169 - Sterility + Stability Studies (answer with term)
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Medj mema sorry no time to polish
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Sterile Dosage Forms
Dosage forms that are free of viable microorganisms and pyrogen free
Parenteral Products
Ophthalmic Products
Solutions for Irrigation
Dry Products Ready to be Reconstituted
Examples of Sterile Dosage Forms? [4]
Pyrogen
Fever-producing compounds that are primarily associated with Gram-negative bacteria
Endotoxin
A type of pyrogen and is a component of the exterior cell wall of Gram-negative bacteria
When bacterial pyrogens are injected in sufficient amounts (microgram quantities), the fever produced is accompanied by:
chills,
body aches,
rise in blood pressure
possibly a state of shock and death
increased capillary permeability
a-wide variety of other circulatory changes.
Why avoid pyrogens and endotoxins?
Must be free from any viable microorganisms and extraneous materials
Must be free from pyrogens and endotoxins
Must be of the right pH and isotonicity
Must be uniform across units
Quality Control of Sterile DDS [4]
A. Sterility test
B. Particulate matter in injection
[Match the following to the appropriate QC test]
Must be free from any viable microorganisms and extraneous materials
A. Sterility test
B. Particulate matter in injection
C. Pyrogen test
D. Endotoxin test
E. pH
F. Uniformity of Dosage Units
C. Pyrogen test
D. Endotoxin test
[Match the following to the appropriate QC test]
Must be free from pyrogens and endotoxins
A. Sterility test
B. Particulate matter in injection
C. Pyrogen test
D. Endotoxin test
E. pH
F. Uniformity of Dosage Units
Pyrogen Testing (USP <151>)
Designed to limit to an acceptable level the risks of febrile reaction in the patient upon injection of the product
Pyrogen Testing (USP <151>)
The test involves measuring the rise in temperature of rabbits following the intravenous injection of a test solution, and is designed for products that can be tolerated by the test rabbit in a dose not to exceed 10 mL per kg injected IV within a period of not more than 10 minutes.
Use healthy, mature rabbits. House the rabbits individually in an area of uniform temperature between 20° and 23° and free from disturbances likely to excite them. The temperature varies not more than 13° from the selected tem- perature. Before using a rabbit for the first time in a pyrogen test, condition it not more than seven days before use by a sham test that includes all of the steps as directed for Procedure except injection. Do not use a rabbit for pyrogen testing more frequently than once every 48 hours, nor prior to 2 weeks following a maximum rise of its temperature of 0.6° or more while being subjected to the pyrogen test, or following its having been given a test specimen that was adjudged pyrogenic.
Procedure for Pyrogen Testing
Maximum of 8 rabbits, first stage use 3 rabbits, if any of the rabbits exceeded 0.5°C, you have to add 5 more rabbits
Total temperature change of rabbits should not exceed 3.3°C
Maximum number of rabbits in Pyrogen Testing?
Endotoxin Test
is a test to detect or quantify endotoxins from Gram-negative bacteria using amoebocyte lysate from horseshoe crab (Limulus polyphemus), This can detect the presence of endotoxin and quantify the amount
Gel-clot technique (most common)
Turbidimetric technique
Chromogenic technique
Techniques used in Endotoxin Test [3]
Gel-clot technique
Endpoint: formation of gel (endotoxin present)
Turbidimetric technique
Endopoint: presence of turbidity
Chromogenic technique
Formation of color
[Bacterial Endotoxin Test]
Endpoint for gel-clot, turbidimetric, and chromogenic technique?
Sterility
indicates that no contaminating microorganism is found in the sample examined
Sterility Test
USP <71>
Incubation of preparation in suitable medium for not less than 14 day
Membrane filtration method
May filtration matitira sa filter paper ung microbes -> agar plate -> incubation
Direct inoculation method
Mismong diluted ver directly put in the agar plate
2 Methods in Sterility Test
No microbial growth is found.
If not, check for validity of the test and repeat test as needed
Check microbial growth in negative control
Check facility and testing procedure
Acceptance criteria for Sterility test?
Membrane filtration
Filter the product
0.22 um can filter out microorganisms
If there are microorganisms that are retained in the filter, it will be placed in a medium (supplied the nutritional needs of the microorganism), incubated (if microorganism is present and alive, it will grow)
Membrane filtration
Use membrane filters with 0.45μm nominal pore size, 50mm diameter
Material of membrane filter may vary depending on the preparation tested
Membrane filter removed after filtration, then inoculated
Direct inoculation
Quantities prescribed are directly transferred into the culture medium (product NMT 10% of total volume)
If product is large volume, use concentrated medium taking into account its dilution after addition of product
Direct inoculation
Sample directly put in the medium (either agarian or broth medium) then we would observe the absence or presence of growth
We would want the ABSENCE of growth.
