partial hydrogenation, which leaves some double bonds intact.
What are trans fatty acids?
Fatty acids that are similar in shape to saturated fatty acids and considered unhealthy.
What are polymers?
Large molecules made up of repeating units of smaller molecules (monomers) covalently bonded together.
What happens during polymerization?
Double bonds in monomers are broken and single bonds linking the monomers are formed.
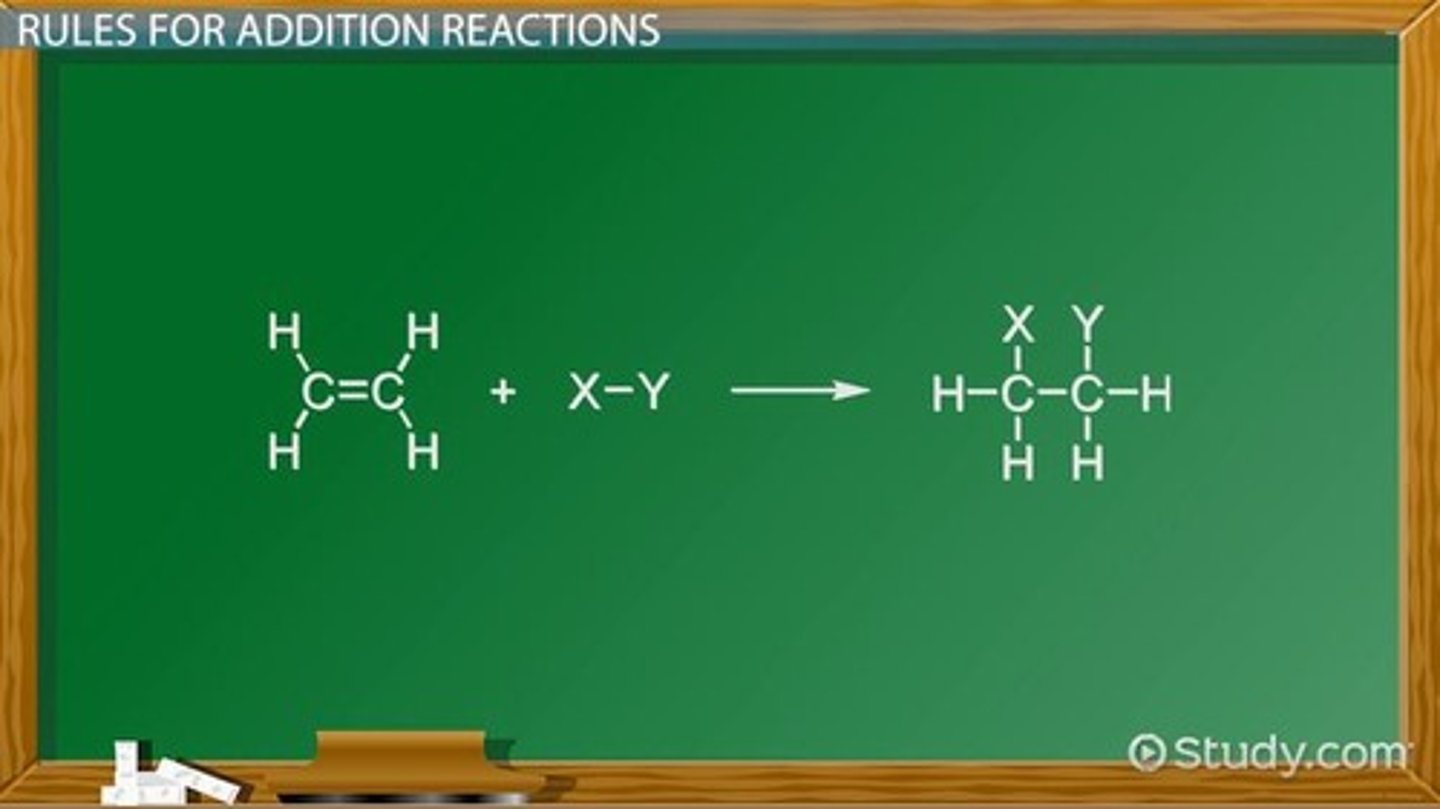
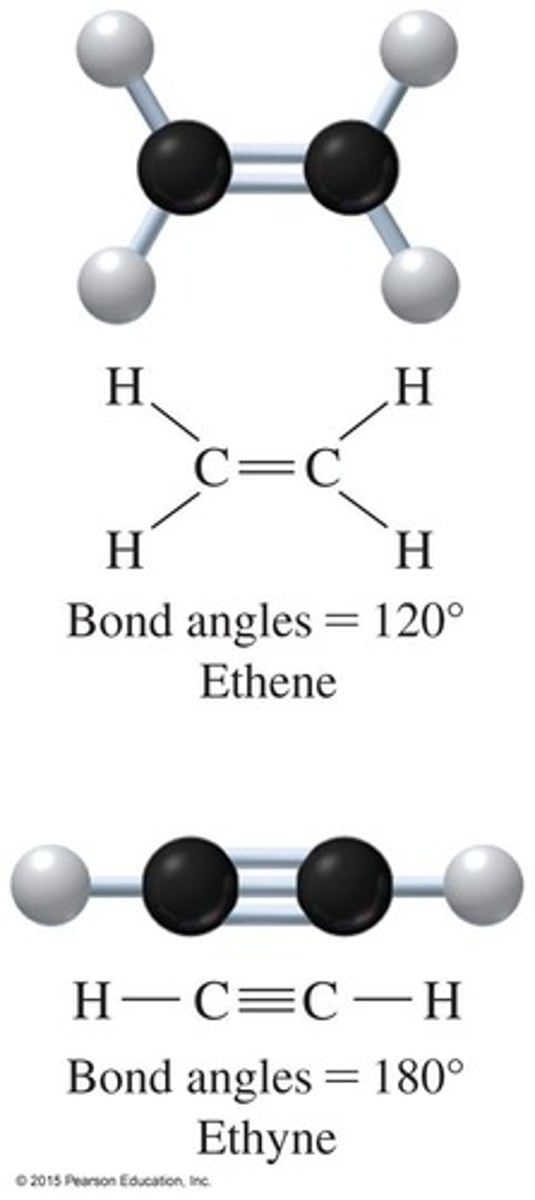
What defines aromatic compounds?
Aromatic compounds contain a benzene ring and have trigonal planar carbon atoms with bond angles of 120 degrees.
How can the double bonds in benzene be represented?
The double bonds in benzene can be arranged in two equivalent ways, alternating with single bonds around the ring.
What is the naming convention for monosubstituted benzenes?
To name a monosubstituted benzene, name the substituent first and then add 'benzene' at the end.
What are common names in the context of monosubstituted benzenes?
Some monosubstituted benzenes have established common names that differ from systematic naming.
What is the naming rule for disubstituted benzenes with different substituents?
For disubstituted benzenes with different substituents, alphabetize the names of the substituents.
How should disubstituted benzenes be named if one substituent is part of a common root?
Name the molecule as a derivative of the monosubstituted benzene that corresponds to the common root.
What is the numbering rule for polysubstituted benzenes?
Number the ring to give the lowest possible numbers to the substituents and alphabetize their names.
How do you name a polysubstituted benzene with a common root?
Name the molecule as a derivative of the common root, placing it at C1 and omitting the '1' from the name.
What is the significance of oxybenzone in sunscreen?
Oxybenzone is a commercial sunscreen that contains two benzene rings and can wash off in water, potentially harming coral reefs.
What is a phenol?
A phenol is a compound consisting of a benzene ring bonded to a hydroxyl group.
What role do phenols play in health and medicine?
Many phenols act as antioxidants, preventing unwanted oxidation reactions; examples include Vitamin E and BHT.
What occurs during the polymerization of ethylene?
Polymerization of ethylene results in the formation of new single bonds between carbon atoms and the cleavage of the pi bond.
What is the structure of toluene?
Toluene consists of a benzene ring linked to a methyl group.