PARTICULATE MATTER IN INJECTIONS
Extraneous mobile undissolved particles, other than gas bubbles, unintentionally present in solutions
irrigating solutions, radiopharmaceutical preparations, for preparations with final filtration step prior to administration (with justification)
Exceptions in PARTICULATE MATTER IN INJECTIONS?
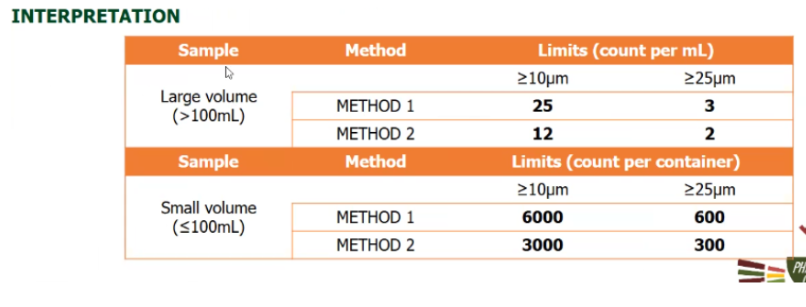
Method 1: Light obscuration particle count test
Has particle counter
Preferred, but can be combined with Method 2
Method 2: Microscopic particle count test
Use if results are not confirmed with method 1, or product has decreased clarity, or viscous preparation
For preparation with reduced clarity or increased viscosity or those that produce gas or air bubbles
10 microns and above should not be seen
Method 1 and 2 in PARTICULATE MATTER IN INJECTIONS
Photostability Testing
Selection of Batches
Specification
Testing Frequency
Container Closure System
Storage Conditions
Evaluation
Stability Commitment
Statements of Labelling
STABILITY STUDY PROTOCOL
Stability
The ability of a drug to retain its chemical, physical, microbiological and biopharmaceutical properties within specified limits throughout its shelf-life
Stability Studies
Consists of a series of tests in order to obtain an assurance of the stability of a drug product namely maintenance of the specifications of the drug product packed in its specified packaging material and stored in the established storage condition within the determined time period.
A. Photostability Testing
B. Selection of Batches
C. Specification
D. Testing Frequency
E. Container Closure System
F. Storage Condition
G. Evaluation
H. Stability Commitment
I. Statements of Labelling
When we design stability studies we need to perform: [9]
Under ICH Quality Guidelines
·
Q1A(R2) - Stability Testing of New Drug Substances
Q1B - Stability Testing: Photostability Testing of New Drug Substances and Products
Q1C - Stability Testing for New Dosage Forms
Q1D - Bracketing and Matrixing Designs for Stability Testing of New Drug Substances and Products
Q1E - Evaluation of Stability Data
Q1F - Stability Data Package for Registration Applications in Climatic Zones III and IV
Stability Studies - ICH Quality Guidelines [6]
Hospital pharmacies are required to respond to therapeutic needs not covered by the pharmaceutical industry simple reconstitutions and/or dilutions of specialized pharmaceutical products
more complex preparations formulated from pharmaceutical specialties or raw materials
Stability Studies of Hospital Pharmaceutical Preparations
ICH (and ASEAN) guidelines
represent an essential methodological base for the development of medications, but they need to be adapted to reflect the realities of clinical practice, particularly in a hospital environment and in the context of outpatient care.
Hydrolysis
Oxidation-Reduction
Photolysis
Racemization and epimerization
Chemical Instabilties [4]
Precipitation
Sorption
Leaching
Chelation and complexation leading to insolubility
Color changes
Physical Instabilities and Incompatibilities [5]
pH
Surfactants
Temperature
Oxygen
Light
Materials
Factors Affecting the Stability of Preparations [6]
Data on active ingredient
API to be used for stability studies should be issued from the same batch
Packaging items
Formulating the preparation [3]
Depends on product's intended use
For products used in multiple concentrations: perform stability studies on minimum of two concentrations: one low and one high
If the difference between the low and high concentrations is too significant (more than a factor of 10) an intermediate concentration stability study may be considered, depending on the clinical interest.
Choice of concentrations to be tested [3]
Stability studies should preferably be conducted on a single manufacturing batch
Must include at least 3 units in the test batch
Units should be prepared in conditions which reflect the circumstances in which the product is intended to be used
It is preferable to create one preparation unit per sampling time-point
Number of tests in stability studies [4]
Temperature (ambient, refrigeration, freezing-thawing, portable infusors)
Residual moisture
Light (day/night ambient light)
Storage conditions [3]
Real-time (up to 1 year)
Accelerated studies (ICH method is followed)
Duration of study [2]
To, minimum of 5 sampling time points (1/24th, 1/12th, 14, 2 and
3/4 of max duration), maximum duration
Sampling time points
Depend on the volume and usage of preparation
It is preferable to prepare a separate preparation unit for each sampling time point, even for multiple doses
Volume sampled on stability studies?
Assay (stability- indicating) and degradation products
Tests depending on dosage form
Analysis to be performed in stability studies? [2]