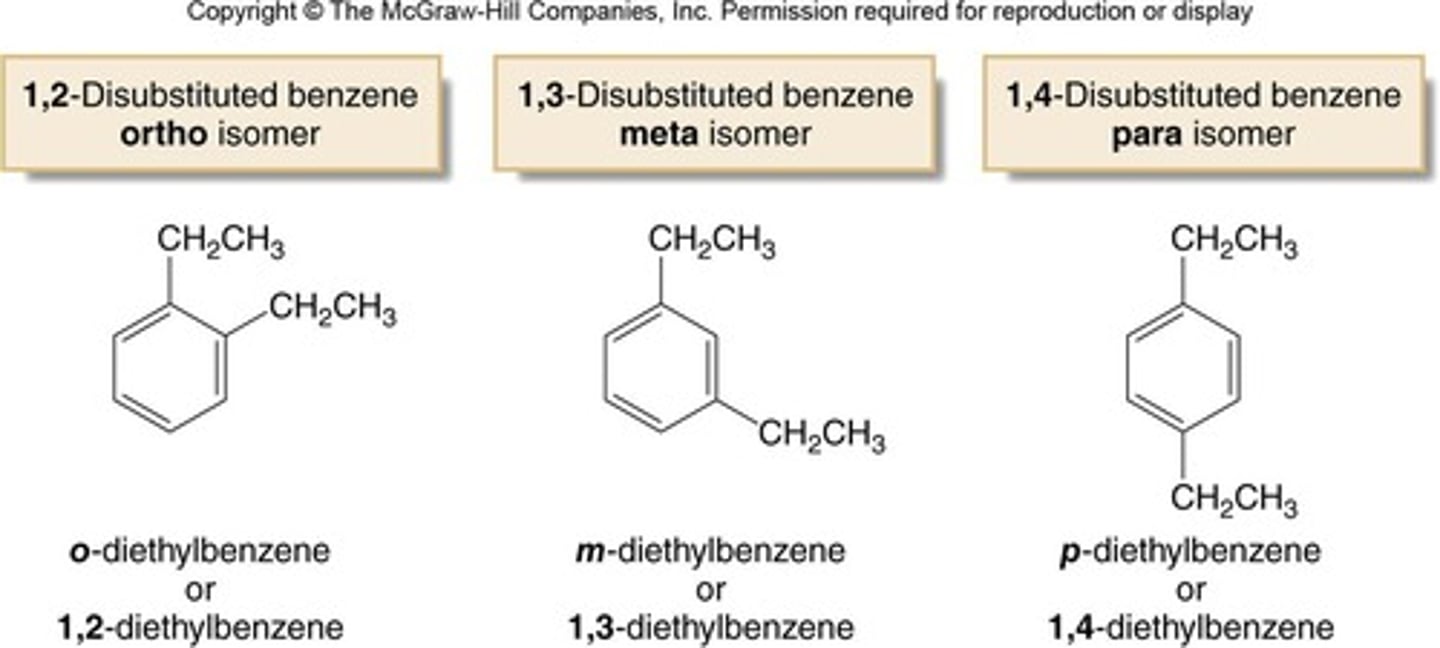
What distinguishes ortho, meta, and para disubstituted benzenes?
Ortho refers to substituents on adjacent carbons, meta refers to substituents on carbons separated by one carbon, and para refers to substituents on opposite sides of the ring.
How is ortho-bromochlorobenzene structured?
Ortho-bromochlorobenzene has bromine and chlorine substituents on carbons 1 and 2 of the benzene ring.
What is the structure of para-bromotoluene?
Para-bromotoluene consists of a methyl group and a bromine group located on opposite sides of the benzene ring.
What is the significance of the common root aniline?
Aniline is a common root for naming derivatives where an amino group is attached to a benzene ring.
What is the general formula for naming a compound with substituents on a benzene ring?
The general formula involves identifying the substituents, numbering the ring for lowest numbers, and alphabetizing the names.
What is the process of hydrogenation in alkenes?
Hydrogenation involves adding hydrogen to an alkene, converting it into an alkane with new carbon-hydrogen bonds.
What happens during hydration of alkenes?
Hydration involves adding water across the double bond of an alkene, resulting in the formation of an alcohol.
What is the structural difference between cis and trans isomers?
In cis isomers, substituents are on the same side of the double bond, while in trans isomers, they are on opposite sides.
What is the significance of the lowest set of numbers in naming?
Assigning the lowest set of numbers ensures that substituents receive the smallest possible locants in the compound's name.
What is the significance of VSEPR in relation to alkenes?
VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory) helps predict the molecular geometry of alkenes.
What are the requirements for cis-trans isomerism in alkenes?
Rotation must be restricted in the molecule, and there must be two nonidentical groups on each doubly bonded carbon atom.
How do you name alkenes according to IUPAC rules?
Name the parent as the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms that contains the double bond, number substituents to give the lowest numbers to the double bonds, and place substituent names in alphabetical order.
What is Markovnikov's Rule?
Markovnikov's Rule states that in the addition of HX to an alkene, the hydrogen atom will attach to the carbon with more hydrogen atoms.
What happens during hydrogenation of alkenes?
Hydrogenation involves adding H2 to the double bond, converting it into a single bond.
What is the product of the hydration reaction of alkenes?
Hydration adds -H to one carbon and -OH to the second carbon of the double bond.
What is the naming suffix for alkynes?
The suffix 'yne' is used for naming alkynes.
What are cycloalkenes?
Cycloalkenes are alkenes that have a double bond within a ring structure.
What is the structure of benzene?
Benzene consists of a six-carbon ring with alternating double bonds and has the molecular formula C6H6.
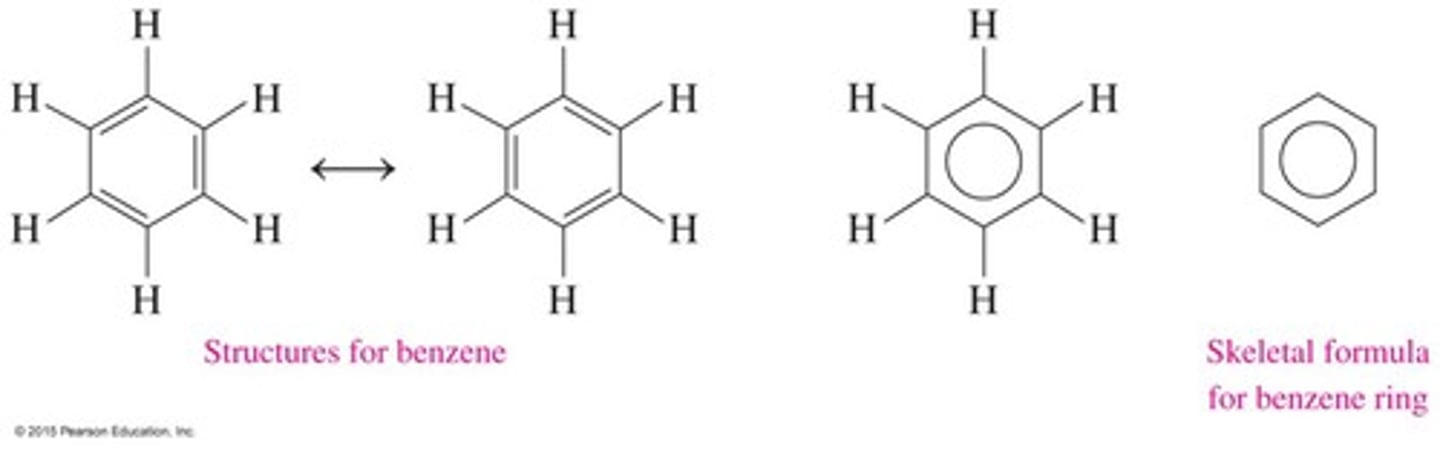
What is an aromatic compound?
An aromatic compound contains a benzene ring and is very stable, typically not undergoing addition reactions.
What are the common side effects of Propofol?
Side effects include pain on injection, hypotension, allergic reactions, and nausea.
What is the role of the nurse anesthetist during Propofol administration?
The nurse anesthetist administers the anesthesia and monitors the patient's vital signs.
What is the duration of action for Propofol?
Propofol has a duration of roughly 9-10 minutes.
What is the significance of the double bond in alkenes regarding molecular rotation?
In alkenes, the structure is rigid, and rotation about doubly bonded carbon atoms is not possible without breaking the bond.
What is polymerization in the context of hydrocarbons?
Polymerization is the process of combining small molecules (monomers) to form a large molecule (polymer), such as polyethylene.
What are the common intermolecular forces present in alkenes?
Alkenes primarily exhibit London dispersion forces and may have dipole-dipole interactions depending on substituents.
What is the IUPAC name for the compound with the structure 5-methyl-2-hexene?
5-methyl-2-hexene is the correct IUPAC name for that compound.
How do you determine the solubility of an alkene in water?
Alkenes are generally not soluble in water due to their nonpolar nature.
What is the product of the hydrogenation of trans-2-butene?
The product of the hydrogenation of trans-2-butene is butane.
What is the product of the addition of water to 2-chloro-1-butene?
The product is 2-chloro-2-butanol.
What is the difference between ortho, meta, and para in aromatic compounds?
Ortho refers to substituents on adjacent carbons, meta refers to substituents separated by one carbon, and para refers to substituents on opposite sides of the ring.